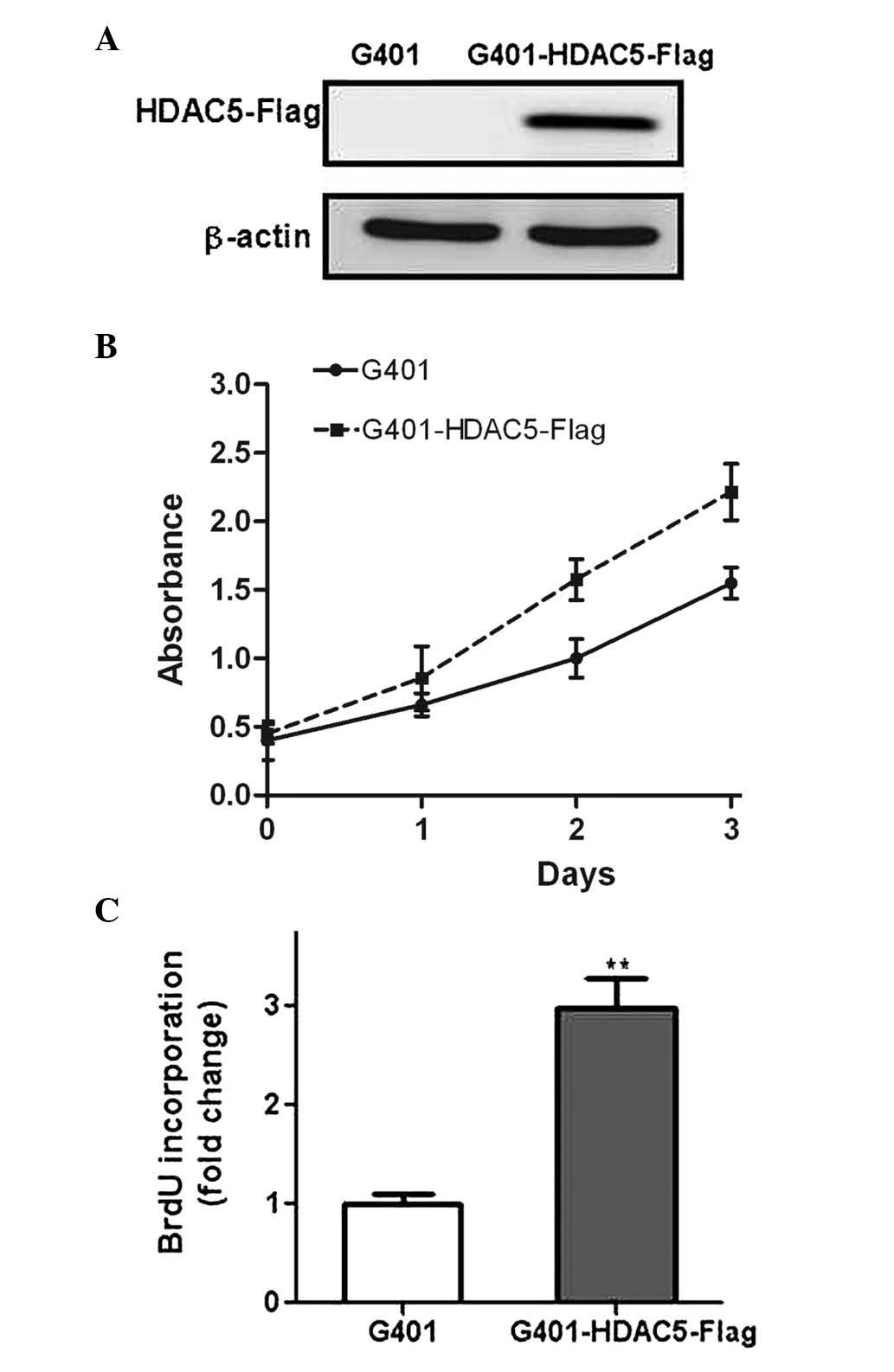
|
1
|
Turnbull C, Perdeaux ER, Pernet D, Naranjo
A, Renwick A, Seal S, Munoz-Xicola RM, Hanks S, Slade I, Zachariou
A, et al: A genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility
loci for Wilms tumor. Nat Genet. 44:681–684. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wegert J, Bausenwein S, Kneitz S, Roth S,
Graf N, Geissinger E and Gessler M: Retinoic acid pathway activity
in Wilms tumors and characterization of biological responses in
vitro. Mol Cancer. 10:1362011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Tian F, Yourek G, Shi X and Yang Y: The
development of Wilms tumor: From WT1 and microRNA to animal models.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1846:180–187. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sonn G and Shortliffe LM: Management of
Wilms tumor: Current standard of care. Nat Clin Pract Urol.
5:551–560. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Acipayam C, Sezgin G, Bayram İ, Yılmaz S,
Özkan A, Tuncel DA, Tanyeli A and Küpeli S: Treatment of Wilms
tumor using carboplatin compared to therapy without carboplatin.
Pediatr Blood Cancer. 61:1578–1583. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
West AC, Mattarollo SR, Shortt J, Cluse
LA, Christiansen AJ, Smyth MJ and Johnstone RW: An intact immune
system is required for the anticancer activities of histone
deacetylase inhibitors. Cancer Res. 73:7265–7276. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wagner JM, Hackanson B, Lübbert M and Jung
M: Histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitors in recent clinical trials
for cancer therapy. Clin Epigenetics. 1:117–136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Witt O, Deubzer HE, Milde T and Oehme I:
HDAC family: What are the cancer relevant targets? Cancer Lett.
277:8–21. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Song SH, Han SW and Bang YJ:
Epigenetic-based therapies in cancer: Progress to date. Drugs.
71:2391–2403. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vigushin DM and Coombes RC: Histone
deacetylase inhibitors in cancer treatment. Anticancer Drugs.
13:1–13. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Khan O and La Thangue NB: HDAC inhibitors
in cancer biology: Emerging mechanisms and clinical applications.
Immunol Cell Biol. 90:85–94. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cao B, Li J, Zhu J, Shen M, Han K, Zhang
Z, Yu Y, Wang Y, Wu D, Chen S, et al: The antiparasitic clioquinol
induces apoptosis in leukemia and myeloma cells by inhibiting
histone deacetylase activity. J Biol Chem. 288:34181–34189. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lai F, Jin L, Gallagher S, Mijatov B,
Zhang XD and Hersey P: Histone deacetylases (HDACs) as mediators of
resistance to apoptosis in melanoma and as targets for combination
therapy with selective BRAF inhibitors. Adv Pharmacol. 65:27–43.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang Y, Matkovich SJ, Duan X, Diwan A,
Kang MY and Dorn GN II: Receptor-independent protein kinase C alpha
(PKCalpha) signaling by calpain-generated free catalytic domains
induces HDAC5 nuclear export and regulates cardiac transcription. J
Biol Chem. 286:26943–26951. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feng GW, Dong LD, Shang WJ, Pang XL, Li
JF, Liu L and Wang Y: HDAC5 promotes cell proliferation in human
hepatocellular carcinoma by up-regulating Six1 expression. Eur Rev
Med Pharmacol Sci. 18:811–816. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Milde T, Oehme I, Korshunov A,
Kopp-Schneider A, Remke M, Northcott P, Deubzer HE, Lodrini M,
Taylor MD, von Deimling A, et al: HDAC5 and HDAC9 in
medulloblastoma: Novel markers for risk stratification and role in
tumor cell growth. Clin Cancer Res. 16:3240–3252. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Actis M, Inoue A, Evison B, Perry S,
Punchihewa C and Fujii N: Small molecule inhibitors of PCNA/PIP-box
interaction suppress translesion DNA synthesis. Bioorg Med Chem.
21:1972–1977. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Z and Zhu WG: Targeting histone
deacetylases for cancer therapy: From molecular mechanisms to
clinical implications. Int J Biol Sci. 10:757–770. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rincon-Arano H, Halow J, Delrow JJ,
Parkhurst SM and Groudine M: UpSET recruits HDAC complexes and
restricts chromatin accessibility and acetylation at promoter
regions. Cell. 151:1214–1228. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Marek L, Hamacher A, Hansen FK, Kuna K,
Gohlke H, Kassack MU and Kurz T: Histone deacetylase (HDAC)
inhibitors with a novel connecting unit linker region reveal a
selectivity profile for HDAC4 and HDAC5 with improved activity
against chemoresistant cancer cells. J Med Chem. 56:427–436. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Peixoto P, Castronovo V, Matheus N, Polese
C, Peulen O, Gonzalez A, Boxus M, Verdin E, Thiry M, Dequiedt F and
Mottet D: HDAC5 is required for maintenance of pericentric
heterochromatin and controls cell-cycle progression and survival of
human cancer cells. Cell Death Differ. 19:1239–1252. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Xia J, Yu YL, Wang SQ, Wei YB,
Chen FY, Huang GY and Shi JS: HDAC5 promotes osteosarcoma
progression by upregulation of Twist 1 expression. Tumour Biol.
35:1383–1387. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Kondo S, Ojima H, Tsuda H, Hashimoto J,
Morizane C, Ikeda M, Ueno H, Tamura K, Shimada K, Kanai Y and
Okusaka T: Clinical impact of c-Met expression and its gene
amplification in hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol.
18:207–213. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lee JM, Yoo JK, Yoo H, Jung HY, Lee DR,
Jeong HC, Oh SH, Chung HM and Kim JK: The novel miR-7515 decreases
the proliferation and migration of human lung cancer cells by
targeting c-Met. Mol Cancer Res. 11:43–53. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Koon EC, Ma PC, Salgia R, Christensen JG,
Berkowitz RS and Mok SC: Effect of a c-Met-specific,
ATP-competitive small-molecule inhibitor SU11274 on human ovarian
carcinoma cell growth, motility and invasion. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
18:976–984. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Goetsch L, Caussanel V and Corvaia N:
Biological significance and targeting of c-Met tyrosine kinase
receptor in cancer. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 18:454–473. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee YY, Kim HP, Kang MJ, Cho BK, Han SW,
Kim TY and Yi EC: Phosphoproteomic analysis identifies activated
MET-axis PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK in lapatinib-resistant cancer cell
line. Exp Mol Med. 45:e642013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nam HJ, Chae S, Jang SH, Cho H and Lee JH:
The PI3K-Akt mediates oncogenic Met-induced centrosome
amplification and chromosome instability. Carcinogenesis.
31:1531–1540. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Guessous F, Yang Y, Johnson E,
Marcinkiewicz L, Smith M, Zhang Y, Kofman A, Schiff D, Christensen
J and Abounader R: Cooperation between c-Met and focal adhesion
kinase family members in medulloblastoma and implications for
therapy. Mol Cancer Ther. 11:288–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
30
|
Hong SW, Jung KH, Park BH, Zheng HM, Lee
HS, Choi MJ, Yun JI, Kang NS, Lee J and Hong SS: KRC-408, a novel
c-Met inhibitor, suppresses cell proliferation and angiogenesis of
gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 332:74–82. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yang X, Yang Y, Tang S, Tang H, Yang G, Xu
Q and Wu J: Anti-tumor effect of polysaccharides from Scutellaria
barbata D. Don on the 95-D xenograft model via inhibition of the
C-met pathway. J Pharmacol Sci. 125:255–263. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang HT, Wang L, Ai J, Chen Y, He CX, Ji
YC, Huang M, Yang JY, Zhang A, Ding J and Geng MY: SOMG-833, a
novel selective c-MET inhibitor, blocks c-MET-dependent neoplastic
effects and exerts antitumor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther.
350:36–45. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|