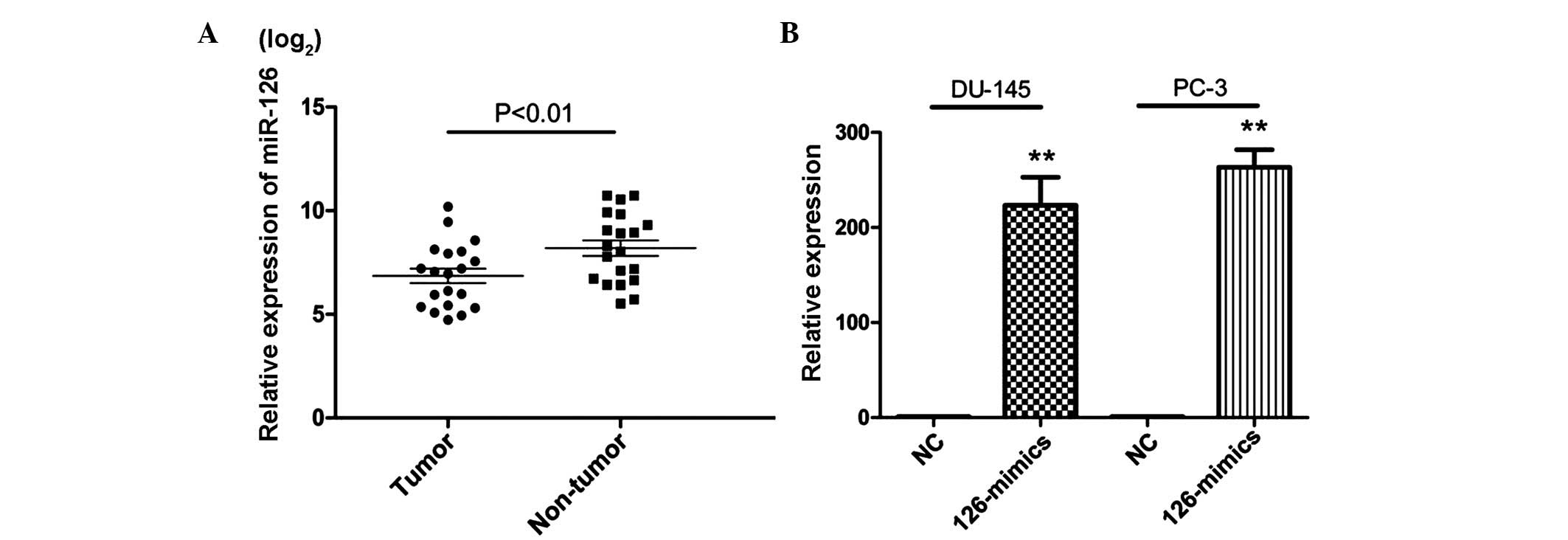
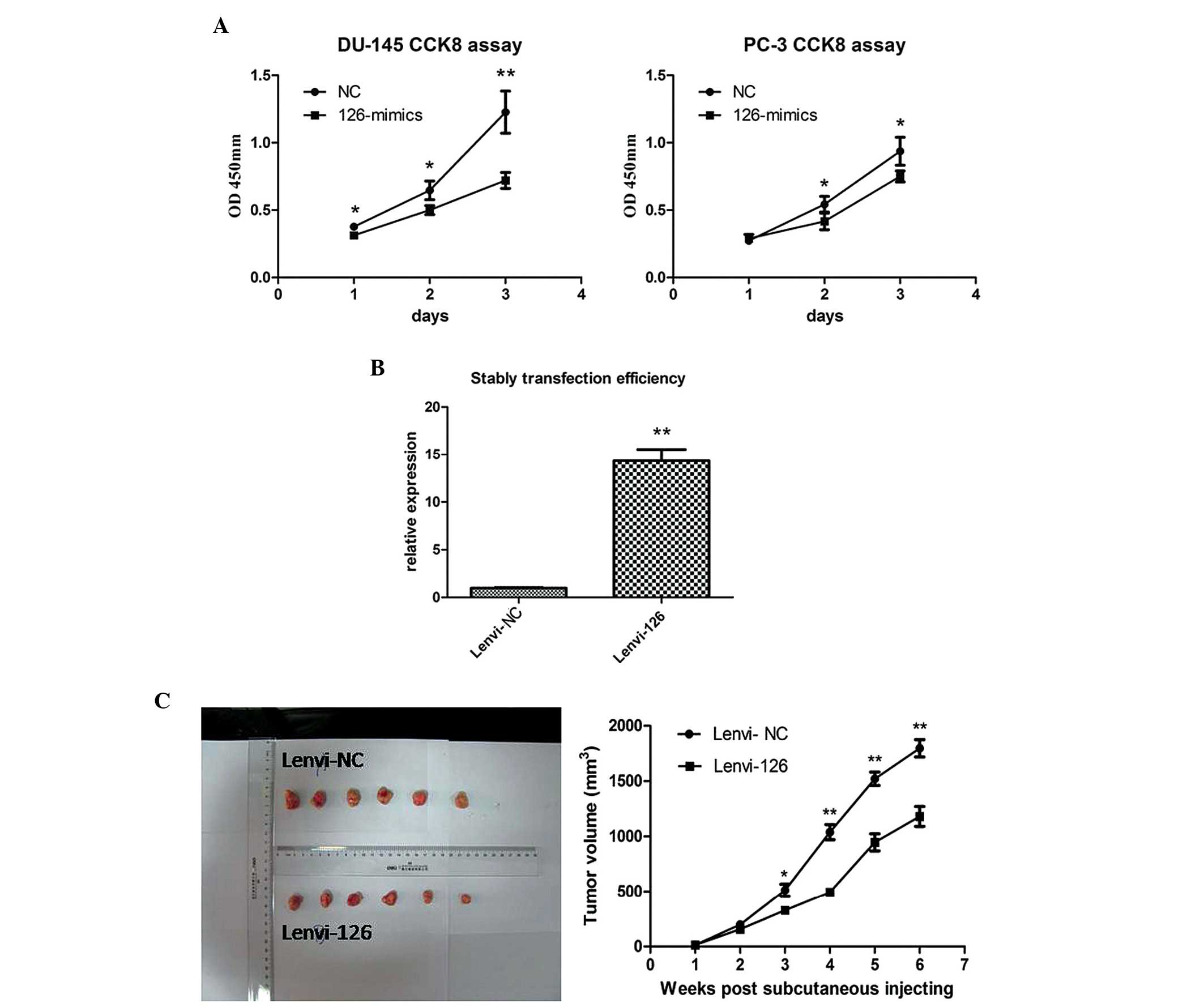
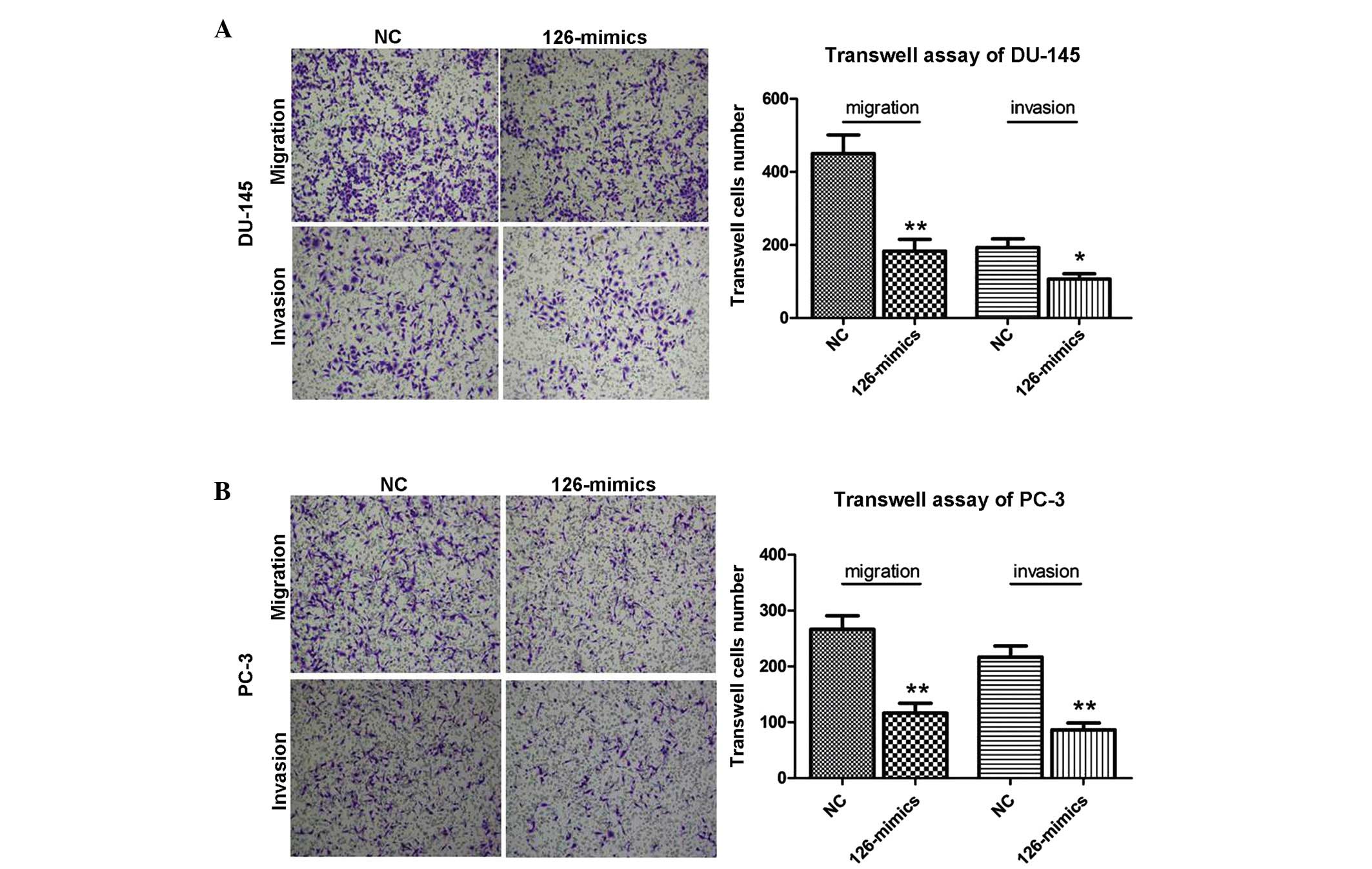
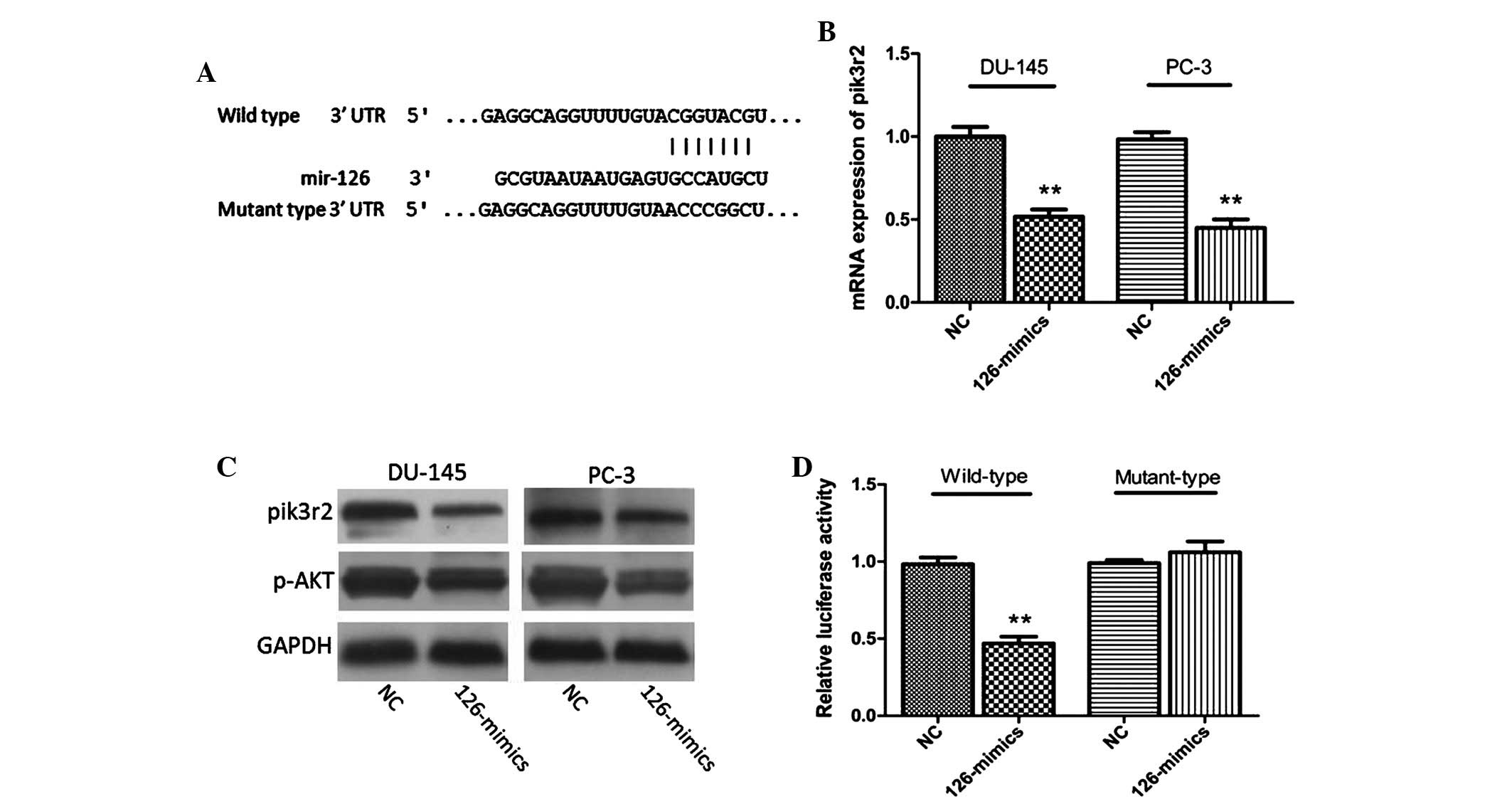
|
1
|
Yamamoto S, Kawakami S, Yonese J, Fujii Y,
Urakami S, Masuda H, Numao N, Ishikawa Y, Kohno A and Fukui I:
Long-term oncological outcome and risk stratification in men with
high-risk prostate cancer treated with radical prostatectomy. Jpn J
Clin Oncol. 42:541–547. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Peyromaure EM, Mao K, Sun Y, Xia S, Jiang
N, Zhang S, Wang G, Liu Z and Debré B: A comparative study of
prostate cancer detection and management in China and in France.
Can J Urol. 16:4472–4477. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Klotz L: Active surveillance for prostate
cancer: For whom? J Clin Oncol. 23:8165–8169. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Walz J, Gallina A, Saad F, Montorsi F,
Perrotte P, Shariat SF, Jeldres C, Graefen M, Bénard F, McCormack
M, et al: A nomogram predicting 10-year life expectancy in
candidates for radical prostatectomy or radiotherapy for prostate
cancer. J Clin Oncol. 25:3576–3581. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Siegel R, Ward E, Brawley O and Jemal A:
Cancer statistics, 2011: The impact of eliminating socioeconomic
and racial disparities on premature cancer deaths. CA Cancer J
Clin. 61:212–236. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Vaiopoulos AG, Athanasoula KCh and
Papavassiliou AG: Epigenetic modifications in colorectal cancer:
Molecular insights and therapeutic challenges. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1842:971–980. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Romero Otero J, Garcia Gomez B, Campos
Juanatey F and Touijer KA: Prostate cancer biomarkers: An update.
Urol Oncol. 32:252–260. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee RC, Feinbaum RL and Ambros V: The C.
elegans heterochronic gene lin-4 encodes small RNAs with antisense
complementarity to lin-14. Cell. 75:843–854. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNA signatures
in human cancers. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:857–866. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Petri A, Lindow M and Kauppinen S:
MicroRNA silencing in primates: Towards development of novel
therapeutics. Cancer Res. 69:393–395. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang J, Zhao H, Xin Y and Fan L:
MicroRNA-198 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of lung
cancer cells via targeting FGFR1. J Cell Biochem. 115:987–995.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Nassirpour R, Mehta PP and Yin MJ: miR-122
regulates tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting
AKT3. PLoS One. 8:e796552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ouyang H, Gore J, Deitz S and Korc M:
microRNA-10b enhances pancreatic cancer cell invasion by
suppressing TIP30 expression and promoting EGF and TGF-β actions.
Oncogene. 33:4664–4674. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Fang JH, Zhou HC, Zeng C, Yang J, Liu Y,
Huang X, Zhang JP, Guan XY and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-29b suppresses
tumor angiogenesis, invasion and metastasis by regulating matrix
metal-loproteinase 2 expression. Hepatology. 54:1729–1740. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu D, Tao T, Xu B, Chen S, Liu C, Zhang
L, Lu K, Huang Y, Jiang L, Zhang X, et al: MiR-361-5p acts as a
tumor suppressor in prostate cancer by targeting signal transducer
and activator of transcription-6 (STAT6). Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 445:151–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fu X, Meng Z, Liang W, Tian Y, Wang X, Han
W, Lou G, Wang X, Lou F, Yen Y, et al: miR-26a enhances miRNA
biogenesis by targeting Lin28B and Zcchc11 to suppress tumor growth
and metastasis. Oncogene. 33:4296–4206. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Huang TH and Chu TY: Repression of miR-126
and upregulation of adrenomedullin in the stromal endothelium by
cancer-stromal cross talks confers angiogenesis of cervical cancer.
Oncogene. 33:3636–3647. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Li Z, Li N, Wu M, Li X, Luo Z and Wang X:
Expression of miR-126 suppresses migration and invasion of colon
cancer cells by targeting CXCR4. Mol Cell Biochem. 381:233–242.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun X, Liu Z, Yang Z, Xiao L, Wang F, He
Y, Su P, Wang J and Jing B: Association of microRNA-126 expression
with clini-copathological features and the risk of biochemical
recurrence in prostate cancer patients undergoing radical
prostatectomy. Diagn Pathol. 8:2082013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Cheng J, Xie HY, Xu X, Wu J, Wei X, Su R,
Zhang W, Lv Z, Zheng S and Zhou L: NDRG1 as a biomarker for
metastasis, recurrence and of poor prognosis in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 310:35–45. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bagchi P, Nandi S, Nayak MK and
Chawla-Sarkar M: Molecular mechanism behind rotavirus NSP1-mediated
PI3 kinase activation: Interaction between NSP1 and the p85 subunit
of PI3 kinase. J Virol. 87:2358–2362. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
23
|
Mulrane L, McGee SF, Gallagher WM and
O'Connor DP: miRNA dysregulation in breast cancer. Cancer Res.
73:6554–6562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Cai J, Yang C, Yang Q, Ding H, Jia J, Guo
J, Wang J and Wang Z: Deregulation of let-7e in epithelial ovarian
cancer promotes the development of resistance to cisplatin.
Oncogenesis. 2:e752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li X, Chen YT, Josson S, Mukhopadhyay NK,
Kim J, Freeman MR and Huang WC: MicroRNA-185 and 342 inhibit
tumorigenicity and induce apoptosis through blockade of the SREBP
metabolic pathway in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One. 8:e709872013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tian L, Fang YX, Xue JL and Chen JZ: Four
microRNAs promote prostate cell proliferation with regulation of
PTEN and its downstream signals in vitro. PLoS One. 8:e758852013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kao CJ, Martiniez A, Shi XB, Yang J, Evans
CP, Dobi A, de Vere White RW and Kung HJ: miR-30 as a tumor
suppressor connects EGF/Src signal to ERG and EMT. Oncogene.
33:2495–2503. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kerbel RS: Tumor angiogenesis. N Engl J
Med. 358:2039–2049. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zhou Y, Feng X, Liu YL, Ye SC, Wang H, Tan
WK, Tian T, Qiu YM and Luo HS: Down-regulation of miR-126 is
associated with colorectal cancer cells proliferation, migration
and invasion by targeting IRS-1 via the AKT and ERK1/2 signaling
pathways. PLoS One. 8:e812032013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
de Giorgio A, Castellano L, Krell J and
Stebbing J: Crosstalk-induced loss of miR-126 promotes
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 33:3634–3635. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Coutte L, Dreyer C, Sablin MP, Faivre S
and Raymond E: PI3K-AKT-mTOR pathway and cancer. Bull Cancer.
99:173–180. 2012.In French.
|
|
32
|
Fish JE, Santoro MM, Morton SU, Yu S, Yeh
RF, Wythe JD, Ivey KN, Bruneau BG, Stainier DY and Srivastava D:
miR-126 regulates angiogenic signaling and vascular integrity. Dev
Cell. 15:272–284. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhang J, Zhang Z, Zhang DY, Zhu J, Zhang T
and Wang C: microRNA 126 inhibits the transition of endothelial
progenitor cells to mesenchymal cells via the PIK3R2-PI3K/Akt
signalling pathway. PLoS One. 8:e832942013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Skeen JE, Bhaskar PT, Chen CC, Chen WS,
Peng XD, Nogueira V, Hahn-Windgassen A, Kiyokawa H and Hay N: Akt
deficiency impairs normal cell proliferation and suppresses
oncogenesis in a p53-independent and mTORC1-dependent manner.
Cancer Cell. 10:269–280. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Phung TL, Ziv K, Dabydeen D, Eyiah-Mensah
G, Riveros M, Perruzzi C, Sun J, Monahan-Earley RA, Shiojima I,
Nagy JA, et al: Pathological angiogenesis is induced by sustained
Akt signaling and inhibited by rapamycin. Cancer Cell. 10:159–167.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|