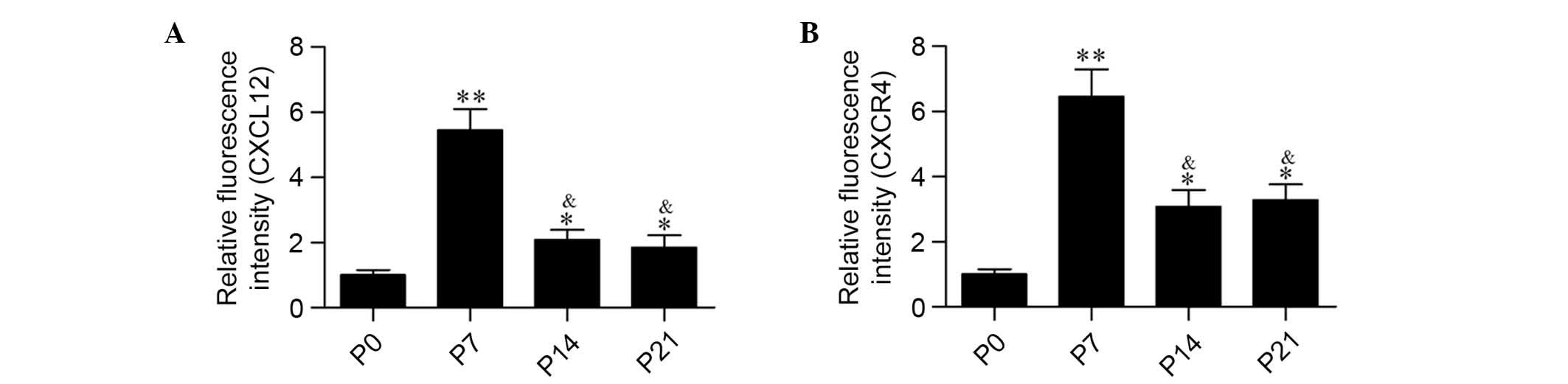
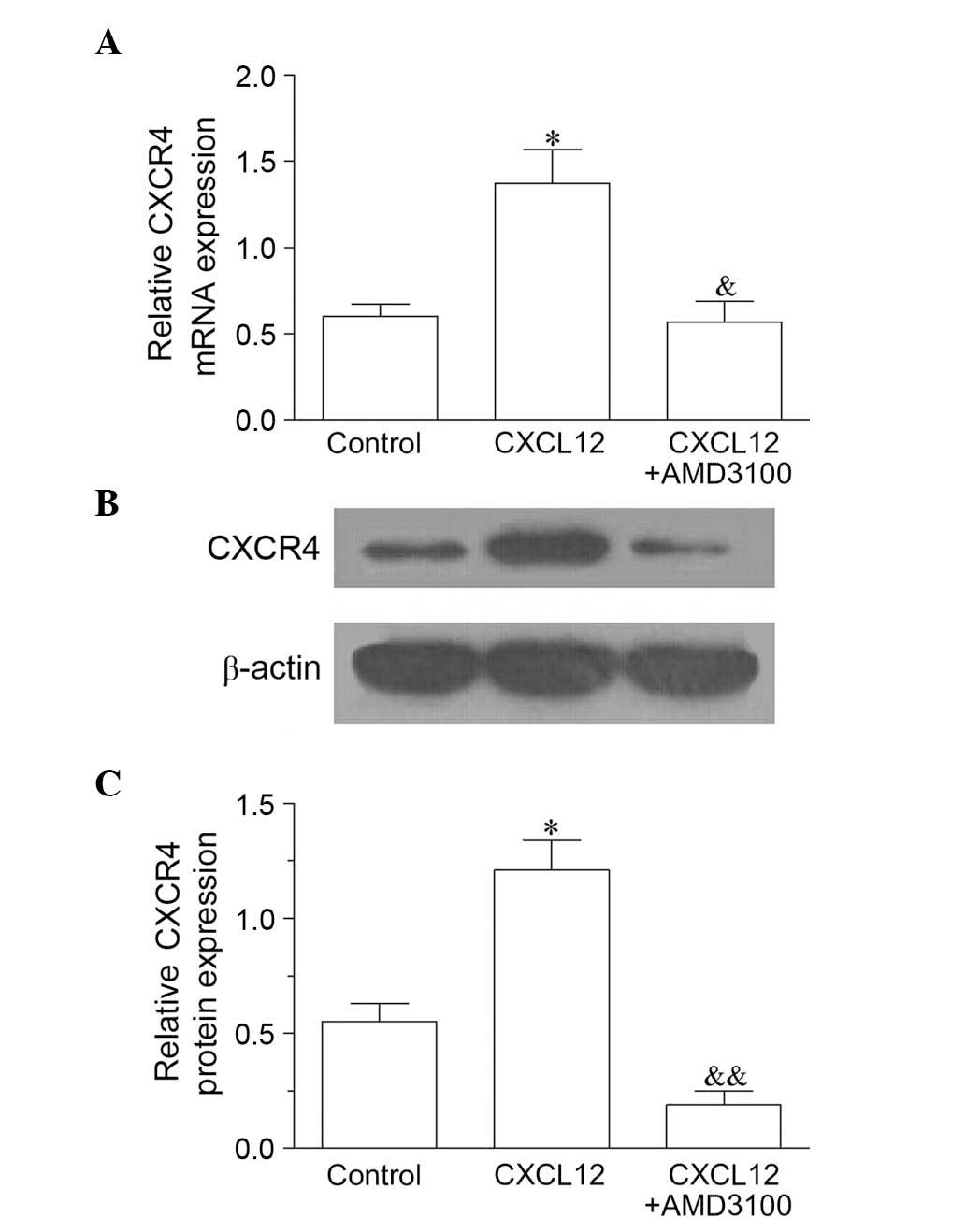
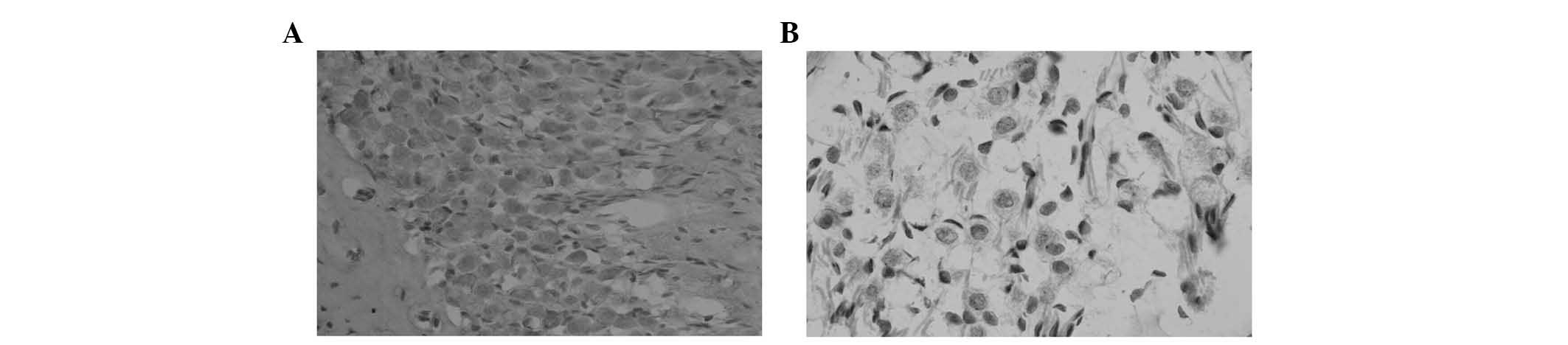
|
1
|
Bok J, Zenczak C, Hwang CH and Wu DK:
Auditory ganglion source of Sonic hedgehog regulates timing of cell
cycle exit and differentiation of mammalian cochlear hair cells.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 110:13869–13874. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tateya T, Imayoshi I, Tateya I, Hamaguchi
K, Torii H, Ito J and Kageyama R: Hedgehog signaling regulates
prosensory cell properties during the basal-to-apical wave of hair
cell differentiation in the mammalian cochlea. Development.
140:3848–3857. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Barclay M, Ryan AF and Housley GD: Type I
vs type II spiral ganglion neurons exhibit differential survival
and neuritogenesis during cochlear development. Neural Dev.
6:332011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Leake PA, Hradek GT, Hetherington AM and
Stakhovskaya O: Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promotes cochlear
spiral ganglion cell survival and function in deafened, developing
cats. J Comp Neurol. 519:1526–1545. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dabdoub A, Puligilla C, Jones JM, Fritzsch
B, Cheah KS, Pevny LH and Kelley MW: Sox2 signaling in prosensory
domain specification and subsequent hair cell differentiation in
the developing cochlea. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:18396–18401.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang S, Edman LC, Sánchez-Alcañiz JA,
Fritz N, Bonilla S, Hecht J, Uhlén P, Pleasure SJ, Villaescusa JC,
Marín O and Arenas E: Cxcl12/Cxcr4 signaling controls the migration
and process orientation of A9-A10 dopaminergic neurons.
Development. 140:4554–4564. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zou YR, Kottmann AH, Kuroda M, Taniuchi I
and Littman DR: Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in
haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature. 393:595–599.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nagasawa T: CXC chemokine ligand 12
(CXCL12) and its receptor CXCR4. J Mol Med Berl. 92:433–439. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma Q, Jones D, Borghesani PR, Segal RA,
Nagasawa T, Kishimoto T, Bronson RT and Springer TA: Impaired
B-lymphopoiesis, myelopoiesis, and derailed cerebellar neuron
migration in CXCR4- and SDF-1-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 95:9448–9453. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhu Y, Matsumoto T, Mikami S, Nagasawa T
and Murakami F: SDF1/CXCR4 signalling regulates two distinct
processes of precerebellar neuronal migration and its depletion
leads to abnormal pontine nuclei formation. Development.
136:1919–1928. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Stumm RK, Zhou C, Ara T, Lazarini F,
Dubois-Dalcq M, Nagasawa T, Höllt V and Schulz S: CXCR4 regulates
interneuron migration in the developing neocortex. J Neurosci.
23:5123–5130. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lieberam I, Agalliu D, Nagasawa T, Ericson
J and Jessell TM: A Cxcl12-CXCR4 chemokine signaling pathway
defines the initial trajectory of mammalian motor axons. Neuron.
47:667–679. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
García-Hernández S, Potashner SJ and
Morest DK: Role of fibroblast growth factor 8 in neurite outgrowth
from spiral ganglion neurons in vitro. Brain Res. 1529:39–45. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak and Schmittgen: Analysis of relative
gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the
2−ΔΔCt method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Xu N, Engbers J, Khaja S, Xu L, Clark JJ
and Hansen MR: Influence of cAMP and protein kinase A on neurite
length from spiral ganglion neurons. Hear Res. 283:33–44. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
16
|
Wang F, Gao X, Chen J, Liu SL, Wang FY,
Hei RY, Chen Y and Qiu JH: Effect of early postnatal air-conduction
auditory deprivation on the development and function of the rat
spiral ganglion. J Laryngol Otol. 125:917–923. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Peng H, Kolb R, Kennedy JE and Zheng J:
Differential expression of CXCL12 and CXCR4 during human fetal
neural progenitor cell differentiation. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol.
2:251–258. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schols D, Struyf S, Van Damme J, Esté JA,
Henson G and De Clercq E: Inhibition of T-tropic HIV strains by
selective antagonization of the chemokine receptor CXCR4. J Exp
Med. 186:1383–1388. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hartnick CJ, Staecker H, Malgrange B,
Lefebvre PP, Liu W, Moonen G and Van de Water TR: Neurotrophic
effects of BDNF and CNTF, alone and in combination, on postnatal
day 5 rat acoustic ganglion neurons. J Neurobiol. 30:246–254. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mullen LM, Pak KK, Chavez E, Kondo K,
Brand Y and Ryan AF: Ras/p38 and PI3K/Akt but not Mek/Erk signaling
mediate BDNF-induced neurite formation on neonatal cochlear spiral
ganglion explants. Brain Res. 1430:25–34. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Aletsee C, Beros A, Mullen L, Palacios S,
Pak K, Dazert S and Ryan AF: Ras/MEK but not p38 signaling mediates
NT-3-induced neurite extension from spiral ganglion neurons. J
Assoc Res Otolaryngol. 2:377–387. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Li M and Ransohoff RM: Multiple roles of
chemokine CXCL12 in the central nervous system: A migration from
immunology to neurobiology. Prog Neurobiol. 84:116–131. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Banisadr G, Fontanges P, Haour F, Kitabgi
P, Rostène W and Mélik Parsadaniantz S: Neuroanatomical
distribution of CXCR4 in adult rat brain and its localization in
cholinergic and dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci. 16:1661–1671.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Krumbholz M, Theil D, Cepok S, Hemmer B,
Kivisäkk P, Ransohoff RM, Hofbauer M, Farina C, Derfuss T, Hartle
C, et al: Chemokines in multiple sclerosis: CXCL12 and CXCL13
up-regulation is differentially linked to CNS immune cell
recruitment. Brain. 129:200–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Stumm RK, Rummel J, Junker V, Culmsee C,
Pfeiffer M, Krieglstein J, Höllt V and Schulz S: A dual role for
the SDF-1/CXCR4 chemokine receptor system in adult brain:
Isoform-selective regulation of SDF-1 expression modulates
CXCR4-dependent neuronal plasticity and cerebral leukocyte
recruitment after focal ischemia. J Neurosci. 22:5865–5878.
2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Oh SB, Tran PB, Gillard SE, Hurley RW,
Hammond DL and Miller RJ: Chemokines and glycoprotein120 produce
pain hypersensitivity by directly exciting primary nociceptive
neurons. J Neurosci. 21:5027–5035. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Limatola C, Giovannelli A, Maggi L,
Ragozzino D, Castellani L, Ciotti MT, Vacca F, Mercanti D, Santoni
A and Eusebi F: SDF-1α-mediated modulation of synaptic transmission
in rat cerebellum. Eur J Neurosci. 12:2497–2504. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gillard SE, Lu M, Mastracci RM and Miller
RJ: Expression of functional chemokine receptors by rat cerebellar
neurons. J Neuroimmunol. 124:16–28. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ragozzino D, Renzi M, Giovannelli A and
Eusebi F: Stimulation of chemokine CXC receptor 4 induces synaptic
depression of evoked parallel fibers inputs onto Purkinje neurons
in mouse cerebellum. J Neuroimmunol. 127:30–36. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kilpatrick LA, Zhu J, Lee FS and Lang H:
Role of stromal cell-derived factor-1 expression in the injured
mouse auditory nerve. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 145:1007–1015.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang PZ, He Y, Jiang XW, Chen FQ, Chen Y,
Xue T, Zhou K, Li X, Wang Y, Wu YX, et al: Up-regulation of stromal
cell-derived factor-1 enhances migration of transplanted neural
stem cells to injury region following degeneration of spiral
ganglion neurons in the adult rat inner ear. Neurosci Lett.
534:101–106. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|