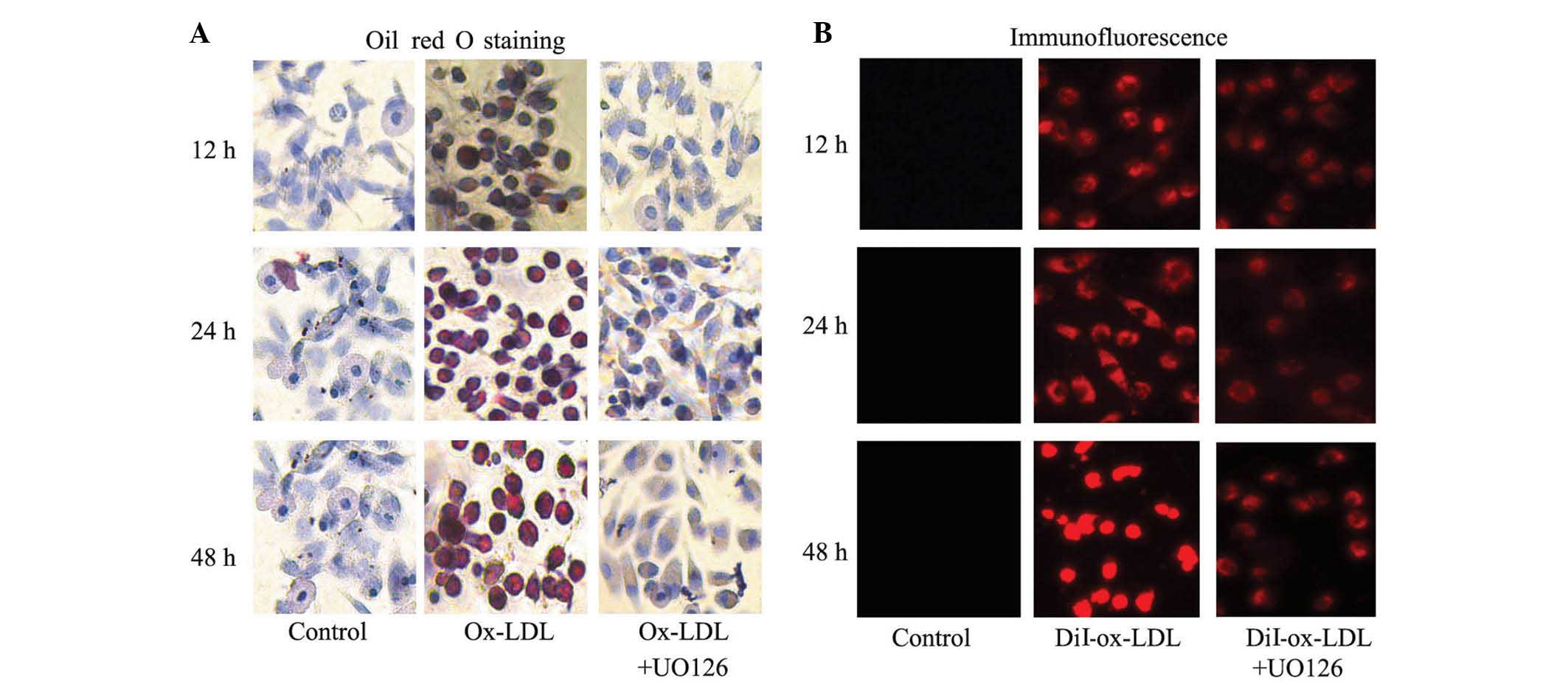
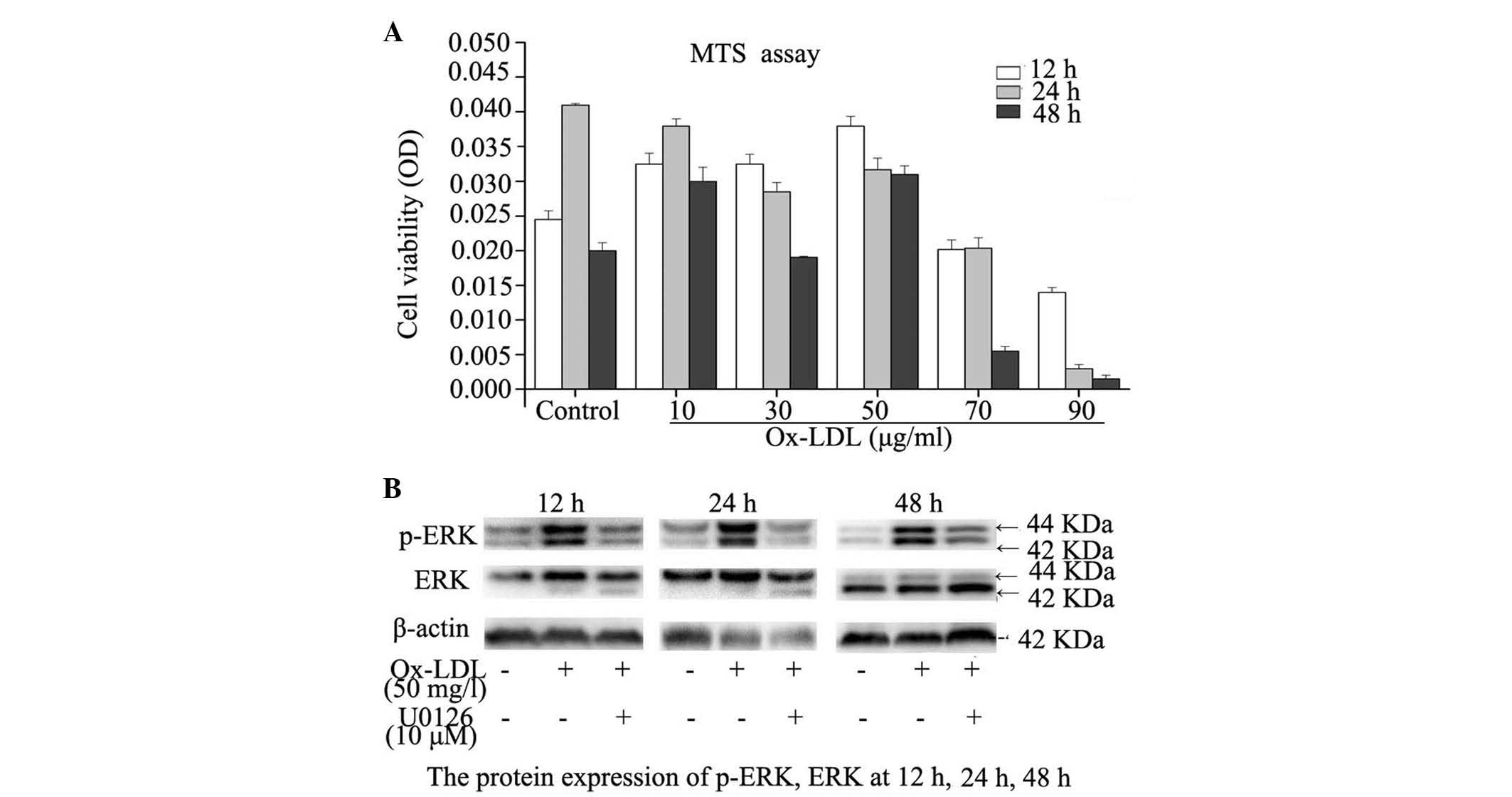
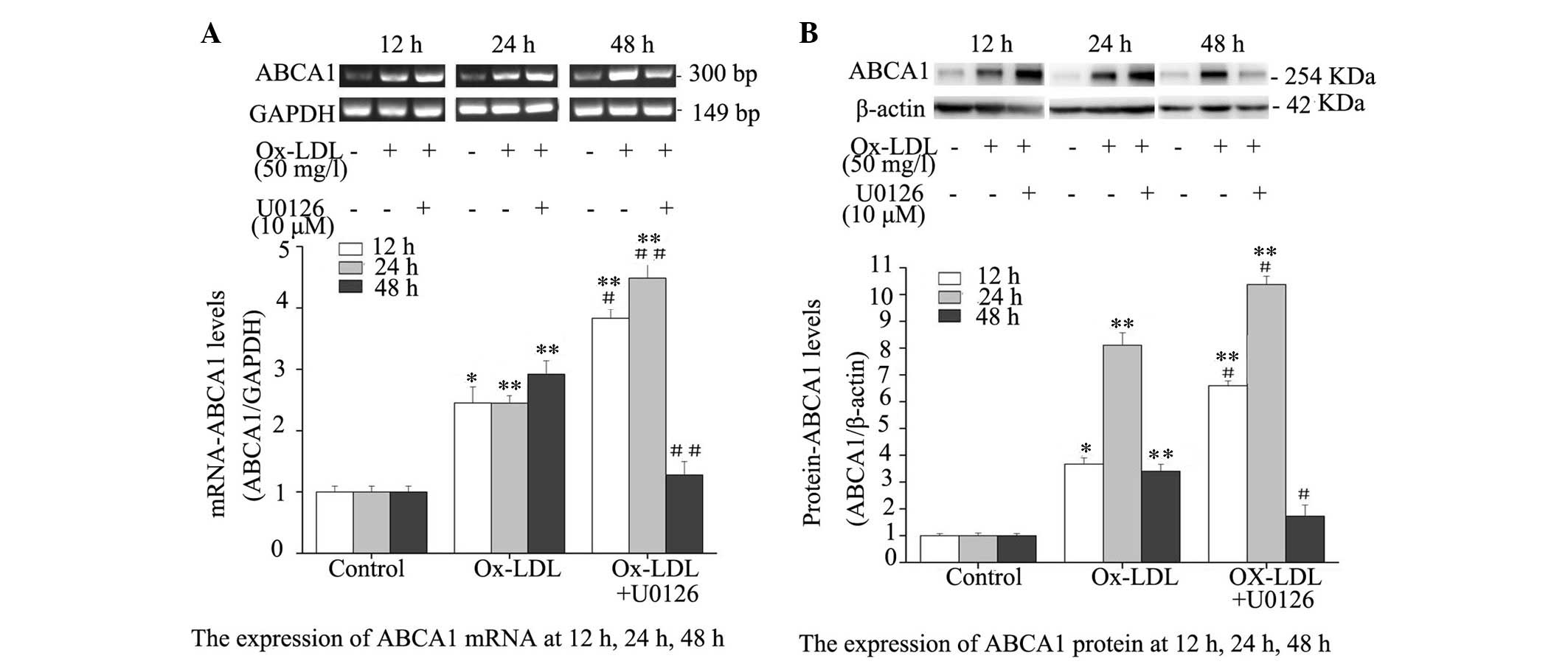
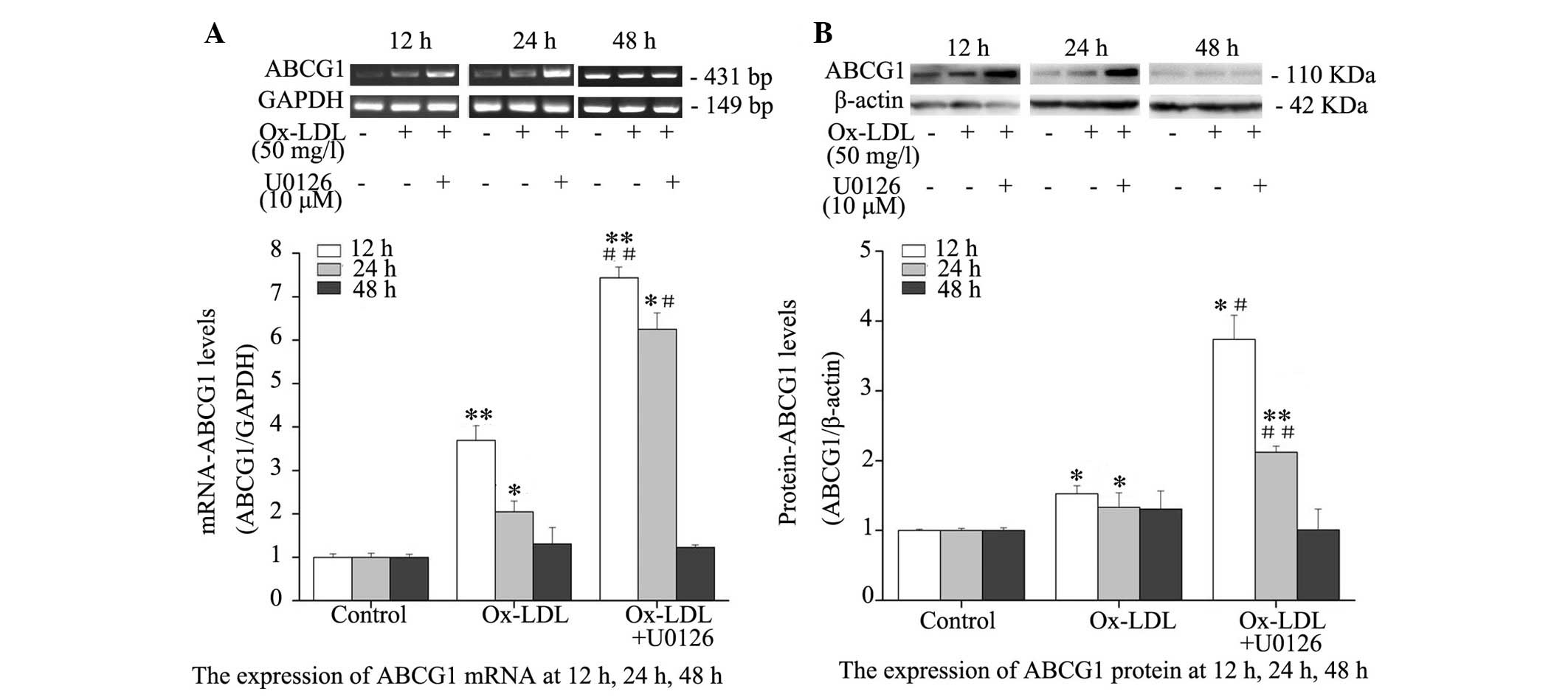
|
1
|
Lusis AJ: Atherosclerosis. Nature.
407:233–241. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Febbraio M and Silverstein RL: CD36:
Implications in cardiovascular disease. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:2012–2030. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rahaman SO, Lennon DJ, Febbraio M, Podrez
EA, Hazen SL and Silverstein RL: A CD36-dependent signaling cascade
is necessary for macrophage foam cell formation. Cell Metab.
4:211–221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Roskoski RJ Jr: ERK1/2 MAP kinases:
Structure, function and regulation. Pharmacol Res. 66:105–143.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou X, Yin Z, Guo X, Hajjar DP and Han J:
Inhibition of ERK1/2 and activation of liver X receptor
synergistically induce macrophage ABCA1 expression and cholesterol
efflux. J Biol Chem. 285:6316–6326. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Ye D, Lammers B, Zhao Y, Meurs I, Van
Berkel TJ and Van Eck M: ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and
G1, HDL metabolism, cholesterol efflux, and inflammation: Important
targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Curr Drug Targets.
12:647–660. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Silverstein RL and Febbraio M: CD36 and
atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 11:483–491. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu HY, Cui HB, Chen XM, Chen XY, Wang SH,
Du WP, Zhou HL, Zhao RC, Zhou Y, Liu YH, et al: Imbalanced response
of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 and CD36 expression to
increased oxidized low-density lipoprotein loading contributes to
the development of THP-1 derived foam cells. J Biochem. 155:35–42.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Liu W, Jiang J, Yan D, Li D, Li W, Ma Y,
Yang L, Qu Z and Ruan Q: Pentraxin 3 promotes oxLDL uptake and
inhibits cholesterol efflux from macrophage-derived foam cells. Exp
Mol Pathol. 96:292–299. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jing Q, Xin SM, Zhang WB, Wang P, Qin YW
and Pei G: Lysophosphatidylcholine activates p38 and p42/44
mitogen-activated protein kinases in monocytic THP-1 cells, but
only p38 activation is involved in its stimulated chemotaxis. Circ
Res. 87:52–59. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cheng X, Liu X, Song L, He Y, Li X and
Zhang H: Atorvastatin inhibits macrophage-derived foam cell
formation by suppressing the activation of PPARγ and NF-κB pathway.
Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao. 34:896–900. 2014.In Chinese.
PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bhandary B, Lee GH, So BO, Kim SY, Kim MG,
Kwon JW, Song JY, Lee HK, Kim HR, Chae SW and Chae HJ: Rubus
coreanus inhibits oxidized-LDL uptake by macrophages through
regulation of JNK activation. Am J Chin Med. 40:967–978. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Glass CK and Witztum JL: Atherosclerosis.
The road ahead Cell. 104:503–516. 2001.
|
|
14
|
Tiwari RL, Singh V and Barthwal MK:
Macrophages: An elusive yet emerging therapeutic target of
atherosclerosis. Med Res Rev. 28:483–544. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ouimet M: Autophagy in obesity and
atherosclerosis: Interrelationships between cholesterol
homeostasis, lipoprotein metabolism and autophagy in macrophages
and other systems. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:1124–1133. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Webb NR and Moore KJ: Macrophage-derived
foam cells in atherosclerosis: Lessons from murine models and
implications for therapy. Curr Drug Targets. 8:1249–1263. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Morio H, Saito H, Hirai A, Tamura Y and
Yoshida S: Effect of modified LDL on the release of NO and PGI2
from rat peritoneal macrophages. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2:41–45.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hirai A, Kino T, Tokinaga K, Tahara K,
Tamura Y and Yoshida S: Regulation of sterol carrier protein 2
(SCP2) gene expression in rat peritoneal macrophages during foam
cell formation. A key role for free cholesterol content. J Clin
Invest. 94:2215–2223. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nicholson AC and Hajjar DP: CD36, oxidized
LDL and PPAR gamma: Pathological interactions in macrophages and
atherosclerosis. Vascul Pharmacol. 41:139–146. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Min KJ, Um HJ, Cho KH and Kwon TK:
Curcumin inhibits oxLDL-induced CD36 expression and foam cell
formation through the inhibition of p38 MAPK phosphorylation. Food
Chem Toxicol. 58:77–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Febbraio M, Podrez EA, Smith JD, Hajjar
DP, Hazen SL, Hoff HF, Sharma K and Silverstein RL: Targeted
disruption of the class B scavenger receptor CD36 protects against
atherosclerotic lesion development in mice. J Clin Invest.
105:1049–1056. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Febbraio M, Guy E and Silverstein RL: Stem
cell transplantation reveals that absence of macrophage CD36 is
protective against atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
24:2333–2338. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marleau S, Harb D, Bujold K, Avallone R,
Iken K, Wang Y, Demers A, Sirois MG, Febbraio M, Silverstein RL, et
al: EP 80317, a ligand of the CD36 scavenger receptor, protects
apolipoprotein E-deficient mice from developing atherosclerotic
lesions. FASEB J. 19:1869–1871. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhao M, Liu Y, Wang X, New L, Han J and
Brunk UT: Activation of the p38 MAP kinase pathway is required for
foam cell formation from macrophages exposed to oxidized LDL.
APMIS. 110:458–468. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Wang N, Lan D, Chen W, Matsuura F and Tall
AR: ATP-binding cassette transporters G1 and G4 mediate cellular
cholesterol efflux to high-density lipoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 101:9774–9779. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang N, Silver DL, Costet P and Tall AR:
Specific binding of ApoA-I, enhanced cholesterol efflux, and
altered plasma membrane morphology in cells expressing ABC1. J Biol
Chem. 275:33053–33058. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tang CK, Yi GH, Yang JH, Liu LS, Wang Z,
Ruan CG and Yang YZ: Oxidized LDL upregulated ATP binding cassette
transporter-1 in THP-1 macrophages. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 25:581–586.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chang YC, Sheu WH, Chien YS, Tseng PC, Lee
WJ and Chiang AN: Hyperglycemia accelerates ATP-binding cassette
transporter A1 degradation via an ERK-dependent pathway in
macrophages. J Cell Biochem. 114:1364–1373. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Mulay V, Wood P, Manetsch M, Darabi M,
Cairns R, Hoque M, Chan KC, Reverter M, Alvarez-Guaita A, Rye KA,
et al: Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase Erk1/2
promotes protein degradation of ATP binding cassette transporters
A1 and G1 in CHO and HuH7 cells. PLoS One. 8:e626672013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hao XR, Cao DL, Hu YW, Li XX, Liu XH, Xiao
J, Liao DF, Xiang J and Tang CK: IFN-gamma down-regulates ABCA1
expression by inhibiting LXRalpha in a JAK/STAT signaling
pathway-dependent manner. Atherosclerosis. 203:417–428. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Chen M, Li W, Wang N, Zhu Y and Wang X:
ROS and NF-kappaB but not LXR mediate IL-1beta signaling for the
downregulation of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1. Am J Physiol
Cell Physiol. 292:C1493–C1501. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Uehara Y, Miura S, von Eckardstein A, Abe
S, Fujii A, Matsuo Y, Rust S, Lorkowski S, Assmann G, Yamada T and
Saku K: Unsaturated fatty acids suppress the expression of the
ATP-binding cassette transporter G1 (ABCG1) and ABCA1 genes via an
LXR/RXR responsive element. Atherosclerosis. 191:11–21. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Nagelin MH, Srinivasan S, Lee J, Nadler JL
and Hedrick CC: 12/15-Lipoxygenase activity increases the
degradation of macrophage ATP-binding cassette transporter G1.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 28:1811–1819. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang C, Cui K, Diao Y, Du M and Wang S:
Effect of selenium-enriched garlic pil against cytotoxicity induced
by OX-LDL in endothelial cells. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.
2014:5376522014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Xue X, Chen T, Wei W, Zhou X, Lin Z and
Chen L: Effects of Alisma Decoction on lipid metabolism and
inflammatory response are mediated through the activation of the
LXRα pathway in macrophage-derived foam cells. Int J Mol Med.
33:971–977. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tang SL, Chen WJ, Yin K, Zhao GJ, Mo ZC,
Lv YC, Ouyang XP, Yu XH, Kuang HJ, Jiang ZS, et al: PAPP-A
negatively regulates ABCA1, ABCG1 and SR-B1 expression by
inhibiting LXRα through the IGF-I-mediated signaling pathway.
Atherosclerosis. 222:344–354. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ma AZ, Song ZY and Zhang Q: Cholesterol
efflux is LXRα isoform-dependent in human macrophages. BMC
Cardiovasc Disord. 14:802014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Bhatt KH, Sodhi A and Chakraborty R:
Peptidoglycan induced expression of peroxisome
proliferator-activated receptor γ in mouse peritoneal macrophages:
Role of ERK and JNK MAP kinases. Cytokine. 60:778–786. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Stachowska E, Kijowski J, Dziedziejko V,
Siennicka A and Chlubek D: Conjugated linoleic acid regulates
phosphorylation of PPARγ by modulation of ERK 1/2 and p38 signaling
in human macrophages/fatty acid-laden macrophages. J Agric Food
Chem. 59:11846–11852. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Mogilenko DA, Shavva VS, Dizhe EB, Orlov
SV and Perevozchikov AP: PPARγ activates ABCA1 gene transcription
but reduces the level of ABCA1 protein in HepG2 cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 402:477–482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|