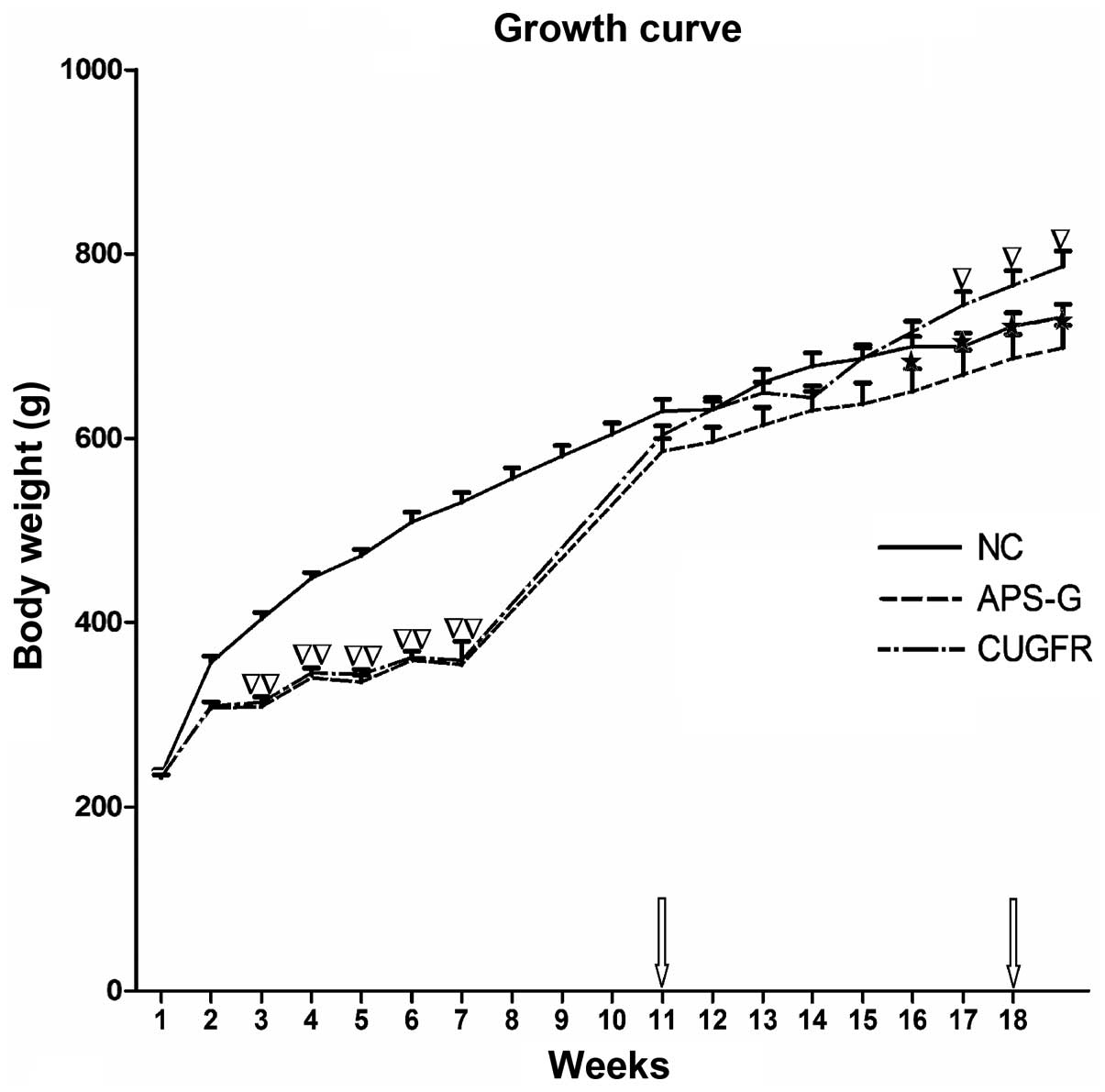
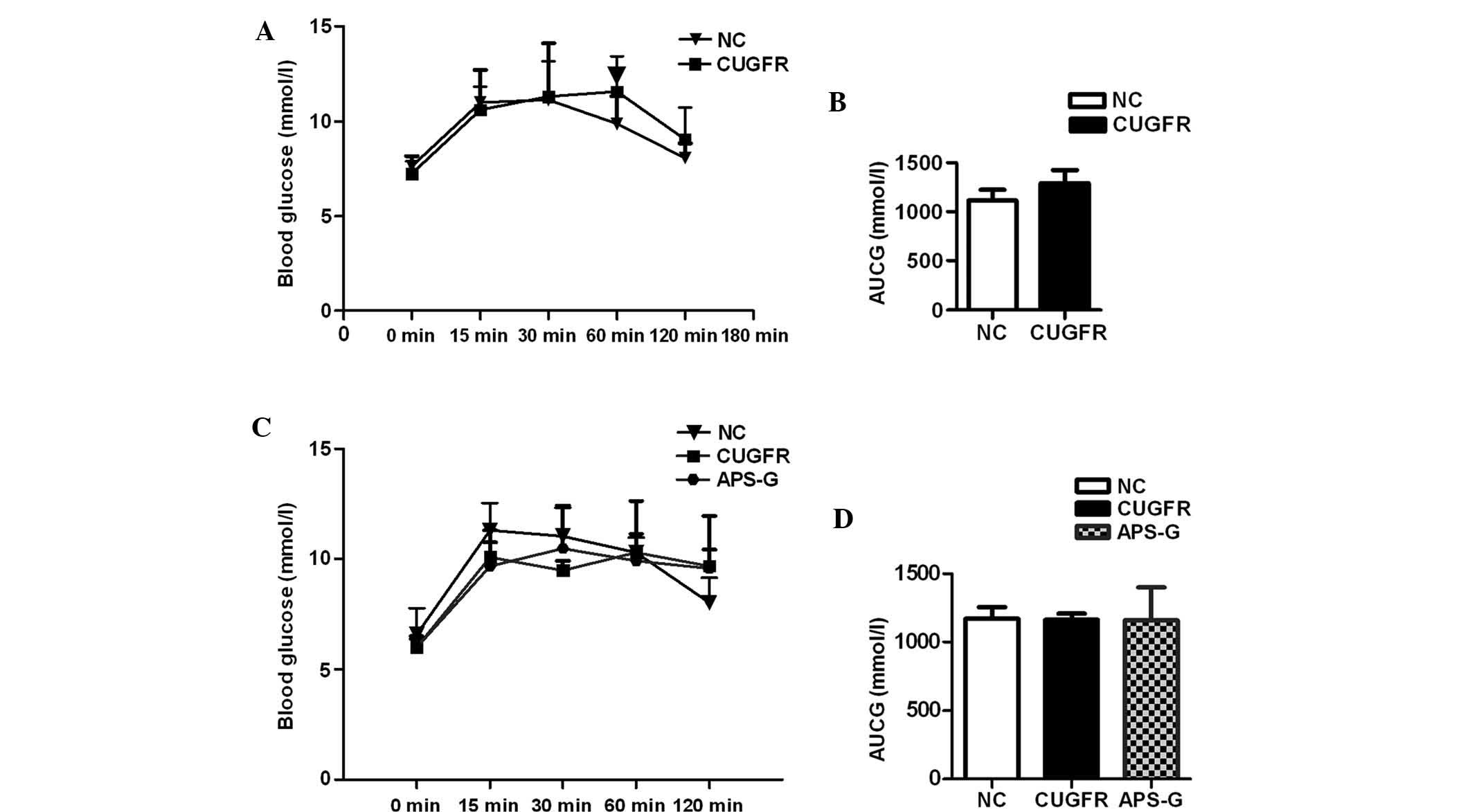
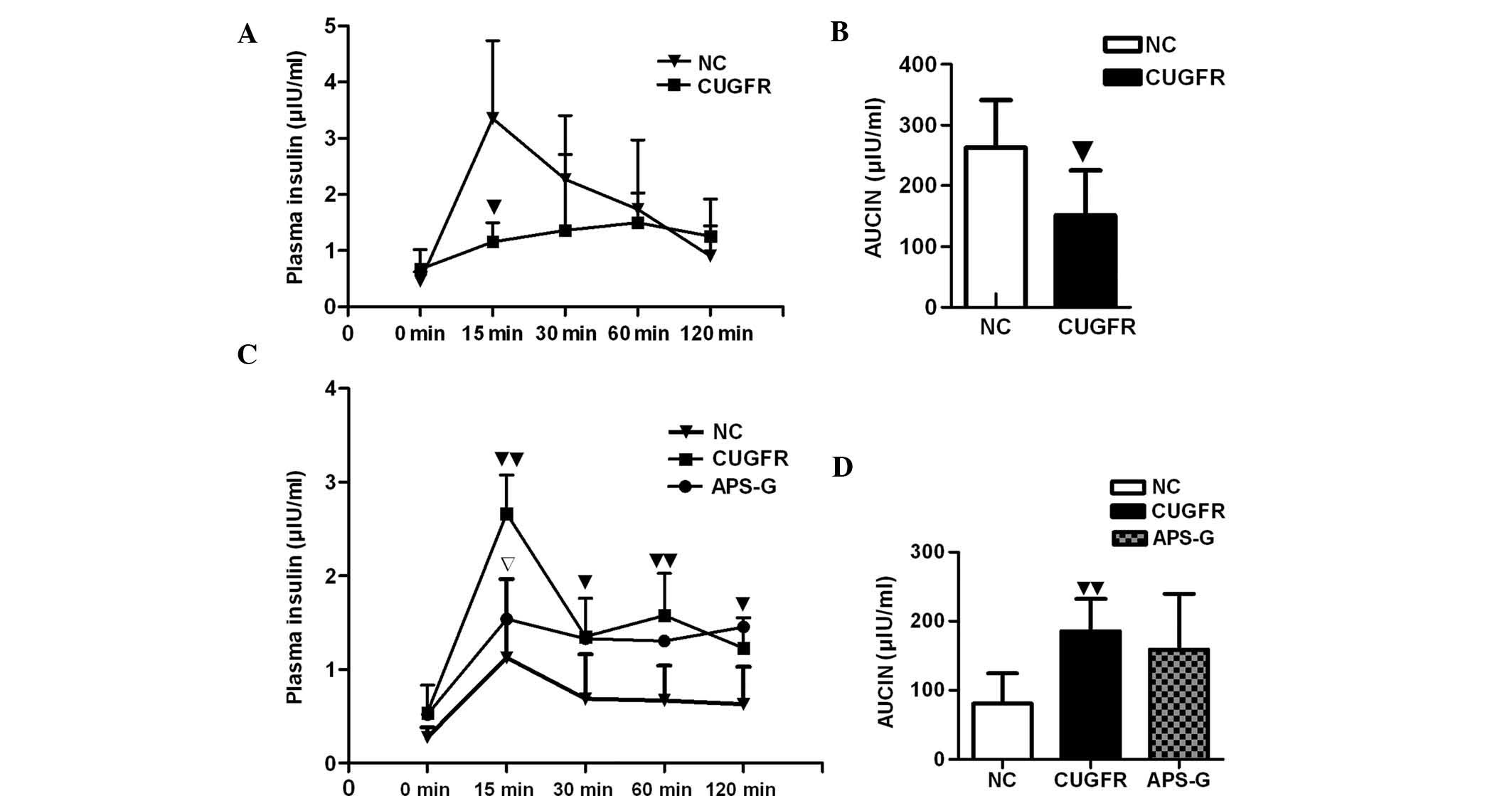
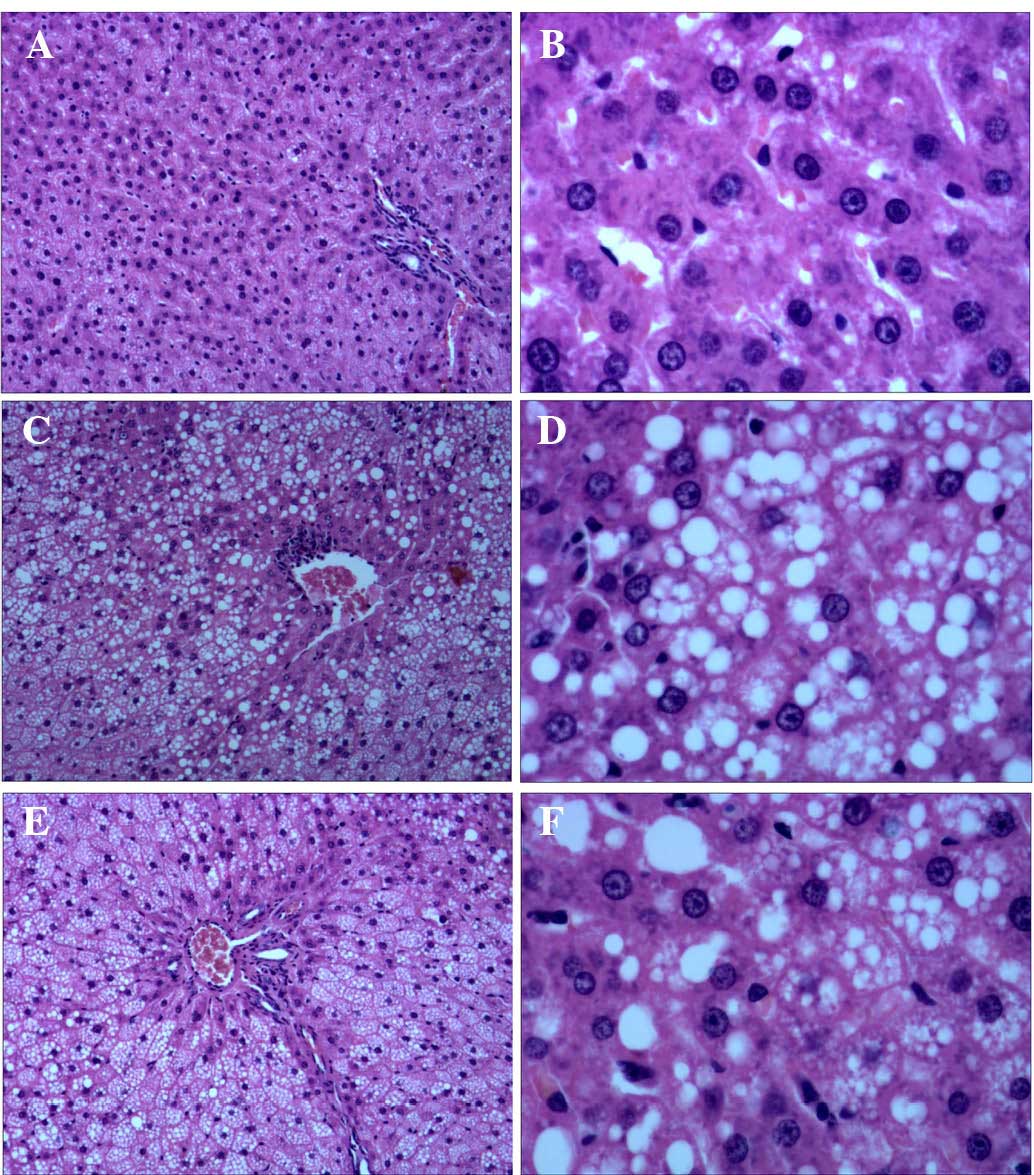
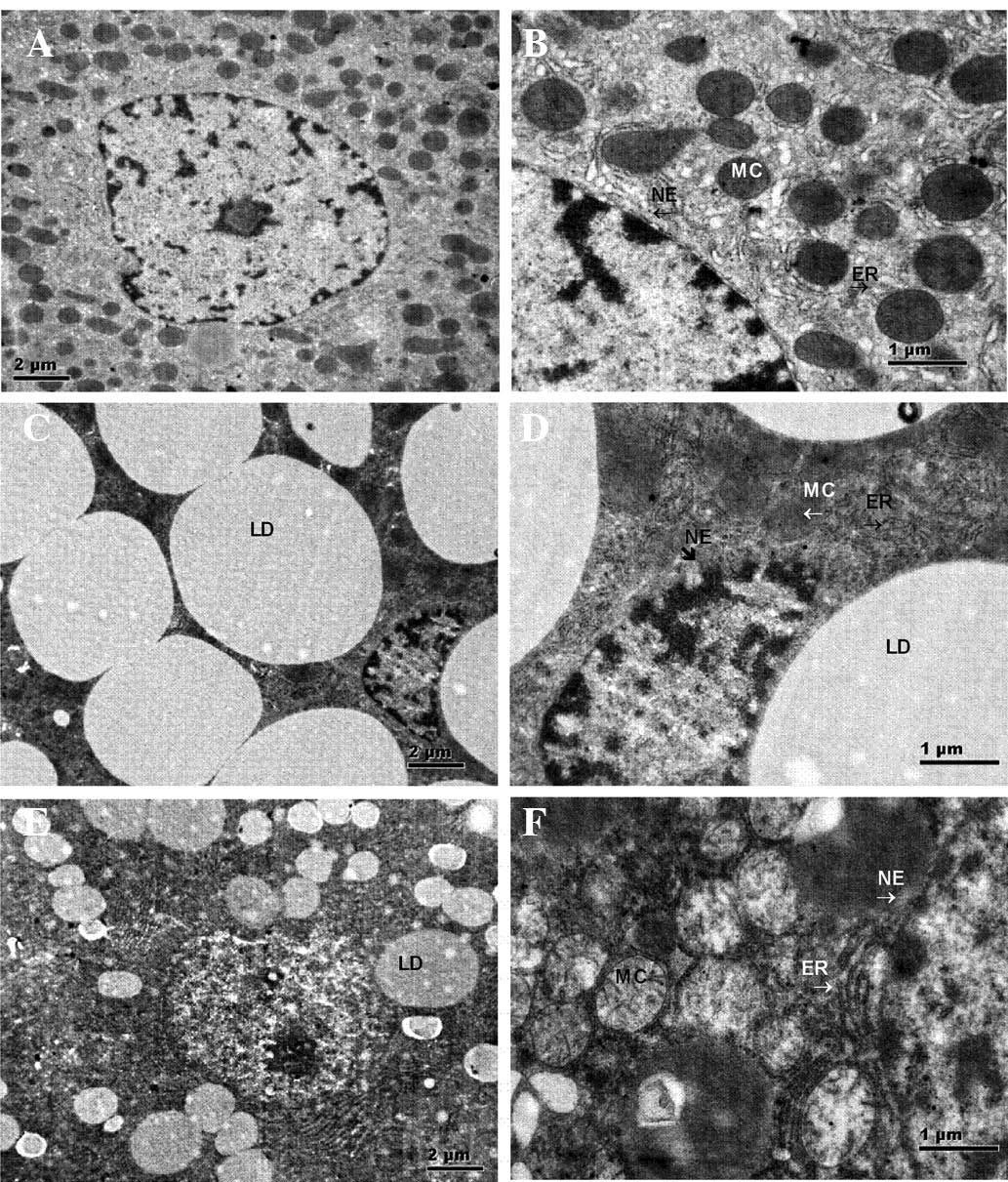
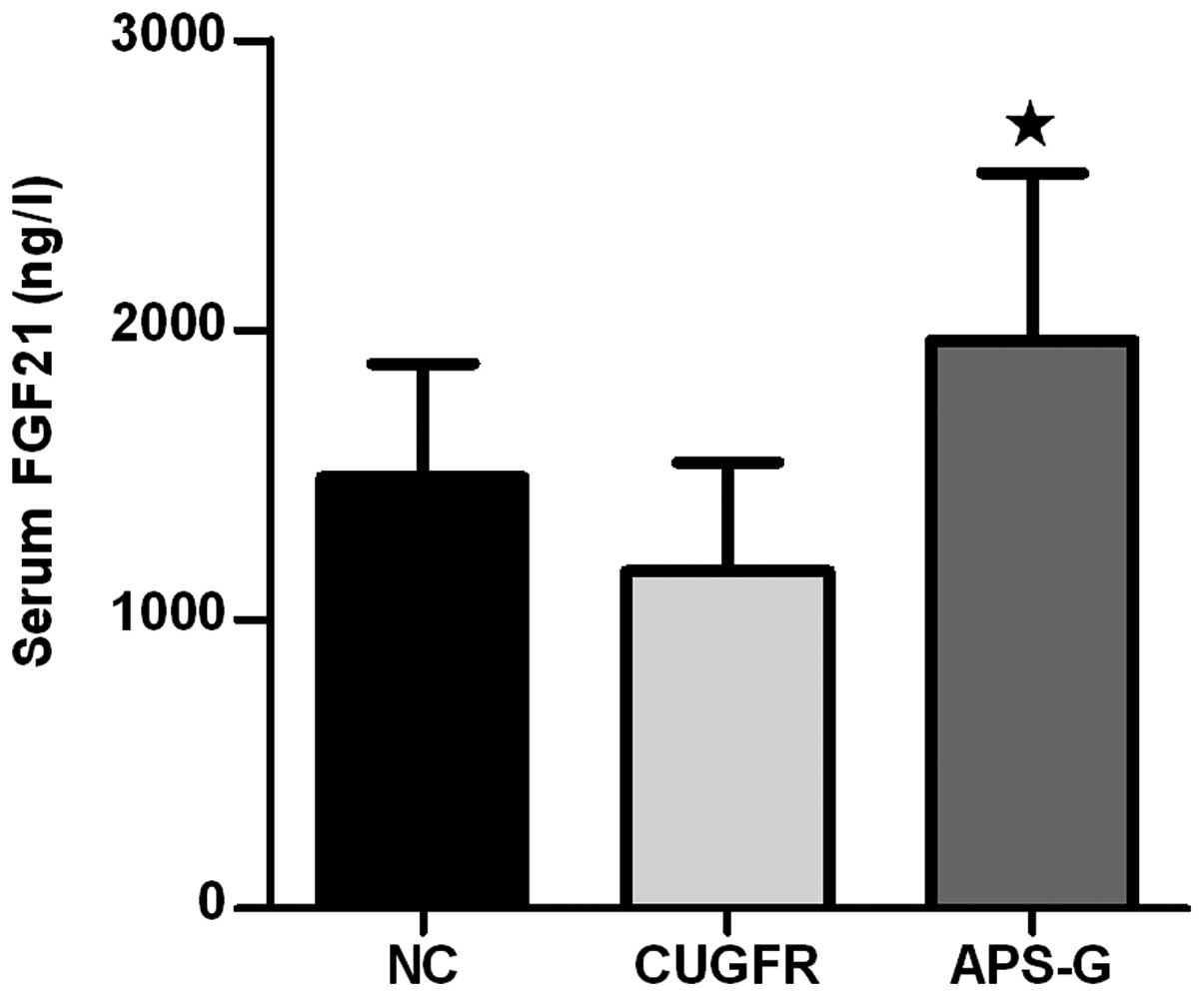
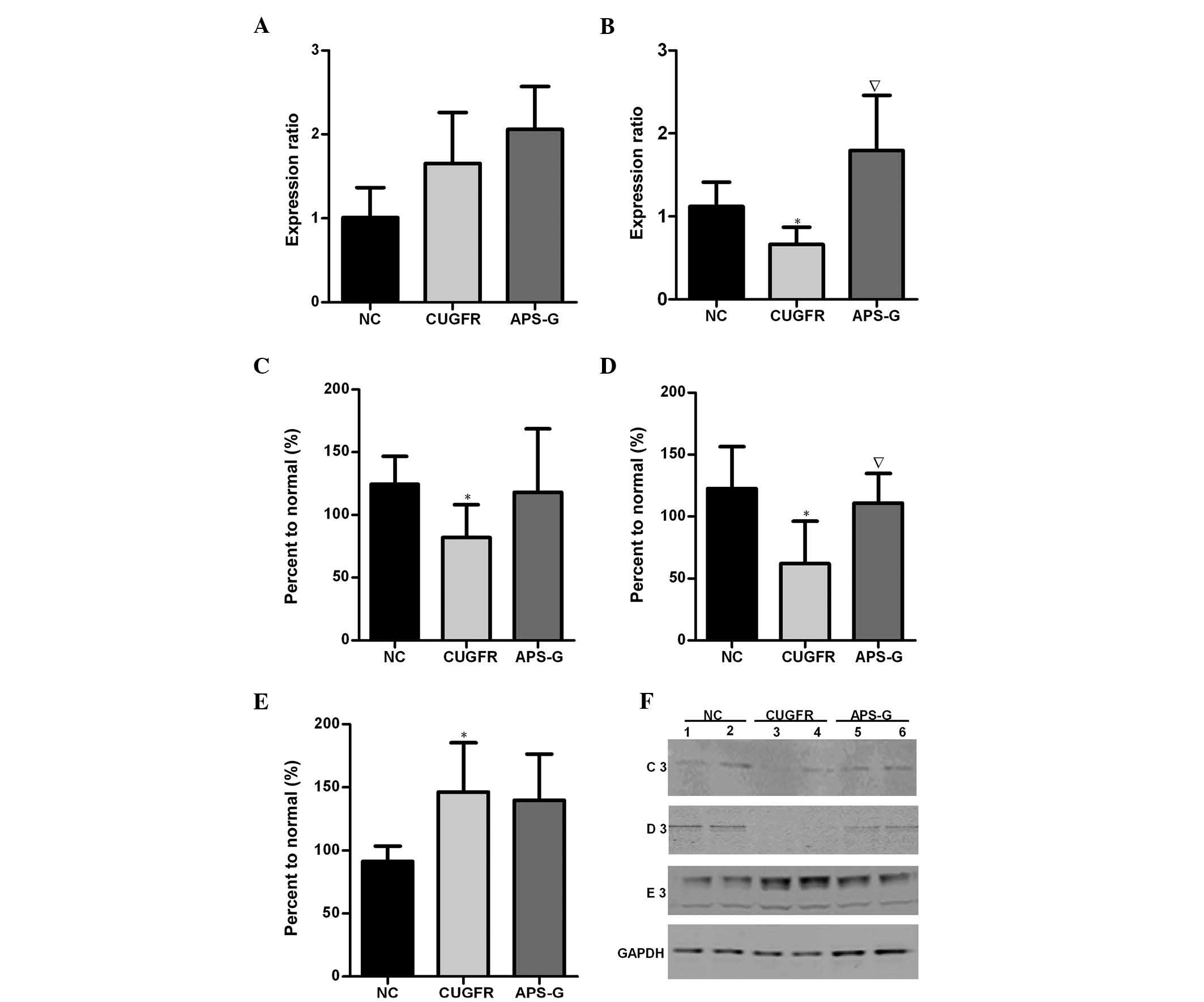
|
1
|
Prader A, Tanner JM and von Harnack GA:
Catch-up growth following illness or starvation. An example of
developmental canalization in man. Pediatrics. 62:646–659. 1963.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Chen LL: Catch-up growth - a new territory
for understanding insulin resistance. Chin J Endocrinol Metab.
24:235–238. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Xiao XH, Zhang ZX, Cohen HJ, Wang H, Li W,
Wang T, Xu T, Liu A, Gai MY, Ying S, et al: Evidence of a
relationship between infant birth weight and later diabetes and
impaired glucose regulation in a Chinese population. Diabetes Care.
31:483–487. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fu Q, McKnight RA, Yu X, Wang L, Callaway
CW and Lane RH: Uteroplacental insufficiency induces site-specific
changes in histone H3 covalent modifications and affects
DNA-histone H3 positioning in day0 IUGR rat liver. Physiol
Genomics. 20:108–116. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lane RH, MacLennan NK, Hsu JL, Janke SM
and Pham TD: Increased hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated
receptor-gamma coactivator-1 gene expression in a rat model of
intrauterine growth retardation and subsequent insulin resistance.
Endocrinology. 143:2486–2490. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yoon JC, Puigserver P, Chen G, Donovan J,
Wu Z, Rhee J, Adelmant G, Stafford J, Kahn CR, Granner DK, et al:
Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis through the transcriptional
coactivator PGC-l. Nature. 413:131–138. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, Keller MD,
Jones DR, Frye RA and Mayo MW: Modulation of NF-kappa B-dependent
transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J.
23:2369–2380. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nannipieri M, Gonzales C, Baldi S, Posadas
R, Williams K, Haffner SM, Stern MP and Ferrannini E; Mexico City
diabetes study: Liver enzymes, the metabolic syndrome and incident
diabetes: The Mexico City diabetes study. Diabetes Care.
28:1757–1762. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cettour-Rose P, Samec S, Russell AP,
Summermatter S, Mainieri D, Carrillo-Theander C, Montani JP,
Seydoux J, Rohner-Jeanrenaud F and Dulloo AG: Redistribution of
glucose from skeletal muscle to adipose tissue during catch-up fat:
A link between catch-up growth and later metabolic syndrome.
Diabetes. 54:751–756. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chen R, Shao H, Lin S, Zhang JJ and Xu KQ:
Treatment with Astragalus membranaceus produces antioxidative
effects and attenuates intestinal mucosa injury induced by
intesti-nalischemia-reperfusion in rats. Am J Chin Med. 39:879–887.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Sang Z, Zhou L, Fan X and McCrimmon RJ:
Radix astragali (huangqi) as a treatment for defective hypoglycemia
counter-regulation in diabetes. Am J Chin Med. 38:1027–1038. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chen W, Xia Y, Zhao X, Wang H, Chen W, Yu
M, Li Y, Ye H and Zhang Y: The critical role of Astragalus
polysaccharides for the improvement of PPARα [correction of
PPRAα]-mediated lipotoxicity in diabetic cardiomyopathy. PLoS One.
7:e455412012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Magee TR, Han G, Cherian B, Khorram O,
Ross MG and Desai M: Down-regulation of transcription factor
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor in programmed hepatic
lipid dysregulation and inflammation in intrauterine
growth-restricted offspring. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 199:271 el–5.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Dushay J, Chui PC, Gopalakrishnan GS,
Varela-Rey M, Crawley M, Fisher FM, Badman MK, Martinez-Chantar ML
and Maratos-Flier E: Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in
obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology.
139:456–463. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li H, Fang Q, Gao F, Fan J, Zhou J, Wang
X, Zhang H, Pan X, Bao Y, Xiang K, et al: Fibroblast growth factor
21 levels are increased in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
patients and are correlated with hepatic triglyceride. J Hepatol.
53:934–940. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Leibiger IB and Berggren PO: Sirt1: A
metabilic a master switch that modulates lifespan. Nat Med.
12:34–36. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gerhart-Hines Z, Rodgers JT, Bare O, Lerin
C, Kim SH, Mostoslavsky R, Alt FW, Wu Z and Puigserver P: Metabolic
control of muscle mitochondrial function and fatty acid oxidation
through SIRT1/PGC-1 alpha. Embo J. 26:1913–1923. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Picard F, Kurtev M, Chung N, Topark-Ngarm
A, Senawong T, Machado De Oliveira R, Leid M, McBurney MW and
Guarente L: Sirt1 promotes fat mobilization in white adpecytes by
repressing PPAR-gamma. Nature. 429:771–776. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ma L, Dong W, Wang R, Li Y, Xu B, Zhang J,
Zhao Z and Wang Y: Effect of caloric restriction on the SIRT1/mTOR
signaling pathways in senile mice. Brain Res Bull. 116:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhao Y, Ling F, Griffin TM, He T, Towner
R, Ruan H and Sun XH: Up-regulation of the Sirtuin 1 (Sirt1) and
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator-1α
(PGC-1α) genes in white adipose tissue of Id1 protein-deficient
mice: Implications in the protection against diet and age-induced
glucose intolerance. J Biol Chem. 289:29112–29122. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lee J, Hong SW, Park SE, Rhee EJ, Park CY,
Oh KW, Park SW and Lee WY: Exendin-4 regulates lipid metabolism and
fibroblast growth factor 21 in hepatic steatosis. Metabolism.
63:1041–1048. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Estall JL, Ruas JL, Choi CS, Laznik D,
Badman M, Maratos-Flier E, Shulman GI and Spiegelman BM: PGC-1α
negatively regulates hepatic FGF21 expression by modulating the
heme/Rev-Erbα axis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:22510–22515. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Yu D, Sun CY, Sun GP, Ren GP, Ye XL, Zhu
SL, Wang WF, Xu PF, Li SJ, Wu Q, et al: The synergistic effect of
FGF-21 and insulin on regulating glucose metabolism and its
mechanism. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 49:977–984. 2014.in Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ge X, Chen C, Hui X, Wang Y, Lam KS and Xu
A: Fibroblast growth factor 21 induces glucose transporter-1
expression through activation of the serum response factor/Ets-like
protein-1 in adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 286:34533–34541. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li L, Hai J, Li Z, Zhang Y, Peng H, Li K
and Weng X: Resveratrol modulates autophagy and NF-κB activity in a
murine model for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food
Chem Toxicol. 63:166–173. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Gariani K, Philippe J and Jornayvaz FR:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and insulin resistance: From
bench to bedside. Diabetes Metab. 39:16–26. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wu F and Chen X: A review of
pharmacological study on Astragalus membranaceus (Fisch) Bge. Zhong
Yao Cai. 27:232–234. 2004.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lu J, Chen X, Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhang L, Li
Z, Liu W, Ouyang J, Han S and He X: Astragalus polysaccharide
induces anti-inflammatory effects dependent on AMPK activity in
palmitate-treated RAW264.7 cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:1463–1470.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
He X, Shu J, Xu L, Lu C and Lu A:
Inhibitory effect of Astragalus polysaccharides on
lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF-a and IL-1β production in THP-1
cells. Molecules. 17:3155–3164. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li XT, Zhang YK, Kuang HX, Jin FX, Liu DW,
Gao MB, Liu Z and Xin XJ: Mitochondrial protection and anti-aging
activity of astragalus polysaccharides and their potential
mechanism. Int J Mol Sci. 13:1747–1761. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang LX and Han ZW: The effect of
astragalus polysaccharide on endotoxin-induced toxicity in mice.
Yao Xue Xue Bao. 27:5–9. 1992.In Chinese.
|
|
32
|
Wang N, Zhang D, Mao X, Zou F, Jin H and
Ouyang J: Astragalus polysaccharides decreased the expression of
PTP1B through relieving ER stress-induced activation of ATF6 in a
rat model of type 2 diabetes. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 307:89–98. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Mao XQ, Wu Y, Wu K, Liu M, Zhang JF, Zou F
and Ou-Yang JP: Astragalus polysaccharide reduces hepatic
endoplasmic reticulum stress and restores glucose homeostasis in a
diabetic KKAy mouse model. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 28:1947–1956. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chen W, Chen WJ, Xia YP, Lu Y and Yu MH:
Effects of astragalus polysaccharides on lipid metabolism and
PPAR-α gene expression in myocardium of diabetic hamsters. Fudan
Univ J Med Sci. 37:194–197. 2010.
|
|
35
|
Caton PW, Holness MJ, Bishop-Bailey D and
Sugden MC: PPAR α-LXR as a novel metabolostatic signalling axis in
skeletal muscle that acts to optimize substrate selection in
response to nutrient status. Biochem J. 437:521–530. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zou F, Mao XQ, Wang N, Liu J and Ou-Yang
JP: Astragalus polysaccharides alleviates glucose toxicity and
restores glucose homeostasis in diabetic states via activation of
AMPK. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:1607–1615. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|