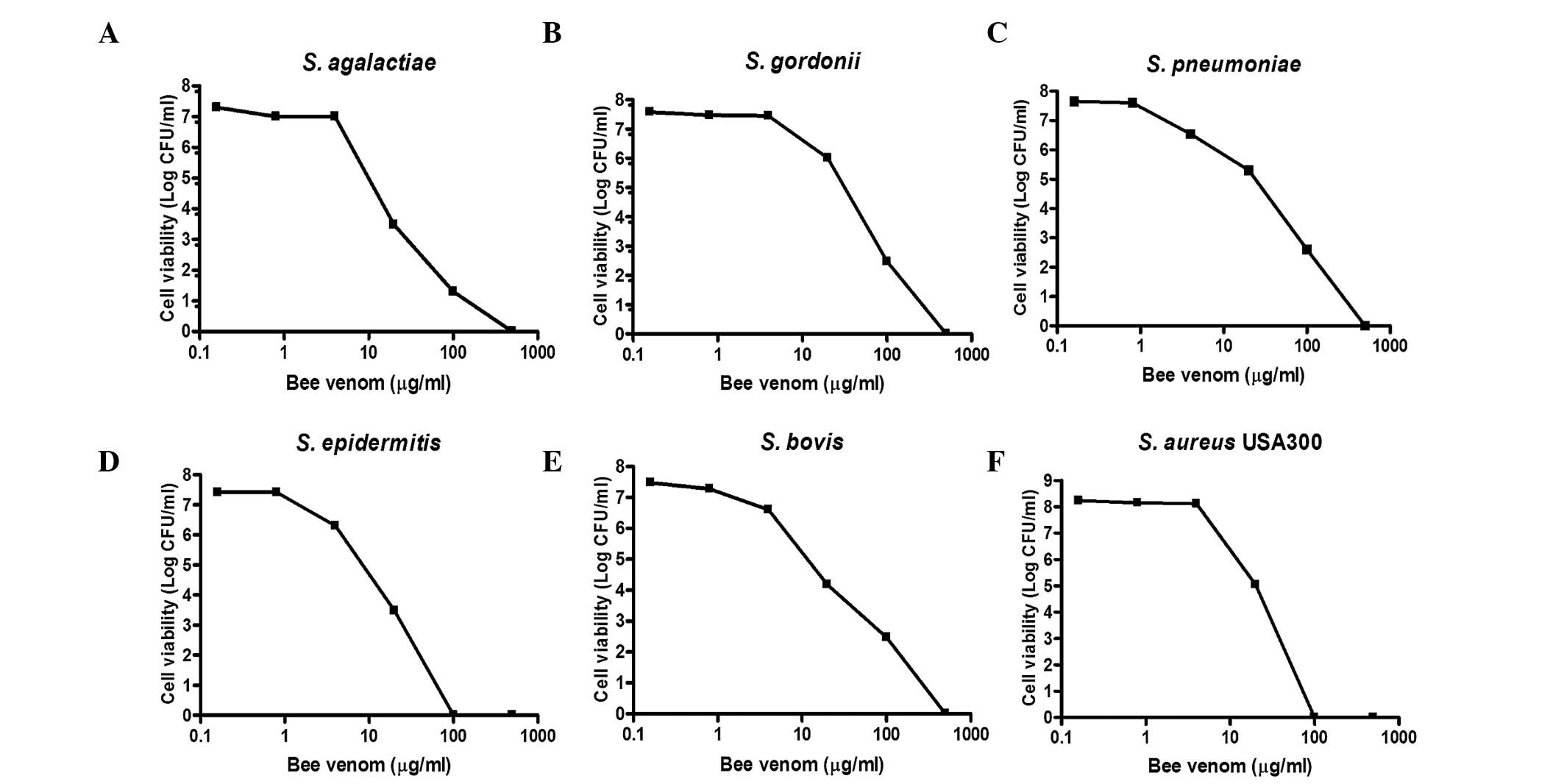
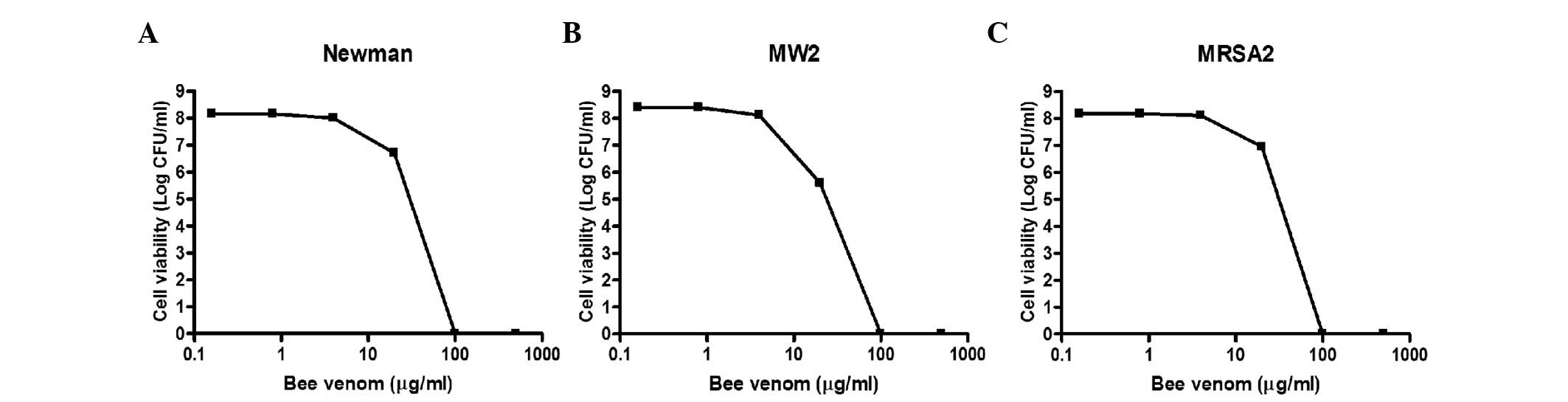
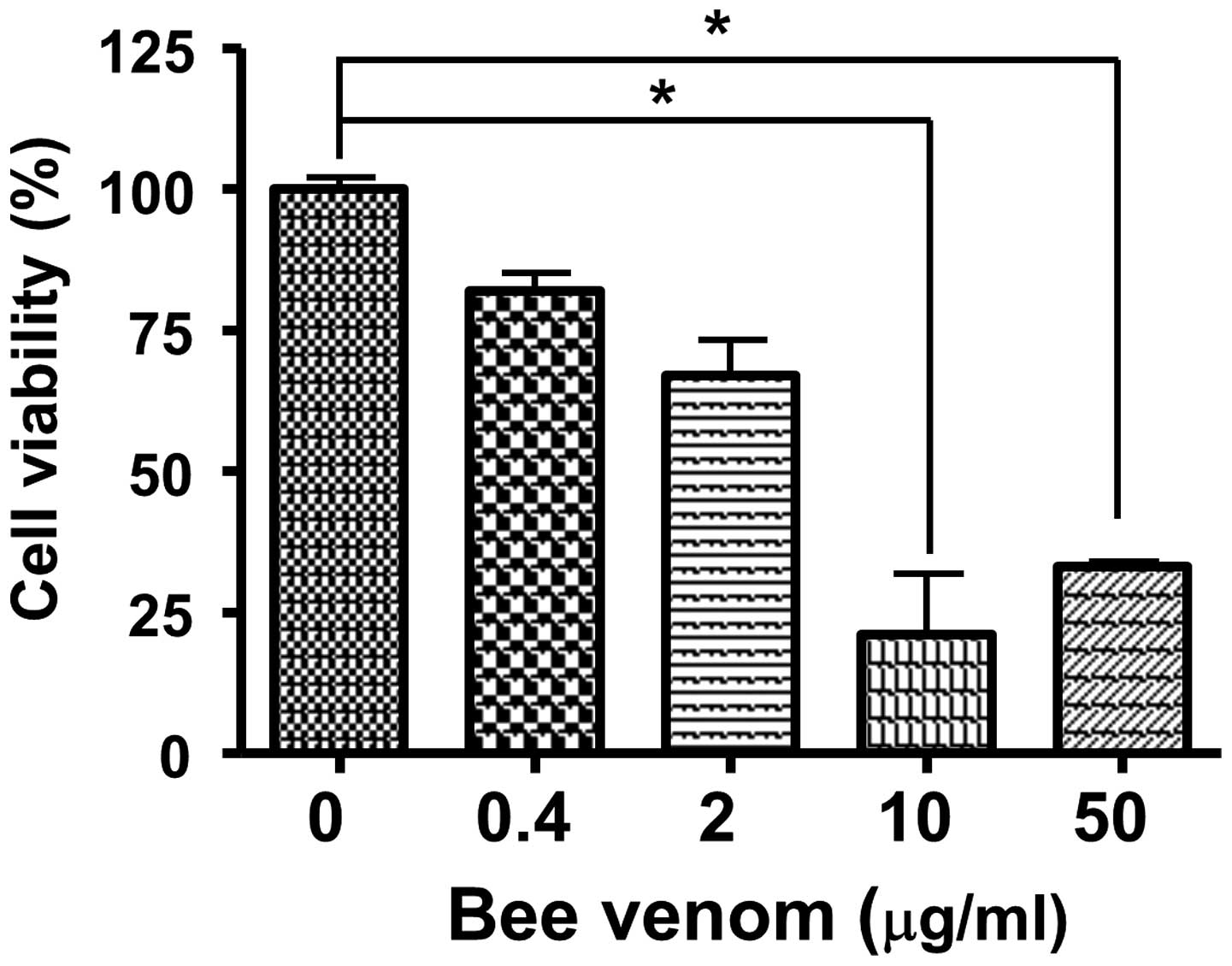
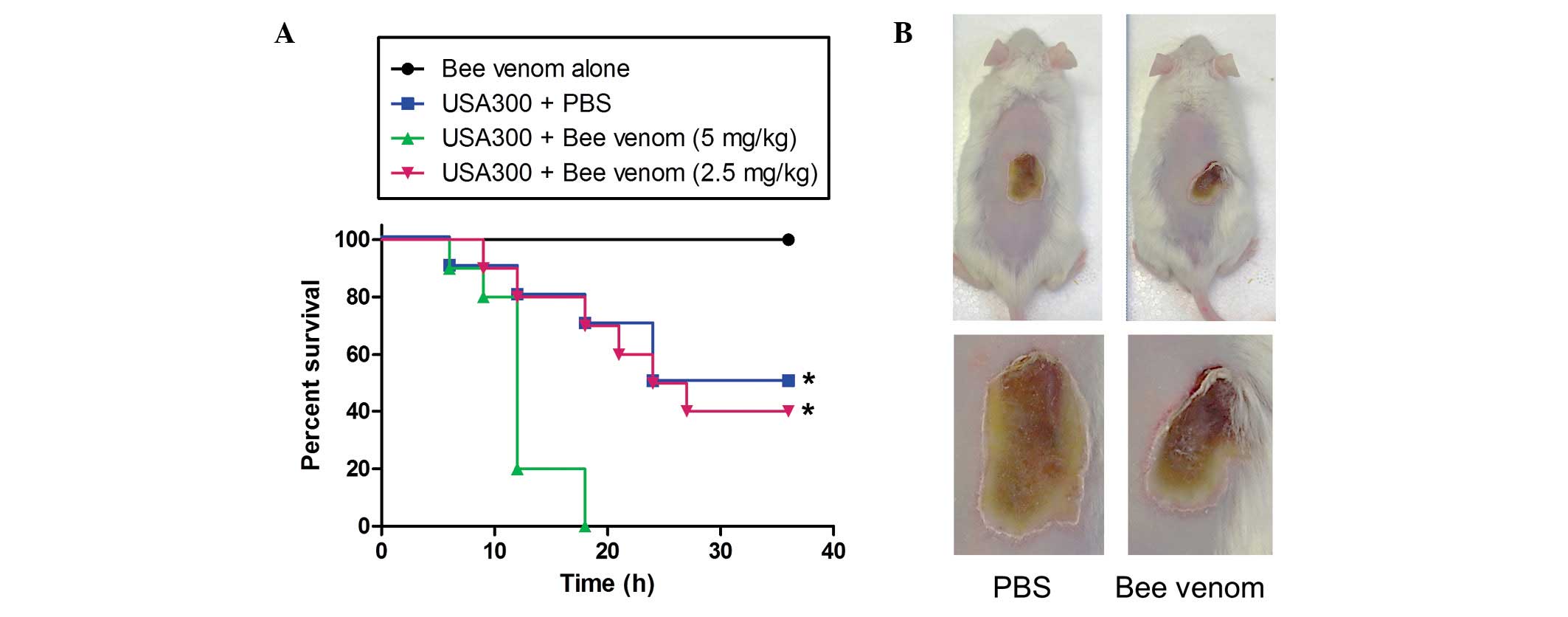
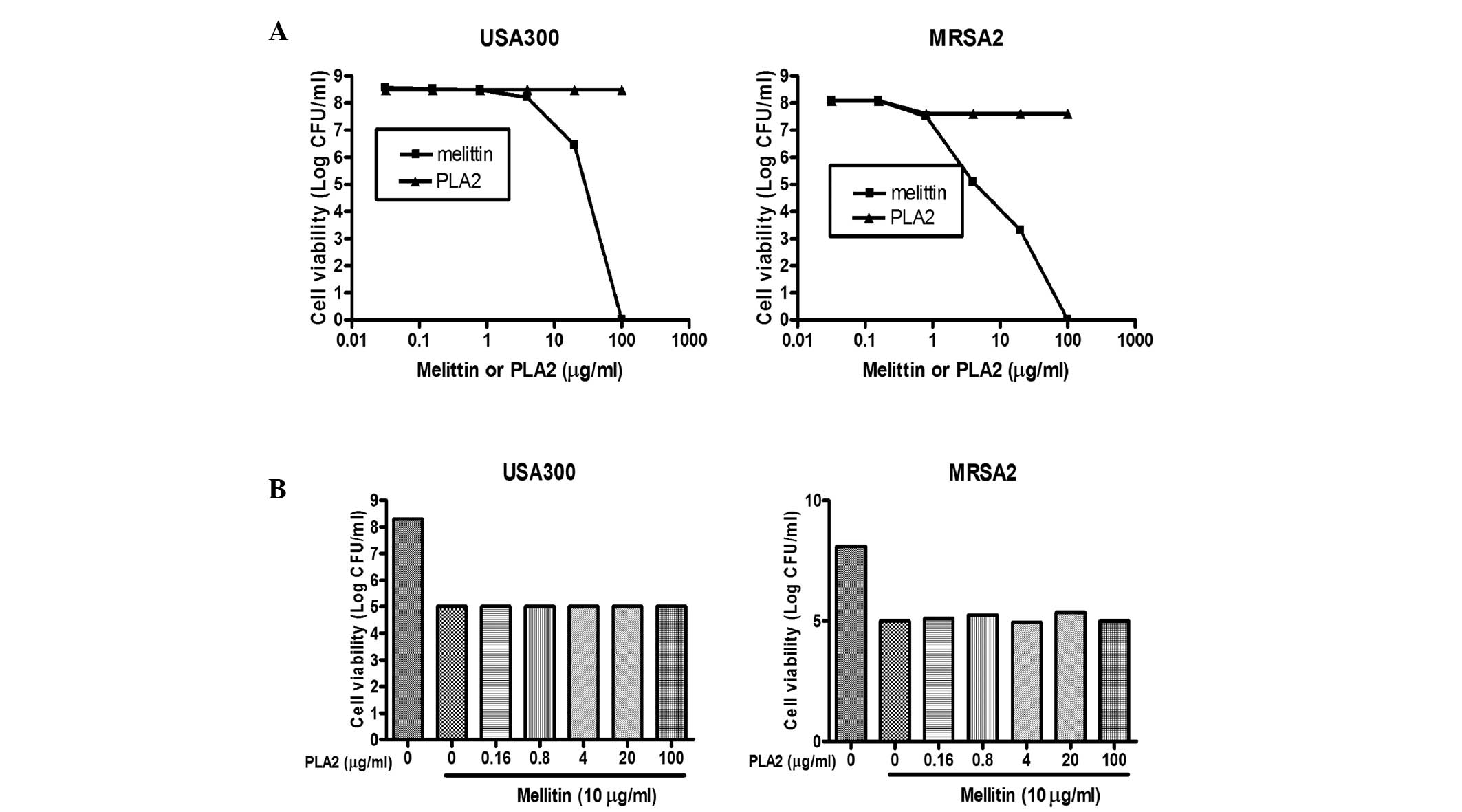
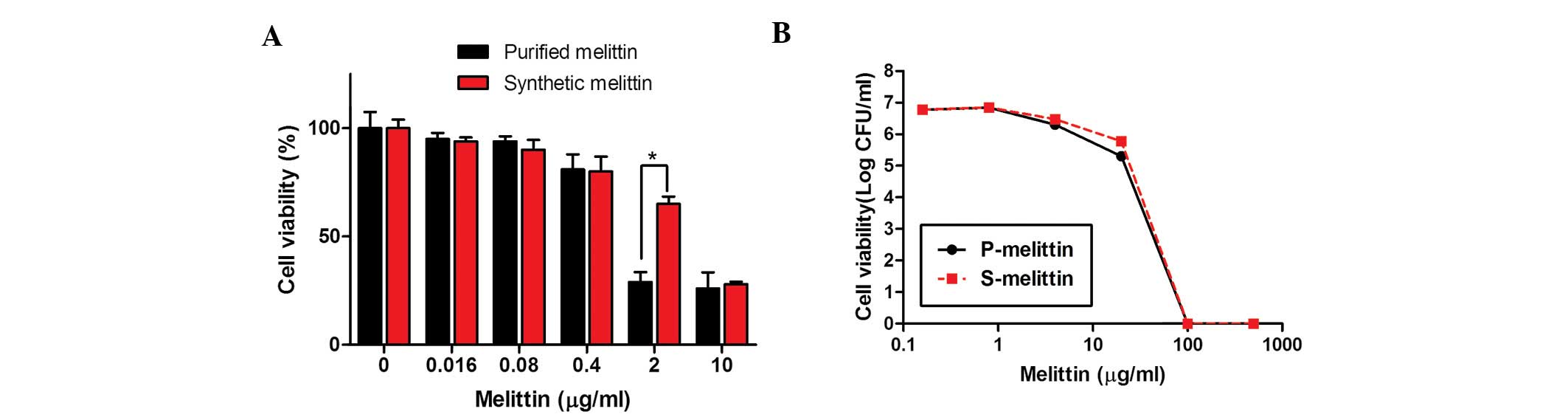
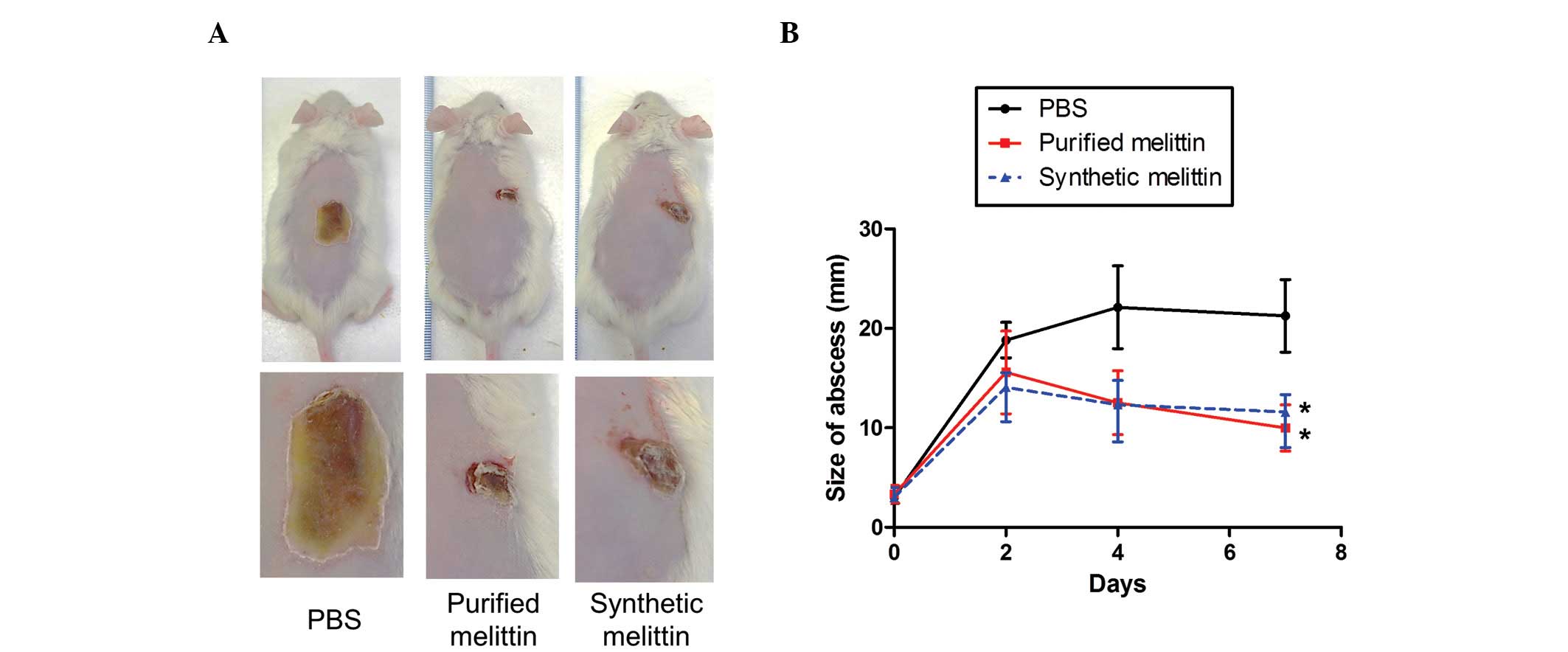
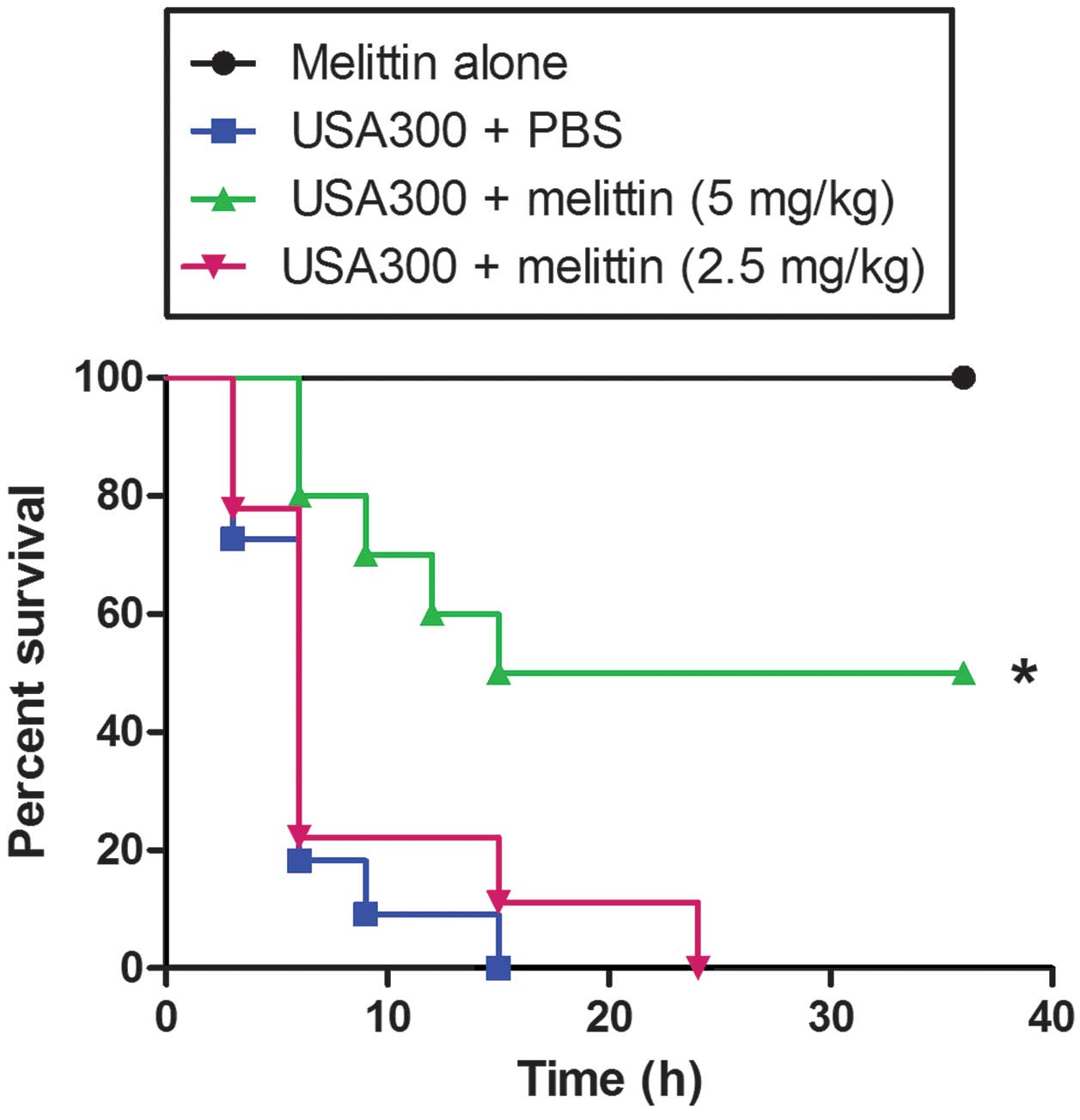
|
1
|
Rasigade JP and Vandenesch F:
Staphylococcus aureus: A pathogen with still unresolved issues.
Infect Genet Evol. 21:510–514. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Taylor AR: Methicillin-resistant
Staphylococcus aureus infections. Prim Care. 40:637–654. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Limbago BM, Kallen AJ, Zhu W, Eggers P,
McDougal LK and Albrecht VS: Report of the 13th
vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus isolate from the United
States. J Clin Microbiol. 52:998–1002. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
4
|
Corey GR: Staphylococcus aureus
bloodstream infections: Definitions and treatment. Clin Infect Dis.
48(Suppl 4): S254–S259. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gould IM: VRSA-doomsday superbug or damp
squib? Lancet Infect Dis. 10:816–818. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bassetti M, Merelli M, Temperoni C and
Astilean A: New antibiotics for bad bugs: Where are we? Ann Clin
Microbiol Antimicrob. 12(22)2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Annila I: Bee venom allergy. Clin Exp
Allergy. 30:1682–1687. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Son DJ, Lee JW, Lee YH, Song HS, Lee CK
and Hong JT: Therapeutic application of anti-arthritis,
pain-releasing and anti-cancer effects of bee venom and its
constituent compounds. Pharmacol Ther. 115:246–270. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kim JY, Lee WR, Kim KH, An HJ, Chang YC,
Han SM, Park YY, Pak SC and Park KK: Effects of bee venom against
Propionibacterium acnes-induced inflammation in human keratinocytes
and monocytes. Int J Mol Med. 35:1651–1656. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee H, Lee EJ, Kim H, Lee G, Um EJ, Kim Y,
Lee BY and Bae H: Bee venom-associated Th1/Th2 immunoglobulin class
switching results in immune tolerance of NZB/W F1 murine lupus
nephritis. Am J Nephrol. 34:163–172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Perumal Samy R, Gopalakrishnakone P, Thwin
MM, Chow TK, Bow H, Yap EH and Thong TW: Antibacterial activity of
snake, scorpion and bee venoms: A comparison with purified venom
phospholipase A2 enzymes. J Appl Microbiol. 102:650–659. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gajski G and Garaj-Vrhovac V: Melittin: A
lytic peptide with anticancer properties. Environ Toxicol
Pharmacol. 36:697–705. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Adade CM, Oliveira IR, Pais JA and
Souto-Padron T: Melittin peptide kills Trypanosoma cruzi parasites
by inducing different cell death pathways. Toxicon. 69:227–239.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jo M, Park MH, Kollipara PS, An BJ, Song
HS, Han SB, Kim JH, Song MJ and Hong JT: Anti-cancer effect of bee
venom toxin and melittin in ovarian cancer cells through induction
of death receptors and inhibition of JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Toxicol
Appl Pharmacol. 258:72–81. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Han SM, Lee GG and Park KK: Acute dermal
toxicity study of bee venom (Apis mellifera L.) in rats. Toxicol
Res. 28:99–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Han SM, Lee KG, Park KK and Pak SC: Skin
sensitization study of bee venom (Apis mellifera L.) in guinea pigs
and rats. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 32:27–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Han SM, Lee GG and Park KK: Skin
sensitization study of bee venom (Apis mellifera L.) in guinea
pigs. Toxicol Res. 28:1–4. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Seo HS, Mu R, Kim BJ, Doran KS and Sullam
PM: Binding of glycoprotein Srr1 of Streptococcus agalactiae to
fibrinogen promotes attachment to brain endothelium and the
eevelopment of meningitis. PLoS Pathog. 8:e10029472012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Clinical and Laboratory Standards
Institute: M100-S16, Performance standards for antimicrobial
susceptibility testing; 16th informational supplement. Clinical and
Laboratory Standards Institute; Wayne, PA: 2007
|
|
20
|
Ganesh VK, Rivera JJ, Smeds E, Ko YP,
Bowden MG, Wann ER, Gurusiddappa S, Fitzgerald JR and Höök M: A
structural model of the Staphylococcus aureus ClfA-fibrinogen
interaction opens new avenues for the design of anti-staphylococcal
therapeutics. PLoS Pathog. 4:e10002262008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bensing BA, Gibson BW and Sullam PM: The
Streptococcus gordonii platelet binding protein GspB undergoes
glycosylation independently of export. J Bacteriol. 186:638–645.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seo HS, Cartee RT, Pritchard DG and Nahm
MH: A new model of pneumococcal lipoteichoic acid structure
resolves biochemical, biosynthetic and serologic inconsistencies of
the current model. J Bacteriol. 190:2379–2387. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Qian Z, Yin Y, Zhang Y, Lu L, Li Y and
Jiang Y: Genomic char-acterization of ribitol teichoic acid
synthesis in Staphylococcus aureus: Genes, genomic organization and
gene duplication. BMC Genomics. 7(74)2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Goldrick BA: MRSA, VRE, and VRSA: How do
we control them in nursing homes? Am J Nurs. 104:50–51. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hebert C and Weber SG: Common approaches
to the control of multidrug-resistant organisms other than
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). Infect Dis Clin
North Am. 25:181–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Todd B: Beyond MRSA: VISA and VRSA: What
will ward off these pathogens in health care facilities? Am J Nurs.
106:28–30. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Park D, Jung JW, Lee MO, Lee SY, Kim B,
Jin HJ, Kim J, Ahn YJ, Lee KW, Song YS, et al: Functional
characterization of naturally occurring melittin peptide isoforms
in two honey bee species, Apis mellifera and Apis cerana. Peptides.
53:185–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Palm NW and Medzhitov R: Role of the
inflammasome in defense against venoms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
110:1809–1814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Fennell JF, Shipman WH and Cole LJ:
Antibacterial action of a bee venom fraction (melittin) against a
penicillin-resistant staphylococcus and other microorganisms.
USNRDL-TR-67-101. Res Dev Tech Rep. 5:1–13. 1967.
|
|
30
|
Putz T, Ramoner R, Gander H, Rahm A,
Bartsch G, Bernardo K, Ramsay S and Thurnher M: Bee venom secretory
phospholipase A2 and phosphatidylinositol-homologues cooperatively
disrupt membrane integrity, abrogate signal transduction and
inhibit proliferation of renal cancer cells. Cancer Immunol
Immunother. 56:627–640. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Carballido JM, Carballido-Perrig N,
Schwärzler C and Lametschwandtner G: Regulation of human T helper
cell differentiation by antigen-presenting cells: The bee venom
phospholipase A2 model. Chem Immunol Allergy. 91:147–158. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Lapointe S, Brkovic A, Cloutier I, Tanguay
JF, Arm JP and Sirois MG: Group V secreted phospholipase A2
contributes to LPS-induced leukocyte recruitment. J Cell Physiol.
224:127–134. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sitkiewicz I, Stockbauer KE and Musser JM:
Secreted bacterial phospholipase A2 enzymes: Better living through
phospholipolysis. Trends Microbiol. 15:63–69. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Hunt CL, Nauseef WM and Weiss JP: Effect
of D-alanylation of (lipo) teichoic acids of Staphylococcus aureus
on host secretory phospholipase A2 action before and after
phagocytosis by human neutrophils. J Immunol. 176:4987–4994. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Koprivnjak T, Peschel A, Gelb MH, Liang NS
and Weiss JP: Role of charge properties of bacterial envelope in
bactericidal action of human group IIA phospholipase A2 against
Staphylococcus aureus. J Biol Chem. 277:47636–47644. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fennell JF, Shipman WH and Cole LJ:
Antibacterial action of melittin, a polypeptide from bee venom.
Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 127:707–710. 1968. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Park JH, Kim KH, Lee WR, Han SM and Park
KK: Protective effect of melittin on inflammation and apoptosis in
acute liver failure. Apoptosis. 17:61–69. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Park HJ, Lee HJ, Choi MS, Son DJ, Song HS,
Song MJ, Lee JM, Han SB, Kim Y and Hong JT: JNK pathway is involved
in the inhibition of inflammatory target gene expression and
NF-kappaB activation by melittin. J Inflamm (Lond). 5:72008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Moon DO, Park SY, Choi YH, Kim ND, Lee C
and Kim GY: Melittin induces Bcl-2 and caspase-3-dependent
apoptosis through downregulation of Akt phosphorylation in human
leukemic U937 cells. Toxicon. 51:112–120. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Sommer A, Fries A, Cornelsen I, Speck N,
Koch-Nolte F, Gimpl G, Andrä J, Bhakdi S and Reiss K: Melittin
modulates keratinocyte function through P2 receptor-dependent ADAM
activation. J Biol Chem. 287:23678–23689. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dempsey CE: The actions of melittin on
membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1031:143–161. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kim SJ, Park JH, Kim KH, Lee WR, Kim KS
and Park KK: Melittin inhibits atherosclerosis in LPS/high-fat
treated mice through athero-protective actions. J Atheroscler
Thromb. 18:1117–1126. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|