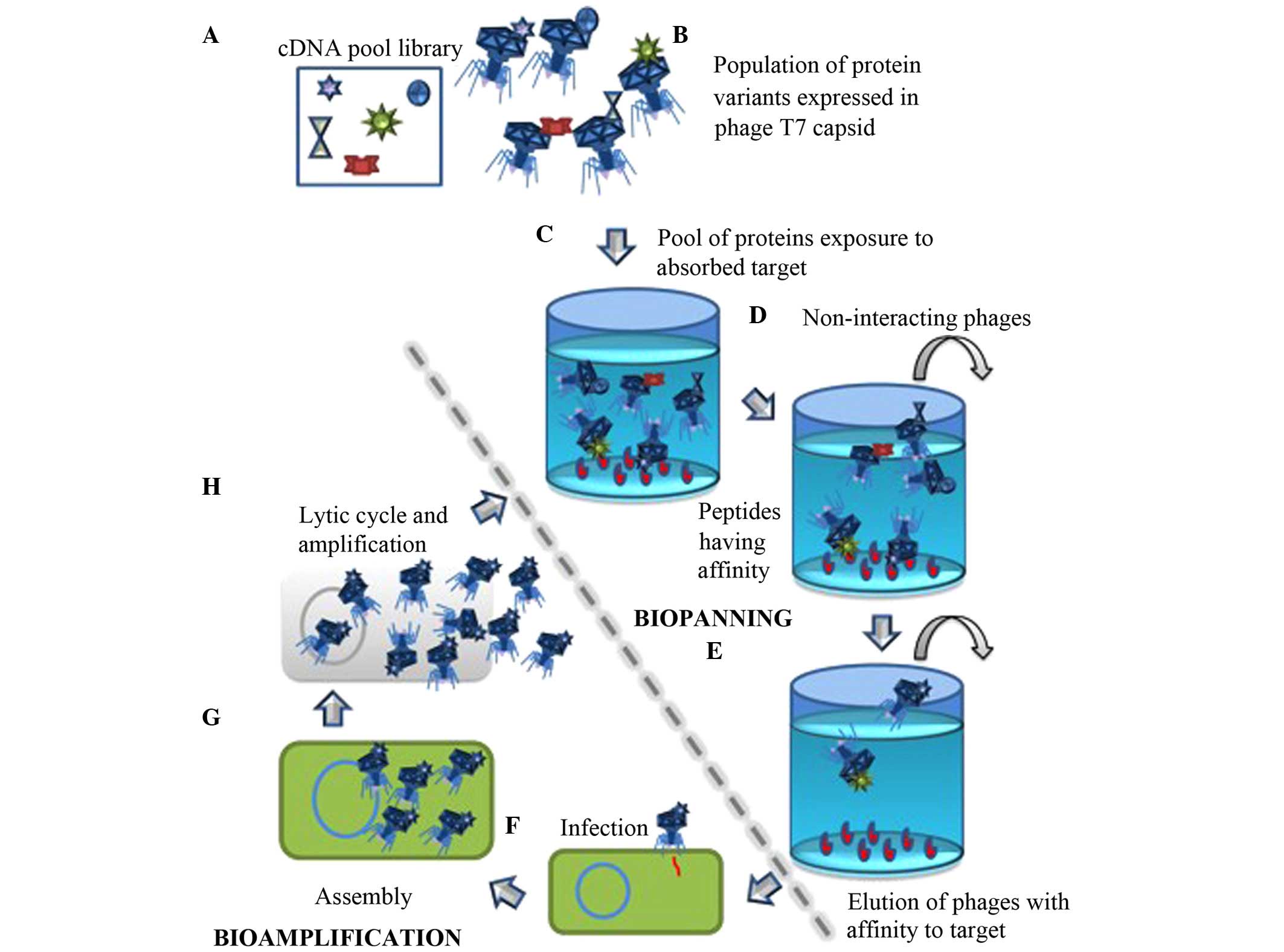
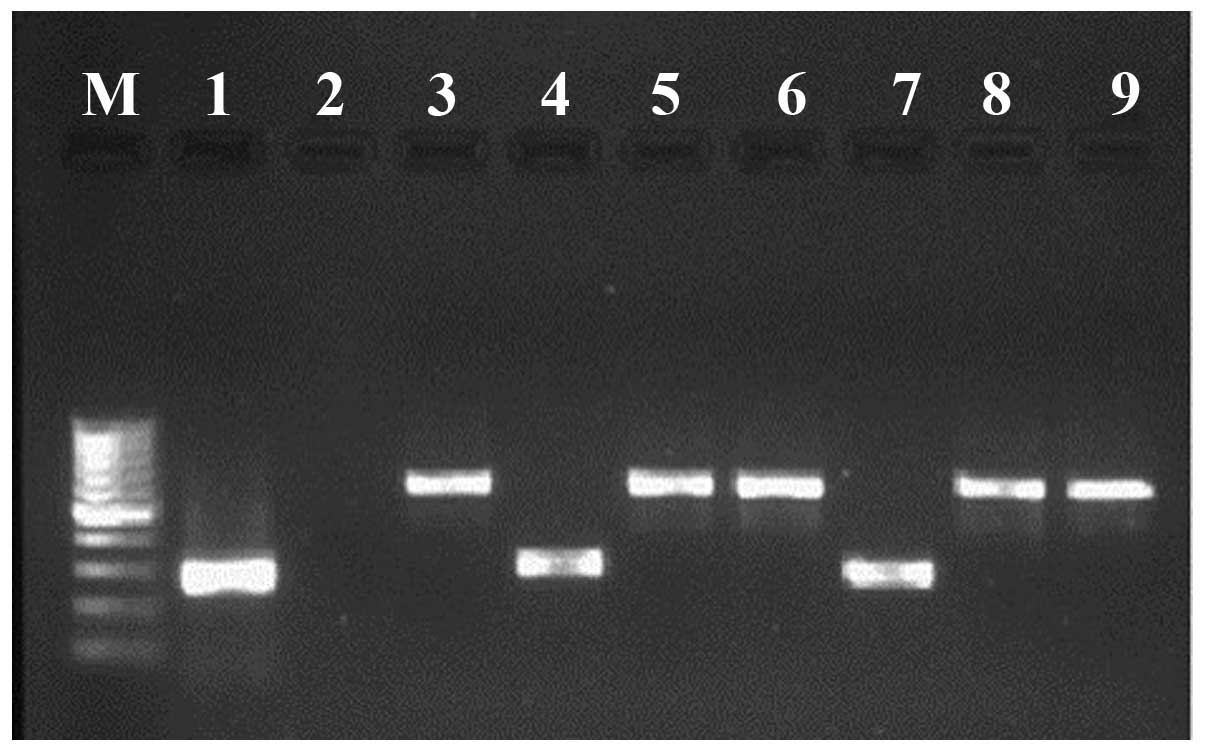
|
1
|
Akbulut A, Akbulut H, Özgüler M, İnci N
and Yalçın Ş:: Gastrointestinal anthrax: A case and review of
literature. Adv Infect Dis. 2:67–71. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Sirisanthana T and Brown AE: Anthrax of
the gastrointestinal tract. Emerg Infect Dis. 8:649–651. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Glomski IJ, Piris-Gimenez A, Huerre M,
Mock M and Goossens PL: Primary involvement of pharynx and peyer's
patch in inhalational and intestinal anthrax. PLoS Pathog.
3:e762007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tonry JH, Popov SG, Narayanan A, Kashanchi
F, Hakami RM, Carpenter C, Bailey C and Chung MC: In vivo murine
and in vitro M-like cell models of gastrointestinal anthrax.
Microbes Infect. 15:37–44. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Iqbal N, Basheer A, Ramesh AN, Vimal J,
Mookkappan S, Kanungo R, Anandhalakshmi and Princess I:
Gastrointestinal anthrax in coastal south India: A critical alert
on a fatal masquerader. JMM Case Rep. 2:e0.0000132015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hashemi SA, Azimian A, Nojumi S, Garivani
T, Safamanesh S and Ghafouri M: A case of fatal gastrointestinal
anthrax in north eastern Iran. Case Rep Infect Dis.
2015:8758292015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bouzianas DG: Medical countermeasures to
protect humans from anthrax bioterrorism. Trends Microbiol.
17:522–528. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pannifer AD, Wong TY, Schwarzenbacher R,
Renatus M, Petosa C, Bienkowska J, Lacy DB, Collier RJ, Park S,
Leppla SH, et al: Crystal structure of the anthrax lethal factor.
Nature. 414:229–233. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Duesbery NS, Webb CP, Leppla SH, Gordon
VM, Klimpel KR, Copeland TD, Ahn NG, Oskarsson MK, Fukasawa K,
Paull KD and Vande Woude GF: Proteolytic inactivation of
MAP-kinase-kinase by anthrax lethal factor. Science. 280:734–737.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pearson G, Robinson F, Beers Gibson T, Xu
BE, Karandikar M, Berman K and Cobb MH: Mitogen-activated protein
(MAP) kinase pathways: Regulation and physiological functions.
Endocr Rev. 22:153–183. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yang J, Boerm M, McCarty M, Bucana C,
Fidler IJ, Zhuang Y and Su B: Mekk3 is essential for early
embryonic cardiovascular development. Nat Genet. 24:309–313. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park JM, Greten FR, Li ZW and Karin M:
Macrophage apoptosis by anthrax lethal factor through p38 MAP
kinase inhibition. Science. 297:2048–2051. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miao EA, Rajan JV and Aderem A:
Caspase-1-induced pyroptotic cell death. Immunol Rev. 243:206–214.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sun C, Fang H, Xie T, Auth RD, Patel N,
Murray PR, Snoy PJ and Frucht DM: Anthrax lethal toxin disrupts
intestinal barrier function and causes systemic infections with
enteric bacteria. PloS One. 7:e335832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu S, Moayeri M and Leppla SH: Anthrax
lethal and edema toxins in anthrax pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol.
22:317–325. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Levinsohn JL, Newman ZL, Hellmich KA,
Fattah R, Getz MA, Liu S, Sastalla I, Leppla SH and Moayeri M:
Anthrax lethal factor cleavage of Nlrp1 is required for activation
of the inflammasome. PLoS Pathog. 8:e10026382012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Moayeri M, Sastalla I and Leppla SH:
Anthrax and the inflammasome. Microbes Infect. 14:392–400. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
18
|
Lightfoot YL, Yang T, Sahay B, Zadeh M,
Cheng SX, Wang GP, Owen JL and Mohamadzadeh M: Colonic immune
suppression, barrier dysfunction and dysbiosis by gastrointestinal
Bacillus anthracis infection. PloS One. 9:e1005322014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Baldari CT, Tonello F, Paccani SR and
Montecucco C: Anthrax toxins: A paradigm of bacterial immune
suppression. Trends Immunol. 27:434–440. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Klimpel KR, Arora N and Leppla SH: Anthrax
toxin lethal factor contains a zinc metalloprotease consensus
sequence which is required for lethal toxin activity. Mol
Microbiol. 13:1093–1100. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW
and Lipman DJ: Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol.
215:403–410. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pirovano W, Feenstra KA and Heringa J:
PRALINETM: A strategy for improved multiple alignment of
transmembrane proteins. Bioinformatics. 24:492–497. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hellmich KA, Levinsohn JL, Fattah R,
Newman ZL, Maier N, Sastalla I, Liu S, Leppla SH and Moayeri M:
Anthrax lethal factor cleaves mouse nlrp1b in both toxin-sensitive
and toxin-resistant macrophages. PLoS One. 7:e497412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vitale G, Pellizzari R, Recchi C,
Napolitani G, Mock M and Montecucco C: Anthrax lethal factor
cleaves the N-terminus of MAPKKs and induces tyrosine/threonine
phosphorylation of MAPKs in cultured macrophages. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 248:706–711. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Bishop BL, Lodolce JP, Kolodziej LE, Boone
DL and Tang WJ: The role of anthrolysin O in gut epithelial barrier
disruption during Bacillus anthracis infection. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 394:254–259. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Menard A, Papini E, Mock M and Montecucco
C: The cytotoxic activity of Bacillus anthracis lethal factor is
inhibited by leukotriene A4 hydrolase and metallopeptidase
inhibitors. Biochem J. 320:687–691. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kuzmič P, Sun CQ, Zhao ZC and Rich DH:
Long range electrostatic effects in pepsin catalysis. Tetrahedron.
47:2519–2534. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Kandadi MR, Hua Y, Ma H, Li Q, Kuo SR,
Frankel AE and Ren J: Anthrax lethal toxin suppresses murine
cardiomyocyte contractile function and intracellular Ca2+ handling
via a NADPH oxidase-dependent mechanism. PloS One. 5:e133352010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Uhlen M, Oksvold P, Fagerberg L, Lundberg
E, Jonasson K, Forsberg M, Zwahlen M, Kampf C, Wester K, Hober S,
et al: Towards a knowledge-based human protein atlas. Nat
Biotechnol. 28:1248–1250. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Durand DB, Shaw JP, Bush MR, Replogle RE,
Belagaje R and Crabtree GR: Characterization of antigen receptor
response elements within the interleukin-2 enhancer. Mol Cell Biol.
8:1715–1724. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Fang H, Cordoba-Rodriguez R, Lankford CS
and Frucht DM: Anthrax lethal toxin blocks MAPK kinase-dependent
IL-2 production in CD4+ T cells. J Immunol. 174:4966–4971. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Palmgren MG and Nissen P: P-type ATPases.
Annu Rev Biophys. 40:243–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
van Veen S, Sørensen DM, Holemans T, Holen
HW, Palmgren MG and Vangheluwe P: Cellular function and
pathological role of ATP13A2 and related P-type transport ATPases
in Parkinson's disease and other neurological disorders. Front Mol
Neurosci. 7:482014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Brunori M, Antonini G, Malatesta F, Sarti
P and Wilson MT: Cytochrome-c oxidase. Subunit structure and proton
pumping. Eur J Biochem. 169:1–8. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Chung MC, Narayanan A, Popova TG,
Kashanchi F, Bailey CL and Popov SG: Bacillus anthracis derived
nitric oxide induces protein S-nitrosylation contributing to
macrophage death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 430:125–130. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Harada T, Iwai A and Miyazaki T:
Identification of DELE, a novel DAP3-binding protein which is
crucial for death receptor-mediated apoptosis induction. Apoptosis.
15:1247–1255. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Morinaga T, Enomoto A, Shimono Y, Hirose
F, Fukuda N, Dambara A, Jijiwa M, Kawai K, Hashimoto K, Ichihara M,
et al: GDNF-inducible zinc finger protein 1 is a sequence-specific
transcriptional repressor that binds to the HOXA10 gene regulatory
region. Nucleic Acids Res. 33:4191–4201. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Brown RS, Sander C and Argos P: The
primary structure of transcription factor TFIIIA has 12 consecutive
repeats. FEBS Lett. 186:271–274. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Xie T, Sun C, Uslu K, Auth RD, Fang H,
Ouyang W and Frucht DM: A new murine model for gastrointestinal
anthrax infection. PloS One. 8:e669432013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Burgos R: Isolation of interacting
peptides to Bacillus anthracis lethal toxin (LF) by T7 phage
display (unpublished Master's dissertation). University of Puerto
Rico; 2010
|