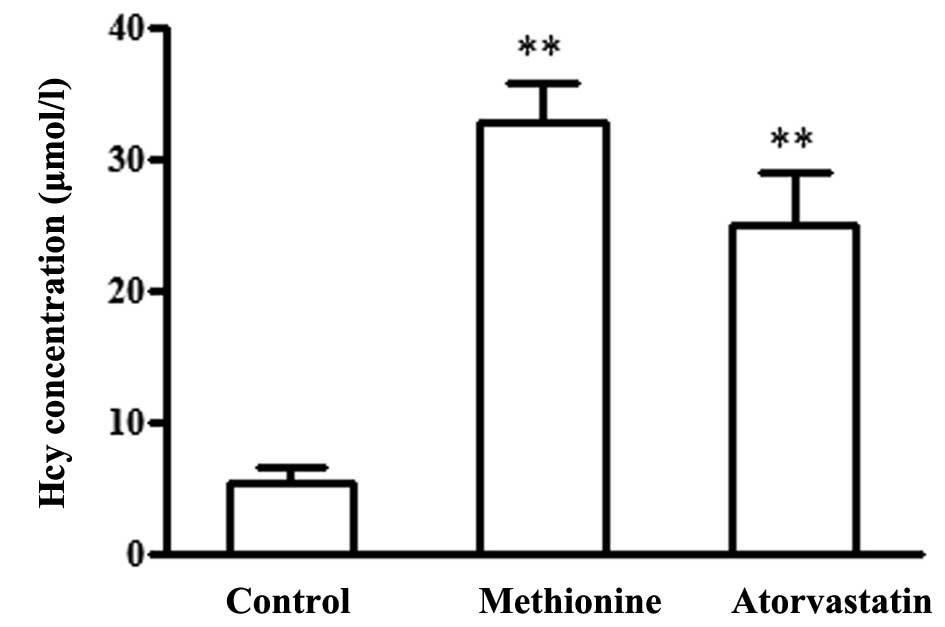
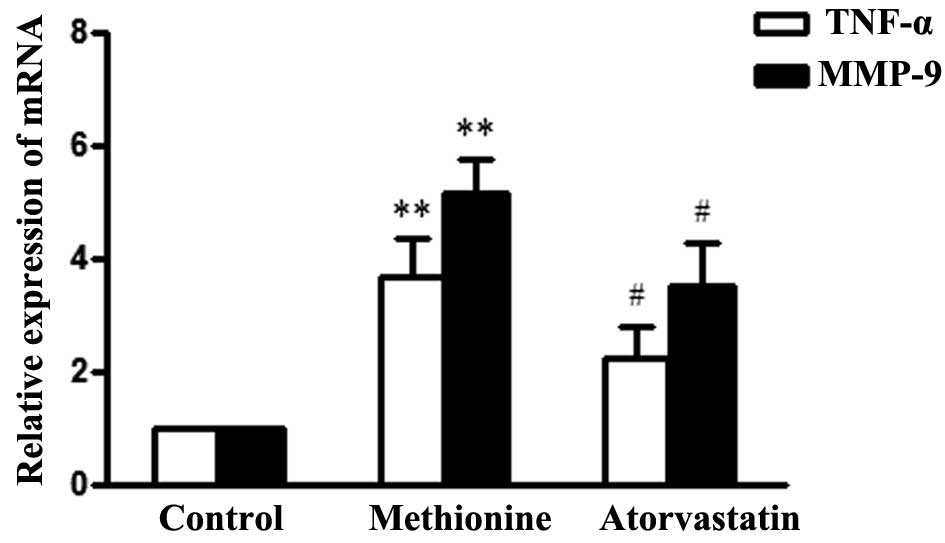
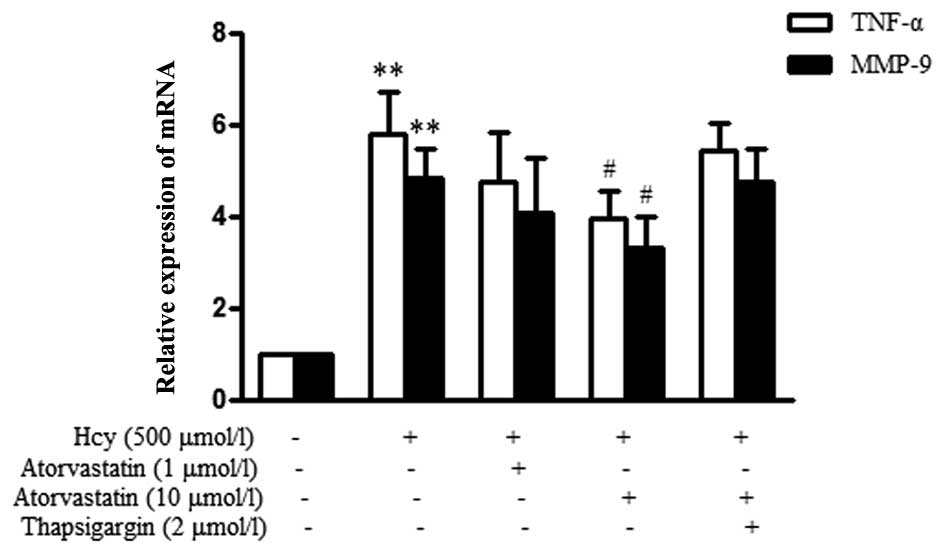
|
1
|
Silvestre-Roig C, de Winther MP, Weber C,
Daemen MJ, Lutgens E and Soehnlein O: Atherosclerotic plaque
destabilization: Mechanisms, models, and therapeutic strategies.
Circ Res. 114:214–226. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hopkins PN: Molecular biology of
atherosclerosis. Physiol Rev. 93:1317–1542. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gautier EL, Huby T, Witztum JL, Ouzilleau
B, Miller ER, Saint-Charles F, Aucouturier P, Chapman MJ and Lesnik
P: Macrophage apoptosis exerts divergent effects on atherogenesis
as a function of lesion stage. Circulation. 119:1795–1804. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tabas I: The role of endoplasmic reticulum
stress in the progression of atherosclerosis. Circ Res.
107:839–850. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yao S, Miao C, Tian H, Sang H, Yang N,
Jiao P, Han J, Zong C and Qin S: Endoplasmic reticulum stress
promotes macrophage-derived foam cell formation by up-regulating
cluster of differentiation 36 (CD36) expression. J Biol Chem.
289:4032–4042. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Gao J, Ishigaki Y, Yamada T, Kondo K,
Yamaguchi S, Imai J, Uno K, Hasegawa Y, Sawada S, Ishihara H, et
al: Involvement of endoplasmic stress protein C/EBP homologous
protein in arteriosclerosis acceleration with augmented biological
stress responses. Circulation. 124:830–839. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McAlpine CS, Bowes AJ, Khan MI, Shi Y and
Werstuck GH: Endoplasmic reticulum stress and glycogen synthase
kinase-3β activation in apolipoprotein E-deficient mouse models of
accelerated atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
32:82–91. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zhou J and Austin RC: Contributions of
hyperhomocysteinemia to atherosclerosis: Causal relationship and
potential mechanisms. Biofactors. 35:120–129. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qiu G and Hill JS: Atorvastatin inhibits
ABCA1 expression and cholesterol efflux in THP-1 macrophages by an
LXR-dependent pathway. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 51:388–395. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Llaverias G, Noé V, Peñuelas S,
Vázquez-Carrera M, Sánchez RM, Laguna JC, Ciudad CJ and Alegret M:
Atorvastatin reduces CD68, FABP4, and HBP expression in
oxLDL-treated human macrophages. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
318:265–274. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gómez-Hernández A, Sánchez-Galán E,
Martín-Ventura JL, Vidal C, Blanco-Colio LM, Ortego M, Vega M,
Serrano J, Ortega L, Hernández G, et al: Atorvastatin reduces the
expression of prostaglandin E2 receptors in human carotid
atherosclerotic plaques and monocytic cells: Potential implications
for plaque stabilization. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 47:60–69. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jia F, Wu C, Chen Z and Lu G:
AMP-activated protein kinase inhibits homocysteine-induced
dysfunction and apoptosis in endothelial progenitor cells.
Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 25:21–29. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bao XM, Wu CF and Lu GP: Atorvastatin
attenuates homocysteine-induced apoptosis in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells via inhibiting NADPH oxidase-related oxidative
stress-triggered p38MAPK signaling. Acta Pharmacol Sin.
30:1392–1398. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Institutes of Health; The National Academies
Press, Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
15
|
Jacobsen DW, Gatautis VJ, Green R,
Robinson K, Savon SR, Secic M, Ji J, Otto JM and Taylor LM Jr:
Rapid HPLC determination of total homocysteine and other thiols in
serum and plasma: Sex differences and correlation with cobalamin
and folate concentrations in healthy subjects. Clin Chem.
40:873–881. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Shah PK: Molecular mechanisms of plaque
instability. Curr Opin Lipidol. 18:492–499. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cavieres V, Valdes K, Moreno B,
Moore-Carrasco R and Gonzalez DR: Vascular hypercontractility and
endothelial dysfunction before development of atherosclerosis in
moderate dyslipidemia: Role for nitric oxide and interleukin-6. Am
J Cardiovasc Dis. 4:114–122. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McLaren JE, Michael DR, Ashlin TG and
Ramji DP: Cytokines, macrophage lipid metabolism and foam cells:
Implications for cardiovascular disease therapy. Prog Lipid Res.
50:331–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vizzardi E, Cavazzana I, Sciatti E,
Bonadei I, D'Aloia A, Tincani A, Franceschini F and Metra M:
Evaluation of ascending aorta wall in rheumatoid arthritis by
tissue and strain Doppler imaging during anti-tumor necrosis
factor-α therapy. Clin Cardiol. 37:738–743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lim HS and Lip GY: Circulating matrix
metalloproteinase-9 levels in atherosclerotic vascular disease: A
possible measurement of systemic or specific disease
pathophysiology? J Intern Med. 263:620–622. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Galán M, Kassan M, Kadowitz PJ, Trebak M,
Belmadani S and Matrougui K: Mechanism of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced vascular endothelial dysfunction. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1843:1063–1075. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Civelek M, Manduchi E, Riley RJ, Stoeckert
CJ Jr and Davies PF: Chronic endoplasmic reticulum stress activates
unfolded protein response in arterial endothelium in regions of
susceptibility to atherosclerosis. Circ Res. 105:453–461. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou AX and Tabas I: The UPR in
atherosclerosis. Semin Immunopathol. 35:321–332. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Oh J, Riek AE, Weng S, Petty M, Kim D,
Colonna M, Cella M and Bernal-Mizrachi C: Endoplasmic reticulum
stress controls M2 macrophage differentiation and foam cell
formation. J Biol Chem. 287:11629–11641. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Myoishi M, Hao H, Minamino T, Watanabe K,
Nishihira K, Hatakeyama K, Asada Y, Okada K, Ishibashi-Ueda H,
Gabbiani G, et al: Increased endoplasmic reticulum stress in
atherosclerotic plaques associated with acute coronary syndrome.
Circulation. 116:1226–1233. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Song XJ, Yang CY, Liu B, Wei Q, Korkor MT,
Liu JY and Yang P: Atorvastatin inhibits myocardial cell apoptosis
in a rat model with post-myocardial infarction heart failure by
downregulating ER stress response. Int J Med Sci. 8:564–572. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xia JG, Xu FF, Qu Y, Song DG, Shen H and
Liu XH: Atorvastatin post-conditioning attenuates myocardial
ischemia reperfusion injury via inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
stress-related apoptosis. Shock. 42:365–371. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|