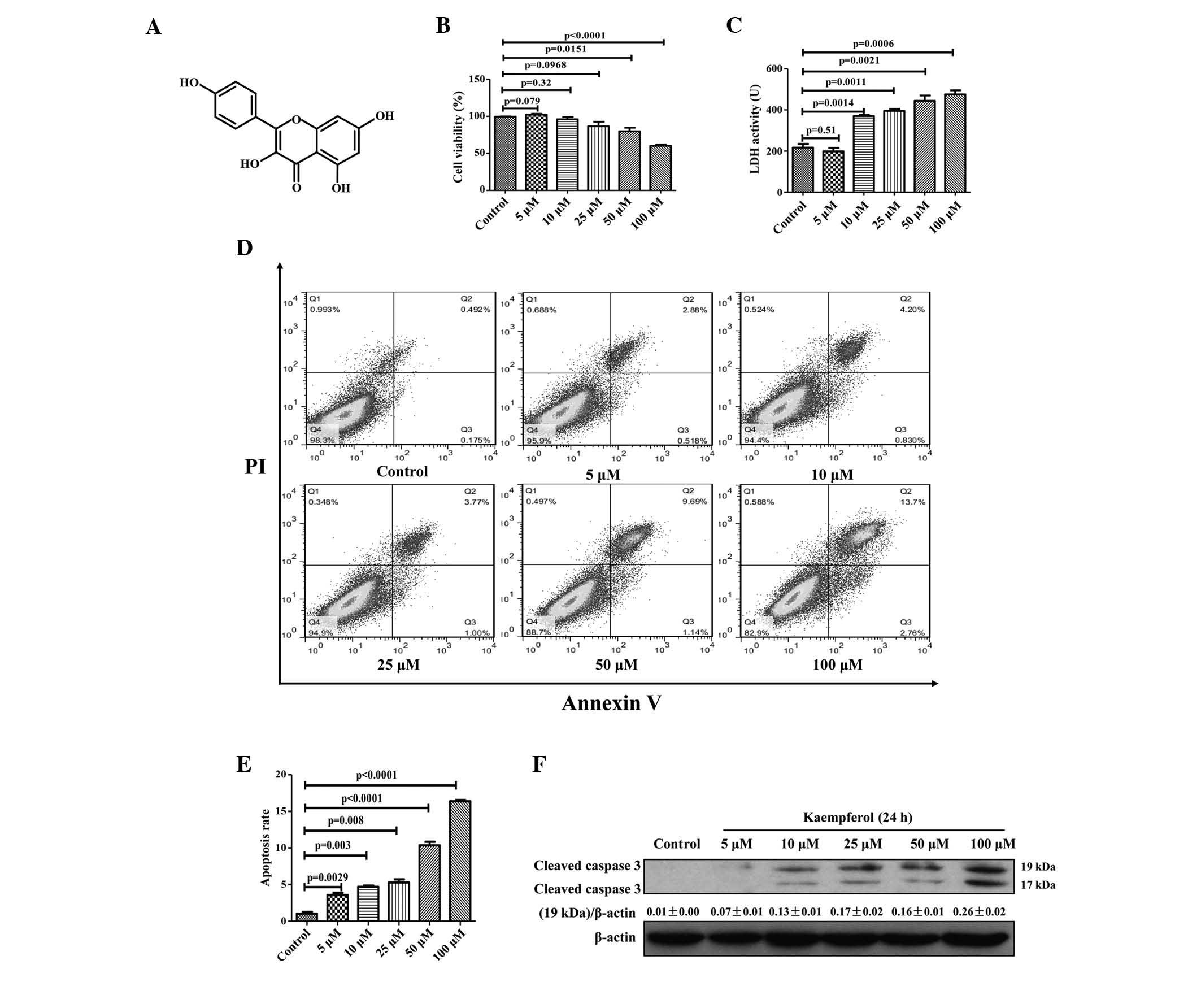
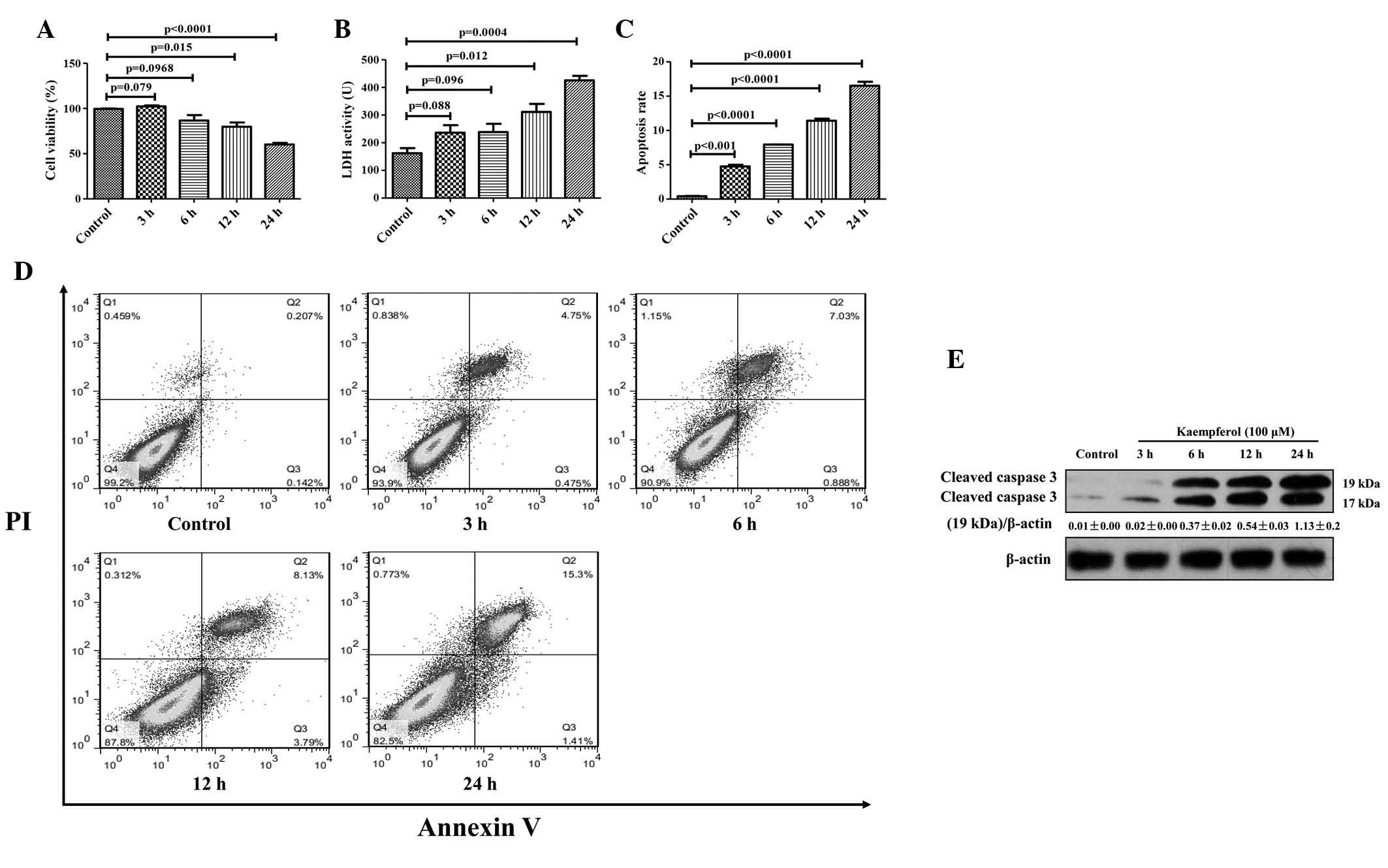
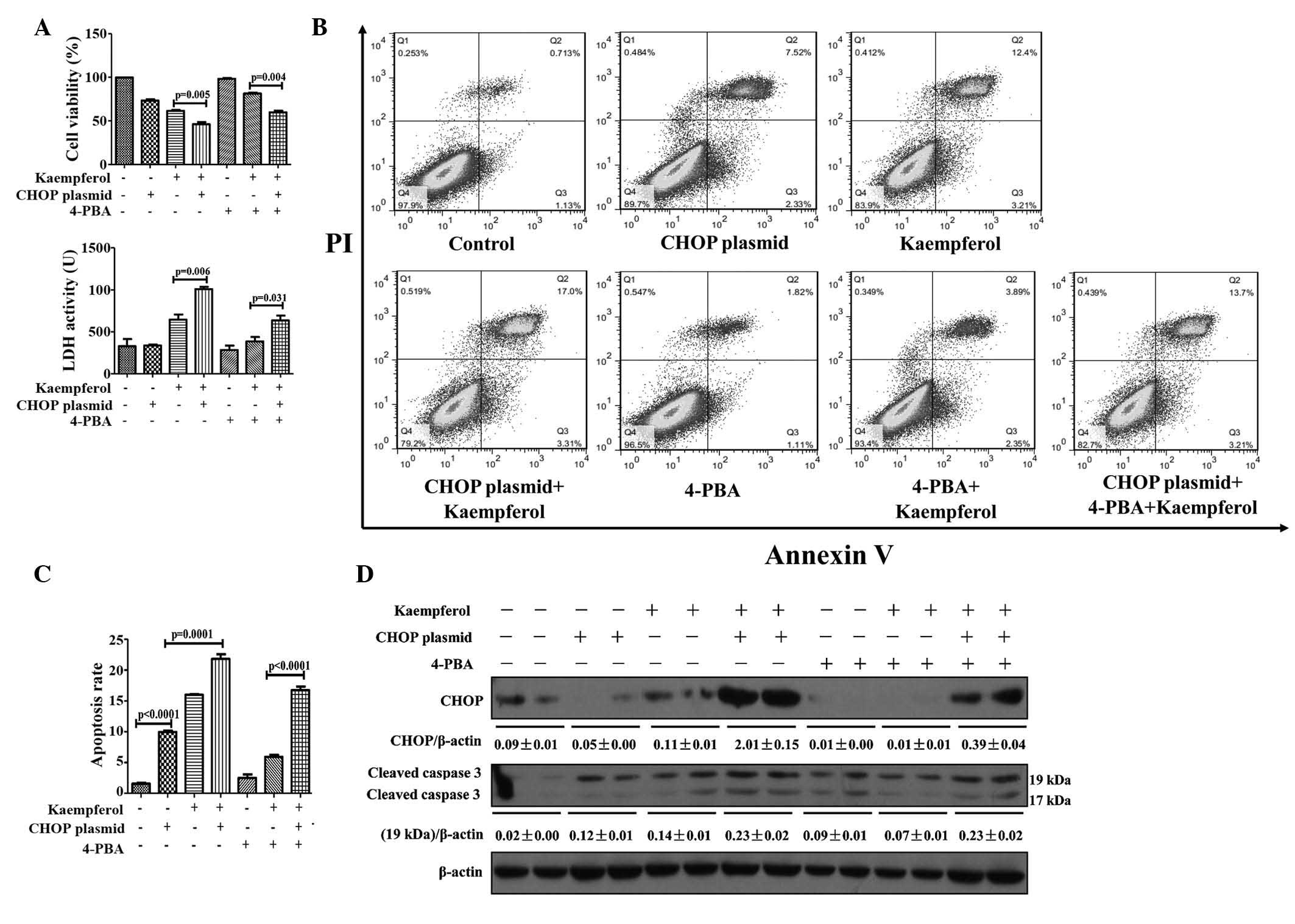
|
1
|
Xiao J, Chen T and Cao H: Flavonoid
glycosylation and biological benefits. Biotechnol Adv.
S0734-9750(14)00092-5. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Georgiev V, Ananga A and Tsolova V: Recent
advances and uses of grape flavonoids as nutraceuticals. Nutrients.
6:391–415. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Huang YB, Lin MW, Chao Y, Huang CT, Tsai
YH and Wu PC: Anti-oxidant activity and attenuation of bladder
hyperactivity by the flavonoid compound kaempferol. Int J Urol.
21:94–98. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Gong JH, Shin D, Han SY, Kim JL and Kang
YH: Kaempferol suppresses eosionphil infiltration and airway
inflammation in airway epithelial cells and in mice with allergic
asthma. J Nutr. 142:47–56. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Singh M, Kaur M and Silakari O: Flavones:
An important scaffold for medicinal chemistry. Eur J Med Chem.
84:206–239. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lin CW, Chen PN, Chen MK, Yang WE, Tang
CH, Yang SF and Hsieh YS: Kaempferol reduces matrix
metalloproteinase-2 expression by down-regulating ERK1/2 and the
activator protein-1 signaling pathways in oral cancer cells. PLoS
One. 8:e808832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li W, Du B, Wang T, Wang S and Zhang J:
Kaempferol induces apoptosis in human HCT116 colon cancer cells via
the Ataxia-Telangiectasia Mutated-p53 pathway with the involvement
of p53 Upregulated Modulator of Apoptosis. Chem Biol Interact.
177:121–127. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Deepa M, Sureshkumar T, Satheeshkumar PK
and Priya S: Antioxidant rich Morus alba leaf extract induces
apoptosis in human colon and breast cancer cells by the
downregulation of nitric oxide produced by inducible nitric oxide
synthase. Nutr Cancer. 65:305–310. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Radhika M, Ghoshal N and Chatterjee A:
Comparison of effectiveness in antitumor activity between
flavonoids and polyphenols of the methanolic extract of roots of
Potentilla fulgens in breast cancer cells. J Complement Integr Med.
9:242012.
|
|
10
|
Szliszka E, Zydowicz G, Janoszka B, Dobosz
C, Kowalczyk-Ziomek G and Krol W: Ethanolic extract of Brazilian
green propolis sensitizes prostate cancer cells to TRAIL-induced
apoptosis. Int J Oncol. 38:941–953. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gasmi J and Sanderson JT: Growth
inhibitory, antiandrogenic, and pro-apoptotic effects of punicic
acid in LNCaP human prostate cancer cells. J Agric Food Chem.
58:12149–12156. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Nandi D, Besra SE, Vedasiromoni JR, Giri
VS, Rana P and Jaisankar P: Anti-leukemic activity of Wattakaka
volubilis leaf extract against human myeloid leukemia cell lines. J
Ethnopharmacol. 144:466–473. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Huang WW, Tsai SC, Peng SF, Lin MW, Chiang
JH, Chiu YJ, Fushiya S, Tseng MT and Yang JS: Kaempferol induces
autophagy through AMPK and AKT signaling molecules and causes G2/M
arrest via downregulation of CDK1/cyclin B in SK-HEP-1 human
hepatic cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 42:2069–2077. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen S, Xuan J, Couch L, Iyer A, Wu Y, Li
QZ and Guo L: Sertraline induces endoplasmic reticulum stress in
hepatic cells. Toxicology. 322:78–88. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhang Y, Xue R, Zhang Z, Yang X and Shi H:
Palmitic and linoleic acids induce ER stress and apoptosis in
hepatoma cells. Lipids Health Dis. 11:12012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marhfour I, Lopez XM, Lefkaditis D, Salmon
I, Allagnat F, Richardson SJ, Morgan NG and Eizirik DL: Expression
of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers in the islets of patients
with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia. 55:2417–2420. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
McCloy RA, Shelley EJ, Roberts CG, Boslem
E, Biden TJ, Nicholson RI, Gee JM, Sutherland RL, Musgrove EA,
Burgess A and Butt AJ: Role of endoplasmic reticulum stress
induction by the plant toxin, persin, in overcoming resistance to
the apoptotic effects of tamoxifen in human breast cancer cells. Br
J Cancer. 109:3034–3041. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Xie Y, Tao X, Cheng Z, Guan Q, Yang W and
Zhu Y: Discrepancy of uterine leiomyoma and myometrium to
hypoxia-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress after uterine
occlusion therapy accounts for therapeutic effect. Arch Gynecol
Obstet. 289:1039–1045. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Gorman AM, Healy SJ, Jäger R and Samali A:
Stress management at the ER: Regulators of ER stress-induced
apoptosis. Pharmacol Ther. 134:306–316. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Huang WW, Chiu YJ, Fan MJ, Lu HF, Yeh HF,
Li KH, Chen PY, Chung JG and Yang JS: Kaempferol induced apoptosis
via endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondria-dependent pathway
in human osteosarcoma U-2 OS cells. Mol Nutr Food Res.
54:1585–1595. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mylonis I, Lakka A, Tsakalof A and Simos
G: The dietary flavonoid kaempferol effectively inhibits HIF-1
activity and hepatoma cancer cell viability under hypoxic
conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 398:74–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niering P, Michels G, Wätjen W, Ohler S,
Steffan B, Chovolou Y, Kampkötter A, Proksch P and Kahl R:
Protective and detrimental effects of kaempferol in rat H4IIE
cells: Implication of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 209:114–122. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Berger A, Venturelli S, Kallnischkies M,
Böcker A, Busch C, Weiland T, Noor S, Leischner C, Weiss TS, Lauer
UM, et al: Kaempferol, a new nutrition-derived pan-inhibitor of
human histone deacetylases. J Nutr Biochem. 24:977–985. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Guo L, Dial S, Shi L, Branham W, Liu J,
Fang JL, Green B, Deng H, Kaput J and Ning B: Similarities and
differences in the expression of drug-metabolizing enzymes between
human hepatic cell lines and primary human hepatocytes. Drug Metab
Dispos. 39:528–538. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
26
|
Ozcan U, Yilmaz E, Ozcan L, Furuhashi M,
Vaillancourt E, Smith RO, Görgün CZ and Hotamisligil GS: Chemical
chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a
mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science. 313:1137–1140. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zode GS, Kuehn MH, Nishimura DY, Searby
CC, Mohan K, Grozdanic SD, Bugge K, Anderson MG, Clark AF, Stone EM
and Sheffield VC: Reduction of ER stress via a chemical chaperone
prevents disease phenotypes in a mouse model of primary open angle
glaucoma. J Clin Invest. 121:3542–3553. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ron D and Walter P: Signal integration in
the endoplasmic reticulum unfolded protein response. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 8:519–529. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Xu C, Bailly-Maitre B and Reed JC:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress: Cell life and death decisions. J Clin
Invest. 115:2656–2664. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kim I, Xu W and Reed JC: Cell death and
endoplasmic reticulum stress: Disease relevance and therapeutic
opportunities. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:1013–1030. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kim DS, Ha KC, Kwon DY, Kim MS, Kim HR,
Chae SW and Chae HJ: Kaempferol protects
ischemia/reperfusion-induced cardiac damage through the regulation
of endoplasmic reticulum stress. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol.
30:257–270. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chandrika BB, Maney SK, Lekshmi SU, Joseph
J and Seervi M: Bax deficiency mediated drug resistance can be
reversed by endoplasmic reticulum stress induced death signaling.
Biochem Pharmacol. 79:1589–1599. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|