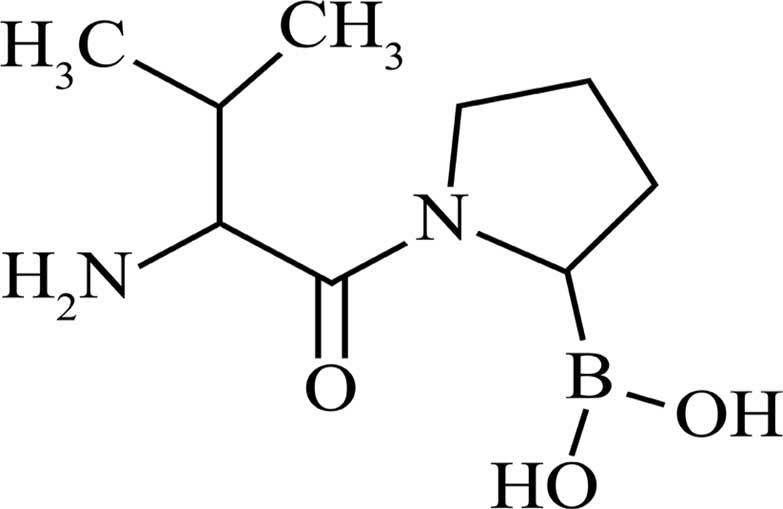
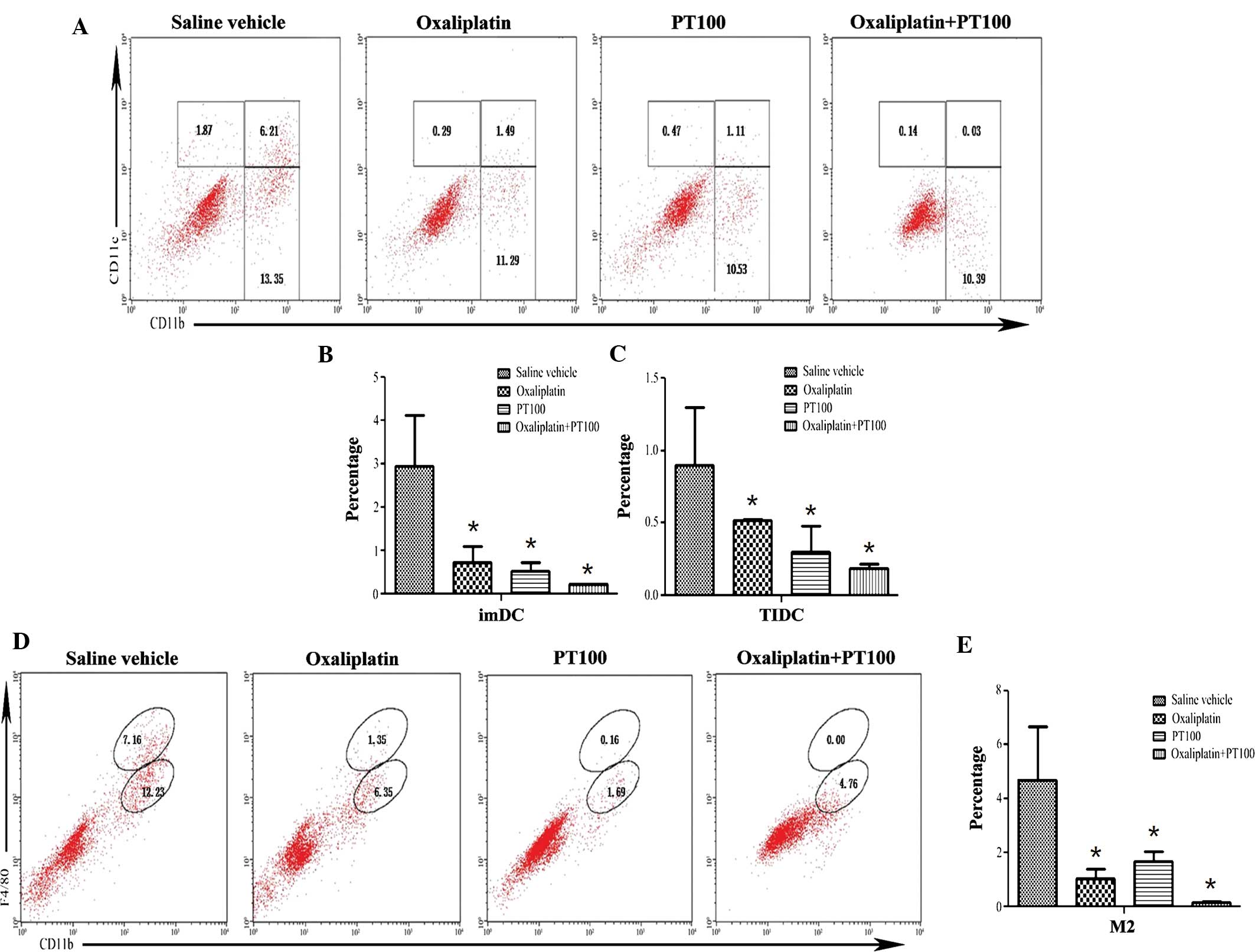
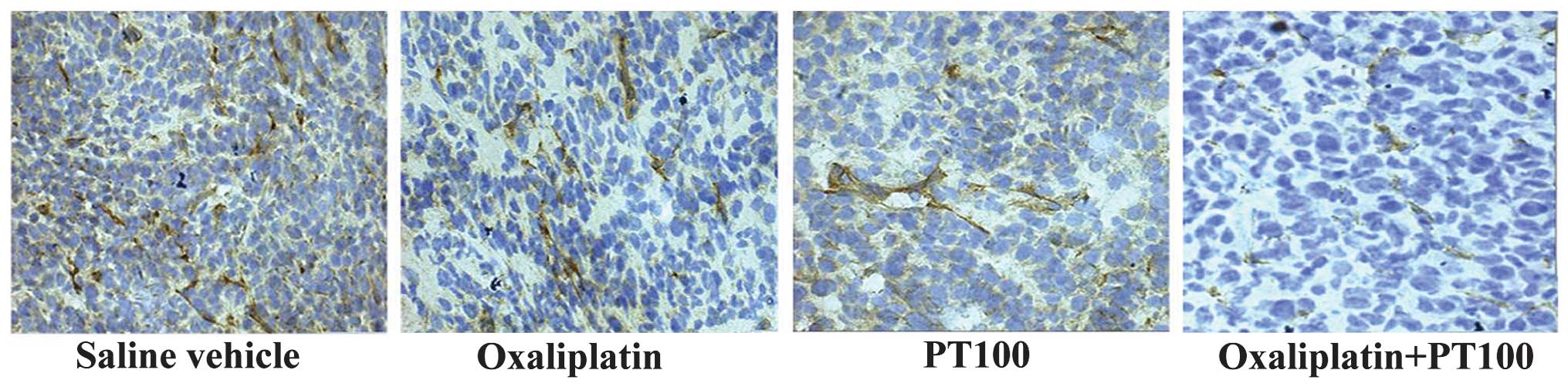
|
1
|
Kessenbrock K, Plaks V and Werb Z: Matrix
metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell.
141:52–67. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ozao-Choy J, Ma G, Kao J, Wang GX, Meseck
M, Sung M, Schwartz M, Divino CM, Pan PY and Chen SH: The novel
role of tyrosine kinase inhibitor in the reversal of immune
suppression and modulation of tumor microenvironment for
immune-based cancer therapies. Cancer Res. 69:2514–2522. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Swartz MA, Lida N, Roberts EW, Sangaletti
S, Wong MH, Yull FE, Coussens LM and DeClerck YA: Tumor
microenvironment complexity: Emerging roles in cancer therapy.
Cancer Res. 72:2473–2480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Albini A and Sporn MB: The tumour
microenvironment as a target for chemoprevention. Nat Rev Cancer.
7:139–147. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zi F, He J, He D, Li Y, Yang L and Cai Z:
Fibroblast activation protein α in tumor microenvironment: recent
progression and implications (review). Mol Med Rep. 11:3203–3211.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Whiteside TL: The tumor microenvironment
and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene. 27:5904–5912.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mueller MM and Fusenig NE: Friends or foes
- bipolar effects of the tumour stroma in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
4:839–849. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kojima Y, Acar A, Eaton EN, Mellody KT,
Scheel C, Ben-Porath I, Onder TT, Wang ZC, Richardson AL, Weinberg
RA and Orimo A: Autocrine TGF-beta and stromal cell-derived
factor-1(SDF-1) signaling drives the evolution of tumor-promoting
mammary stromal myofibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:20009–20014. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Billottet C, Tuefferd M, Gentien D,
Rapinat A, Thiery JP, Broët P and Jouanneau J: Modulation of
several waves of gene expression during FGF-1 induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of carcinoma cells. J Cell
Biochem. 104:826–839. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Potenta S, Zeisberg E and Kalluri R: The
role of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer
progression. Br J Cancer. 99:1375–1379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Xu J, Lamouille S and Derynck R:
TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res.
19:156–172. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Anderberg C, Li H, Fredriksson L, Andrae
J, Betsholtz C, Li X, Eriksson U and Pietras K: Paracrine signaling
by platelet-derived growth factor-CC promotes tumor growth by
recruitment of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res.
69:369–378. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hughes CC: Endothelial-stromal
interactions in angiogenesis. Curr Opin Hematol. 15:204–209. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yang L, Pang Y and Moses HL: TGF-beta and
immune cells: An important regulatory axis in the tumor
microenvironment and progression. Trends Immunol. 31:220–227. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Arron ST and
Hanahan D: Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Are Activated in Incipient
Neoplasia to Orchestrate Tumor-Promoting Inflammation in an
NF-kappaB-Dependent Manner. Cancer Cell. 17:135–147. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fukumura D, Xavier R, Sugiura T, Chen Y,
Park EC, Lu N, Selig M, Nielsen G, Taksir T, Jain RK and Seed B:
Tumor induction of VEGF promoter activity in stromal cells. Cell.
94:715–725. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Infante JR, Matsubayashi H, Sato N,
Tonascia J, Klein AP, Riall TA, Yeo C, Iacobuzio-Donahue C and
Goggins M: Peritumoral fibroblast SPARC expression and patient
outcome with resectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Clin Oncol.
25:319–325. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Micke P, Kappert K, Ohshima M, Sundquist
C, Scheidl S, Lindahl P, Heldin CH, Botling J, Ponten F and Ostman
A: In situ identification of genes regulated specifically in
fibroblasts of human basal cell carcinoma. J Invest Dermatol.
127:1516–1523. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tsujino T, Seshimo I, Yamamoto H, Ngan CY,
Ezumi K, Takemasa I, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Matsuura N and Monden M:
Stromal myofibroblasts predict disease recurrence for colorectal
cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 13:2082–2090. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Aertgeerts K, Levin I, Shi L, Snell GP,
Jennings A, Prasad GS, Zhang Y, Kraus ML, Salakian S, Sridhar V, et
al: Structural and kinetic analysis of the substrate specificity of
human fibroblast activation protein alpha. J Biol Chem.
280:19441–19444. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Aggarwal S, Brennen WN, Kole TP, Schneider
E, Topaloglu O, Yates M, Cotter RJ and Denmeade SR: Fibroblast
activation protein peptide substrates identified from human
collagen I derived gelatin cleavage sites. Biochemistry.
47:1076–1086. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Edosada CY, Quan C, Wiesmann C, Tran T,
Sutherlin D, Reynolds M, Elliott JM, Raab H, Fairbrother W and Wolf
BB: Selective inhibition of fibroblast activation protein protease
based on dipeptide substrate specificity. J Biol Chem.
281:7437–7444. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ostermann E, Garin-Chesa P, Heider KH,
Kalat M, Lamche H, Puri C, Kerjaschki D, Rettig WJ and Adolf GR:
Effective immunoconjugate therapy in cancer models targeting a
serine protease of tumor fibroblasts. Clin Cancer Res.
14:4584–4592. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Niedermeyer J, Enenkel B, Park JE, Lenter
M, Rettig WJ, Damm K and Schnapp A: Mouse fibroblast-activation
protein: Conserved Fap gene organization and biochemical function
as a serine protease. Eur J Biochem. 254:650–654. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cheng JD, Dunbrack RL Jr, Valianou M,
Rogatko A, Alpaugh RK and Weiner LM: Promotion of tumor growth by
murine fibroblast activation protein, a serine protease in an
animal model. Cancer Res. 62:4767–4772. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rasmussen HB, Branner S, Wiberg FC and
Wagtmann N: Crystal structure of human dipeptidyl peptidase IV/CD26
in complex with a substrate analog. Nat Struct Biol. 10:19–25.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Jones B, Adams S, Miller GT, Jesson MI,
Watanabe T and Wallner BP: Hematopoietic stimulation by a
dipeptidyl peptidase inhibitor reveal a novel regulatory mechanism
and therapeutic treatment for blood cell deficiencies. Blood.
102:1641–1648. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Diaz-Rubio E, Sastre J, Zaniboni A,
Labianca R, Cortés-Funes H, de Braud F, Boni C, Benavides M,
Dallavalle G and Homerin M: Oxaliplatin as single agent in
previously untreated colorectal carcinoma patients: A phase II
multicentric study. Ann Oncol. 9:105–108. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Raymond E, Chaney SG, Taamma A and
Cvitkovic E: Oxaliplatin: A review of preclinical and clinical
studies. Ann Oncol. 9:1053–1071. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Loeffler M, Krüger JA, Niethammer AG and
Reisfeld RA: Targeting tumor-associated fibroblasts improves cancer
chemotherapy by increasing intratumoral drug uptake. J Clin Invest.
116:1955–1962. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dean M: ABC transporters, drug resistance,
and cancer stem cells. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia. 14:3–9.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Redmond KM, Wilson TR, Johnston PG and
Longley DB: Resistance mechanisms to cancer chemotherapy. Front
Biosci. 13:5138–5154. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ma Y, Shurin GV, Gutkin DW and Shurin MR:
Tumor associated regulatory dendritic cells. Semin Cancer Biol.
22:298–306. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qian BZ and Pollard JW: Macrophage
diversity enhances tumor progression and metastasis. Cell.
141:39–51. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cubillos-Ruiz JR, Engle X, Scarlett UK,
Martinez D, Barber A, Elgueta R, Wang L, Nesbeth Y, Durant Y and
Gewirtz AT: Polyethylenimine-based siRNA nanocomplexes reprogram
tumor-associated dendritic cells via TLR5 to elicit therapeutic
antitumor immunity. J Clin Invest. 119:2231–2244. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Perugorria MJ, Castillo J, Latasa MU, Goñi
S, Segura V, Sangro B, Prieto J, Avila MA and Berasain C: Wilms'
tumor 1 gene expression in hepatocellular carcinoma promotes cell
dedifferentiation and resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Res.
69:1358–1367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Plumb JA, Strathdee G, Sludden J, Kaye SB
and Brown R: Reversal of drug resistance in human tumor xenografts
by 2′-deoxy-5-azacytidine-induced demethylation of the hMLH1 gene
promoter. Cancer Res. 60:6039–6044. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Trédan O, Galmarini CM, Patel K and
Tannock IF: Drug resistance and the solid tumor microenvironment. J
Natl Cancer Inst. 99:1441–1454. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J and Pouysségur
J: Hypoxia and cancer. J Mol Med (Berl). 85:1301–1307. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Pouysségur J, Dayan F and Mazure NM:
Hypoxia signalling in cancer and approaches to enforce tumour
regression. Nature. 441:437–443. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Kalluri R and Zeisberg M: Fibroblasts in
cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 6:392–401. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Condeelis J and Pollard JW: Macrophages:
Obligate partners for tumor cell migration, invasion and
metastasis. Cell. 124:263–266. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Liao D, Luo Y, Markowitz D, Xiang R and
Reisfeld RA: Cancer associated fibroblasts promote tumor growth and
metastasis by modulating the tumor immune microenvironment in a 4T1
murine breast cancer mode. PLoS One. 4:e79652009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
DeClerck K and Elble RC: The role of
hypoxia and acidosis in promoting metastasis and resistance to
chemotherapy. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 15:213–225. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Saharinen P, Eklund L, Pulkki K, Bono P
and Alitalo K: VEGF and angiopoietin signaling in tumor
angiogenesis and metastasis. Trends Mol Med. 17:347–362. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Desmoulière A, Guyot C and Gabbiani G: The
stroma reaction myofibroblast: A key player in the control of tumor
cell behavior. Int J Dev Biol. 48:509–517. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zeisberg EM, Potenta S, Xie L, Zeisberg M
and Kalluri R: Discovery of endothelial to mesenchymal transition
as a source for carcinoma-associated fibroblasts. Cancer Res.
67:10123–10128. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|