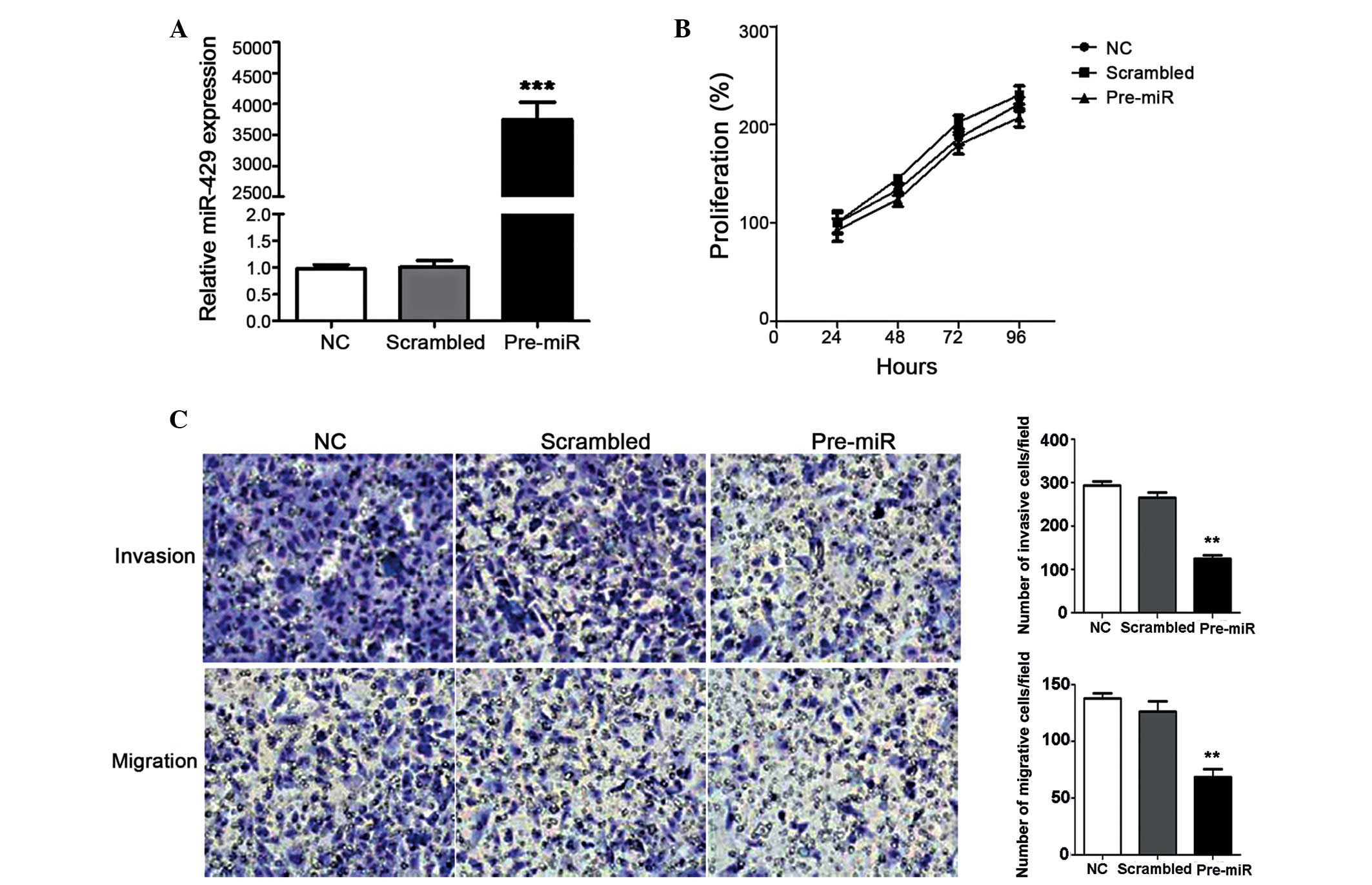
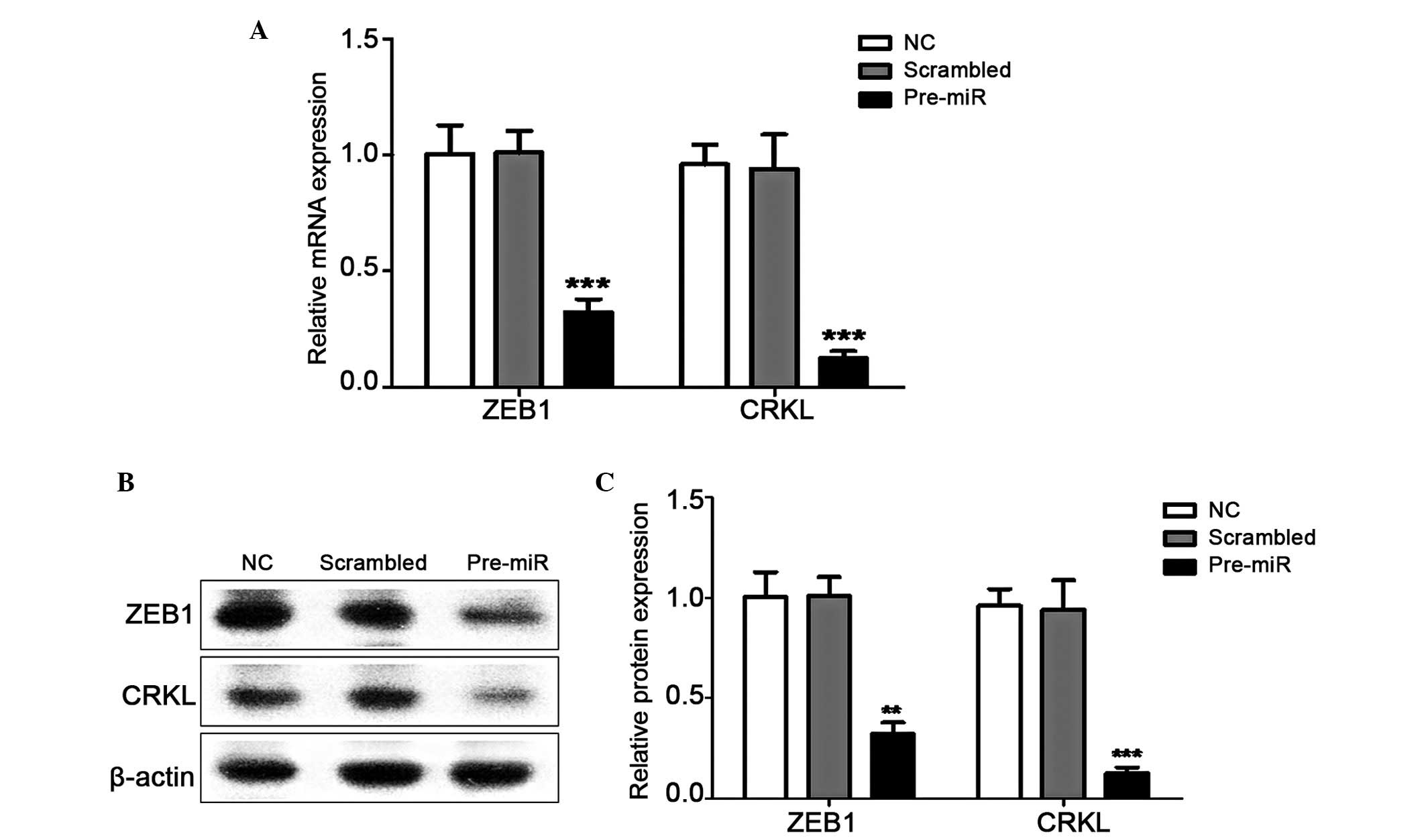
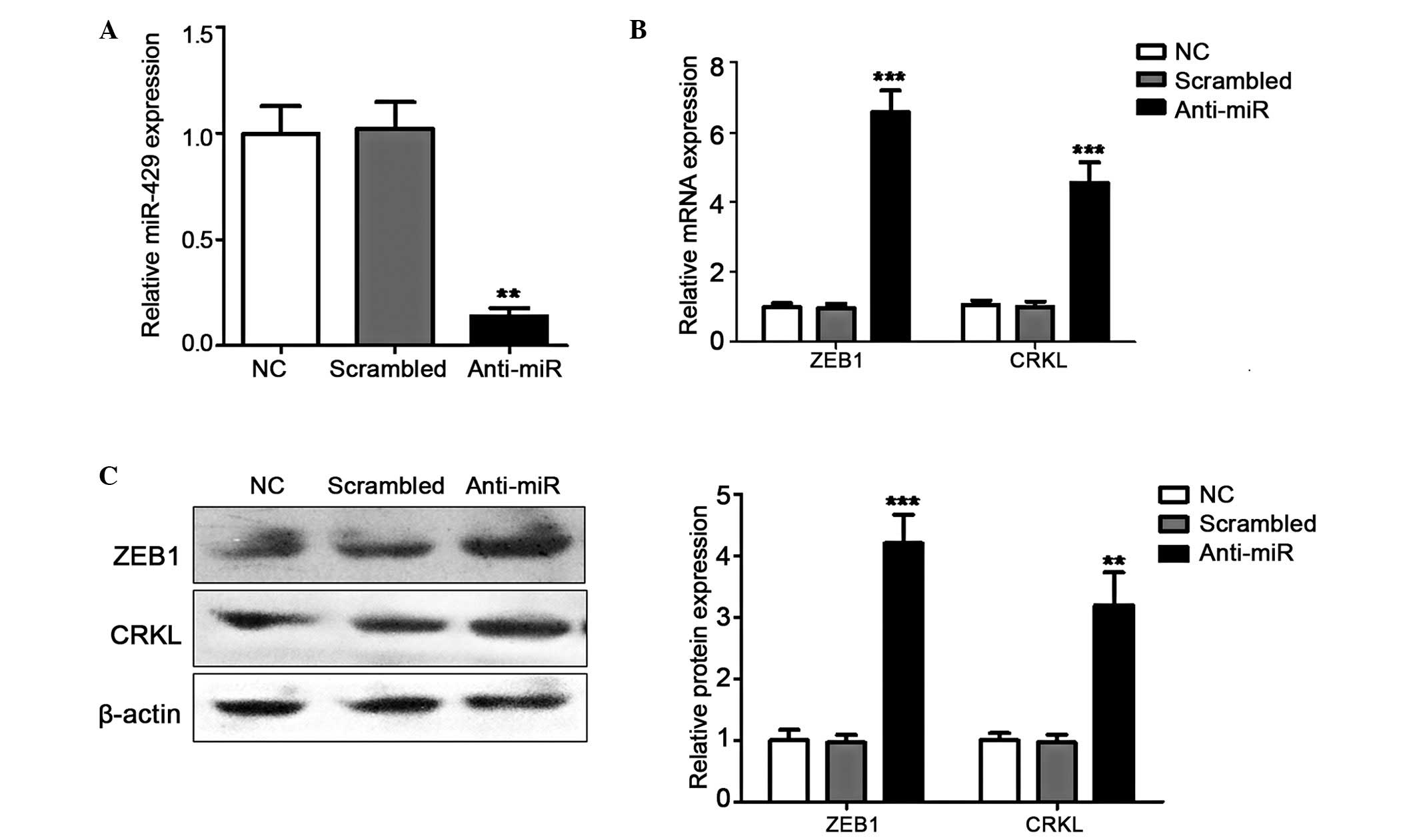
|
1
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Schirle NT, Sheu-Gruttadauria J and MacRae
IJ: Structural basis for microRNA targeting. Science. 346:608–613.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xie YJ, Long ZF and He XS: Involvement of
EBV-encoded BART-miRNAs and dysregulated cellular miRNAs in
naso-pharyngeal carcinoma genesis. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:5637–5644. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Buffa FM, Camps C, Winchester L, Snell CE,
Gee HE, Sheldon H, Taylor M, Harris AL and Ragoussis J:
microRNA-associated progression pathways and potential therapeutic
targets identified by integrated mRNA and microRNA expression
profiling in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 71:5635–5645. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bojmar L, Karlsson E, Ellegård S, Olsson
H, Björnsson B, Hallböök O, Larsson M, Stål O and Sandström P: The
role of microRNA-200 in progression of human colorectal and breast
cancer. PloS One. 8:e848152013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Baranwal S and Alahari SK: miRNA control
of tumor cell invasion and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 126:1283–1290.
2010.
|
|
8
|
Brennan B: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma.
Orphanet J Rare Dis. 1:232006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lo KW, To KF and Huang DP: Focus on
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Cell. 5:423–428. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lung ML: Unlocking the rosetta stone
enigma for naso-pharyngeal carcinoma: Genetics, viral infection and
epidemiological factors. Semin Cancer Biol. 22:77–78. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nor Hashim NA, Ramzi NH, Velapasamy S,
Alex L, Chahil JK, Lye SH, Munretnam K, Haron MR and Ler LW:
Identification of genetic and non-genetic risk factors for
naso-pharyngeal carcinoma in a Southeast Asian population. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:6005–6010. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hildesheim A and Wang CP: Genetic
predisposition factors and nasopharyngeal carcinoma risk: A review
of epidemiological association studies, 2000–2011: Rosetta Stone
for NPC: Genetics, viral infection and other environmental factors.
Semin Cancer Biol. 22:107–116. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu N, Chen NY, Cui RX, Li WF, Li Y, Wei
RR, Zhang MY, Sun Y, Huang BJ, Chen M, et al: Prognostic value of a
microRNA signature in nasopharyngeal carcinoma: A microRNA
expression analysis. Lancet Oncol. 13:633–641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu BL, Peng XH, Zhao FP, Liu X, Lu J, Wang
L, Li G, Chen HH and Li XP: MicroRNA-378 functions as an onco-miR
in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing TOB2 expression. Int J
Oncol. 44:1215–1222. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Deng M, Tang H, Zhou Y, Zhou M, Xiong W,
Zheng Y, Ye Q, Zeng X, Liao Q, Guo X, et al: miR-216b suppresses
tumor growth and invasion by targeting KRAS in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma. J Cell Sci. 124:2997–3005. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Xia H, Ng SS, Jiang S, Cheung WK, Sze J,
Bian XW, Kung HF and Lin MC: miR-200a-mediated downregulation of
ZEB2 and CTNNB1 differentially inhibits nasopharyngeal carcinoma
cell growth, migration and invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
391:535–541. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Sun XJ, Liu H, Zhang P, Zhang XD, Jiang ZW
and Jiang CC: miR-10b promotes migration and invasion in
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
14:5533–5537. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Luo Z, Zhang L, Li Z, Li X and Li G, Yu H,
Jiang C, Dai Y, Guo X, Xiang J and Li G: An in silico analysis of
dynamic changes in microRNA expression profiles in stepwise
development of naso-pharyngeal carcinoma. BMC Med Genomics.
5:32012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen J, Wang L, Matyunina LV, Hill CG and
McDonald JF: Overexpression of miR-429 induces
mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) in metastatic ovarian
cancer cells. Gynecol Oncol. 121:200–205. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhu W, He J, Chen D, Zhang B, Xu L, Ma H,
Liu X, Zhang Y and Le H: Expression of miR-29c, miR-93 and miR-429
as potential biomarkers for detection of early stage non-small lung
cancer. PloS One. 9:e877802014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sun Y, Shen S, Liu X, Tang H, Wang Z, Yu
Z, Li X and Wu M: MiR-429 inhibits cells growth and invasion and
regulates EMT-related marker genes by targeting Onecut2 in
colorectal carcinoma. Mol Cell Biochem. 390:19–30. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ye ZB, Ma G, Zhao YH, Xiao Y, Zhan Y, Jing
C, Gao K, Liu ZH and Yu SJ: miR-429 inhibits migration and invasion
of breast cancer cells in vitro. Int J Oncol. 46:531–538. 2015.
|
|
23
|
Zhang S, Wu Y, Zeng Y, Zech L and Klein G:
Cytogenetic studies on an epithelioid cell line derived from
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Hereditas. 97:23–28. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Sizhong Z, Xiukung G and Yi Z: Cytogenetic
studies on an epithelial cell line derived from poorly
differentiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 31:587–590.
1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tsao SW, Wang X, Liu Y, Cheung YC, Feng H,
Zheng Z, Wong N, Yuen PW, Lo AK, Wong YC and Huang DP:
Establishment of two immortalized nasopharyngeal epithelial cell
lines using SV40 large T and HPV16E6/E7 viral oncogenes. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1590:150–158. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee
DH, Nguyen JT, Barbisin M, Xu NL, Mahuvakar VR, Andersen MR, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tsang WP and Kwok TT: The
miR-18a* microRNA functions as a potential tumor
suppressor by targeting on K-Ras. Carcinogenesis. 30:953–959. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu X, Lv XB, Wang XP, Sang Y, Xu S, Hu K,
Wu M, Liang Y, Liu P, Tang J, et al: MiR-138 suppressed
nasopharyngeal carcinoma growth and tumorigenesis by targeting the
CCND1 oncogene. Cell Cycle. 11:2495–2506. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Peinado H, Olmeda D and Cano A: Snail, Zeb
and bHLH factors in tumour progression: An alliance against the
epithelial phenotype? Nat Rev Cancer. 7:415–428. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Yu MC and Yuan JM: Epidemiology of
nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Semin Cancer Biol. 12:421–429. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chou J, Lin YC, Kim J, You L, Xu Z, He B
and Jablons DM: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma-review of the molecular
mechanisms of tumorigenesis. Head Neck. 30:946–963. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lee AW, Foo W, Law SC, Poon YF, Sze WM, O
SK, Tung SY and Lau WH: Nasopharyngeal carcinoma: presenting
symptoms and duration before diagnosis. Hong Kong Med J. 3:355–361.
1997.
|
|
34
|
Zeng Z, Zhou Y, Xiong W, Luo X, Zhang W,
Li X, Fan S, Cao L, Tang K, Wu M and Li G: Analysis of gene
expression identifies candidate molecular markers in nasopharyngeal
carcinoma using microdissection and cDNA microarray. J Cancer Res
Clin Oncol. 133:71–81. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Li G, Liu Y, Su Z, Ren S, Zhu G, Tian Y
and Qiu Y: MicroRNA-324–3p regulates nasopharyngeal carcinoma
radioresistance by directly targeting WNT2B. Eur J Cancer.
49:2596–2607. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lu J, Xu X, Liu X, Peng Y, Zhang B, Wang
L, Luo H, Peng X, Li G, Tian W, et al: Predictive value of miR-9 as
a potential biomarker for nasopharyngeal carcinoma metastasis. Br J
Cancer. 110:392–398. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
37
|
Korpal M and Kang Y: The emerging role of
miR-200 family of microRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
and cancer metastasis. RNA Biol. 5:115–119. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Wang Y, Li M, Zang W, Ma Y, Wang N, Li P,
Wang T and Zhao G: MiR-429 up-regulation induces apoptosis and
suppresses invasion by targeting Bcl-2 and SP-1 in esophageal
carcinoma. Cell Oncol (Dordr). 36:385–394. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Eger A, Aigner K, Sonderegger S, Dampier
B, Oehler S, Schreiber M, Berx G, Cano A, Beug H and Foisner R:
DeltaEF1 is a transcriptional repressor of E-cadherin and regulates
epithelial plasticity in breast cancer cells. Oncogene.
24:2375–2385. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Senechal K, Halpern J and Sawyers CL: The
CRKL adaptor protein transforms fibroblasts and functions in
transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene. J Biol Chem.
271:23255–23261. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|