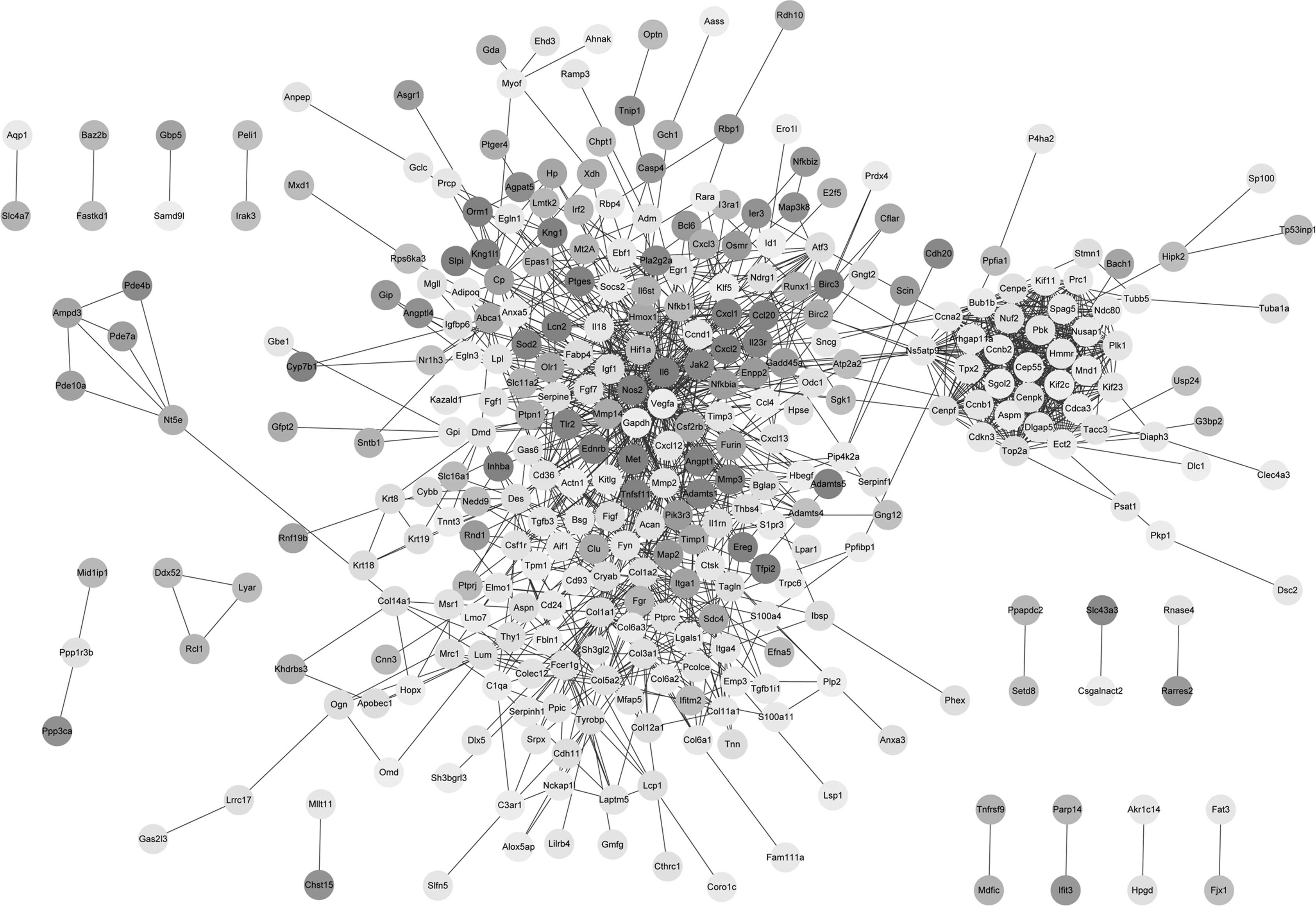
|
1
|
Bolger C: Spine disorders (medical and
surgical management). The Surgeon. 8:1852010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
McCann MR, Tamplin OJ, Rossant J and
Séguin CA: Tracing notochord-derived cells using a Noto-cre mouse:
Implications for intervertebral disc development. Dis Model Mech.
5:73–82. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
3
|
Roberts S, Evans H, Trivedi J and Menage
J: Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 88(Suppl 2): 10–14. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vo NV, Hartman RA, Yurube T, Jacobs LJ,
Sowa GA and Kang JD: Expression and regulation of
metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in intervertebral disc
aging and degeneration. Spine J. 13:331–341. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Adams MA and Roughley PJ: What is
intervertebral disc degeneration and what causes it? Spine (Phila
Pa 1976). 31:2151–2161. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Johnson WE and Roberts S: 'Rumours of my
death may have been greatly exaggerated': A brief review of cell
death in human intervertebral disc disease and implications for
cell transplantation therapy. Biochem Soc Trans. 35:680–682. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Le Maitre C, Pockert A, Buttle D, Freemont
A and Hoyland J: Matrix synthesis and degradation in human
intervertebral disc degeneration. Biochem Soc Trans. 35:652–655.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Markova DZ, Kepler CK, Addya S, Murray HB,
Vaccaro AR, Shapiro IM, Anderson DG, Albert TJ and Risbud MV: An
organ culture system to model early degenerative changes of the
intervertebral disc II: Profiling global gene expression changes.
Arthritis Res Ther. 15:R1212013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Irizarry RA, Hobbs B, Collin F,
Beazer-Barclay YD, Antonellis KJ, Scherf U and Speed TP:
Exploration, normalization and summaries of high density
oligonucleotide array probe level data. Biostatistics. 4:249–264.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Carvalho BS and Irizarry RA: A framework
for oligonucleotide microarray preprocessing. Bioinformatics.
26:2363–2367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Diboun I, Wernisch L, Orengo CA and
Koltzenburg M: Microarray analysis after RNA amplification can
detect pronounced differences in gene expression using limma. BMC
Genomics. 7:2522006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J R Stat Soc B (Methodological). 57:289–300.
1995.
|
|
13
|
Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein
D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT,
et al: Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The gene
ontology consortium. Nat Genet. 25:25–29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: Kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID Gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: A database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Albert R and Barabási AL: Statistical
mechanics of complex networks. Rev Mod Phys. 74:47–97. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
He X and Zhang J: Why do hubs tend to be
essential in protein networks? PLoS Genet. 2:e882006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matys V, Fricke E, Geffers R, Gössling E,
Haubrock M, Hehl R, Hornischer K, Karas D, Kel AE, Kel-Margoulis
OV, et al: TRANSFAC: Transcriptional regulation, from patterns to
profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:374–378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bader GD and Hogue CW: An automated method
for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction
networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 4:22003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Akhatib B, Onnerfjord P, Gawri R, Ouellet
J, Jarzem P, Heinegård D, Mort J, Roughley P and Haglund L:
Chondroadherin fragmentation mediated by the protease HTRA1
distinguishes human intervertebral disc degeneration from normal
aging. J Biol Chem. 288:19280–19287. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ariga K, Miyamoto S, Nakase T, Okuda S,
Meng W, Yonenobu K and Yoshikawa H: The relationship between
apoptosis of endplate chondrocytes and aging and degeneration of
the intervertebral disc. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 26:2414–2420. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Lockshin RA and Zakeri Z: Apoptosis,
autophagy and more. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2405–2419. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fuchs Y and Steller H: Programmed cell
death in animal development and disease. Cell. 147:742–758. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Moreno S, Imbroglini V, Ferraro E,
Bernardi C, Romagnoli A, Berrebi AS and Cecconi F: Apoptosome
impairment during development results in activation of an autophagy
program in cerebral cortex. Apoptosis. 11:1595–1602. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ye W, Xu K, Huang D, Liang A, Peng Y, Zhu
W and Li C: Age-related increases of macroautophagy and
chaperone-mediated autophagy in rat nucleus pulposus. Connect
Tissue Res. 52:472–478. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Boos N, Weissbach S, Rohrbach H, Weiler C,
Spratt KF and Nerlich AG: Classification of age-related changes in
lumbar intervertebral discs: 2002 Volvo Award in basic science.
Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 27:2631–2644. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gruber HE and Hanley EN Jr: Analysis of
aging and degeneration of the human intervertebral disc: Comparison
of surgical specimens with normal controls. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).
23:751–757. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Karban AS, Okazaki T, Panhuysen CI,
Gallegos T, Potter JJ, Bailey-Wilson JE, Silverberg MS, Duerr RH,
Cho JH, Gregersen PK, et al: Functional annotation of a novel NFKB1
promoter polymorphism that increases risk for ulcerative colitis.
Hum Mol Genet. 13:35–45. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Baldwin AS: Series introduction: The
transcription factor NF-kappaB and human disease. J Clin Invest.
107:3–6. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wuertz K, Vo N, Kletsas D and Boos N:
Inflammatory and catabolic signalling in intervertebral discs: The
roles of NF-κB and MAP kinases. Eur Cell Mater. 23:103–119.
2012.
|
|
33
|
Akeda K, An H, Gemba T, Okuma M, Miyamoto
K, Chujo T, Kitahara S and Masuda K: A new gene therapy approach:
In vivo transfection of naked NFkB decoy oligonucleotide restored
disc degeneration in the rabbit annular needle puncture model.
Trans Orthop Res Soc. 30:452005.
|
|
34
|
Wu F and Chakravarti S: Differential
expression of inflammatory and fibrogenic genes and their
regulation by NF-kappaB inhibition in a mouse model of chronic
colitis. J Immunol. 179:6988–7000. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M,
Roberts K and Walter P: The extracellular matrix of animals.
2002
|
|
36
|
Postlethwaite AE, Raghow R, Stricklin GP,
Poppleton H, Seyer JM and Kang AH: Modulation of fibroblast
functions by interleukin 1: Increased steady-state accumulation of
type I procollagen messenger RNAs and stimulation of other
functions but not chemotaxis by human recombinant interleukin 1
alpha and beta. J Cell Biol. 106:311–318. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Scharffetter K, Heckmann M, Hatamochi A,
Mauch C, Stein B, Riethmüller G, Ziegler-Heitbrock HW and Krieg T:
Synergistic effect of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and
interferon-gamma on collagen synthesis of human skin fibroblasts in
vitro. Expe Cell Res. 181:409–419. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mori K, Hatamochi A, Ueki H, Olsen A and
Jimenez S: The transcription of human alpha 1 (I) procollagen gene
(COL1A1) is suppressed by tumour necrosis factor-alpha through
proximal short promoter elements: Evidence for suppression
mechanisms mediated by two nuclear-factor binding sites. Biochem J.
319:811–816. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Feng H, Danfelter M, Strömqvist B and
Heinegård D: Extracellular matrix in disc degeneration. J Bone
Joint Surg Am. 88(Suppl 2): 25–29. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Benoist M: The natural history of lumbar
disc herniation and radiculopathy. Joint Bone Spine. 69:155–160.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Noponen-Hietala N, Virtanen I, Karttunen
R, Schwenke S, Jakkula E, Li H, Merikivi R, Barral S, Ott J,
Karppinen J and Ala-Kokko L: Genetic variations in IL6 associate
with intervertebral disc disease characterized by sciatica. Pain.
114:186–194. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Zou H, Kang X, Pang LJ, Hu W, Zhao J, Qi
Y, Hu J, Liu C, Li H, Liang W, et al: Xp11 translocation renal cell
carcinoma in adults: A clinicopathological and comparative genomic
hybridization study. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 7:236–245, eCollection
2014. 2013.
|
|
43
|
Wu WJ, Zhang XK, Zheng XF, Yang YH, Jiang
SD and Jiang LS: SHH-dependent knockout of HIF-1 alpha accelerates
the degenerative process in mouse intervertebral disc. Int J
Immunopathol Pharmacol. 26:601–609. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|