|
1
|
Aravalli RN, Steer CJ and Cressman EN:
Molecular mechanisms of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
48:2047–2063. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Niu J, Lin Y, Guo Z, Niu M and Su C: The
epidemiological investigation on the risk factors of hepatocellular
carcinoma: A case-control study in Southeast China. Medicine
(Baltimore). 95:e27582016. View Article : Google Scholar
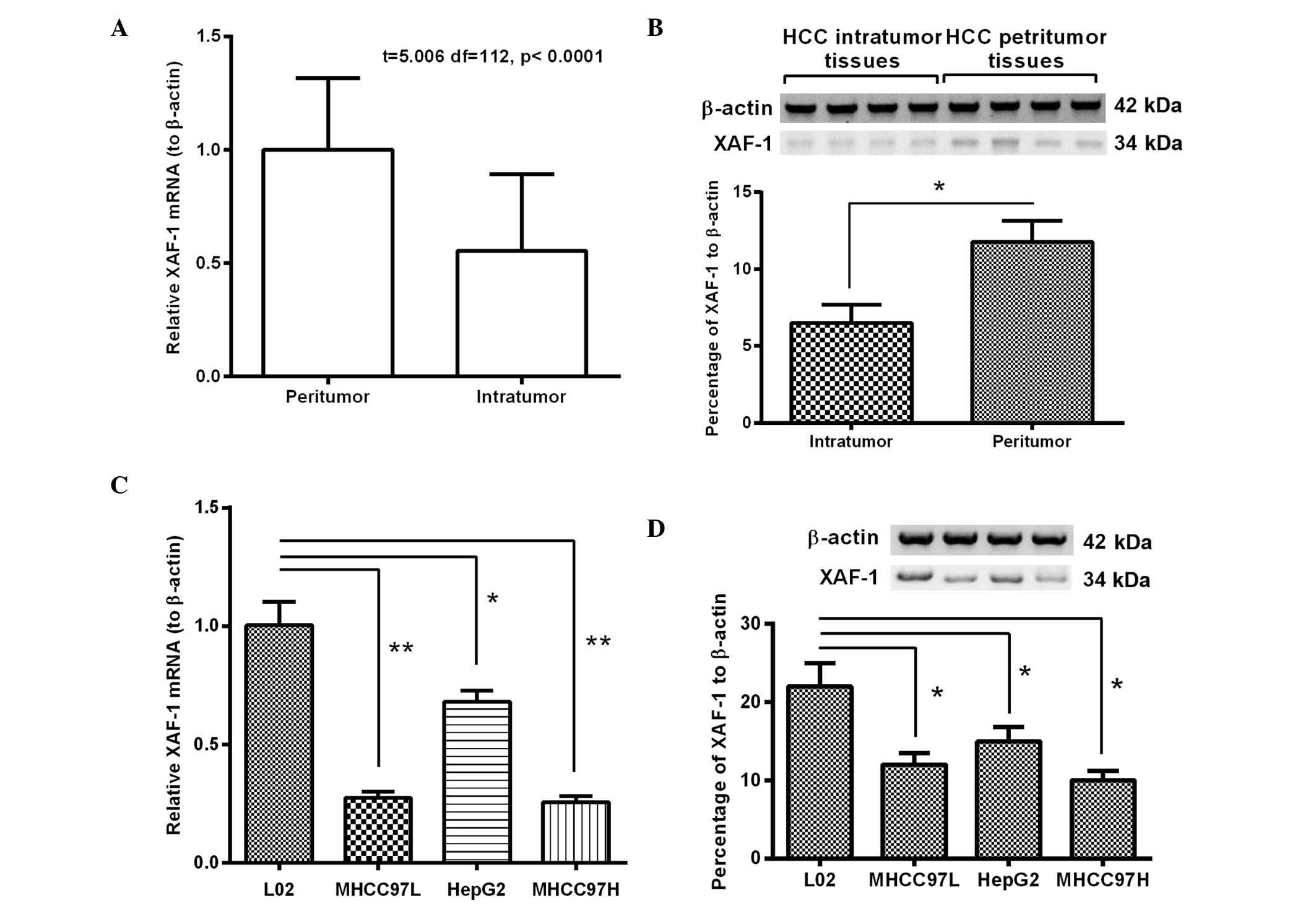
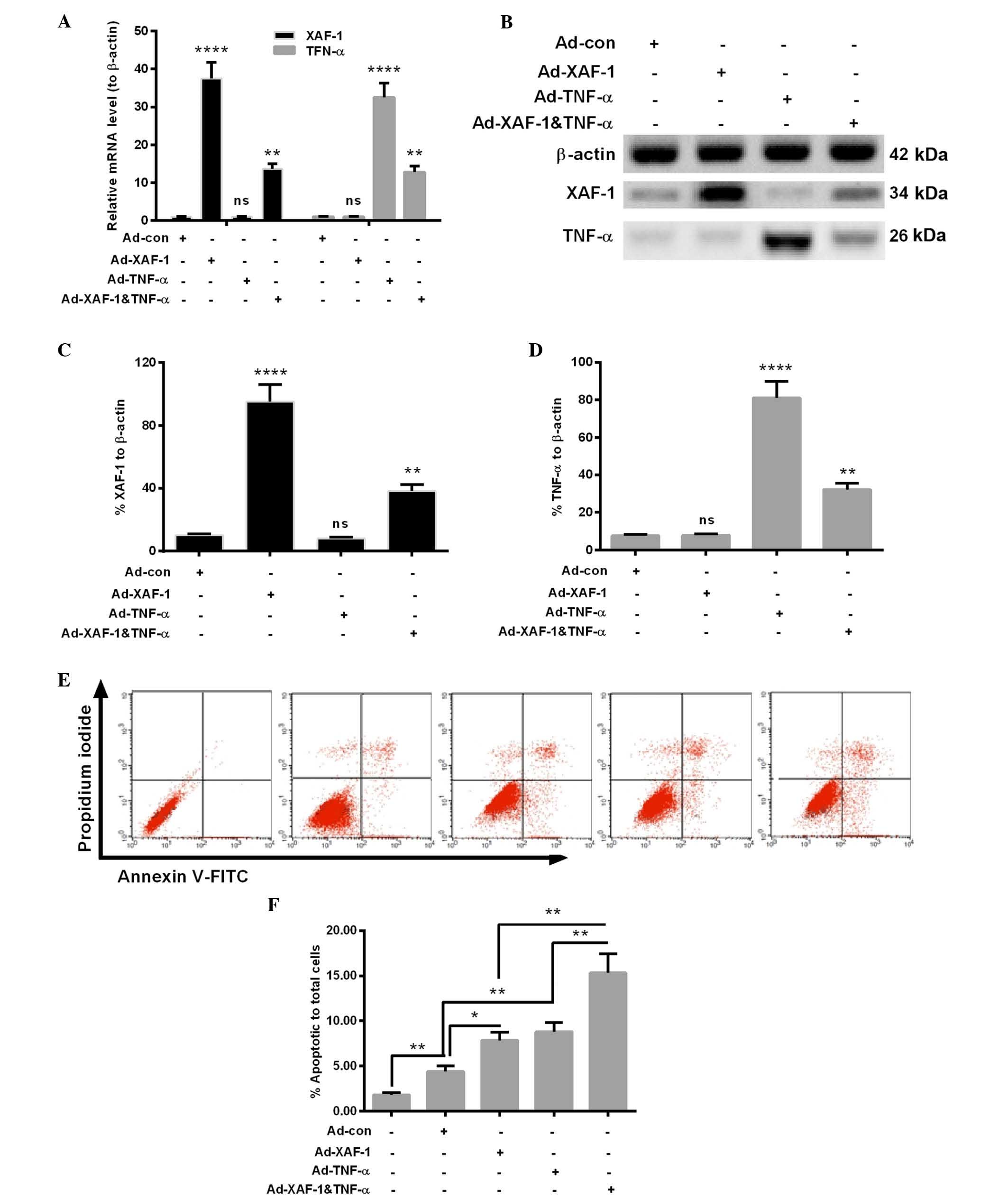
|
|
3
|
Schafer DF and Sorrell MF: Hepatocellular
carcinoma. Lancet. 353:1253–1257. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thorgeirsson SS and Grisham JW: Molecular
pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet.
31:339–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Huang J, Zhang X, Zhang M, Zhu JD, Zhang
YL, Lin Y, Wang KS, Qi XF, Zhang Q, Liu GZ, et al: Up-regulation of
DLK1 as an imprinted gene could contribute to human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Carcinogenesis. 28:1094–1103. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Huang J, Zheng DL, Qin FS, Cheng N, Chen
H, Wan BB, Wang YP, Xiao HS and Han ZG: Genetic and epigenetic
silencing of SCARA5 may contribute to human hepatocellular
carcinoma by activating FAK signaling. J Clin Invest. 120:223–241.
2010. View
Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Iizuka N, Oka M, Yamada-Okabe H, Mori N,
Tamesa T, Okada T, Takemoto N, Tangoku A, Hamada K, Nakayama H, et
al: Comparison of gene expression profiles between hepatitis B
virus- and hepatitis C virus-infected hepatocellular carcinoma by
oligonucleotide microarray data on the basis of a supervised
learning method. Cancer Res. 62:3939–3944. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Okada T, Iizuka N, Yamada-Okabe H, Mori N,
Tamesa T, Takemoto N, Tangoku A, Hamada K, Nakayama H, Miyamoto T,
et al: Gene expression profile linked to p53 status in hepatitis C
virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 555:583–590.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Oliva J, Bardag-Gorce F, French BA, Li J,
McPhaul L, Amidi F, Dedes J, Habibi A, Nguyen S and French SW:
Fat10 is an epigenetic marker for liver preneoplasia in a
drug-primed mouse model of tumorigenesis. Exp Mol Pathol.
84:102–112. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schnabl B, Valletta D, Kirovski G and
Hellerbrand C: Zinc finger protein 267 is up-regulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes tumor cell proliferation and
migration. Exp Mol Pathol. 91:695–701. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jiang J, Zhang H, Tang Q, Hao B and Shi R:
Expression of HIWI in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Biochem
Biophys. 61:53–58. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jain S, Singhal S, Lee P and Xu R:
Molecular genetics of hepatocellular neoplasia. Am J Transl Res.
2:105–118. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu LM, Shi DM, Dai Q, Cheng XJ, Yao WY,
Sun PH, Ding Y, Qiao MM, Wu YL, Jiang SH and Tu SP: Tumor
suppressor XAF1 induces apoptosis, inhibits angiogenesis and
inhibits tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
5:5403–5415. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Henry LR, Lee HO, Lee JS, Klein-Szanto A,
Watts P, Ross EA, Chen WT and Cheng JD: Clinical implications of
fibroblast activation protein in patients with colon cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 13:1736–1741. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Salvesen GS and Duckett CS: IAP proteins:
Blocking the road to death's door. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
3:401–410. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang YL and Li XM: The IAP family:
Endogenous caspase inhibitors with multiple biological activities.
Cell Res. 10:169–177. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ngan CY, Yamamoto H, Seshimo I, Tsujino T,
Man-i M, Ikeda JI, Konishi K, Takemasa I, Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, et
al: Quantitative evaluation of vimentin expression in tumour stroma
of colorectal cancer. Br J Cancer. 96:986–992. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhu L, Cheng X, Ding Y, Shi J, Jin H, Wang
H, Wu Y, Ye J, Lu Y, Wang TC, et al: Bone marrow-derived
myofibroblasts promote colon tumorigenesis through the
IL-6/JAK2/STAT3 pathway. Cancer Lett. 343:80–89. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Wu WY, Kim H, Zhang CL, Meng XL and Wu ZS:
Clinical significance of autophagic protein LC3 levels and its
correlation with XIAP expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Med
Oncol. 31:1082014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Pan Q, Liu B, Liu J, Cai R, Liu X and Qian
C: Synergistic antitumor activity of XIAP-shRNA and TRAIL expressed
by oncolytic adenoviruses in experimental HCC. Acta Oncol.
47:135–144. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Plenchette S, Cheung HH, Fong WG, LaCasse
EC and Korneluk RG: The role of XAF1 in cancer. Curr Opin Investig
Drugs. 8:469–476. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Leaman DW, Chawla-Sarkar M, Vyas K,
Reheman M, Tamai K, Toji S and Borden EC: Identification of
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis-associated factor-1 as an
interferon-stimulated gene that augments TRAIL Apo2L-induced
apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 277:28504–28511. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Szymczak AL, Workman CJ, Wang Y, Vignali
KM, Dilioglou S, Vanin EF and Vignali DA: Correction of multi-gene
deficiency in vivo using a single 'self-cleaving' 2A peptide-based
retroviral vector. Nat Biotechnol. 22:589–594. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schmittgen TD and Livak KJ: Analyzing
real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat Protoc.
3:1101–1108. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang J, Gu Q, Li M, Zhang W, Yang M, Zou
B, Chan S, Qiao L, Jiang B, Tu S, et al: Identification of XAF1 as
a novel cell cycle regulator through modulating G(2)/M checkpoint
and interaction with checkpoint kinase 1 in gastrointestinal
cancer. Carcinogenesis. 30:1507–1516. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kempkensteffen C, Fritzsche FR, Johannsen
M, Weikert S, Hinz S, Dietel M, Riener MO, Moch H, Jung K, Krause
H, et al: Down-regulation of the pro-apoptotic XIAP associated
factor-1 (XAF1) during progression of clear-cell renal cancer. BMC
Cancer. 9:2762009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Huang J, Yao WY, Zhu Q, Tu SP, Yuan F,
Wang HF, Zhang YP and Yuan YZ: XAF1 as a prognostic biomarker and
therapeutic target in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci. 101:559–567.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Chen XY, He QY and Guo MZ: XAF1 is
frequently methylated in human esophageal cancer. World J
Gastroenterol. 18:2844–2849. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yang WT, Chen DL, Zhang FQ, Xia YC, Zhu
RY, Zhou DS and Chen YB: Experimental study on inhibition effects
of the XAF1 gene against lung cancer cell proliferation. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 15:7825–7829. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tu SP, Sun YW, Cui JT, Zou B, Lin MC, Gu
Q, Jiang SH, Kung HF, Korneluk RG and Wong BC: Tumor suppressor
XIAP-Associated factor 1 (XAF1) cooperates with tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand to suppress colon cancer
growth and trigger tumor regression. Cancer. 116:1252–1263. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tu SP, Liston P, Cui JT, Lin MC, Jiang XH,
Yang Y, Gu Q, Jiang SH, Lum CT, Kung HF, et al: Restoration of XAF1
expression induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor growth in gastric
cancer. Int J Cancer. 125:688–697. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sun PH, Zhu LM, Qiao MM, Zhang YP, Jiang
SH, Wu YL and Tu SP: The XAF1 tumor suppressor induces autophagic
cell death via upregulation of Beclin-1 and inhibition of Akt
pathway. Cancer Lett. 310:170–180. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Qi R, Gu J, Zhang Z, Yang K, Li B, Fan J,
Wang C, He Z, Qiao L, Lin Z and Liu XY: Potent antitumor efficacy
of XAF1 delivered by conditionally replicative adenovirus vector
via caspase-independent apoptosis. Cancer Gene Ther. 14:82–90.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
De Giorgi M, Cinti A, Pelikant-Małecka I,
Chisci E, Lavitrano M, Giovannoni R and Smolenski RT: Co-expression
of functional human heme oxygenase 1, ecto-5′-nucleotidase and
ecto-nucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase-1 by
'self-cleaving' 2A peptide system. Plasmid. 79:22–29. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chng J, Wang T, Nian R, Lau A, Hoi KM, Ho
SC, Gagnon P, Bi X and Yang Y: Cleavage efficient 2A peptides for
high level monoclonal antibody expression in CHO cells. MAbs.
7:403–412. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|