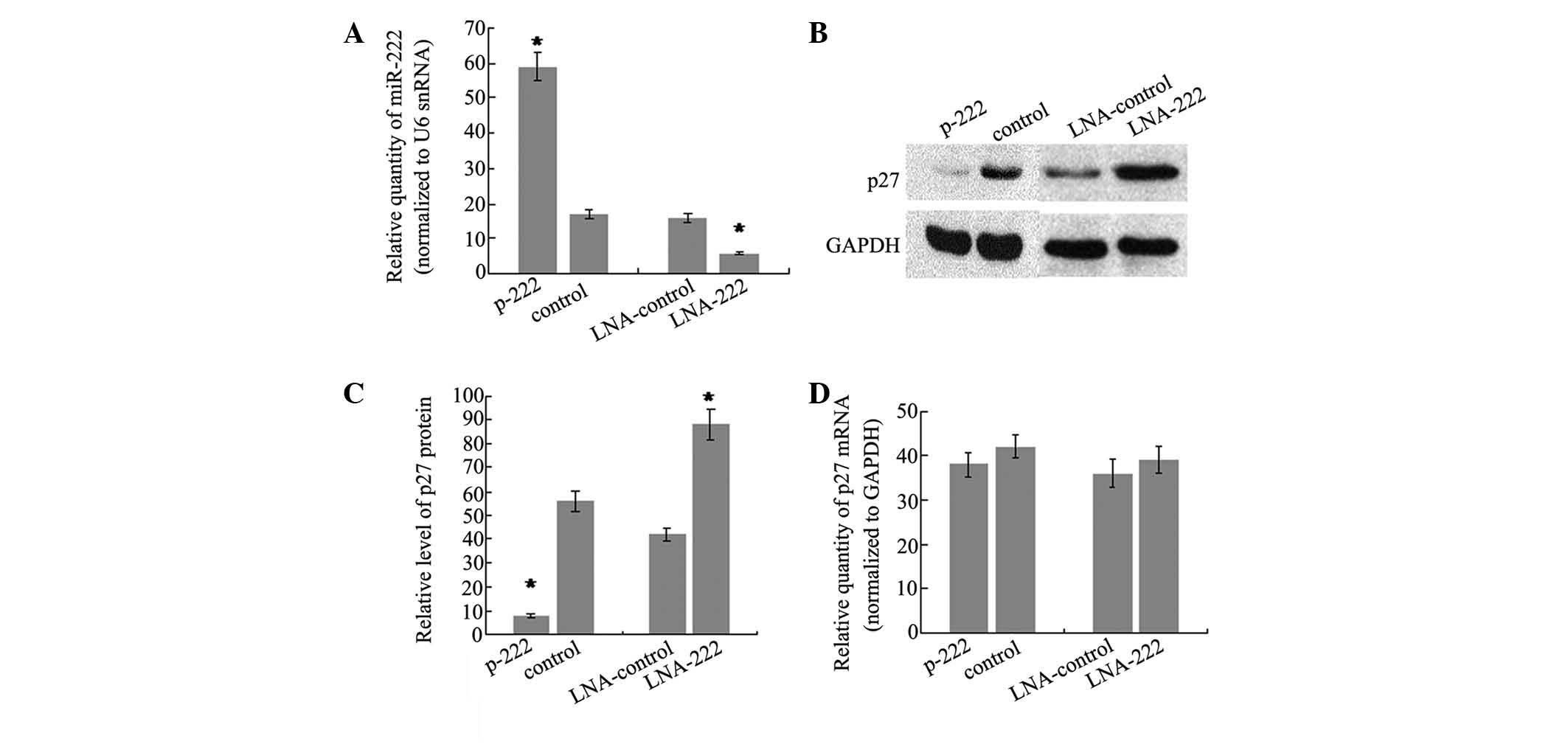
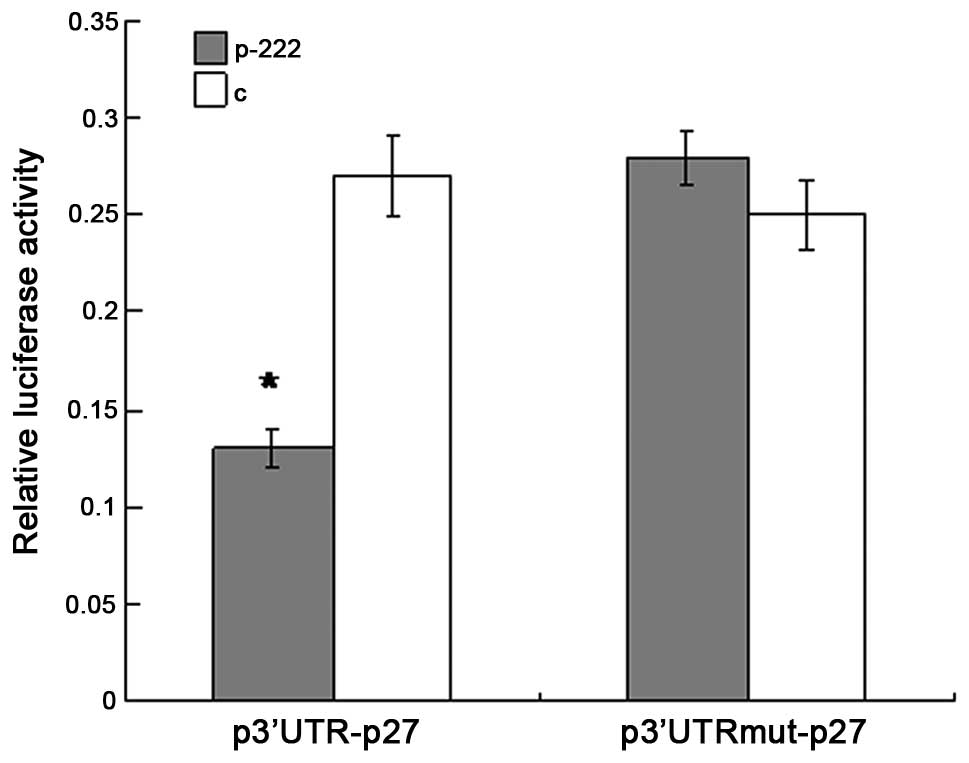
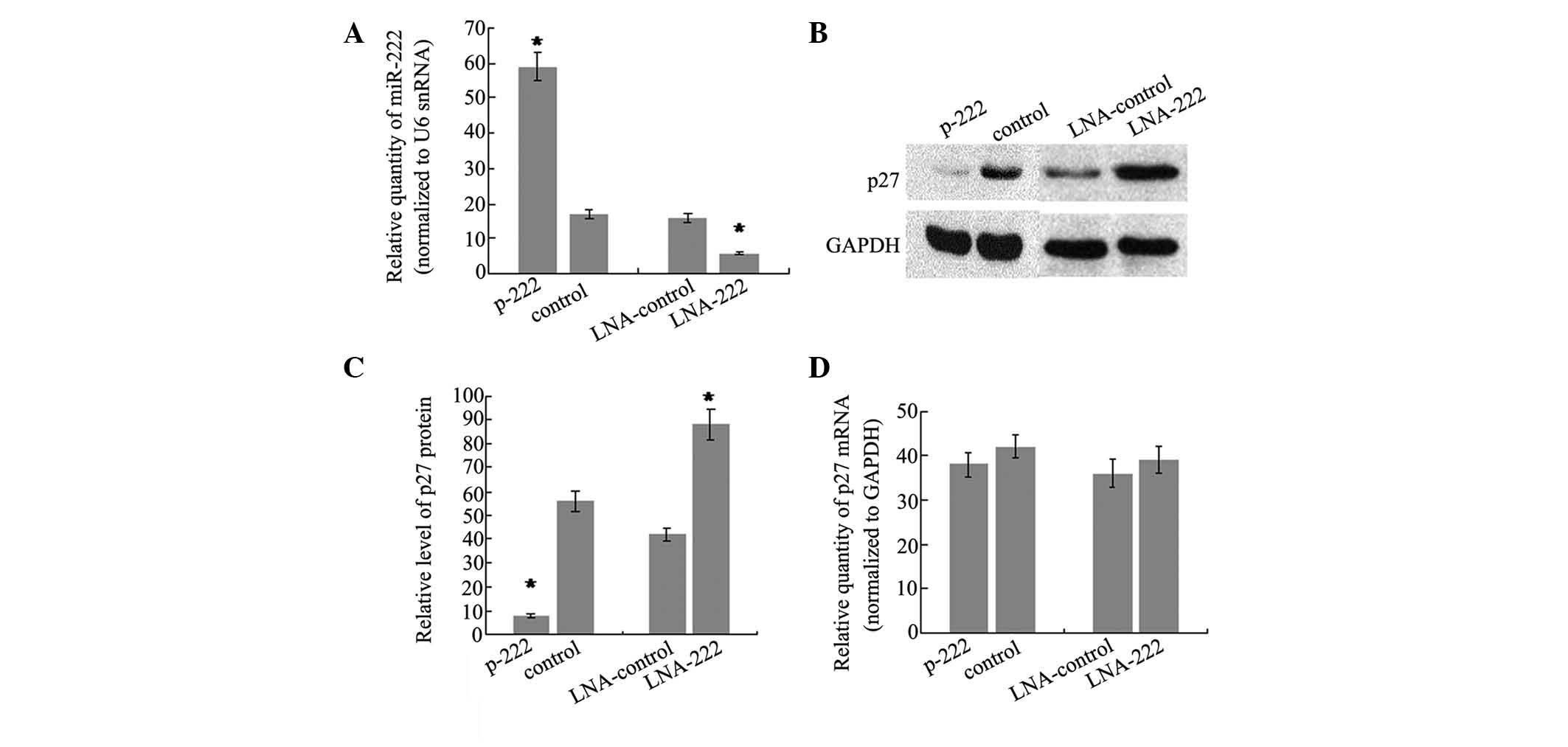
|
1
|
Cornutiu G: The Epidemiological Scale of
Alzheimer's Disease. J Clin Med Res. 7:657–666. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Blennow K, de Leon MJ and Zetterberg H:
Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 368:387–403. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kim VN: Small RNAs: Classification,
biogenesis and function. Mol Cells. 19:1–15. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Petersen CP, Bordeleau ME, Pelletier J and
Sharp PA: Short RNAs repress translation after initiation in
mammalian cells. Mol Cell. 21:533–542. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hébert SS and De Strooper B: Molecular
biology. miRNAs in neurodegeneration. Science. 317:1179–1180. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kosik KS: The neuronal microRNA system.
Nat Rev Neurosci. 7:911–920. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lukiw WJ: Micro-RNA speciation in fetal,
adult and Alzheimer's disease hippocampus. Neuroreport. 18:297–300.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang WX, Rajeev BW, Stromberg AJ, Ren N,
Tang G, Huang Q, Rigoutsos I and Nelson PT: The expression of
microRNA miR-107 decreases early in Alzheimer's disease and may
accelerate disease progression through regulation of beta-site
amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1. J Neurosci.
28:1213–1223. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Krichevsky AM, King KS, Donahue CP,
Khrapko K and Kosik KS: A microRNA array reveals extensive
regulation of microRNAs during brain development. RNA. 9:1274–1281.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hébert SS and De Strooper B: Alterations
of the microRNA network cause neurodegenerative disease. Trends
Neurosci. 32:199–206. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nelson PT, Wang WX and Rajeev BW:
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Pathol.
18:130–138. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Polyak K, Lee MH, Erdjument-Bromage H,
Koff A, Roberts JM, Tempst P and Massagué J: Cloning of
p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a
potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell.
78:59–66. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Toyoshima H and Hunter T: p27, a novel
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to
p21. Cell. 78:67–74. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ogawa O, Lee HG, Zhu X, Raina A, Harris
PL, Castellani RJ, Perry G and Smith MA: Increased p27, an
essential component of cell cycle control, in Alzheimer's disease.
Aging Cell. 2:105–110. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Delobel P, Lavenir I, Ghetti B, Holzer M
and Goedert M: Cell-cycle markers in a transgenic mouse model of
human tauopathy: Increased levels of cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitors p21Cip1 and p27Kip1. Am J Pathol.
168:878–887. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Jankowsky JL, Fadale DJ, Anderson J, Xu
GM, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Lee MK, Younkin LH, Wagner
SL, et al: Mutant presenilins specifically elevate the levels of
the 42 residue beta-amyloid peptide in vivo: Evidence for
augmentation of a 42-specific gamma secretase. Hum Mol Genet.
13:159–170. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Borchelt DR, Davis J, Fischer M, Lee MK,
Slunt HH, Ratovitsky T, Regard J, Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Sisodia
SS and Price DL: A vector for expressing foreign genes in the
brains and hearts of transgenic mice. Genet Anal. 13:159–163. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lesuisse C, Xu G, Anderson J, Wong M,
Jankowsky J, Holtz G, Gonzalez V, Wong PC, Price DL, Tang F, et al:
Hyper-expression of human apolipoprotein E4 in astroglia and
neurons does not enhance amyloid deposition in transgenic mice. Hum
Mol Genet. 10:2525–2537. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mason TJ and Matthews M: Aquatic
environment, housing, and management in the eighth edition of the
Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals: Additional
considerations and recommendations. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci.
51:329–332. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yang YF, Wang F, Xiao JJ, Song Y, Zhao YY,
Cao Y, Bei YH and Yang CQ: MiR-222 overexpression promotes
proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells by
downregulating p27. Int J Clin Exp Med. 7:893–902. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kim J, Inoue K, Ishii J, Vanti WB, Voronov
SV, Murchison E, Hannon G and Abeliovich A: A MicroRNA feedback
circuit in midbrain dopamine neurons. Science. 317:1220–1224. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schaefer A, O'Carroll D, Tan CL, Hillman
D, Sugimori M, Llinas R and Greengard P: Cerebellar
neurodegeneration in the absence of microRNA. J Exp Med.
204:1553–1558. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Bilen J, Liu N, Burnett BG, Pittman RN and
Bonini NM: MicroRNA pathways modulate polyglutamine-induced
neuro-degeneration. Mol Cell. 24:157–163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Galardi S, Mercatelli N, Giorda E,
Massalini S, Frajese GV, Ciafrè SA and Farace MG: miR-221 and
miR-222 expression affects the proliferation potential of human
prostate carcinoma cell lines by targeting p27Kip1. J
Biol Chem. 282:23716–23724. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Greither T, Grochola LF, Udelnow A,
Lautenschläger C, Würl P and Taubert H: Elevated expression of
microRNAs 155, 203, 210 and 222 in pancreatic tumors is associated
with poorer survival. Int J Cancer. 126:73–80. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Visone R, Russo L, Pallante P, De Martino
I, Ferraro A, Leone V, Borbone E, Petrocca F, Alder H, Croce CM and
Fusco A: MicroRNAs (miR)-221 and miR-222, both overexpressed in
human thyroid papillary carcinomas, regulate p27Kip1
protein levels and cell cycle. Endocr Relat Cancer. 14:791–798.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Quintavalle C, Garofalo M, Zanca C, Romano
G, Iaboni M, del Basso De Caro M, Martinez-Montero JC, Incoronato
M, Nuovo G, Croce CM and Condorelli G: miR-221/222 over-expression
in human glioblastoma increases invasiveness by targeting the
protein phosphate PTPµ. Oncogene. 31:858–868. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Stinson S, Lackner MR, Adai AT, Yu N, Kim
HJ, O'Briene C, Spoerke J, Jhunjhunwala S, Boyd Z, Januario T, et
al: miR-221/222 targeting of trichorhinophalangeal 1 (TRPS1)
promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Sci
Signal. 4:pt52011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Stinson S, Lackner MR, Adai AT, Yu N, Kim
HJ, O'Brien C, Spoerke J, Jhunjhunwala S, Boyd Z, Januario T, et
al: TRPS1 targeting by miR-221/222 promotes the
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer. Sci Signal.
4:ra412011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang CJ, Shen WG, Liu CJ, Chen YW, Lu HH,
Tsai MM and Lin SC: miR-221 and miR-222 expression increased the
growth and tumorigenesis of oral carcinoma cells. J Oral Pathol
Med. 40:560–566. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arendt T, Rödel L, Gärtner U and Holzer M:
Expression of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p16 in
Alzheimer's disease. Neuroreport. 7:3047–3049. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
McShea A, Harris PL, Webster KR, Wahl AF
and Smith MA: Abnormal expression of the cell cycle regulators P16
and CDK4 in Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 150:1933–1939.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Busser J, Geldmacher DS and Herrup K:
Ectopic cell cycle proteins predict the sites of neuronal cell
death in Alzheimer's disease brain. J Neurosci. 18:2801–2807.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arendt T, Holzer M and Gärtner U: Neuronal
expression of cycline dependent kinase inhibitors of the INK4
family in Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm. 105:949–960. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Tsujioka Y, Takahashi M, Tsuboi Y,
Yamamoto T and Yamada T: Localization and expression of cdc2 and
cdk4 in Alzheimer brain tissue. Dement Geriat Cogn Disord.
10:192–198. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Jordan-Sciutto KL, Malaiyandi LM and
Bowser R: Altered distribution of cell cycle transcriptional
regulators during Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
61:358–367. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hoozemans JJ, Bruckner MK, Rozemuller AJ,
Veerhuis R, Eikelenboom P and Arendt T: Cyclin D1 and cyclin E are
co-localized with cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) in pyramidal neurons in
Alzheimer disease temporal cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
61:678–688. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nagy Z, Esiri MM, Cato AM and Smith AD:
Cell cycle markers in the hippocampus in Alzheimer's disease. Acta
Neuropathol. 94:6–15. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Ding XL, Husseman J, Tomashevski A,
Nochlin D, Jin LW and Vincent I: The cell cycle Cdc25A tyrosine
phosphatase is activated in degenerating postmitotic neurons in
Alzheimer's disease. Am J Pathol. 157:1983–1990. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|