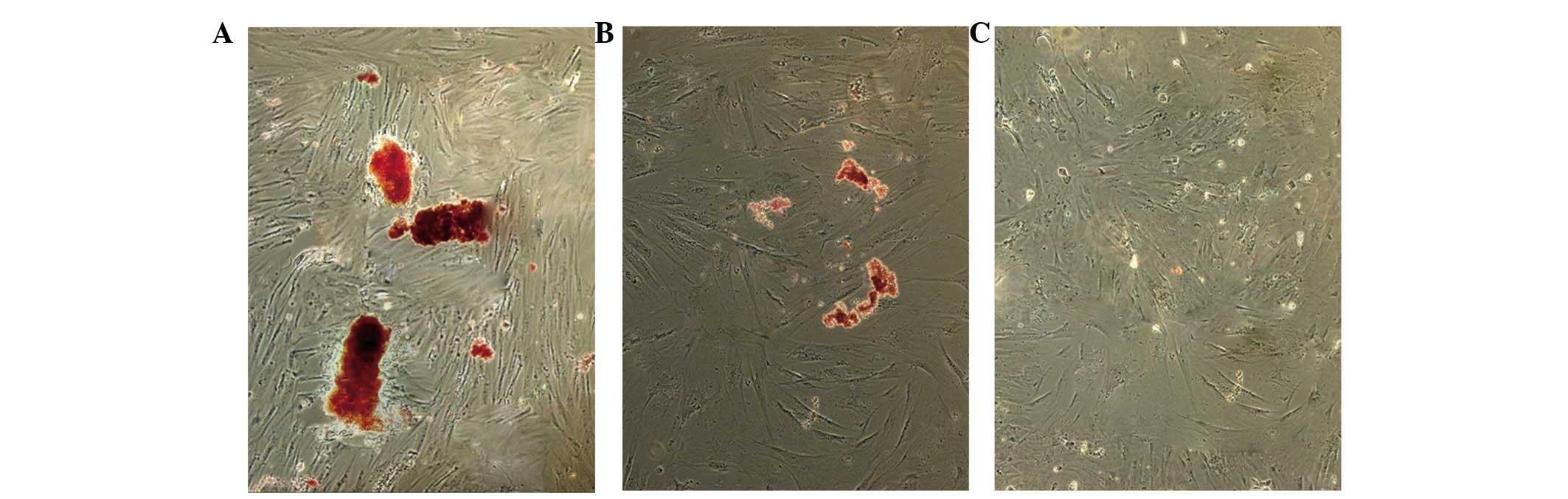
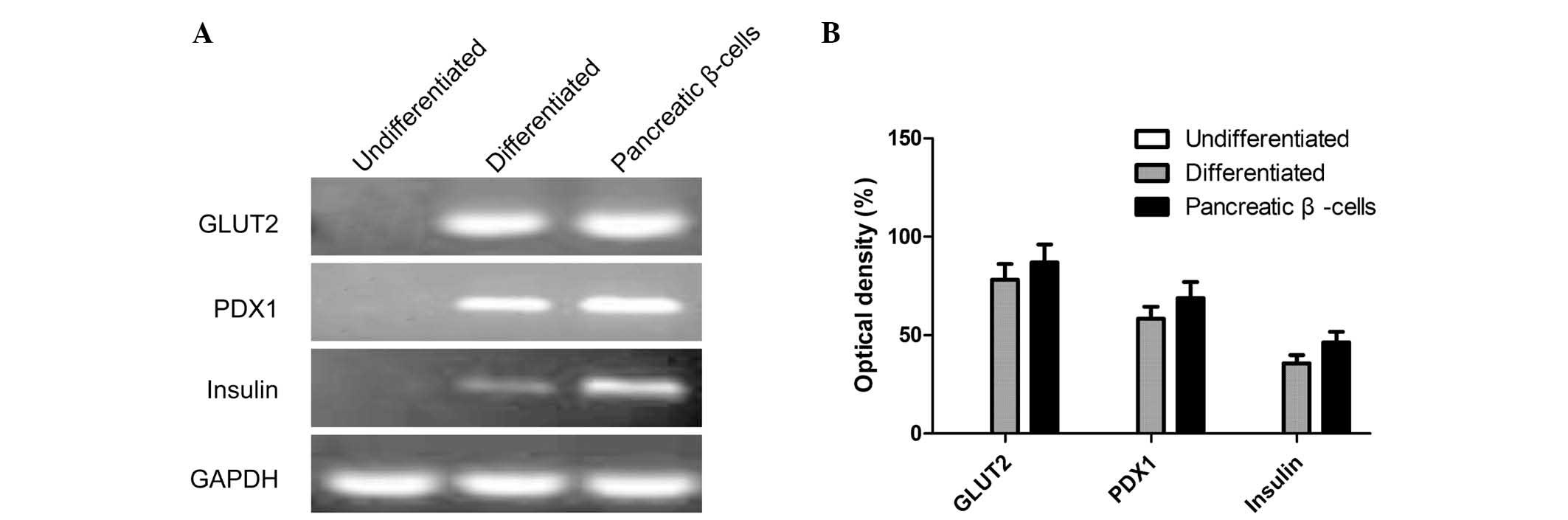
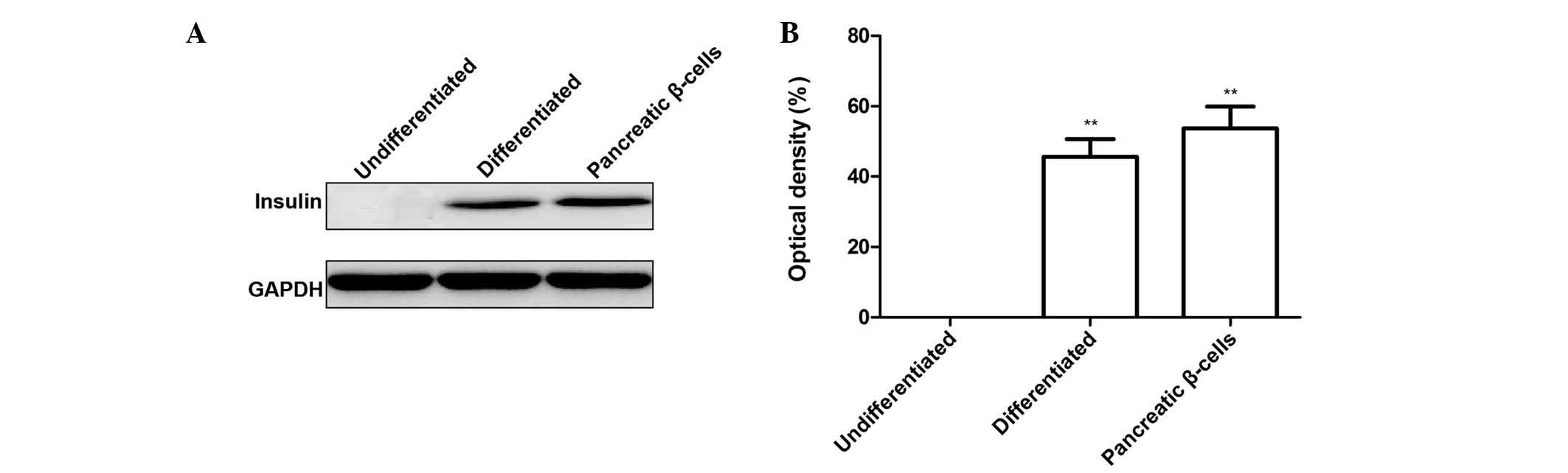
|
1
|
Gao D, Xie J, Zhang J, Feng C, Yao B, Ma
K, Li J, Wu X, Huang S and Fu X: MSC attenuate diabetes-induced
functional impairment in adipocytes via secretion of insulin-like
growth factor-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 452:99–105. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
American Diabetes A: Diagnosis and
classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 36(Suppl 1):
S67–S74. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shaw JE, Sicree RA and Zimmet PZ: Global
estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2010 and 2030. Diabetes
Res Clin Pract. 87:4–14. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Chen LB, Jiang XB and Yang L:
Differentiation of rat marrow mesenchymal stem cells into
pancreatic islet beta-cells. World J Gastroenterol. 10:3016–3020.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oh SH, Muzzonigro TM, Bae SH, LaPlante JM,
Hatch HM and Petersen BE: Adult bone marrow-derived cells
trans-differentiating into insulin-producing cells for the
treatment of type I diabetes. Lab Invest. 84:607–617. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vija L, Farge D, Gautier JF, Vexiau P,
Dumitrache C, Bourgarit A, Verrecchia F and Larghero J: Mesenchymal
stem cells: Stem cell therapy perspectives for type 1 diabetes.
Diabetes Metab. 35:85–93. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wu XH, Liu CP, Xu KF, Mao XD, Zhu J, Jiang
JJ, Cui D, Zhang M, Xu Y and Liu C: Reversal of hyperglycemia in
diabetic rats by portal vein transplantation of islet-like cells
generated from bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. World J
Gastroenterol. 13:3342–3349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nejad-Dehbashi F, Hashemitabar M,
Orazizadeh M, Bahramzadeh S, Shahhosseini Pourshoushtary E and
Khorsandi L: The effects of exendine-4 on insulin producing cell
differentiation from rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem
cells. Cell J. 16:187–194. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang YH, Wang HF, Liu W, Wei B, Bing LJ
and Gao YM: Insulin-producing cells derived from rat bone marrow
and their autologous transplantation in the duodenal wall for
treating diabetes. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 292:728–735. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Gimble JM, Katz AJ and Bunnell BA:
Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Circ Res.
100:1249–1260. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, Jaiswal
RK, Douglas R, Mosca JD, Moorman MA, Simonetti DW, Craig S and
Marshak DR: Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem
cells. Science. 284:143–147. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Noël D, Caton D, Roche S, Bony C, Lehmann
S, Casteilla L, Jorgensen C and Cousin B: Cell specific differences
between human adipose-derived and mesenchymalstromal cells despite
similar differentiation potentials. Exp Cell Res. 314:1575–1584.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Tyndall A, Walker UA, Cope A, Dazzi F, De
Bari C, Fibbe W, Guiducci S, Jones S, Jorgensen C, Le Blanc K, et
al: Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells: A review
based on an interdisciplinary meeting held at the Kennedy Institute
of Rheumatology Division, London, UK, 31 October 2005. Arthritis
Res Ther. 9:3012007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Krampera M, Pasini A, Pizzolo G, Cosmi L,
Romagnani S and Annunziato F: Regenerative and immunomodulatory
potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Curr Opin Pharmacol.
6:435–441. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takahara K, Ii M, Inamoto T, Komura K,
Ibuki N, Minami K, Uehara H, Hirano H, Nomi H, Kiyama S, et al:
Adipose-derived stromal cells inhibit prostate cancer cell
proliferation inducing apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
446:1102–1107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Li F, Qi H, Feng G, Yuan K, Deng H
and Zhou H: Coexpression of Pdx1 and betacellulin in mesenchymal
stem cells could promote the differentiation of nestin-positive
epithelium-like progenitors and pancreatic islet-like spheroids.
Stem Cells and Dev. 17:815–823. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Bruin JE, Erener S, Vela J, Hu X, Johnson
JD, Kurata HT, Lynn FC, Piret JM, Asadi A, Rezania A and Kieffer
TJ: Characterization of polyhormonal insulin-producing cells
derived in vitro from human embryonic stem cells. Stem Cell Res.
12:194–208. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wei R, Yang J, Hou W, Liu G, Gao M, Zhang
L, Wang H, Mao G, Gao H, Chen G and Hong T: Insulin-producing cells
derived from human embryonic stem cells: Comparison of definitive
endoderm- and nestin-positive progenitor-based differentiation
strategies. PloS one. 8:e725132013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gao F, Wu DQ, Hu YH, Jin GX, Li GD, Sun TW
and Li FJ: In vitro cultivation of islet-like cell clusters from
human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Transl
Res. 151:293–302. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chandra V, Swetha G, Muthyala S, Jaiswal
AK, Bellare JR, Nair PD and Bhonde RR: Islet-like cell aggregates
generated from human adipose tissue derived stem cells ameliorate
experimental diabetes in mice. PloS one. 6:e206152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, De Ugarte DA,
Huang JI, Mizuno H, Alfonso ZC, Fraser JK, Benhaim P and Hedrick
MH: Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol
Biol Cell. 13:4279–4295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Moshtagh PR, Emami SH and Sharifi AM:
Differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell into
insulin-producing cells: An in vitro study. J Physiol Biochem.
69:451–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Bregenholt S, Møldrup A, Blume N, Karlsen
AE, Nissen Friedrichsen B, Tornhave D, Knudsen LB and Petersen JS:
The long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue, liraglutide,
inhibits beta-cell apoptosis in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
330:577–584. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hui H, Nourparvar A, Zhao X and Perfetti
R: Glucagon-like peptide-1 inhibits apoptosis of insulin-secreting
cells via a cyclic 5′-adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein
kinase A- and a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway.
Endocrinology. 144:1444–1455. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li LX, MacDonald PE, Ahn DS, Oudit GY,
Backx PH and Brubaker PL: Role of phosphatidylinositol
3-kinasegamma in the beta-cell: Interactions with glucagon-like
peptide-1. Endocrinology. 147:3318–3325. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Zhou J, Doyle ME and Egan JM:
Glucagon-like peptide-1 causes pancreatic duodenal homeobox-1
protein translocation from the cytoplasm to the nucleus of
pancreatic beta-cells by a cyclic adenosine monophosphate/protein
kinase A-dependent mechanism. Endocrinology. 142:1820–1827.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ji D, Li GY and Osborne NN: Nicotinamide
attenuates retinal ischemia and light insults to neurones.
Neurochem Int. 52:786–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang SJ, Choi JM, Kim L, Park SE, Rhee EJ,
Lee WY, Oh KW, Park SW and Park CY: Nicotinamide improves glucose
metabolism and affects the hepatic NAD-sirtuin pathway in a rodent
model of obesity and type 2 diabetes. J Nutr Biochem. 25:66–72.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|