|
1
|
Smith WL, DeWitt DL and Garavito RM:
Cyclooxygenases: Structural, cellular, and molecular biology. Annu
Rev Biochem. 69:145–182. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsatsanis C, Androulidaki A, Venihaki M
and Margioris AN: Signalling networks regulating cyclooxygenase-2.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 38:1654–1661. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Griswold DE and Adams JL: Constitutive
cyclooxygenase (COX-1) and inducible cyclooxygenase (COX-2):
Rationale for selective inhibition and progress to date. Med Res
Rev. 16:181–206. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tanigawa T, Odkhuu E, Morikawa A, Hayashi
K, Sato T, Shibata R, Goto F, Ueda H and Yokochi T: Immunological
role of prostaglandin E2 production in mouse auditory cells in
response to LPS. Innate Immun. 20:639–646. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Gschwendt M, Müller HJ, Kielbassa K, Zang
R, Kittstein W, Rincke G and Marks F: Rottlerin, a novel protein
kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 199:93–98. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cross T, Griffiths G, Deacon E, Sallis R,
Gough M, Watters D and Lord JM: PKC-delta is an apoptotic lamin
kinase. Oncogene. 9:2331–2337. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kontny E, Kurowska M, Szczepańska K and
Maśliński W: Rottlerin, a PKC isozyme-selective inhibitor, affects
signaling events and cytokine production in human monocytes. J
Leukoc Biol. 67:249–258. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hsieh HL, Wang HH, Wu CY, Jou MJ, Yen MH,
Parker P and Yang CM: BK-induced COX-2 expression via
PKC-delta-dependent activation of p42/p44 MAPK and NF-kappaB in
astrocytes. Cell Signal. 19:330–340. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Soltoff SP: Rottlerin: An inappropriate
and ineffective inhibitor of PKCdelta. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
8:453–458. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Song KS, Kim JS, Yun EJ, Kim YR, Seo KS,
Park JH, Jung YJ, Park JI, Kweon GR, Yoon WH, et al: Rottlerin
induces autophagy and apoptotic cell death through a
PKC-delta-independent pathway in HT1080 human fibrosarcoma cells:
The protective role of autophagy in apoptosis. Autophagy.
4:650–658. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lim JH, Park JW, Choi KS, Park YB and Kwon
TK: Rottlerin induces apoptosis via death receptor 5 (DR5)
upregulation through CHOP-dependent and PKC delta-independent
mechanism in human malignant tumor cells. Carcinogenesis.
30:729–736. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Park EJ, Lim JH, Nam SI, Park JW and Kwon
TK: Rottlerin induces heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1) up-regulation through
reactive oxygen species (ROS) dependent and PKC delta-independent
pathway in human colon cancer HT29 cells. Biochimie. 92:110–115.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
LeBel CP, Ischiropoulos H and Bondy SC:
Evaluation of the probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin as an indicator of
reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress. Chem Res
Toxicol. 5:227–231. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lu Y and Wahl LM: Oxidative stress
augments the production of matrix metalloproteinase-1,
cyclooxygenase-2, and prostaglandin E2 through enhancement of
NF-kappa B activity in lipopolysaccharide-activated human primary
monocytes. J Immunol. 175:5423–5429. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chen JJ, Huang WC and Chen CC:
Transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 in response to
proteasome inhibitors involves reactive oxygen species-mediated
signaling pathway and recruitment of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein
delta and CREB-binding protein. Mol Biol Cell. 16:5579–5591. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hung JH, Su IJ, Lei HY, Wang HC, Lin WC,
Chang WT, Huang W, Chang WC, Chang YS, Chen CC and Lai MD:
Endoplasmic reticulum stress stimulates the expression of
cyclooxygenase-2 through activation of NF-kappaB and pp38
mitogen-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 279:46384–46392.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Huang ZF, Massey JB and Via DP:
Differential regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) mRNA stability
by interleukin-1 beta (IL-1 beta) and tumor necrosis factor-alpha
(TNF-alpha) in human in vitro differentiated macrophages. Biochem
Pharmacol. 59:187–194. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Nakao S, Ogtata Y, Shimizu E, Yamazaki M,
Furuyama S and Sugiya H: Tumor necrosis factor alpha
(TNF-alpha)-induced prostaglandin E2 release is mediated by the
activation of cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX-2) transcription via NFkappaB
in human gingival fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biochem. 238:11–18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
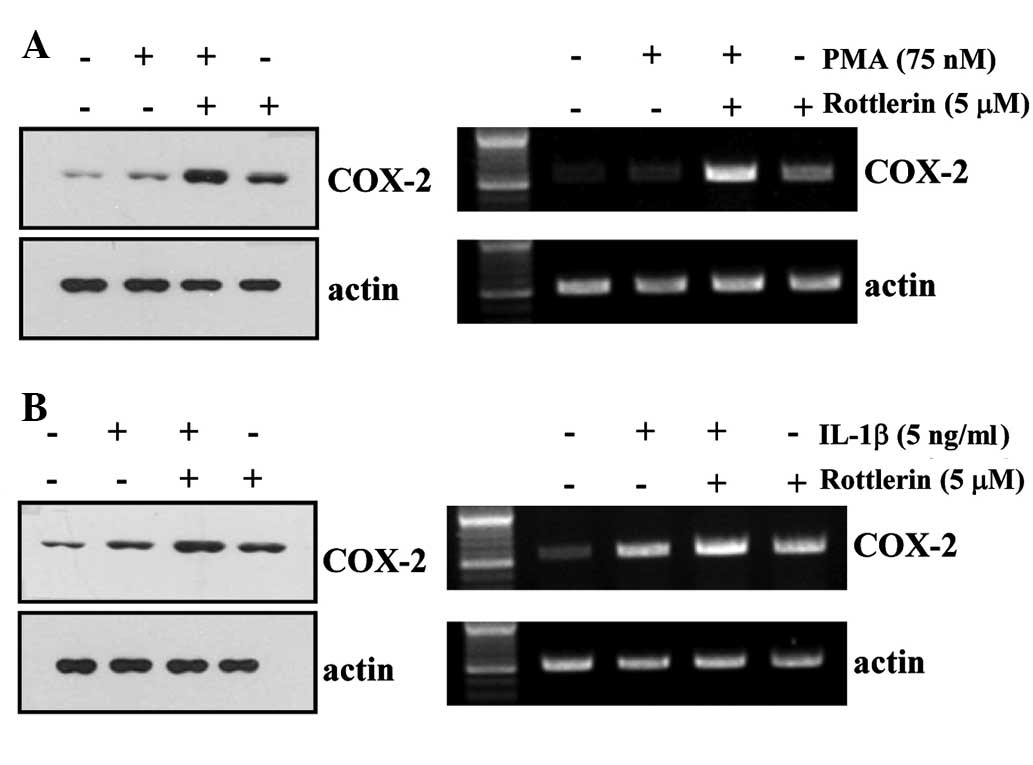
Molina-Holgado E, Ortiz S, Molina-Holgado
F and Guaza C: Induction of COX-2 and PGE(2) biosynthesis by
IL-1beta is mediated by PKC and mitogen-activated protein kinases
in murine astrocytes. Br J Pharmacol. 131:152–159. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miralpeix M, Camacho M, López-Belmonte J,
Canalías F, Beleta J, Palacios JM and Vila L: Selective induction
of cyclo-oxygenase-2 activity in the permanent human endothelial
cell line HUV-EC-C: Biochemical and pharmacological
characterization. Br J Pharmacol. 121:171–180. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shishodia S, Koul D and Aggarwal BB:
Cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 inhibitor celecoxib abrogates TNF-induced
NF-kappa B activation through inhibition of activation of I kappa B
alpha kinase and Akt in human non-small cell lung carcinoma:
Correlation with suppression of COX-2 synthesis. J Immunol.
73:2011–2022. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Mitchell JA, Belvisi MG, Akarasereenont P,
Robbins RA, Kwon OJ, Croxtall J, Barnes PJ and Vane JR: Induction
of cyclo-oxygenase-2 by cytokines in human pulmonary epithelial
cells: Regulation by dexamethasone. Br J Pharmacol. 113:1008–1014.
1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang YJ, Lu B, Choy PC and Hatch GM:
Regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A2, cyclooxygenase-1 and -2
expression by PMA, TNFalpha, LPS and M-CSF in human monocytes and
macrophages. Mol Cell Biochem. 246:31–38. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang YJ, Mbonye UR, DeLong CJ, Wada M and
Smith WL: Regulation of intracellular cyclooxygenase levels by gene
transcription and protein degradation. Prog Lipid Res. 46:108–125.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tamura M, Sebastian S, Yang S, Gurates B,
Fang Z, Okamura K and Bulun SE: Induction of cyclooxygenase-2 in
human endometrial stromal cells by malignant endometrial epithelial
cells: Evidence for the involvement of extracellularly regulated
kinases and CCAAT/enhancer binding proteins. J Mol Endocrinol.
31:95–104. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wardlaw SA, Zhang N and Belinsky SA:
Transcriptional regulation of basal cyclooxygenase-2 expression in
murine lung tumor-derived cell lines by CCAAT/enhancer-binding
protein and activating transcription factor/cAMP response
element-binding protein. Mol Pharmacol. 62:326–333. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lasa M, Mahtani KR, Finch A, Brewer G,
Saklatvala J and Clark AR: Regulation of cyclooxygenase 2 mRNA
stability by the mitogen-activated protein kinase p38 signaling
cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 20:4265–4274. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Lim JH, Park JW, Kim SH, Choi YH, Choi KS
and Kwon TK: Rottlerin induces pro-apoptotic endoplasmic reticulum
stress through the protein kinase C-delta-independent pathway in
human colon cancer cells. Apoptosis. 13:1378–1385. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
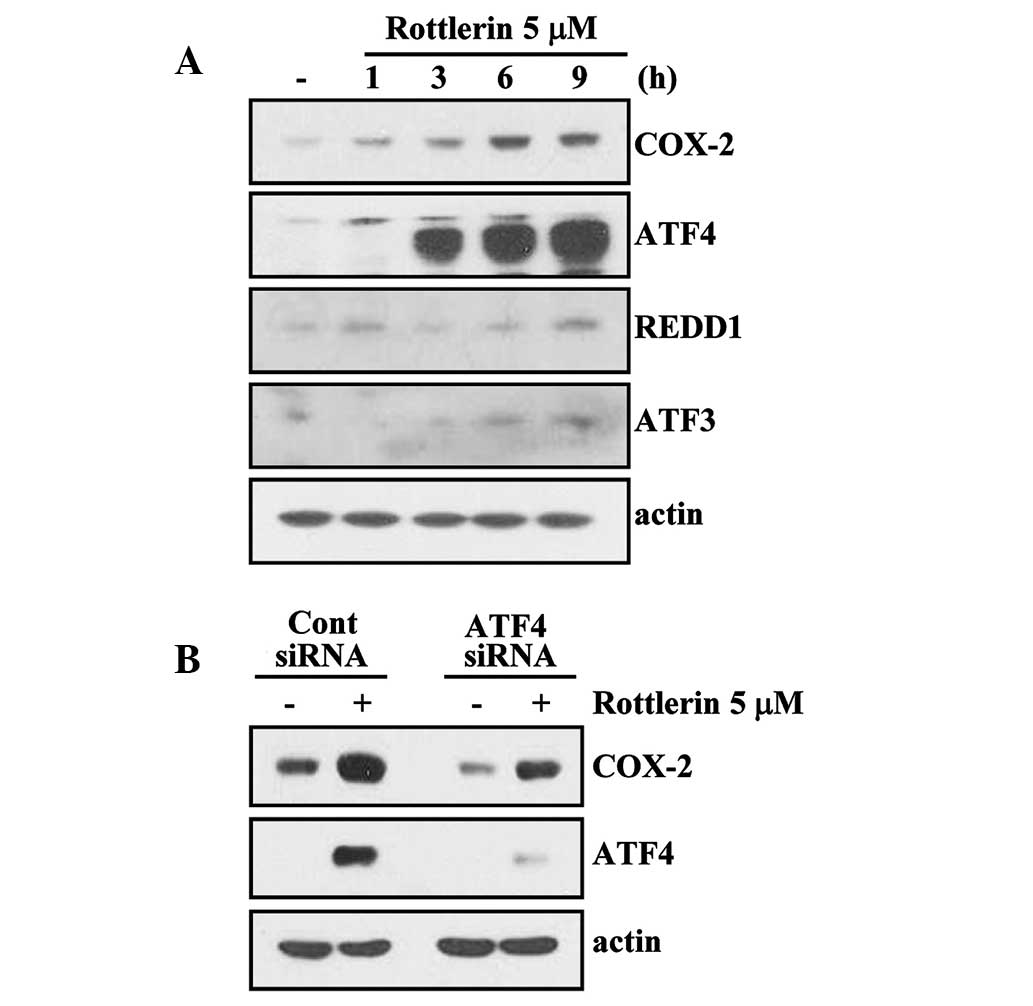
Rasheed Z and Haqqi TM: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress induces the expression of COX-2 through activation
of eIF2α, p38-MAPK and NF-κB in advanced glycation end products
stimulated human chondrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1823:2179–2189. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
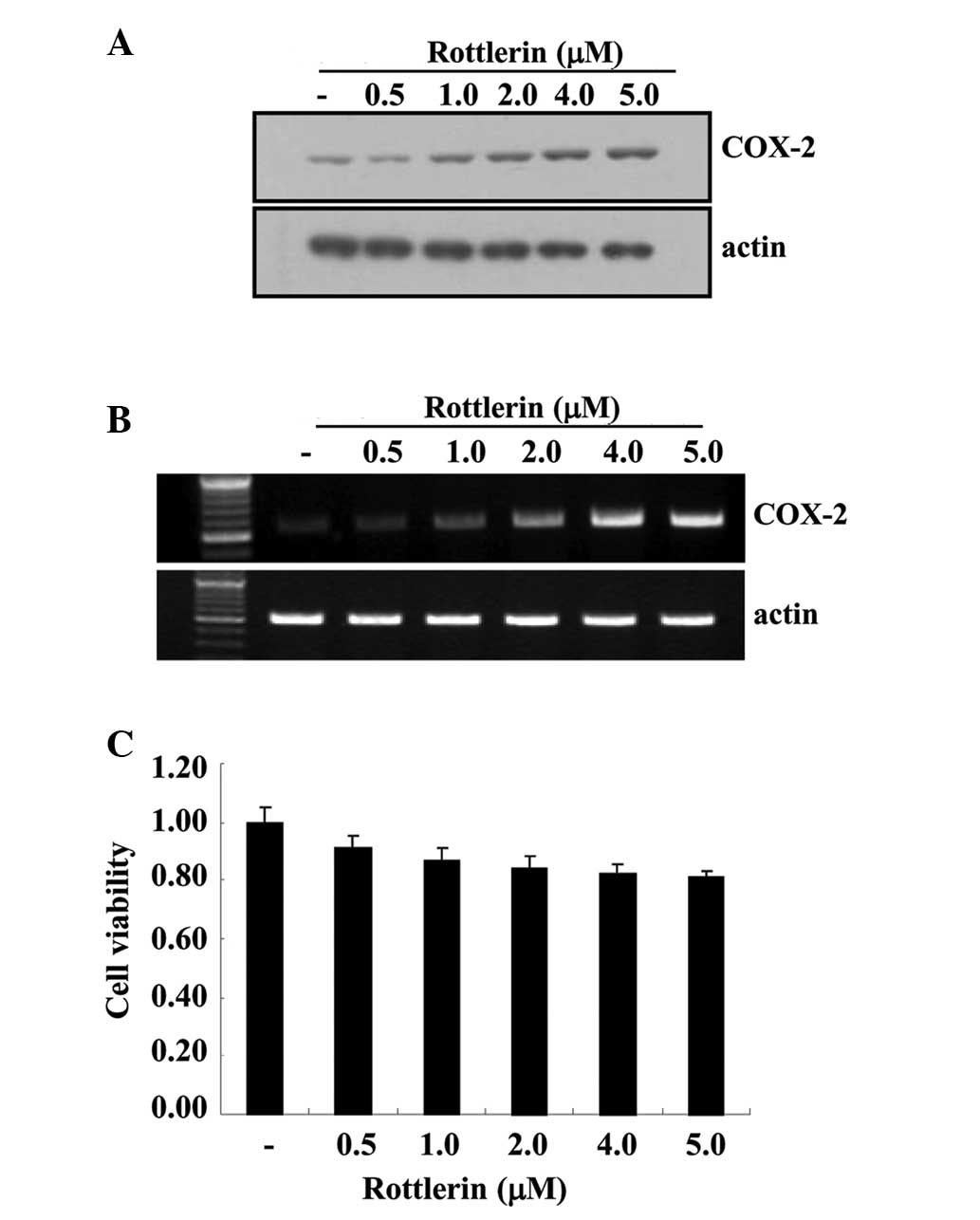
Park EJ and Kwon TK: Rottlerin enhances
IL-1β-induced COX-2 expression through sustained p38 MAPK
activation in MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells. Exp Mol Med.
43:669–675. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
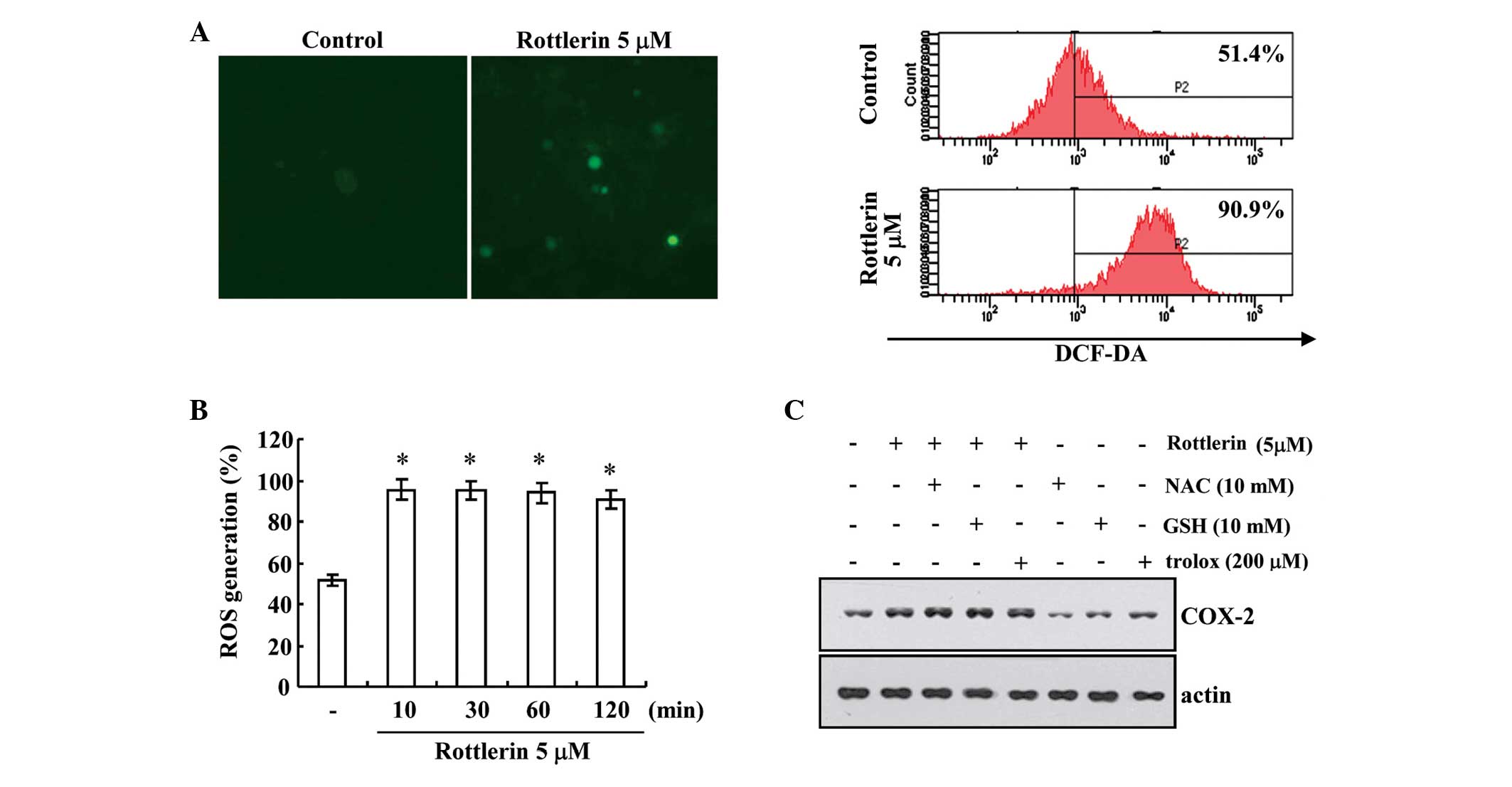
Feng L, Xia Y, Garcia GE, Hwang D and
Wilson CB: Involvement of reactive oxygen intermediates in
cyclooxygenase-2 expression induced by interleukin-1, tumor
necrosis factor-alpha, and lipopolysaccharide. J Clin Invest.
95:1669–1675. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|