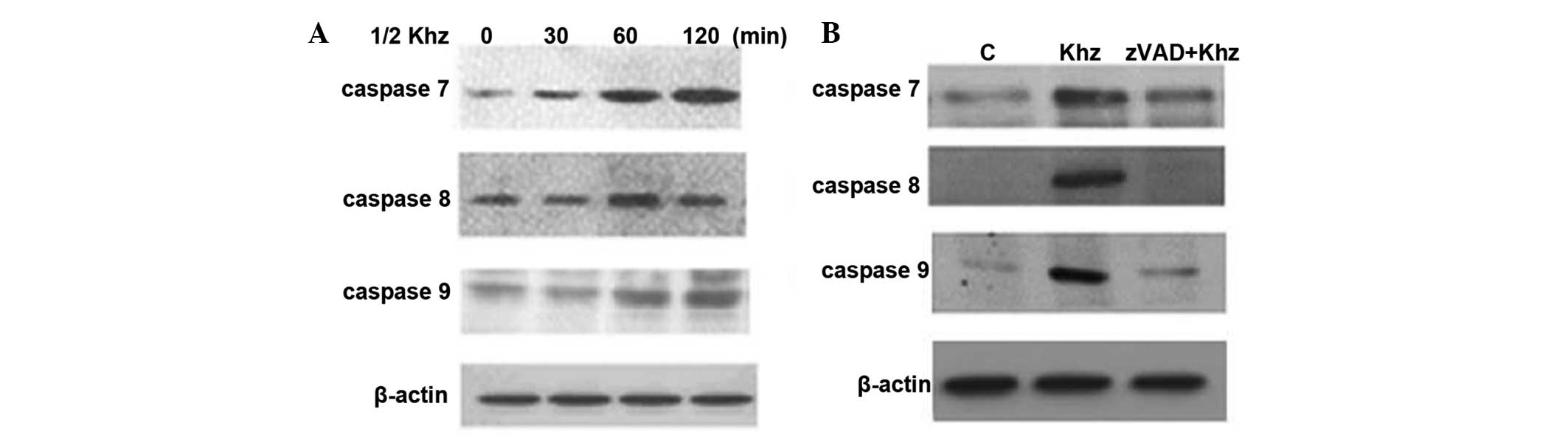
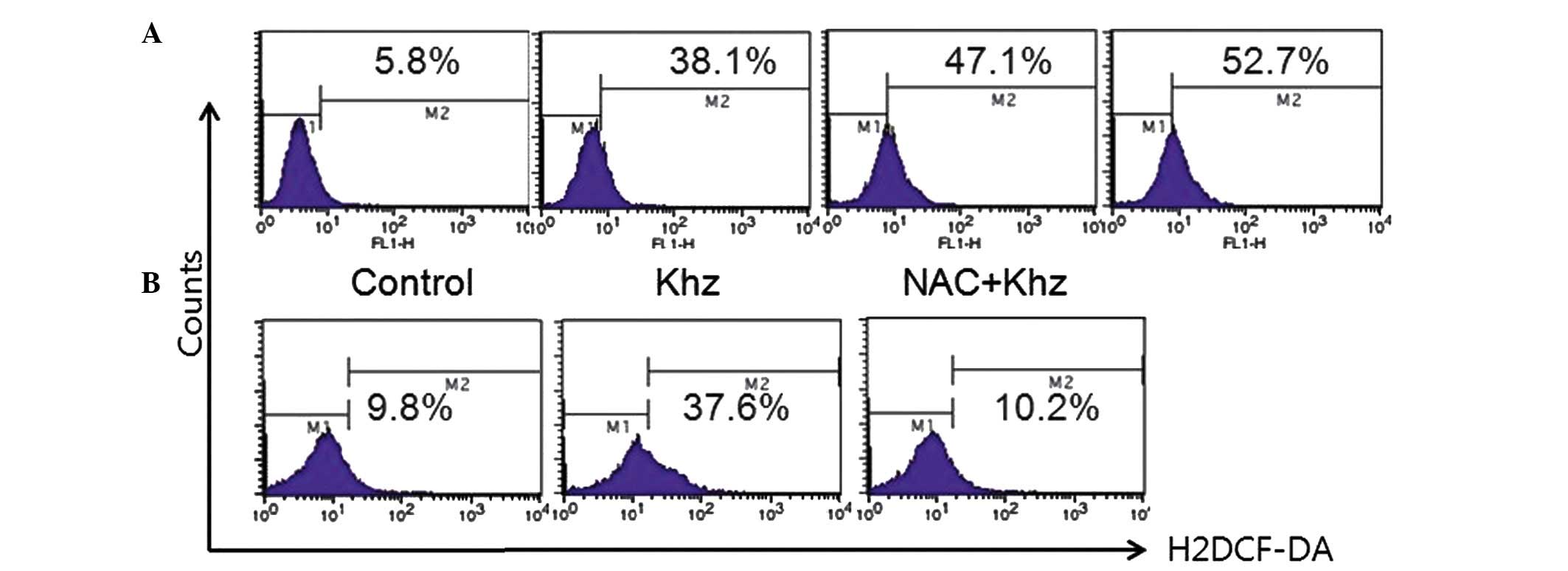
|
1
|
Lin ZB and Zhang HN: Anti-tumor and
immunoregulatory activities of Ganoderma lucidum and its possible
mechanisms. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:1387–1395. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sandodiya BS, Thakur GS, Baqhel RK, Prasad
GB and Bisen PS: Ganoderma lucidum: A potent pharmacological
macrofungus. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 10:717–742. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Gao Y, Gao H, Chan E, Tang W, Xu A, Yang
H, Huang M, Lan J, Li X, Duan W, et al: Antitumor activity and
underlying mechanisms of ganopoly, the refined polysaccarides
extracted from Ganoderma lucidum, in mice. Immunol Invest.
34:171–198. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yue GG, Fung KP, Tse GM, Leung PC and Lau
CB: Comparative studies of various Ganoderma species and their
different parts with regard to antitumor and immunomodulating
activities in vitro. J Altern Complement Med. 12:777–789. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
IIIana-Esteban C: The fungus maitake
(Grifola frondosa) and its therapeutic potential. Rev Iberoam
Micol. 25:141–144. 2008.In Spanish. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jang KJ, Han MH, Lee BH, Kim BW, Kim CH,
Yoon HM and Choi YH: Induction of apoptosis by ethanol extracts of
Ganoderma lucidum in human gastric carcinoma cells. J Acupunct
Meridian Stud. 3:24–31. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yue QX, Song XY, Ma C, Feng LX, Guan SH,
Wu WY, Yang M, Jiang BH, Liu X, Cui YJ and Guo DA: Effects of
triterpenes from Ganoderma lucidum on protein expression profile of
HeLa cells. Phytomedicine. 17:606–613. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao S, Ye G, Fu G, Cheng JX, Yang BB and
Peng C: Ganoderma lucidum exerts anti-tumor effects on ovarian
cancer cells and enhances their sensitivity to cisplatin. Int J
Oncol. 38:1319–1327. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu RM and Zhong JJ: Ganoderic acid Mf and
S induce mitochondria mediated apoptosis in human cervical
carcinoma HeLa cells. Phytomedicine. 15:349–355. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li L, Li T, Wang XJ, Xu JP and Wang SG:
Effects of Ganoderma lucidum spores on HepG2 cells proliferation
and growth cycle. Zhong Yao Cai. 31:1514–1518. 2008.In Chinese.
|
|
11
|
Zhao YY, Chao X, Zhang Y, Lin RC and Sun
WJ: Cytotoxic steroids from Polyporus umbellatus. Planta Med.
76:1755–1758. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tang W, Liu JW, Zhao WM, Wei DZ and Zhong
JJ: Ganoderic acid T from Ganoderma lucidum mycelia induces
mitochondria mediated apoptosis in lung cancer cells. Life Sci.
80:205–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liang ZE, Yi YJ, Guo YT, Wang RC, Hu QL
and Xiong XY: Inhibition of migration and induction of apoptosis in
LoVo human colon cancer cells by polysaccharides from Ganoderma
lucidum. Mol Med Rep. 12:7629–7636. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ruan W, Wei Y and Popovich DG: Distinct
responses of cytotoxic Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids in human
carcinoma cells. Phytother Res. 29:1744–1752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sun Z, Huang K, Fu X, Zhou Z, Cui Y and Li
H: A chemically sulfated polysaccharide derived from Ganoderma
lucidum induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis in human
osteosarcoma MG63 cells. Tumour Biol. 35:9919–9926. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kim JE, Koo KH, Kim YH, Sohn J and Park
YG: Identification of potential lung cancer biomarkers using an in
vitro carcinogenesis model. Exp Mol Med. 40:709–720. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Palombo JD, Ganguly A, Bistrian BR and
Menard MP: The anti-proliferative effects of biologically active
isomers of conjugated linoleic acid on human colorectal and
prostatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 177:163–172. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Klein-Szanto AJ, Iizasa T, Momiki S,
Garcia-Palazzo I, Caamano J, Metcalf R, Welsh J and Harris CC: A
tobacco-specific N-nitrosamine or cigarette smoke condensate causes
neoplastic transformation of xenotransplanted human bronchial
epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:6693–6697. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kang KS, Wang P, Yamabe N, Fukui M, Jay T
and Zhu BT: Docosahexaenoic acid induces apoptosis in MCF-7 cells
in vitro and in vivo via reactive oxygen species formation and
caspase 8 activation. PLoS One. 5:e102962010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu SJ, Kim HS, Cho SW and Sohn J: IL-4
inhibits proliferation of renal carcinoma cells by increasing the
expression of p21WAF1 and IRF-1. Exp Mol Med. 36:372–379. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yan Z, Yang R, Jiang Y, Yang Z, Yang J,
Zhao Q and Lu Y: Induction of apoptosis in human promyelocytic
leukemia HL60 cells by panaxynol and panaxydol. Molecules.
16:5561–5573. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
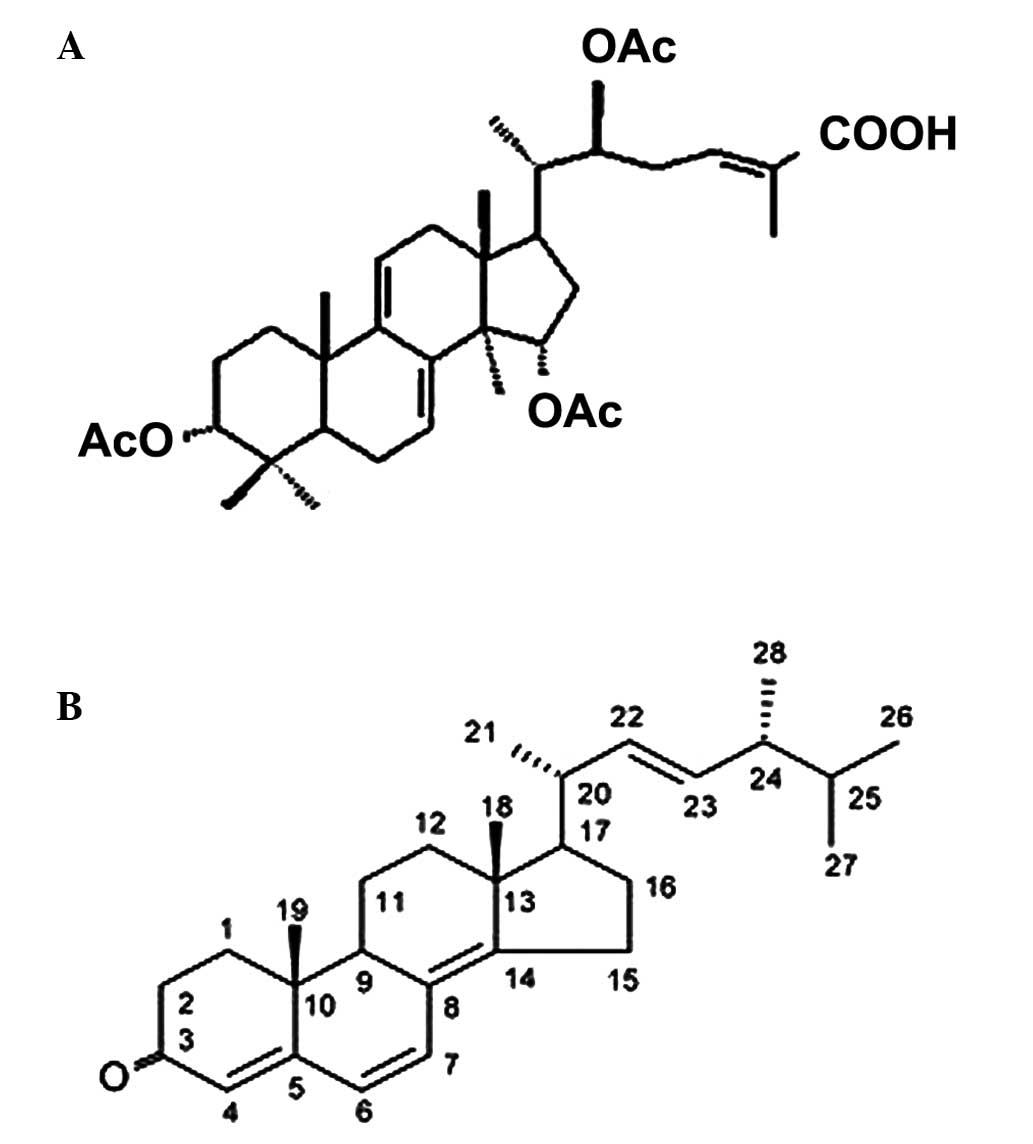
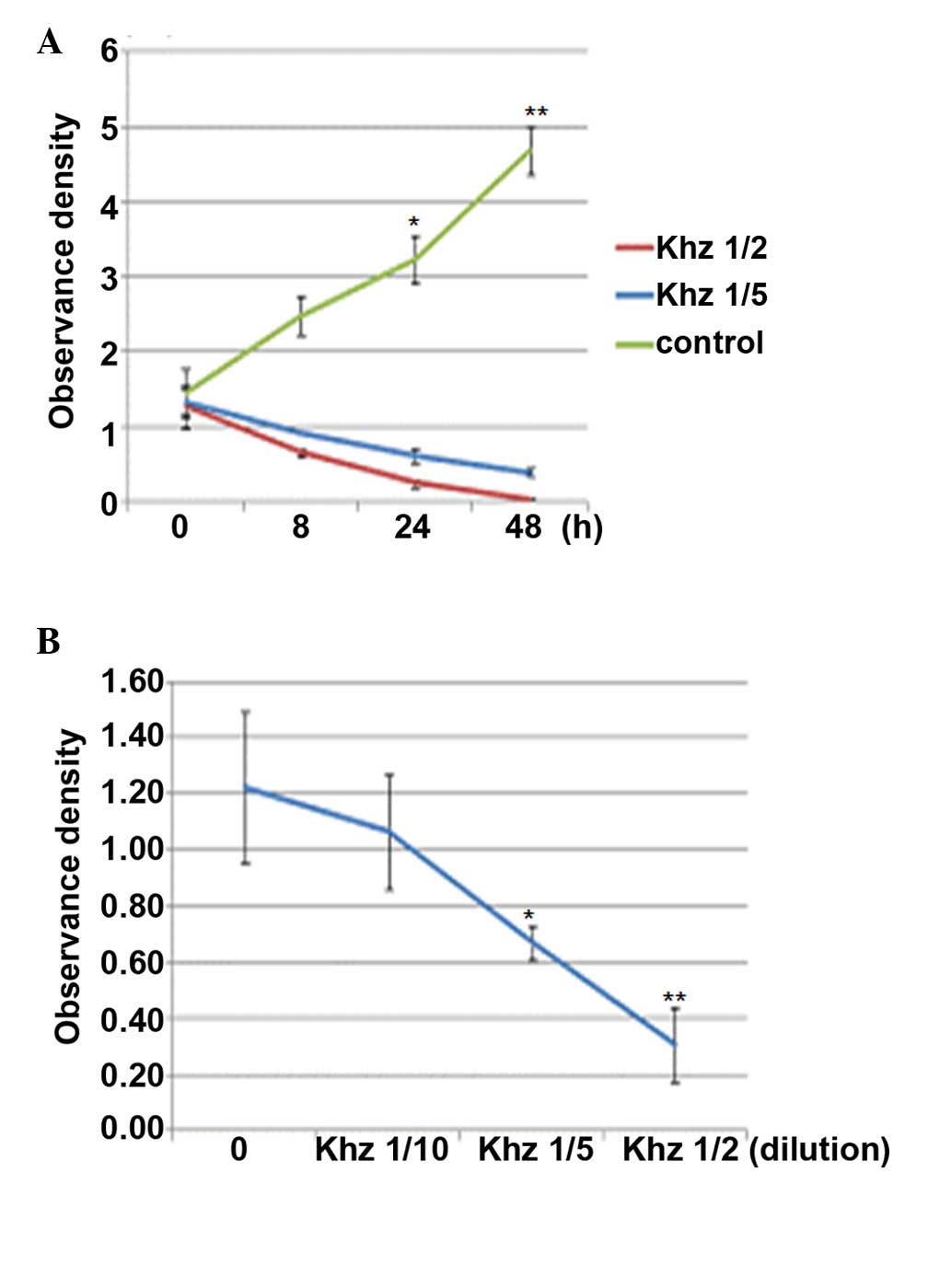
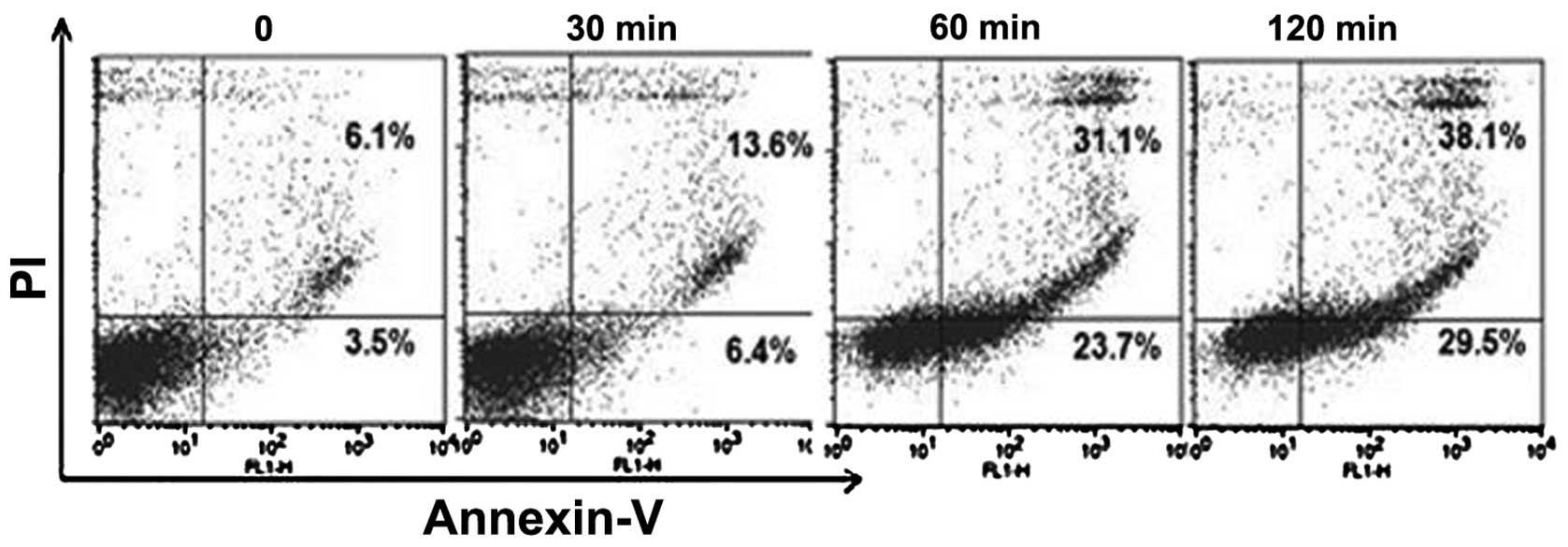
Kim TH, Kim JS, Kim ZH, Huang RB and Wang
RS: Khz (fusion of Ganoderma lucidum and Polyporus umbellatus
mycelia) induces apoptosis by increasing intracellular calcium
levels and activating JNK and NADPH oxidase-dependent generation of
reactive oxygen species. PLoS One. 7:e462082012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim TH, Kim JS, Kim ZH, Huang RB and Wang
RS: Khz (Fusion of Ganoderma lucidum and Polyporus umbellatus
Mycelia) induces apoptosis in A549 human lung cancer cells by
generating reactive oxygen species and decreasing the Mitochondrial
membrane potential. Food Sci Biotechnol. 23:859–864. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kim TH, Kim JS, Kim ZH, Huang RB, Chae YL
and Wang RS: Khz (Fusion product of Ganoderma lucidum and Polyporus
umbellatus mycelia) induces apoptosis in human colon carcinoma
HCT116 cells, accompanied by an increase in reactive oxygen
species, activation of caspase 3 and increased intracellular
Ca2+. J Med Food. 18:332–336. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Kim TH, Kim JS, Kim ZH, Huang RB, Chae YL
and Wang RS: Khz-cp (crude polysaccharide extract obtained from the
fusion of Ganoderma lucidum and Polyporus umbellatus mycelia)
induces apoptosis by increasing intracellular calcium levels and
activating P38 and NADPH oxidase-dependent generation of reactive
oxygen species in SNU-1 cells. BMC Complement Altern Med.
14:2362014. View Article : Google Scholar
|