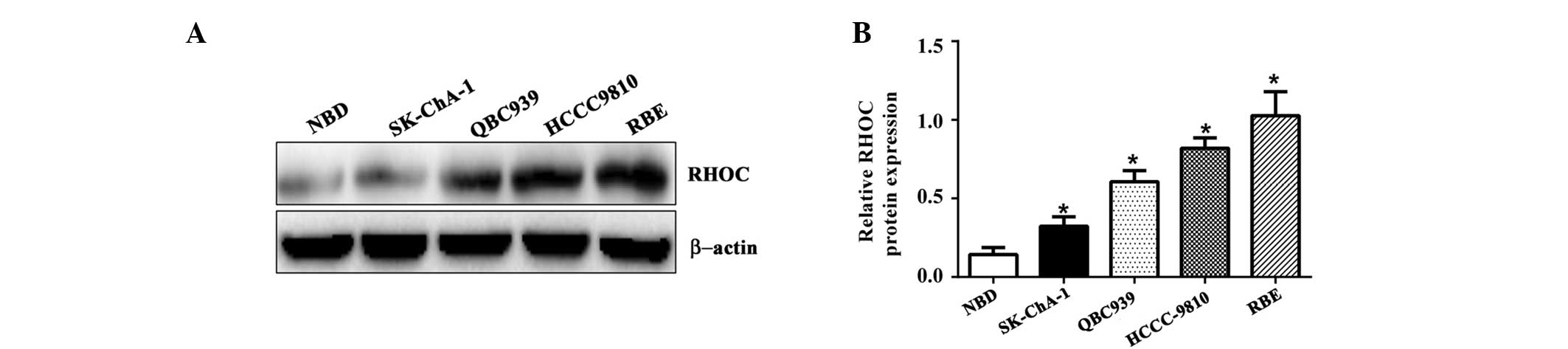
|
1
|
Razumilava N and Gores GJ:
Cholangiocarcinoma. Lancet. 383:2168–2179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vogel A, Wege H, Caca K, Nashan B and
Neumann U: The diagnosis and treatment of cholangiocarcinoma. Dtsch
Arztebl Int. 111:748–754. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ghouri YA, Mian I and Blechacz B: Cancer
review: Cholangiocarcinoma. J Carcinog. 14:12015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Groot Koerkamp B and Fong Y: Outcomes in
biliary malignancy. J Surg Oncol. 110:585–591. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Huang Y, Li X and Zhao Y: Progression of
targeted therapy in advanced cholangiocarcinoma. Chin J Cancer Res.
27:122–127. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sirica AE: Cholangiocarcinoma: Molecular
targeting strategies for chemoprevention and therapy. Hepatology.
41:5–15. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Turner SJ, Zhuang S, Zhang T, Boss GR and
Pilz RB: Effects of lovastatin on Rho isoform expression, activity
and association with guanine nucleotide dissociation inhibitors.
Biochem Pharmacol. 75:405–413. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Amin E, Dubey BN, Zhang SC, Gremer L,
Dvorsky R, Moll JM, Taha MS, Nagel-Steger L, Piekorz RP, Somlyo AV
and Ahmadian MR: Rho-kinase: Regulation, (dys) function and
inhibition. Biol Chem. 394:1399–1410. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Schaefer A, Reinhard NR and Hordijk PL:
Toward understanding RhoGTPase specificity: Structure, function and
local activation. Small GTPases. 5:62014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Donnelly SK, Bravo-Cordero JJ and Hodgson
L: Rho GTPase isoforms in cell motility: Don't fret, we have FRET.
Cell Adh Migr. 8:526–534. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
O'Connor K and Chen M: Dynamic functions
of RhoA in tumor cell migration and invasion. Small GTPases.
4:141–147. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Vega FM, Thomas M, Reymond N and Ridley
AJ: The Rho GTPase RhoB regulates cadherin expression and
epithelial cell-cell interaction. Cell Commun Signal. 13:62015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Bravo-Cordero JJ, Hodgson L and Condeelis
JS: Spatial regulation of tumor cell protrusions by RhoC. Cell Adh
Migr. 8:263–267. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Q, Tang H, Yin S and Dong C:
Downregulation of microRNA-138 enhances the proliferation,
migration and invasion of cholangiocarcinoma cells through the
upregulation of RhoC/p-ERK/MMP-2/MMP-9. Oncol Rep. 29:2046–2052.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shi Z, Chen ML, He QL and Zeng JH:
Antisense RhoC gene suppresses proliferation and invasion capacity
of human QBC939 cholangiocarcinoma cells. Hepatobiliary Pancreat
Dis Int. 6:516–520. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Edge SB and Compton CC: The American joint
committee on cancer: The 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging
manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 17:1471–1474. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu M, Wu ZF, Rosenthal DT, Rhee EM and
Merajver SD: Characterization of the roles of RHOC and RHOA GTPases
in invasion, motility and matrix adhesion in inflammatory and
aggressive breast cancers. Cancer. 116:2768–2782. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Skipworth JR, Keane MG and Pereira SP:
Update on the management of cholangiocarcinoma. Dig Dis.
32:570–578. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rosenthal DT, Zhang J, Bao L, Zhu L, Wu Z,
Toy K, Kleer CG and Merajver SD: RhoC impacts the metastatic
potential and abundance of breast cancer stem cells. PLoS One.
7:e409792012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shikada Y, Yoshino I, Okamoto T, Fukuyama
S, Kameyama T and Maehara Y: Higher expression of RhoC is related
to invasiveness in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
9:5282–5286. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bellovin DI, Simpson KJ, Danilov T,
Maynard E, Rimm DL, Oettgen P and Mercurio AM: Reciprocal
regulation of RhoA and RhoC characterizes the EMT and identifies
RhoC as a prognostic marker of colon carcinoma. Oncogene.
25:6959–6967. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Goundiam O, Nagel MD and Vayssade M: Akt
and RhoA inhibition promotes anoikis of aggregated B16F10 melanoma
cells. Cell Biol Int. 36:311–319. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Xie S, Zhu M, Lv G, Geng Y, Chen G, Ma J
and Wang G: Overexpression of Ras homologous C (RhoC) induces
malignant transformation of hepatocytes in vitro and in nude mouse
xenografts. PLoS One. 8:e544932013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Islam M, Sharma S, Kumar B and Teknos TN:
Atorvastatin inhibits RhoC function and limits head and neck cancer
metastasis. Oral Oncol. 49:778–786. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Iiizumi M, Bandyopadhyay S, Pai SK, Watabe
M, Hirota S, Hosobe S, Tsukada T, Miura K, Saito K, Furuta E, et
al: RhoC promotes metastasis via activation of the Pyk2 pathway in
prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 68:7613–7620. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Julian L and Olson MF: Rho-associated
coiled-coil containing kinases (ROCK): Structure, regulation and
functions. Small GTPases. 5:e298462014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Xue F, Takahara T, Yata Y, Xia Q, Nonome
K, Shinno E, Kanayama M, Takahara S and Sugiyama T: Blockade of
Rho/Rho-associated coiled coil-forming kinase signaling can prevent
progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in matrix
metalloproteinase-dependent manner. Hepatol Res. 38:810–817. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cockett MI, Murphy G, Birch ML, O'Connell
JP, Crabbe T, Millican AT, Hart IR and Docherty AJ: Matrix
metalloproteinases and metastatic cancer. Biochem Soc Symp.
63:295–313. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liao CG, Kong LM, Zhou P, Yang XL, Huang
JG, Zhang HL and Lu N: miR-10b is overexpressed in hepatocellular
carcinoma and promotes cell proliferation, migration and invasion
through RhoC, uPAR and MMPs. J Transl Med. 12:2342014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Faried A, Faried LS, Kimura H, Nakajima M,
Sohda M, Miyazaki T, Kato H, Usman N and Kuwano H: RhoA and RhoC
proteins promote both cell proliferation and cell invasion of human
oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell lines in vitro and in
vivo. Eur J Cancer. 42:1455–1465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ikoma T, Takahashi T, Nagano S, Li YM,
Ohno Y, Ando K, Fujiwara T, Fujiwara H and Kosai K: A definitive
role of RhoC in metastasis of orthotopic lung cancer in mice. Clin
Cancer Res. 10:1192–1200. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kothari AN, Mi Z, Zapf M and Kuo PC: Novel
clinical therapeutics targeting the epithelial to mesenchymal
transition. Clin Transl Med. 3:352014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kaufhold S and Bonavida B: Central role of
Snail1 in the regulation of EMT and resistance in cancer: A target
for therapeutic intervention. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 33:622014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Alves CC, Carneiro F, Hoefler H and Becker
KF: Role of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulator slug in
primary human cancers. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 14:3035–3050.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Sequeira L, Dubyk CW, Riesenberger TA,
Cooper CR and van Golen KL: Rho GTPases in PC-3 prostate cancer
cell morphology, invasion and tumor cell diapedesis. Clin Exp
Metastasis. 25:569–579. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gou WF, Zhao Y, Lu H, Yang XF, Xiu YL,
Zhao S, Liu JM, Zhu ZT, Sun HZ, Liu YP, et al: The role of RhoC in
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of ovarian carcinoma cells.
BMC Cancer. 14:4772014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|