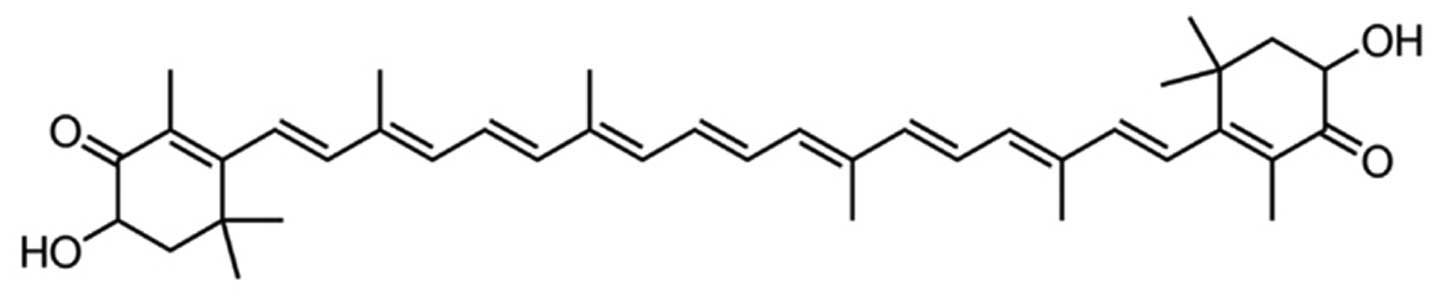
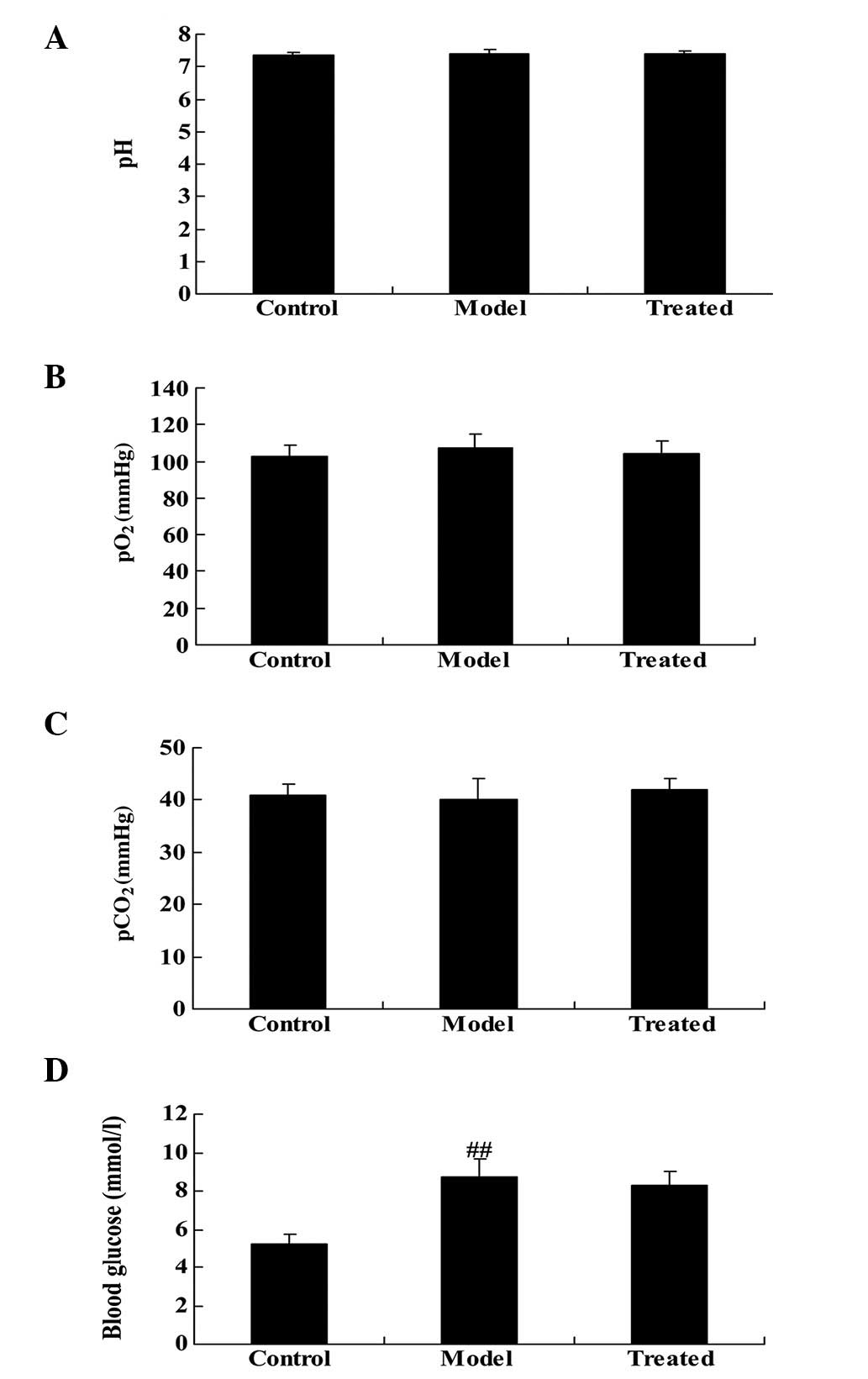
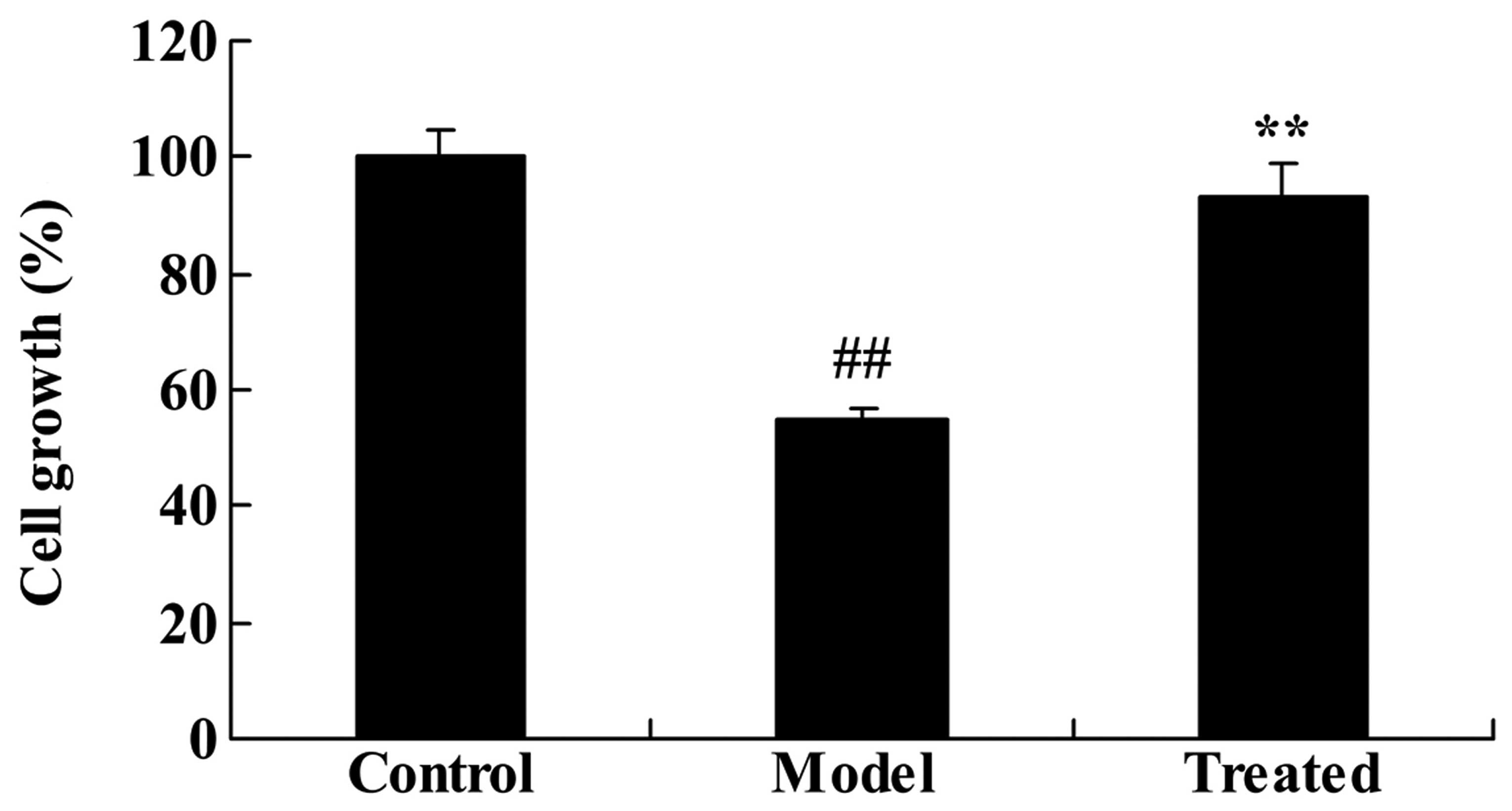
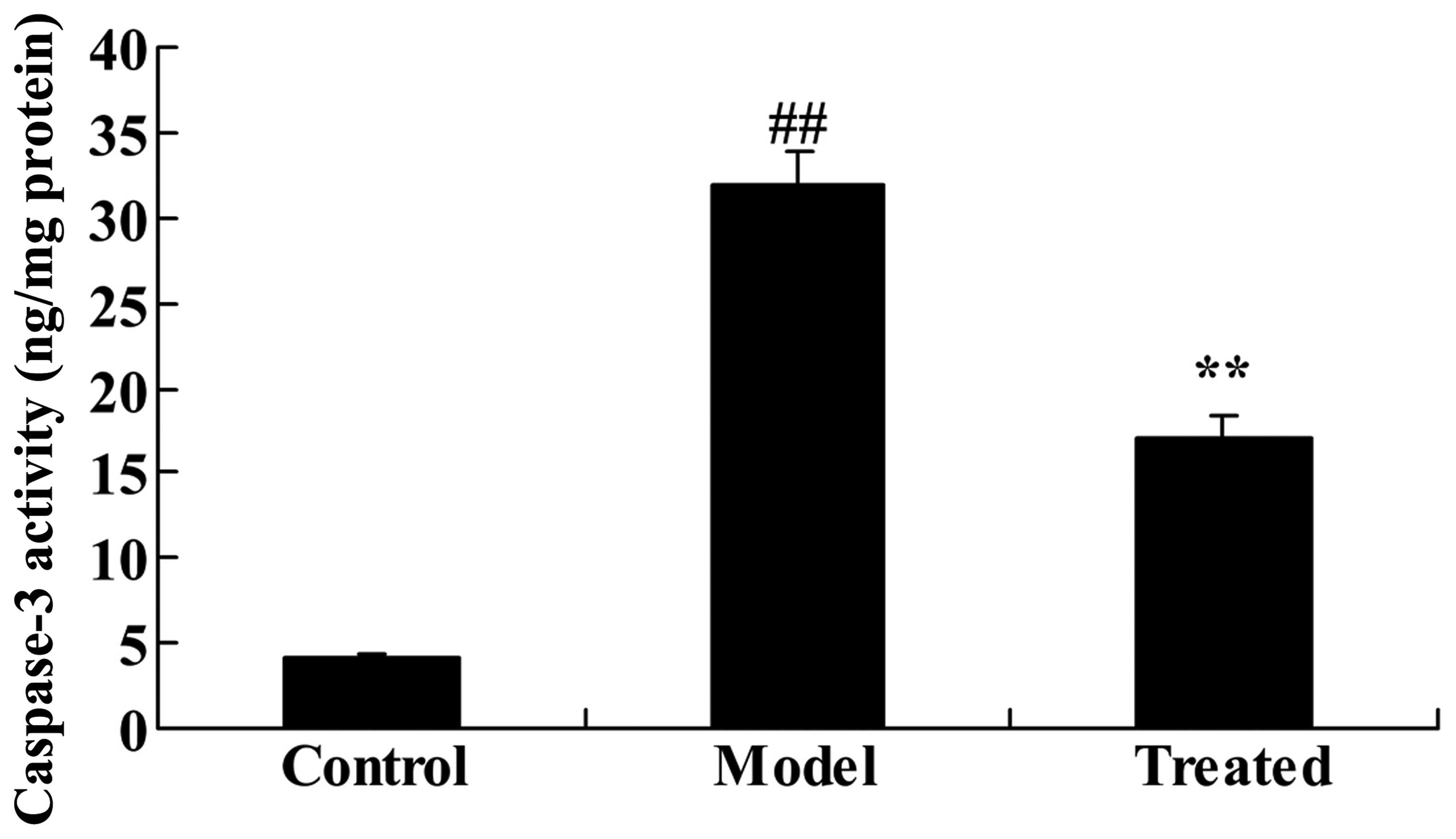
|
1
|
Johnson SA, Young C and Olney JW:
Isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis in the developing brain of
nonhypoglycemic mice. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol. 20:21–28. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Deng M, Hofacer RD, Jiang C, Joseph B,
Hughes EA, Jia B, Danzer SC and Loepke AW: Brain regional
vulnerability to anaesthesia-induced neuroapoptosis shifts with age
at exposure and extends into adulthood for some regions. Br J
Anaesth. 113:443–451. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang W, Chen X, Zhang J, Zhao Y, Li S, Tan
L, Gao J, Fang X and Luo A: Glycyrrhizin attenuates
isoflurane-induced cognitive deficits in neonatal rats via its
anti-inflammatory activity. Neuroscience. 316:328–336. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Brambrink AM, Back SA, Riddle A, Gong X,
Moravec MD, Dissen GA, Creeley CE, Dikranian KT and Olney JW:
Isoflurane-induced apoptosis of oligodendrocytes in the neonatal
primate brain. Ann Neurol. 72:525–535. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cattano D, Williamson P, Fukui K, Avidan
M, Evers AS, Olney JW and Young C: Potential of xenon to induce or
to protect against neuroapoptosis in the developing mouse brain.
Can J Anaesth. 55:429–436. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ge HW, Hu WW, Ma LL and Kong FJ:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress pathway mediates isoflurane-induced
neuroapoptosis and cognitive impairments in aged rats. Physiol
Behav. 151:16–23. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Zeng M, Chen W, Liu C, Wang F, Han
X, Zuo Z and Peng S: Dexmedetomidine reduces isoflurane-induced
neuroapoptosis partly by preserving PI3K/Akt pathway in the
hippocampus of neonatal rats. PLoS One. 9:e936392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Creeley CE, Dikranian KT, Dissen GA, Back
SA, Olney JW and Brambrink AM: Isoflurane-induced apoptosis of
neurons and oligodendrocytes in the fetal rhesus macaque brain.
Anesthesiology. 120:626–638. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Manunta C: Astaxanthin in insects and
other terrestrial arthropods. Nature. 162:2981948. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ambati RR, Phang SM, Ravi S and
Aswathanarayana RG: Astaxanthin: Sources, extraction, stability,
biological activities and its commercial applications - a review.
Mar Drugs. 12:128–152. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fassett RG and Coombes JS: Astaxanthin in
cardiovascular health and disease. Molecules. 17:2030–2048. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li Y, Yuan Z, Liu B, Sailhamer EA, Shults
C, Velmahos GC, Demoya M and Alam HB: Prevention of hypoxia-induced
neuronal apoptosis through histone deacetylase inhibition. J
Trauma. 64:863–870; discussion 870–871. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rivera LR, Thacker M, Pontell L, Cho HJ
and Furness JB: Deleterious effects of intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion injury in the mouse enteric nervous system are
associated with protein nitrosylation. Cell Tissue Res.
344:111–123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yel L, Brown LE, Su K, Gollapudi S and
Gupta S: Thimerosal induces neuronal cell apoptosis by causing
cytochrome c and apoptosis-inducing factor release from
mitochondria. Int J Mol Med. 16:971–977. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Payette DJ, Xie J, Shirwany N and Guo Q:
Exacerbation of apoptosis of cortical neurons following traumatic
brain injury in par-4 transgenic mice. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
1:44–56. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fujimura M and Usuki F: Methylmercury
causes neuronal cell death through the suppression of the TrkA
pathway: In vitro and in vivo effects of TrkA pathway activators.
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 282:259–266. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Franceschelli S, Pesce M, Ferrone A, De
Lutiis MA, Patruno A, Grilli A, Felaco M and Speranza L:
Astaxanthin treatment confers protection against oxidative stress
in U937 cells stimulated with lipopolysaccharide reducing
O2-production. PLoS One. 9:e883592014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Lu Y, Xie T, He XX, Mao ZF, Jia LJ, Wang
WP, Zhen JL and Liu LM: Astaxanthin rescues neuron loss and
attenuates oxidative stress induced by amygdala kindling in adult
rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 597:49–53. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Agarwal B, Camara AK, Stowe DF, Bosnjak ZJ
and Dash RK: Enhanced charge-independent mitochondrial free Ca(2+)
and attenuated ADP-induced NADH oxidation by isoflurane:
Implications for cardioprotection. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1817:453–465. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
20
|
Zhong Y, Liang Y, Chen J, Li L, Qin Y,
Guan E, He D, Wei Y, Xie Y and Xiao Q: Propofol inhibits
proliferation and induces neuroapoptosis of hippocampal neurons in
vitro via downregulation of NF-κB p65 and Bcl-2 and upregulation of
caspase-3. Cell Biochem Funct. 32:720–729. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheng Y and Levy RJ: Subclinical carbon
monoxide limits apoptosis in the developing brain after isoflurane
exposure. Anesth Analg. 118:1284–1292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Makaryus R, Lee H, Yu M, Zhang S, Smith
SD, Rebecchi M, Glass PS and Benveniste H: The metabolomic profile
during isoflurane anesthesia differs from propofol anesthesia in
the live rodent brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 31:1432–1442.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Lang XE, Wang X and Jin JH: Mechanisms of
cardioprotection by isoflurane against I/R injury. Front Biosci
(Landmark Ed). 18:387–393. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Bai T, Dong DS and Pei L: Resveratrol
mitigates isoflurane-induced neuroapoptosis by inhibiting the
activation of the Akt-regulated mitochondrial apoptotic signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 32:819–826. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee DH, Kim CS and Lee YJ: Astaxanthin
protects against MPTP/MPP+-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and
ROS production in vivo and in vitro. Food Chem Toxicol. 49:271–280.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chan KC, Mong MC and Yin MC: Antioxidative
and anti-inflammatory neuroprotective effects of astaxanthin and
canthaxanthin in nerve growth factor differentiated PC12 cells. J
Food Sci. 74:H225–H231. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kajimoto M, Atkinson DB, Ledee DR, Kayser
EB, Morgan PG, Sedensky MM, Isern NG, Des Rosiers C and Portman MA:
Propofol compared with isoflurane inhibits mitochondrial metabolism
in immature swine cerebral cortex. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
34:514–521. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Guo LY, Li YM, Qiao L, Liu T, Du YY, Zhang
JQ, He WT, Zhao YX and He DQ: Notch2 regulates matrix
metallopeptidase 9 via PI3K/AKT signaling in human gastric
carcinoma cell MKN-45. World J Gastroenterol. 18:7262–7270. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Guo SX, Zhou HL, Huang CL, You CG, Fang Q,
Wu P, Wang XG and Han CM: Astaxanthin attenuates early acute kidney
injury following severe burns in rats by ameliorating oxidative
stress and mitochondrial-related apoptosis. Mar Drugs.
13:2105–2123. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li Z, Dong X, Liu H, Chen X, Shi H, Fan Y,
Hou D and Zhang X: Astaxanthin protects ARPE-19 cells from
oxidative stress via upregulation of Nrf2-regulated phase II
enzymes through activation of PI3K/Akt. Mol Vis. 19:1656–1666.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|