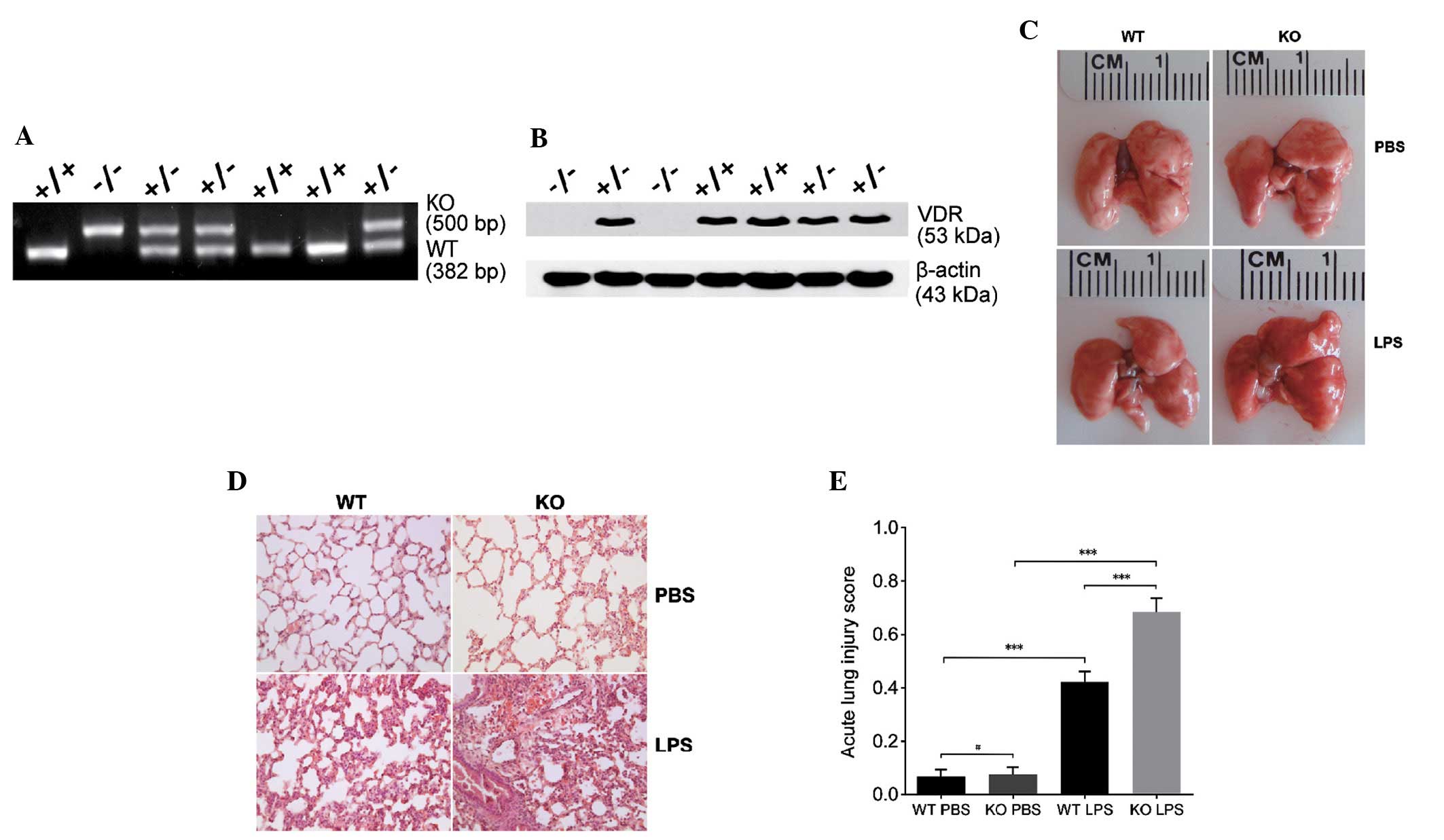
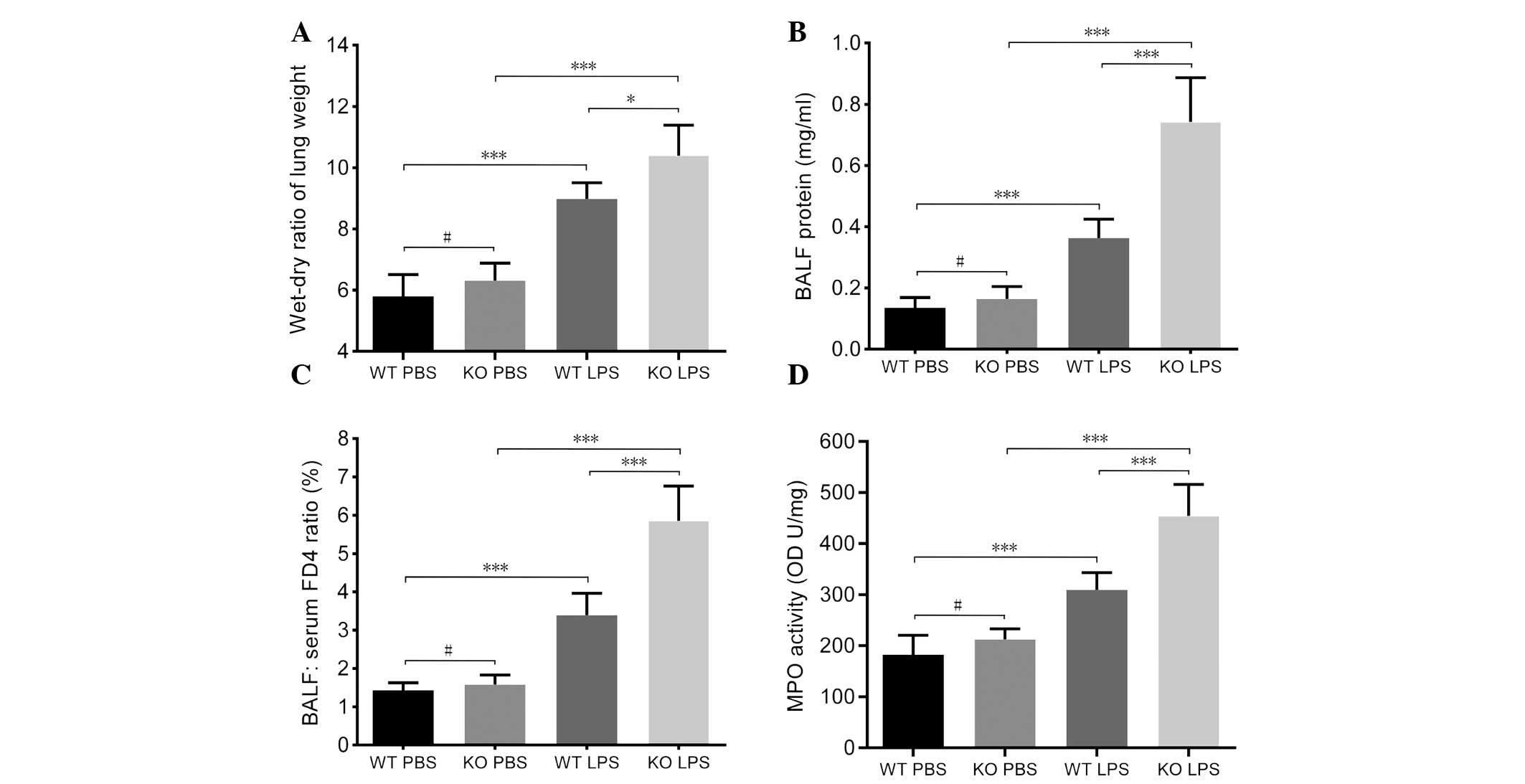
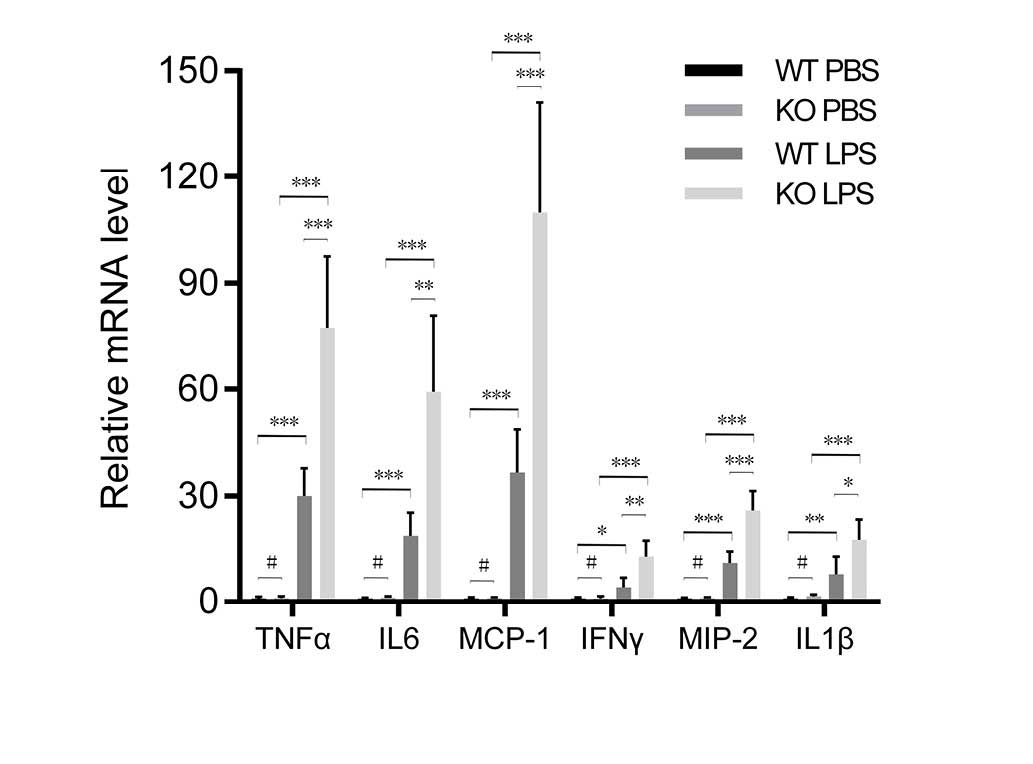
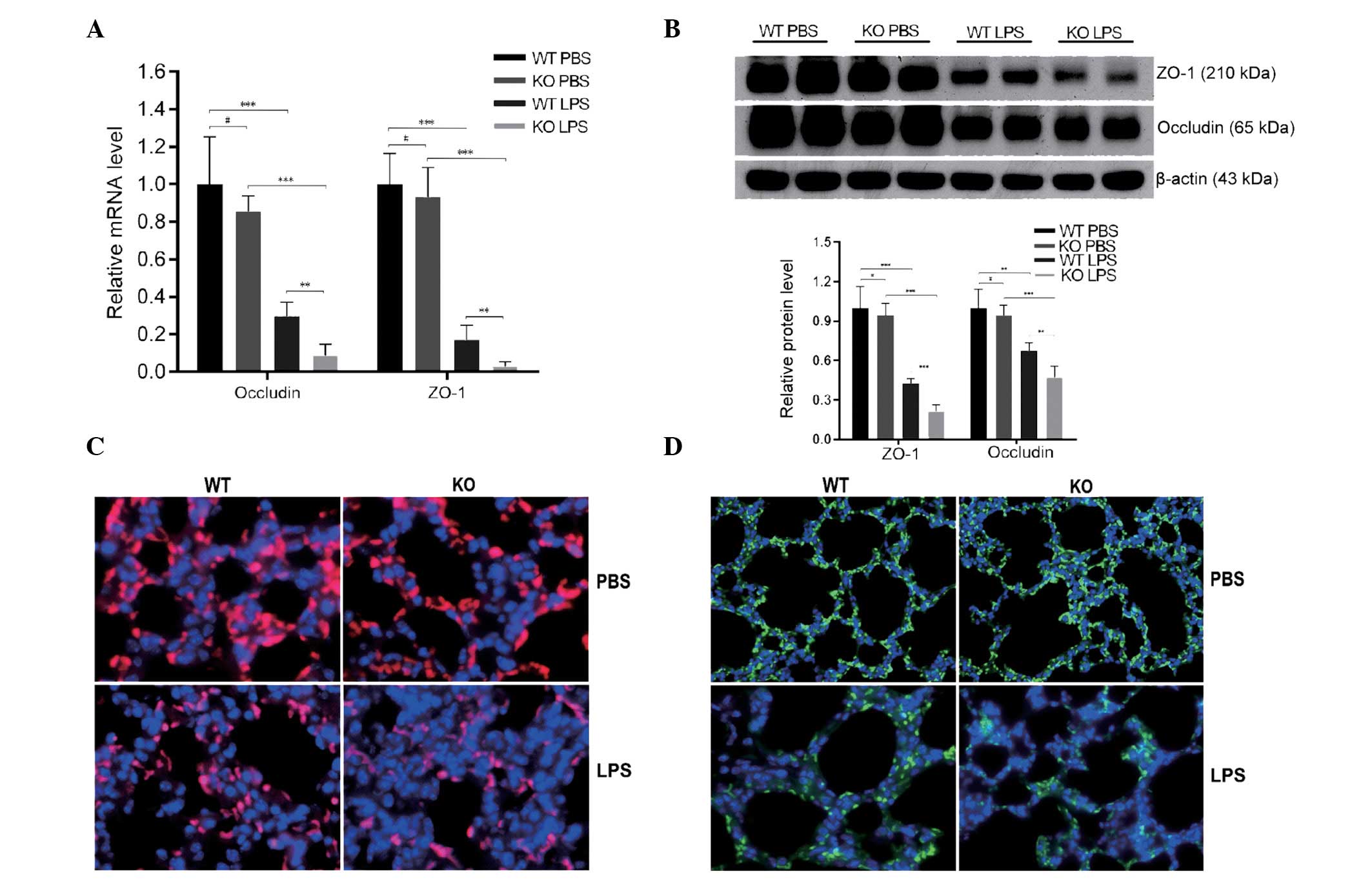
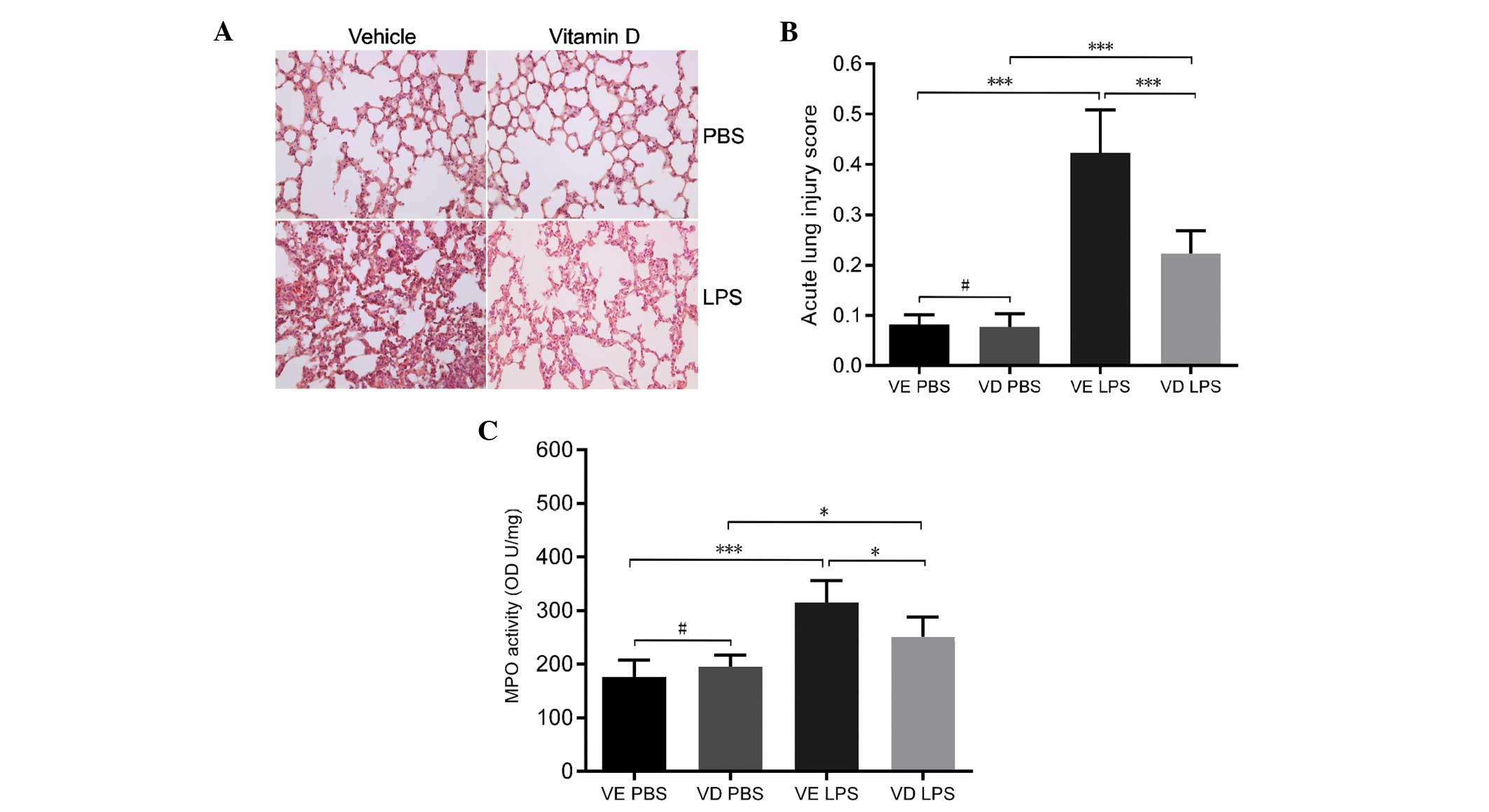
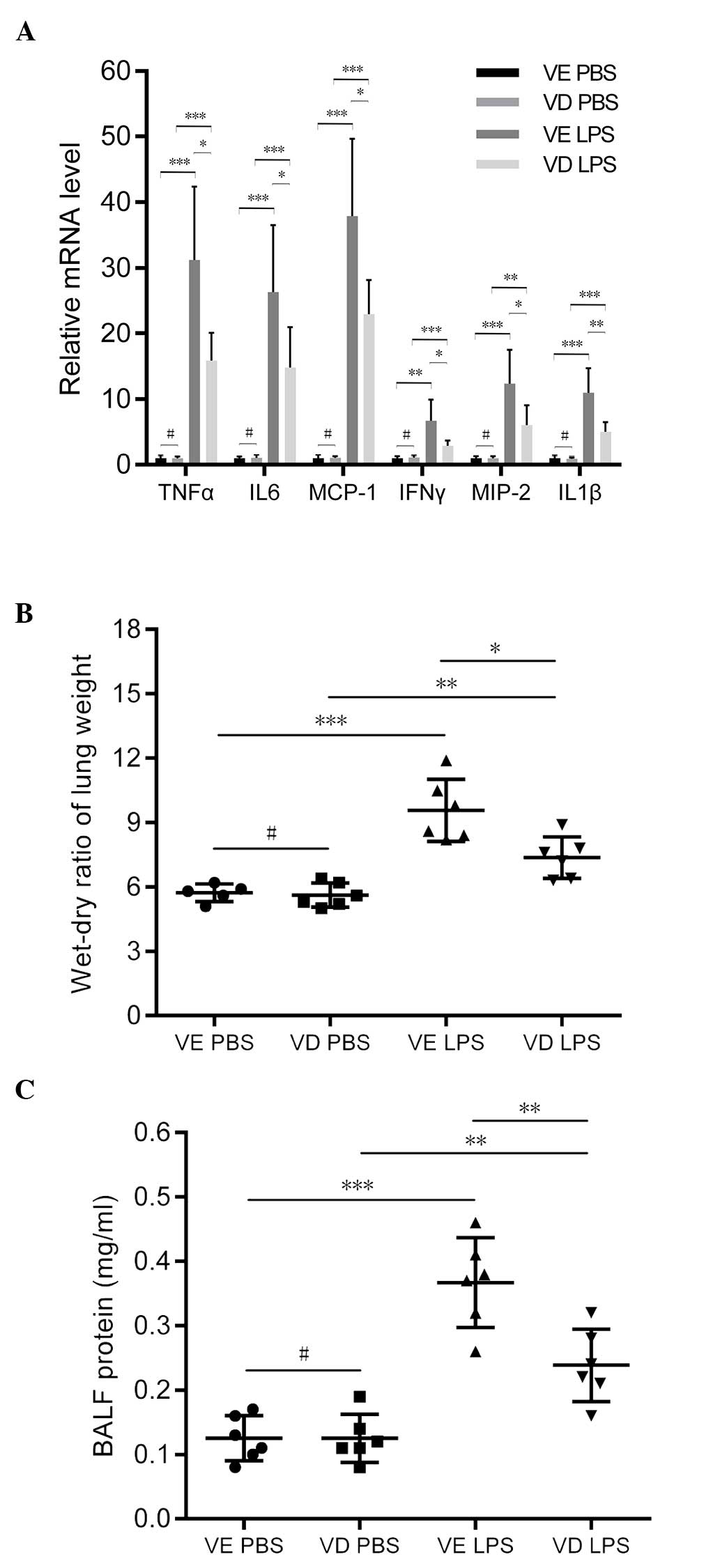
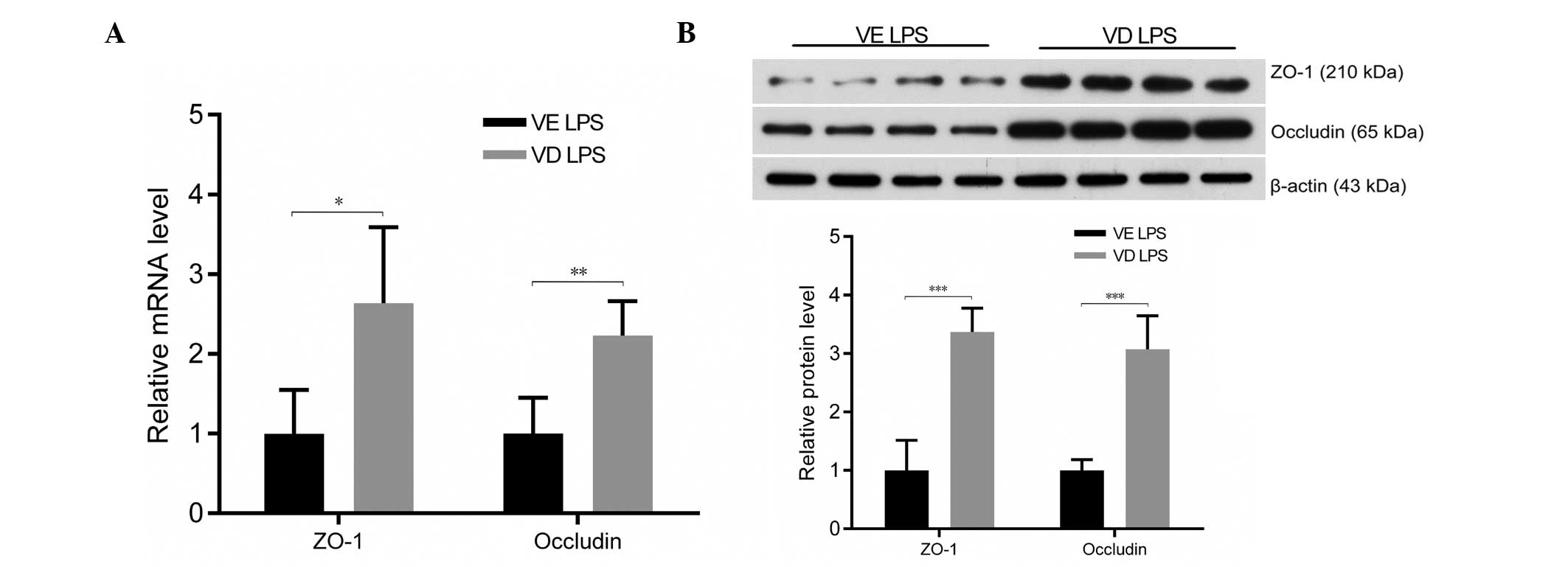
|
1
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1339. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Parekh D, Dancer RC and Thickett DR: Acute
lung injury. Clin Med. 11:615–618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Matthay MA, Zimmerman GA, Esmon C,
Bhattacharya J, Coller B, Doerschuk CM, Floros J, Gimbrone MA Jr,
Hoffman E, Hubmayr RD, et al: Future research directions in acute
lung injury: Summary of a National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
working group. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 167:1027–1035. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Haussler MR, Whitfield GK, Haussler CA,
Hsieh JC, Thompson PD, Selznick SH, Dominguez CE and Jurutka PW:
The nuclear vitamin D receptor: Biological and molecular regulatory
properties revealed. J Bone Miner Res. 13:325–349. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bouillon R, Carmeliet G, Verlinden L, van
Etten E, Verstuyf A, Luderer HF, Lieben L, Mathieu C and Demay M:
Vitamin D and human health: Lessons from vitamin D receptor null
mice. Endocr Rev. 29:726–776. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Adams JS and Hewison M: Update in vitamin
D. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 95:471–478. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hansdottir S, Monick MM, Hinde SL, Lovan
N, Look DC and Hunninghake GW: Respiratory epithelial cells convert
inactive vitamin D to its active form: Potential effects on host
defense. J Immunol. 181:7090–7099. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Afzal S, Lange P, Bojesen SE, Freiberg JJ
and Nordestgaard BG: Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D, lung function and
risk of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax. 69:24–31.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rippel C, South M, Butt WW and
Shekerdemian LS: Vitamin D status in critically ill children.
Intensive Care Med. 38:2055–2062. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee P, Eisman JA and Center JR: Vitamin D
deficiency in critically ill patients. N Engl J Med. 360:1912–1914.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Barnett N, Zhao Z, Koyama T, Janz DR, Wang
CY, May AK, Bernard GR and Ware LB: Vitamin D deficiency and risk
of acute lung injury in severe sepsis and severe trauma: A
case-control study. Ann Intensive Care. 4:5–14. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Parekh D, Dancer RC, Lax S, Cooper MS,
Martineau AR, Fraser WD, Tucker O, Alderson D, Perkins GD,
Gao-Smith F and Thickett DR: Vitamin D to prevent acute lung injury
following oesophagectomy (VINDALOO): Study protocol for a
randomised placebo controlled trial. Trials. 14:100–106. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hollams EM, Hart PH, Holt BJ, Serralha M,
Parsons F, de Klerk NH, Zhang G, Sly PD and Holt PG: Vitamin D and
atopy and asthma phenotypes in children: A longitudinal cohort
study. Eur Respir J. 38:1320–1327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wilkinson RJ, Llewelyn M, Toossi Z, Patel
P, Pasvol G, Lalvani A, Wright D, Latif M and Davidson RN:
Influence of vitamin D deficiency and vitamin D receptor
polymorphisms on tuberculosis among Gujarati Asians in west London:
A case-control study. Lancet. 355:618–621. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Persson LJ, Aanerud M, Hiemstra PS, Hardie
JA, Bakke PS and Eagan TM: Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is
associated with low levels of vitamin D. PLoS One. 7:e38934–e38941.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Amrein K, Zajic P, Schnedl C,
Waltensdorfer A, Fruhwald S, Holl A, Purkart T, Wünsch G, Valentin
T, Grisold A, et al: Vitamin D status and its association with
season, hospital and sepsis mortality in critical illness. Crit
Care. 18:R472014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Parekh D, Thickett DR and Turner AM:
Vitamin D deficiency and acute lung injury. Inflamm Allergy Drug
Targets. 12:253–261. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hartmann B, Riedel R, Jörss K,
Loddenkemper C, Steinmeyer A, Zügel U, Babina M, Radbruch A and
Worm M: Vitamin D receptor activation improves allergen-triggered
eczema in mice. J Invest Dermatol. 132:330–336. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Yin Z, Pintea V, Lin Y, Hammock BD and
Watsky MA: Vitamin D enhances corneal epithelial barrier function.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:7359–7364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kong J, Zhang Z, Musch MW, Ning G, Sun J,
Hart J, Bissonnette M and Li YC: Novel role of the vitamin D
receptor in maintaining the integrity of the intestinal mucosal
barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 294:G208–G216.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
You K, Xu X, Fu J, Xu S, Yue X, Yu Z and
Xue X: Hyperoxia disrupts pulmonary epithelial barrier in newborn
rats via the deterioration of occludin and ZO-1. Respir Res.
13:36–46. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Overgaard CE, Mitchell LA and Koval M:
Roles for claudins in alveolar epithelial barrier function. Ann N Y
Acad Sci. 1257:167–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Budinger GR and Sznajder JI: The
alveolar-epithelial barrier: A target for potential therapy. Clin
Chest Med. 27:655–669, abstract ix. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bhattacharya J and Matthay MA: Regulation
and repair of the alveolar-capillary barrier in acute lung injury.
Annu Rev Physiol. 75:593–615. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Li YC, Pirro AE, Amling M, Delling G,
Baron R, Bronson R and Demay MB: Targeted ablation of the vitamin D
receptor: An animal model of vitamin D-dependent rickets type II
with alopecia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:9831–9835. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Golan MA, Liu W, Shi Y, Chen L, Wang J,
Liu T and Li YC: Transgenic expression of vitamin D receptor in gut
epithelial cells ameliorates spontaneous colitis caused by
interleukin-10 deficiency. Dig Dis Sci. 60:1941–19477. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Matute-Bello G, Downey G, Moore BB,
Groshong SD, Matthay MA, Slutsky AS and Kuebler WM: Acute Lung
Injury in Animals Study Group: An official American Thoracic
Society workshop report: Features and measurements of experimental
acute lung injury in animals. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
44:725–738. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Schneeberger EE and Lynch RD: The tight
junction: a multifunctional complex. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
286:C1213–1228. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Migliori M, Giovannini L, Panichi V,
Filippi C, Taccola D, Origlia N, Mannari C and Camussi G: Treatment
with 1,25-dihy-droxyvitamin D3 preserves glomerular slit
diaphragm-associated protein expression in experimental
glomerulonephritis. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 18:779–790.
2005.
|
|
30
|
Takano Y, Mitsuhashi H and Ueno K:
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 inhibits neutrophil
recruitment in hamster model of acute lung injury. Steroids.
76:1305–1309. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang M, Dong M, Liu W, Wang L, Luo Y, Li
Z and Jin F: 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 ameliorates seawater
aspiration-induced acute lung injury via NF-κB and RhoA/Rho kinase
pathways. PLoS One. 9:e104507–e104516. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Shih PK, Chen YC, Huang YC, Chang YT, Chen
JX and Cheng CM: Pretreatment of vitamin D3 ameliorates lung and
muscle injury induced by reperfusion of bilateral femoral vessels
in a rat model. J Surg Res. 171:323–328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|