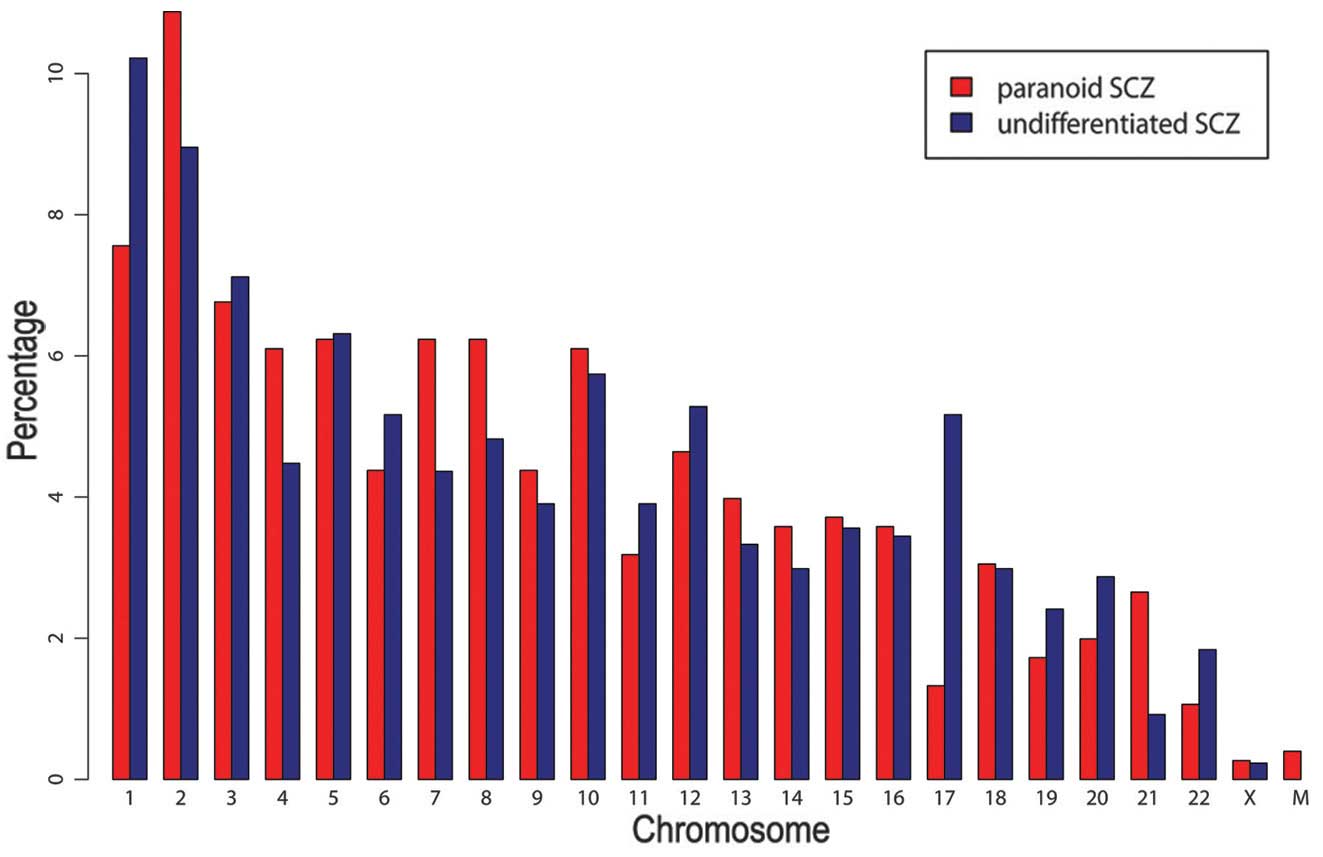
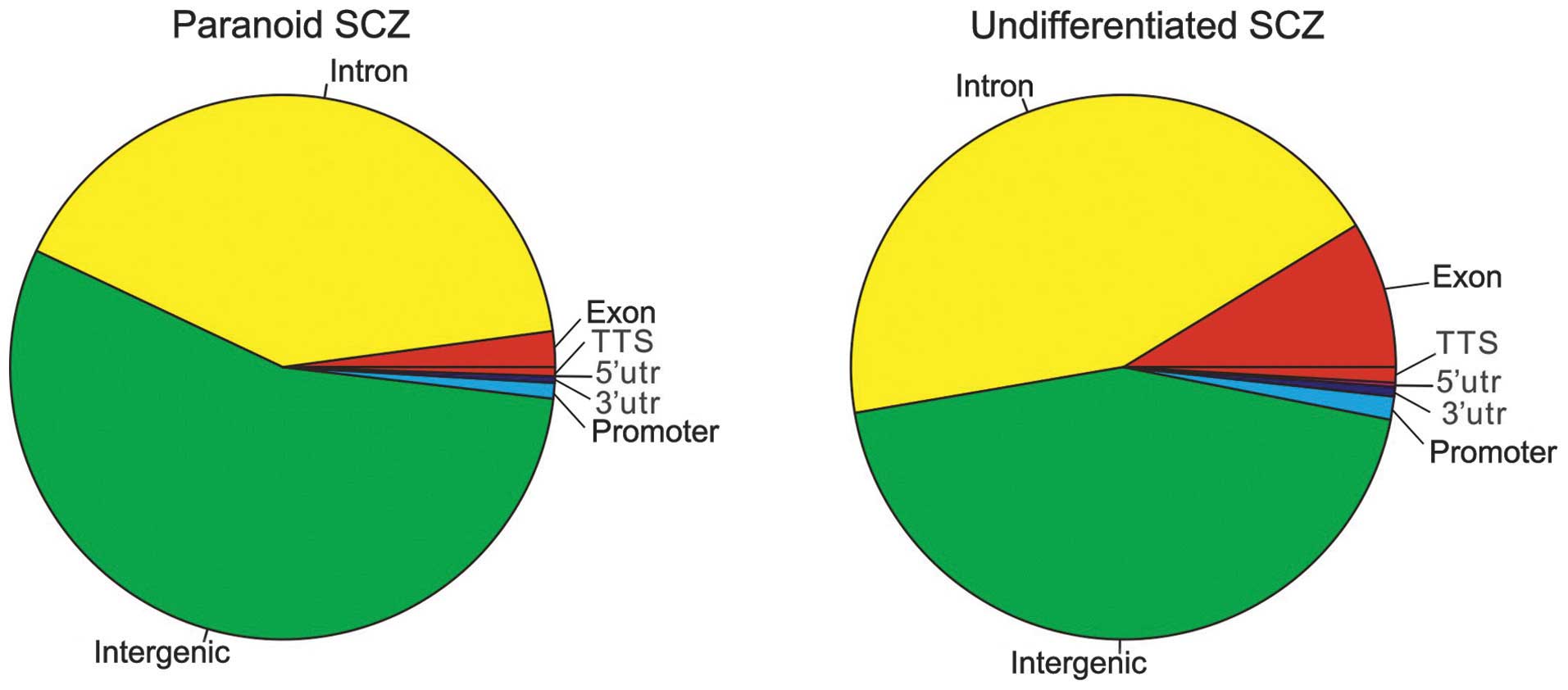
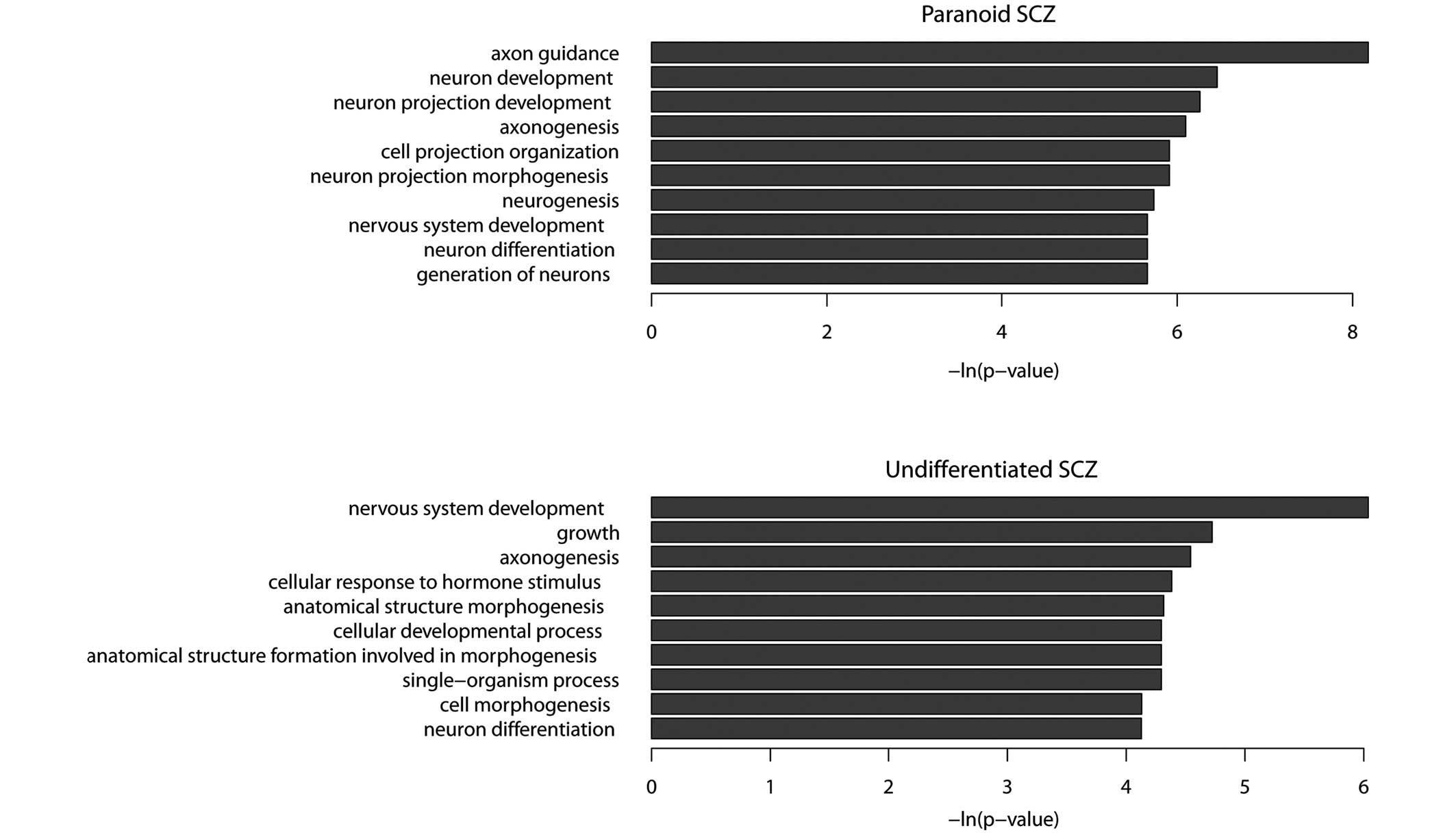
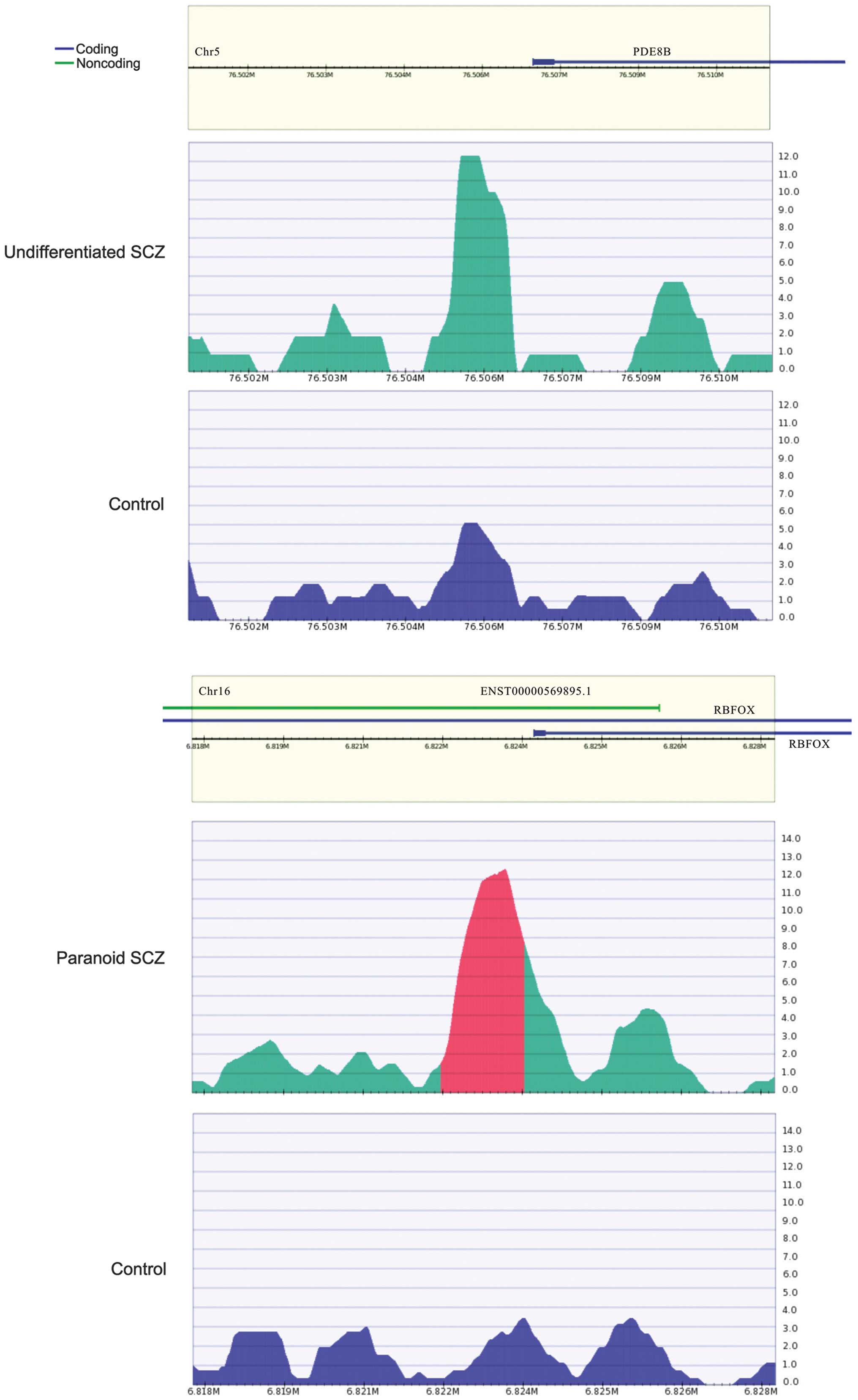
|
1
|
Hall MH, Schulze K, Rijsdijk F, Picchioni
M, Ettinger U, Bramon E, Freedman R, Murray RM and Sham P:
Heritability and reliability of P300, P50 and duration mismatch
negativity. Behav Genet. 36:845–857. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Uhlhaas PJ and Singer W: Abnormal neural
oscillations and synchrony in schizophrenia. Nat Rev Neurosci.
11:100–113. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tamminga CA and Holcomb HH: Phenotype of
schizophrenia: A review and formulation. Mol Psychiatry. 10:27–39.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fanous AH and Kendler KS: Genetics of
clinical features and subtypes of schizophrenia: A review of the
recent literature. Curr Psychiatry Rep. 10:164–170. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S,
Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D, Werge T, Pietiläinen OP, Mors
O, Mortensen PB, et al: Genetic Risk and Outcome in Psychosis
(GROUP): Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature.
460:744–747. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Davies W: Genomic imprinting on the X
chromosome: Implications for brain and behavioral phenotypes. Ann
NY Acad Sci. 1204(Suppl): E14–E19. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sharma RP, Grayson DR and Gavin DP:
Histone deactylase 1 expression is increased in the prefrontal
cortex of schizophrenia subjects: Analysis of the National Brain
Databank microarray collection. Schizophr Res. 98:111–117. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Grayson DR, Jia X, Chen Y, Sharma RP,
Mitchell CP, Guidotti A and Costa E: Reelin promoter
hypermethylation in schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:9341–9346. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Russo A, Smith
CL, Faraone SV, Wilcox M, Shafa R, Glatt SJ, Nguyen G, Ponte JF, et
al: Hypermethylation of the reelin (RELN) promoter in the brain of
schizophrenic patients: A preliminary report. Am J Med Genet B
Neuropsychiatr Genet. 134B:60–66. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Faraone SV,
Wilcox M, Glatt SJ, Gao F, Smith CL, Shafa R, Aeali B, Carnevale J,
et al: Hypomethylation of MB-COMT promoter is a major risk factor
for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Hum Mol Genet.
15:3132–3145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nohesara S, Ghadirivasfi M, Mostafavi S,
Eskandari MR, Ahmadkhaniha H, Thiagalingam S and Abdolmaleky HM:
DNA hypomethylation of MB-COMT promoter in the DNA derived from
saliva in schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. J Psychiatr Res.
45:1432–1438. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Iwamoto K, Bundo M, Yamada K, Takao H,
Iwayama-Shigeno Y, Yoshikawa T and Kato T: DNA methylation status
of SOX10 correlates with its downregulation and oligodendrocyte
dysfunction in schizophrenia. J Neurosci. 25:5376–5381. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tolosa A, Sanjuán J, Dagnall AM, Moltó MD,
Herrero N and de Frutos R: FOXP2 gene and language impairment in
schizophrenia: Association and epigenetic studies. BMC Med Genet.
11:1142010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Pun FW, Zhao C, Lo WS, Ng SK, Tsang SY,
Nimgaonkar V, Chung WS, Ungvari GS and Xue H: Imprinting in the
schizophrenia candidate gene GABRB2 encoding GABA(A) receptor β(2)
subunit. Mol Psychiatry. 16:557–568. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Abdolmaleky HM, Yaqubi S, Papageorgis P,
Lambert AW, Ozturk S, Sivaraman V and Thiagalingam S: Epigenetic
dysregulation of HTR2A in the brain of patients with schizophrenia
and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res. 129:183–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ikegame T, Bundo M, Sunaga F, Asai T,
Nishimura F, Yoshikawa A, Kawamura Y, Hibino H, Tochigi M, Kakiuchi
C, et al: DNA methylation analysis of BDNF gene promoters in
peripheral blood cells of schizophrenia patients. Neurosci Res.
77:208–214. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kordi-Tamandani DM, Vaziri S, Dahmardeh N
and Torkamanzehi A: Evaluation of polymorphism, hypermeth-ylation
and expression pattern of CTLA4 gene in a sample of Iranian
patients with schizophrenia. Mol Biol Rep. 40:5123–5128. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng J, Wang Y, Zhou K, Wang L, Li J,
Zhuang Q, Xu X, Xu L, Zhang K, Dai D, et al: Male-specific
association between dopamine receptor D4 gene methylation and
schizophrenia. PLoS One. 9:e891282014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Folsom TD and Fatemi SH: The involvement
of Reelin in neuro-developmental disorders. Neuropharmacology.
68:122–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Vučićević D, Schrewe H and Orom UA:
Molecular mechanisms of long ncRNAs in neurological disorders.
Front Genet. 5:482014.
|
|
21
|
Barry G, Briggs JA, Vanichkina DP, Poth
EM, Beveridge NJ, Ratnu VS, Nayler SP, Nones K, Hu J, Bredy TW, et
al: The long non-coding RNA Gomafu is acutely regulated in response
to neuronal activation and involved in schizophrenia-associated
alternative splicing. Mol Pyschiatry. 19:486–494. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Okazaki Y, Furuno M, Kasukawa T, Adachi J,
Bono H, Kondo S, Nikaido I, Osato N, Saito R, Suzuki H, et al:
Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on functional annotation
of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature. 420:563–573. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, Otsuki T,
Sugiyama T, Irie R, Wakamatsu A, Hayashi K, Sato H, Nagai K, et al:
Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length
human cDNAs. Nat Genet. 36:40–45. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Sunkin SM, Mehler MF
and Mattick JS: Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the
mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:716–721. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H and Spector DL: Long
noncoding RNAs: Functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev.
23:1494–1504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Taft RJ, Pang KC, Mercer TR, Dinger M and
Mattick JS: Non-coding RNAs: Regulators of disease. J Pathol.
220:126–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pandey RR, Mondal T, Mohammad F, Enroth S,
Redrup L, Komorowski J, Nagano T, Mancini-Dinardo D and Kanduri C:
Kcnq1ot1 antisense noncoding RNA mediates lineage-specific
transcriptional silencing through chromatin-level regulation. Mol
Cell. 32:232–246. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ibala-Romdhane S, Al-Khtib M, Khoueiry R,
Blachère T, Guérin JF and Lefèvre A: Analysis of H19 methylation in
control and abnormal human embryos, sperm and oocytes. Eur J Hum
Genet. 19:1138–1143. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chiesa N, De Crescenzo A, Mishra K, Perone
L, Carella M, Palumbo O, Mussa A, Sparago A, Cerrato F, Russo S, et
al: The KCNQ1OT1 imprinting control region and non-coding RNA: New
properties derived from the study of Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome
and Silver-Russell syndrome cases. Hum Mol Genet. 21:10–25. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
American Psychiatric Association:
Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, text
revision (DSM-IV-TR). American Psychiatric Association; 4th
Edition. 2000
|
|
31
|
Hogart A, Lichtenberg J, Ajay SS, Anderson
S and Margulies EH: Genome-wide DNA methylation profiles in
hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells reveal overrepresentation
of ETS transcription factor binding sites. Genome Res.
22:1407–1418. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Langmead B, Trapnell C, Pop M and Salzberg
SL: Ultrafast and memory-efficient alignment of short DNA sequences
to the human genome. Genome Biol. 10:R252009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang Y, Liu T, Meyer CA, Eeckhoute J,
Johnson DS, Bernstein BE, Nusbaum C, Myers RM, Brown M, Li W, et
al: Model-based analysis of ChIP-Seq (MACS). Genome Biol.
9:R1372008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Heinz S, Benner C, Spann N, Bertolino E,
Lin YC, Laslo P, Cheng JX, Murre C, Singh H and Glass CK: Simple
combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime
cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell
identities. Mol Cell. 38:576–589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nakato R, Itoh T and Shirahige K: DROMPA:
Easy-to-handle peak calling and visualization software for the
computational analysis and validation of ChIP-seq data. Genes
Cells. 18:589–601. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Karolchik D, Hinrichs AS, Furey TS, Roskin
KM, Sugnet CW, Haussler D and Kent WJ: The UCSC Table Browser data
retrieval tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 32:D493–D496. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Ji W, Li T, Pan Y, Tao H, Ju K, Wen Z, Fu
Y, An Z, Zhao Q, Wang T, et al: CNTNAP2 is significantly associated
with schizophrenia and major depression in the Han Chinese
population. Psychiatry Res. 207:225–228. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Rodenas-Cuadrado P, Ho J and Vernes SC:
Shining a light on CNTNAP2: Complex functions to complex disorders.
Eur J Hum Genet. 22:171–178. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Kao HT, Porton B, Czernik AJ, Feng J, Yiu
G, Häring M, Benfenati F and Greengard P: A third member of the
synapsin gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 95:4667–4672. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bousman CA, Glatt SJ, Chandler SD, Lohr J,
Kremen WS, Tsuang MT and Everall IP: Negative symptoms of psychosis
correlate with gene expression of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling
pathway in peripheral blood. Psychiatry J. 2013:8529302013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Berridge MJ: Dysregulation of neural
calcium signaling in Alzheimer disease, bipolar disorder and
schizophrenia. Prion. 7:2–13. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Fogel BL, Wexler E, Wahnich A, Friedrich
T, Vijayendran C, Gao F, Parikshak N, Konopka G and Geschwind DH:
RBFOX1 regulates both splicing and transcriptional networks in
human neuronal development. Hum Mol Genet. 21:4171–4186. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fatemi SH, Folsom TD, Reutiman TJ and
Vazquez G: Phosphodiesterase signaling system is disrupted in the
cerebella of subjects with schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and
major depression. Schizophr Res. 119:266–267. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fatemi SH, Folsom TD, Reutimann TJ, Braun
NN and Lavergne LG: Levels of phosphodiesterase 4A and 4B are
altered by chronic treatment with psychotropic medications in rat
frontal cortex. Synapse. 64:550–555. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Irwin KE, Henderson DC, Knight HP and Pirl
WF: Cancer care for individuals with schizophrenia. Cancer.
120:323–334. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Wang KS, Liu XF and Aragam N: A
genome-wide meta-analysis identifies novel loci associated with
schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res. 124:192–199.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Teo C, Zai C, Borlido C, Tomasetti C,
Strauss J, Shinkai T, Le Foll B, Wong A, Kennedy JL and De Luca V:
Analysis of treatment-resistant schizophrenia and 384 markers from
candidate genes. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 22:807–811. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Al-Sayed MD, Al-Zaidan H, Albakheet A,
Hakami H, Kenana R, Al-Yafee Y, Al-Dosary M, Qari A, Al-Sheddi T,
Al-Muheiza M, et al: Mutations in NALCN cause an
autosomal-recessive syndrome with severe hypotonia, speech
impairment, and cognitive delay. Am J Hum Genet. 93:721–726. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dobson-Stone C, Polly P, Korgaonkar MS,
Williams LM, Gordon E, Schofield PR, Mather K, Armstrong NJ, Wen W,
Sachdev PS and Kwok JB: GSK3B and MAPT polymorphisms are associated
with grey matter and intracranial volume in healthy individuals.
PLoS One. 8:e717502013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Minoretti P, Politi P, Coen E, Di Vito C,
Bertona M, Bianchi M and Emanuele E: The T393C polymorphism of the
GNAS1 gene is associated with deficit schizophrenia in an Italian
population sample. Neurosci Lett. 397:159–163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Zou M, Li S, Klein WH and Xiang M:
Brn3a/Pou4f1 regulates dorsal root ganglion sensory neuron
specification and axonal projection into the spinal cord. Dev Biol.
364:114–127. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Abel KM, Drake R and Goldstein JM: Sex
differences in schizophrenia. Int Rev Psychiatry. 22:417–428. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lindamer LA, Lohr JB, Harris MJ and Jeste
DV: Gender, estrogen, and schizophrenia. Psychopharmacol Bull.
33:221–228. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Mellios N, Galdzicka M, Ginns E, Baker SP,
Rogaev E, Xu J and Akbarian S: Gender-specific reduction of
estrogen-sensitive small RNA, miR-30b, in subjects with
schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull. 38:433–443. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
55
|
Boksa P: Animal models of obstetric
complications in relation to schizophrenia. Brain Res Brain Res
Rev. 45:1–17. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Missios S, Harris BT, Dodge CP, Simoni MK,
Costine BA, Lee YL, Quebada PB, Hillier SC, Adams LB and Duhaime
AC: Scaled cortical impact in immature swine: Effect of age and
gender on lesion volume. J Neurotrauma. 26:1943–1951. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Wilson C and Terry AV Jr:
Neurodevelopmental animal models of schizophrenia: Role in novel
drug discovery and development. Clin Schizophr Relat Psychoses.
4:124–137. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cosimo Melcangi R and Garcia-Segura LM:
Sex-specific therapeutic strategies based on neuroactive steroids:
In search for innovative tools for neuroprotection. Horm Behav.
57:2–11. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Kulkarni J, Gurvich C, Lee SJ, Gilbert H,
Gavrilidis E, de Castella A, Berk M, Dodd S, Fitzgerald PB and
Davis SR: Piloting the effective therapeutic dose of adjunctive
selective estrogen receptor modulator treatment in postmenopausal
women with schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 35:1142–1147.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Roth TL, Lubin FD, Sodhi M and Kleinman
JE: Epigenetic mechanisms in schizophrenia. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1790:869–877. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Feng J, Sun G, Yan J, Noltner K, Li W,
Buzin CH, Longmate J, Heston LL, Rossi J and Sommer SS: Evidence
for X-chromosomal schizophrenia associated with microRNA
alterations. PLoS One. 4:e61212009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Beveridge NJ and Cairns MJ: MicroRNA
dysregulation in schizophrenia. Neurobiol Dis. 46:263–271. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Melas PA, Rogdaki M, Ösby U, Schalling M,
Lavebratt C and Ekström TJ: Epigenetic aberrations in leukocytes of
patients with schizophrenia: Association of global DNA methylation
with antipsychotic drug treatment and disease onset. FASEB J.
26:2712–2718. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Lai CY, Yu SL, Hsieh MH, Chen CH, Chen HY,
Wen CC, Huang YH, Hsiao PC, Hsiao CK and Liu CM: MicroRNA
expression aberration as potential peripheral blood biomarkers for
schizophrenia. PLoS One. 6:e216352011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|