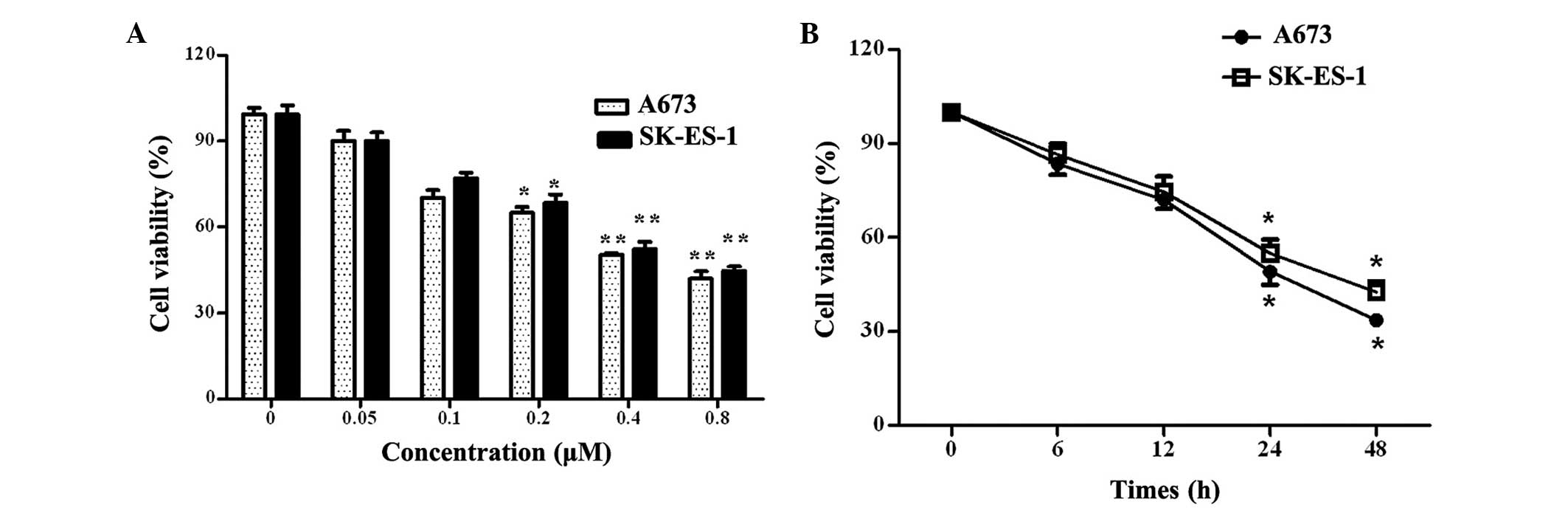
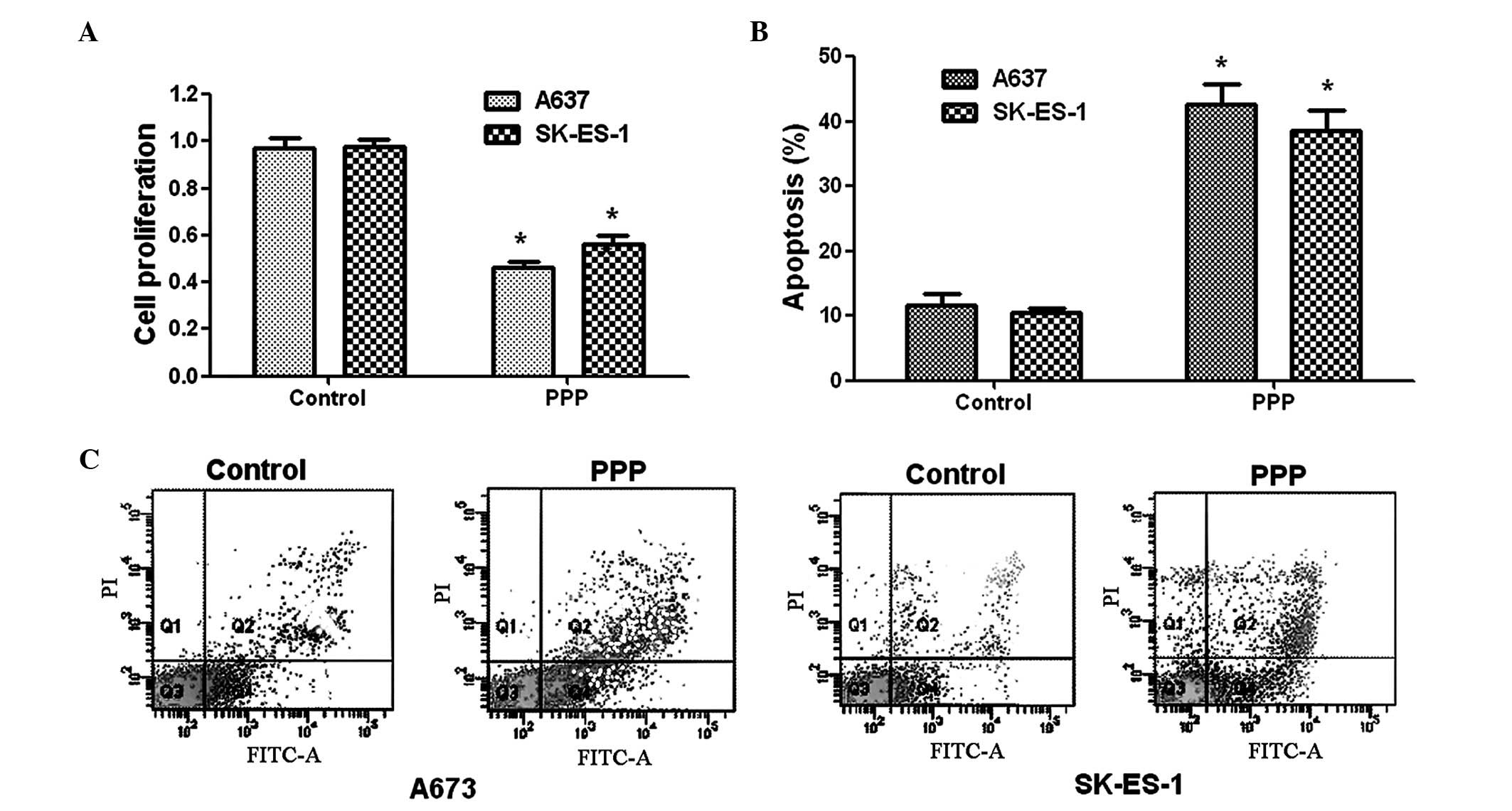
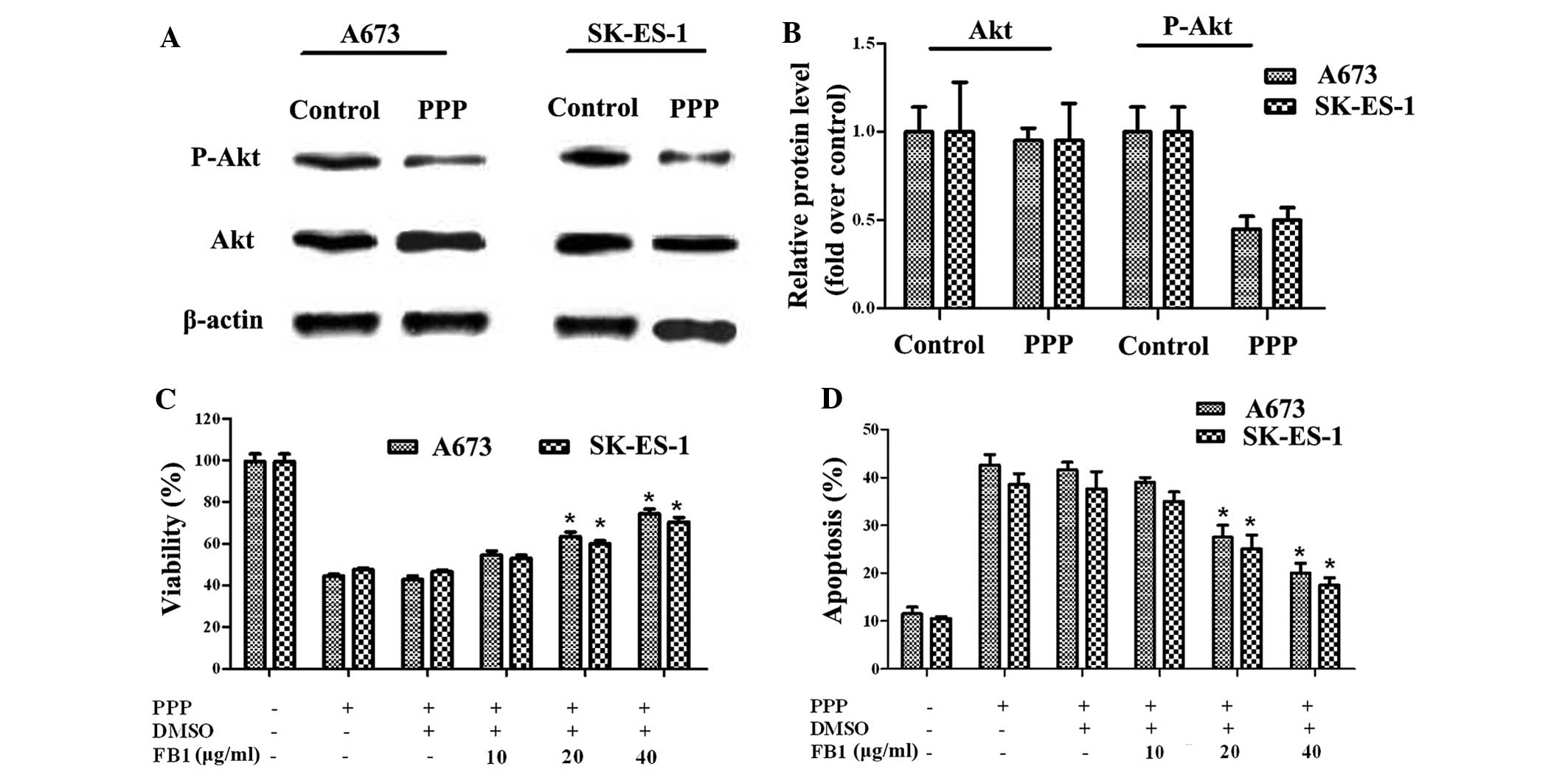
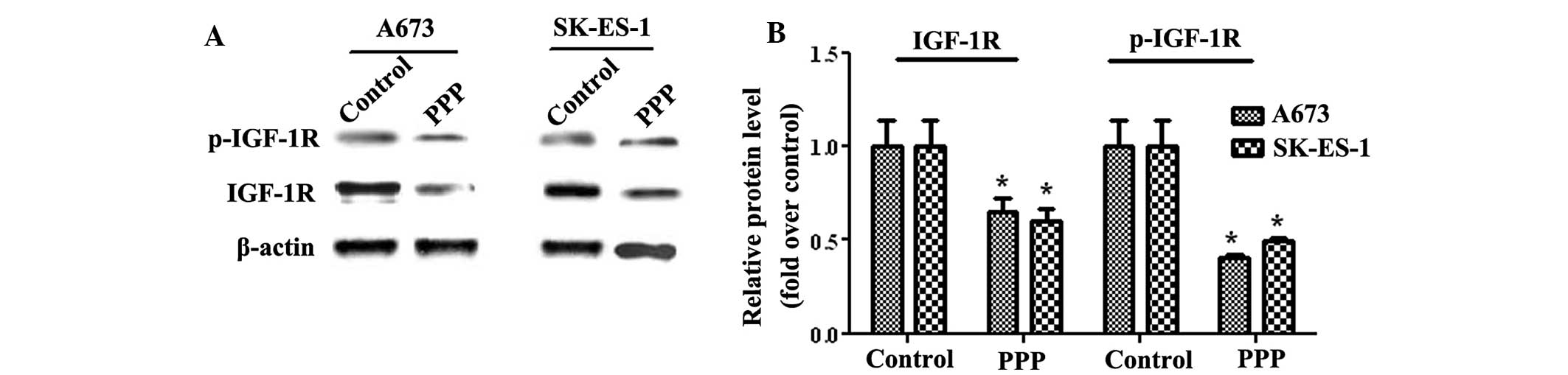
|
1
|
Iwamoto Y: Diagnosis and treatment of
Ewing's sarcoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 37:79–89. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Delattre O, Zucman J, Melot T, Garau XS,
Zucker JM, Lenoir GM, Ambros PF, Sheer D, Turc-Carel C and Triche
TJ: The Ewing family of tumors-a subgroup of small-round-cell
tumors defined by specific chimeric transcripts. N Engl J Med.
331:294–299. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Alava E and Gerald WL: Molecular
biology of the Ewing's sarcoma/primitive neuroectodermal tumor
family. J Clin Oncol. 18:204–213. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burgert EO Jr, Nesbit ME, Garnsey LA,
Gehan EA, Herrmann J, Vietti TJ, Cangir A, Tefft M, Evans R and
Thomas P: Multimodal therapy for the management of nonpelvic,
localized Ewing's sarcoma of bone: Intergroup study IESS-II. J Clin
Oncol. 8:1514–1524. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kontny U: Regulation of apoptosis and
proliferation in Ewing's sarcoma-opportunities for targeted
therapy. Hematol Oncol. 24:14–21. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tanaka K, Iwakuma T, Harimaya K, Sato H
and Iwamoto Y: EWS-Fli1 antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits
proliferation of human Ewing's sarcoma and primitive
neuroectodermal tumor cells. J Clin Invest. 99:239–247. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kinsey M, Smith R and Lessnick SL: NR0B1
is required for the oncogenic phenotype mediated by EWS/FL1 in
Ewing's sarcoma. Mol Cancer Res. 4:851–859. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kauer M, Ban J, Kofler R, Walker B, Davis
S, Meltzer P and Kovar H: A molecular function map of Ewing's
sarcoma. PLoS One. 4:e54152009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rocchi A, Manara MC, Sciandra M, Zambelli
D, Nardi F, Nicoletti G, Garofalo C, Meschini S, Astolfi A, Colombo
MP, et al: CD99 inhibits neural differentiation of human Ewing
sarcoma cells and thereby contributes to oncogenesis. J Clin
Invest. 120:668–680. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Scotlandi K, Maini C, Manara MC, Benini S,
Serra M, Cerisano V, Strammiello R, Baldini N, Lollini PL, Nanni P,
et al: Effectiveness of insulin-like growth factor I receptor
antisense strategy against Ewing's sarcoma cells. Cancer Gene Ther.
9:296–307. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kang HG, Jenabi JM, Liu XF, Reynolds CP,
Triche TJ and Sorensen PH: Inhibition of the insulin-like growth
factor I receptor by epigallocatechin gallate blocks proliferation
and induces the death of Ewing tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
9:1396–1407. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Prieur A, Tirode F, Cohen P and Delattre
O: EWS/FLI-1 silencing and gene profiling of Ewing cells reveal
downstream oncogenic pathways and a crucial role for repression of
insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3. Mol Cell Biol.
24:7275–7283. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Scotlandi K, Avnet S, Benini S, Manara MC,
Serra M, Cerisano V, Perdichizzi S, Lollini PL, De Giovanni C,
Landuzzi L and Picci P: Expression of an IGF-I receptor dominant
negative mutant induces apoptosis, inhibits tumorigenesis and
enhances chemosensitivity in Ewing's sarcoma cells. Int J Cancer.
101:11–16. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Benini S, Manara MC, Baldini N, Cerisano
V, Massimo Serra, Mercuri M, Lollini PL, Nanni P, Picci P and
Scotlandi K: Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor I receptor
increases the antitumor activity of doxorubicin and vincristine
against Ewing's sarcoma cells. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1790–1797.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Scotlandi K, Benini S, Sarti M, Serra M,
Lollini PL, Maurici D, Picci P, Manara MC and Baldini N:
Insulin-like growth factor I receptor-mediated circuit in Ewing's
sarcoma/peripheral neuroectodermal tumor: A possible therapeutic
target. Cancer Res. 56:4570–4574. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scotlandi K, Manara MC, Nicoletti G,
Lollini PL, Lukas S, Benini S, Croci S, Perdichizzi S, Zambelli D,
Serra M, et al: Antitumor activity of the insulin-like growth
factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor NVP-AEW541 in musculoskeletal
tumors. Cancer Res. 65:3868–3876. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Manara MC, Landuzzi L, Nanni P, Nicoletti
G, Zambelli D, Lollini PL, Nanni C, Hofmann F, García-Echeverría C,
Picci P and Scotlandi K: Preclinical in vivo study of new
insulin-like growth factor-I receptor-specific inhibitor in Ewing's
sarcoma. Clin Cancer Res. 13:1322–1330. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang Z, Fang Z, Zhen H, Zhou L, Amin HM
and Shi P: Inhibition of type I insulin-like growth factor receptor
tyrosine kinase by picropodophyllin induces apoptosis and cell
cycle arrest in T lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma.
55:1876–1883. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yin SC, Guo W and Tao ZZ: Picropodophyllin
inhibits tumor growth of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma in a mouse
model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 439:1–5. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang Q, Wei F, Lv G, Li C, Liu T,
Hadjipanayis CG, Zhang G, Hao C and Bellail AC: The association of
TP53 mutations with the resistance of colorectal carcinoma to the
insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor inhibitor picropodophyllin.
BMC Cancer. 13:5212013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu X, Wang L, Mei J, Wang X, Zhu X, Zhang
Q and Lv J: Picropodophyllin inhibits epithelial ovarian cancer
cells in vitro and in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
435:385–390. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hixon ML, Paccagnella L, Millham R,
Perez-Olle R and Gualberto A: Development of inhibitors of the
IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Rev Recent Clin Trials. 5:189–208.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Martin-Piedra MA, Garzon I, Oliveira AC,
Alfonso-Rodriguez CA, Carriel V, Scionti G and Alaminos M: Cell
viability and proliferation capability of long-term human dental
pulp stem cell cultures. Cytotherapy. 16:266–277. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li J, You T and Jing J: MiR-125b inhibits
cell biological progression of Ewing's sarcoma by suppressing the
PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 47:152–160. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bertrand FE, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Shelton JG, White ER, Ludwig DL and McCubrey JA: Synergy
between an IGF-1R antibody and Raf//MEK//ERK and PI3K//Akt//mTOR
pathway inhibitors in suppressing IGF-1R-mediated growth in
hematopoietic cells. Leukemia. 20:1254–1260. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Shelton JG, Steelman LS, White ER and
McCubrey JA: Synergy between PI3K/Akt and Raf/MEK/ERK pathways in
IGF-1R mediated cell cycle progression and prevention of apoptosis
in hematopoietic cells. Cell Cycle. 3:372–379. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yang Y, Li H, Zhang F, Shi H, Zhen T, Dai
S, Kang L, Liang Y, Wang J and Han A: Clinical and biological
significance of hepatoma-derived growth factor in Ewing's sarcoma.
J Pathol. 231:323–334. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gorelik N, Dickson BC, Wunder JS and
Bleakney R: Ewing's sarcoma of the patella. Skeletal Radiol.
42:729–733. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sankar S and Lessnick SL: Promiscuous
partnerships in Ewing's sarcoma. Cancer Genet. 204:351–365. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Duan Z, Choy E, Harmon D, Yang C, Ryu K,
Schwab J, Mankin H and Hornicek FJ: Insulin-like growth factor-I
receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor cyclolignan picropodophyllin
inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in multidrug resistant
osteosarcoma cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:2122–2130. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Menu E, Jernberg-Wiklund H, De Raeve H, De
Leenheer E, Coulton L, Gallagher O, Van Valckenborgh E, Larsson O,
Axelson M, Nilsson K, et al: Targeting the IGF-1R using
picropodophyllin in the therapeutical 5T2MM mouse model of multiple
myeloma: beneficial effects on tumor growth, angio-genesis, bone
disease and survival. Int J Cancer. 121:1857–1861. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Krishnan K, Bruce B, Hewitt S, Thomas D,
Khanna C and Helman LJ: Ezrin mediates growth and survival in
Ewing's sarcoma through the AKT/mTOR, but not the MAPK, signaling
pathway. Clin Exp Metastasis. 23:227–236. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kilic-Eren M, Boylu T and Tabor V:
Targeting PI3K/Akt represses Hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha
activation and sensitizes Rhabdomyosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma
cells for apoptosis. Cancer Cell Int. 13:362013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li J, You T and Jing J: MiR-125b inhibits
cell biological progression of Ewing's sarcoma by suppressing the
PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. Cell Prolif. 47:152–160. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Qi L, Toyoda H, Shankar V, Sakurai N,
Amano K, Kihira K, Iwasa T, Deguchi T, Hori H, Azuma E, et al:
Heterogeneity of neuroblastoma cell lines in insulin-like growth
factor 1 receptor/Akt pathway-mediated cell proliferative
responses. Cancer Sci. 104:1162–1171. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bähr C and Groner B: The insulin like
growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1 R) as a drug target: Novel
approaches to cancer therapy. Growth Horm IGF Res. 14:287–295.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Bianco R, Melisi D, Ciardello F and
Tortora G: Key cancer cell signal transduction pathways as
therapeutic targets. Eur J Cancer. 42:290–294. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Fabian J, Lodrini M, Oehme I, Schier MC,
Thole TM, Hielscher T, Kopp-Schneider A, Opitz L, Capper D, von
Deimling A, et al: GRHL1 acts as tumor suppressor in neuroblastoma
and is negatively regulated by MYCN and HDAC3. Cancer Res.
74:2604–2616. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Estañ MC, Calviño E, de Blas E,
Boyano-Adanez Mdel C, Mena ML, Gómez-Gómez M, Rial E and Aller P:
2-Deoxy-D-glucose cooperates with arsenic trioxide to induce
apoptosis in leukemia cells: Involvement of IGF-1R-regulated
Akt/mTOR, MEK/ERK and LKB-1/AMPK signaling pathways. Biochem
Pharmacol. 84:1604–1616. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Baumgarten SC, Convissar SM, Fierro MA,
Winston NJ, Scoccia B and Stocco C: IGF-1R signaling is necessary
for FSH-induced activation of AKT and differentiation of human
cumulus granulosa cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 99:2995–3004.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Chen C, Xu Y and Song Y: IGF-1
gene-modified muscle-derived stem cells are resistant to oxidative
stress via enhanced activation of IGF-1R/PI3K/AKT signaling and
secretion of VEGF. Mol Cell Biochem. 386:167–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Jiang YY, Huang H, Wang HJ, Wu D, Yang R,
Tashiro S, Onodera S and Ikejima T: Interruption of mitochondrial
complex IV activity and cytochrome c expression activated
O2·-mediated cell survival in silibinin-treated human
melanoma A375-S2 cells via IGF-1R-PI3K-Akt and IGF-1R-PLC gamma-PKC
pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 668:78–87. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|