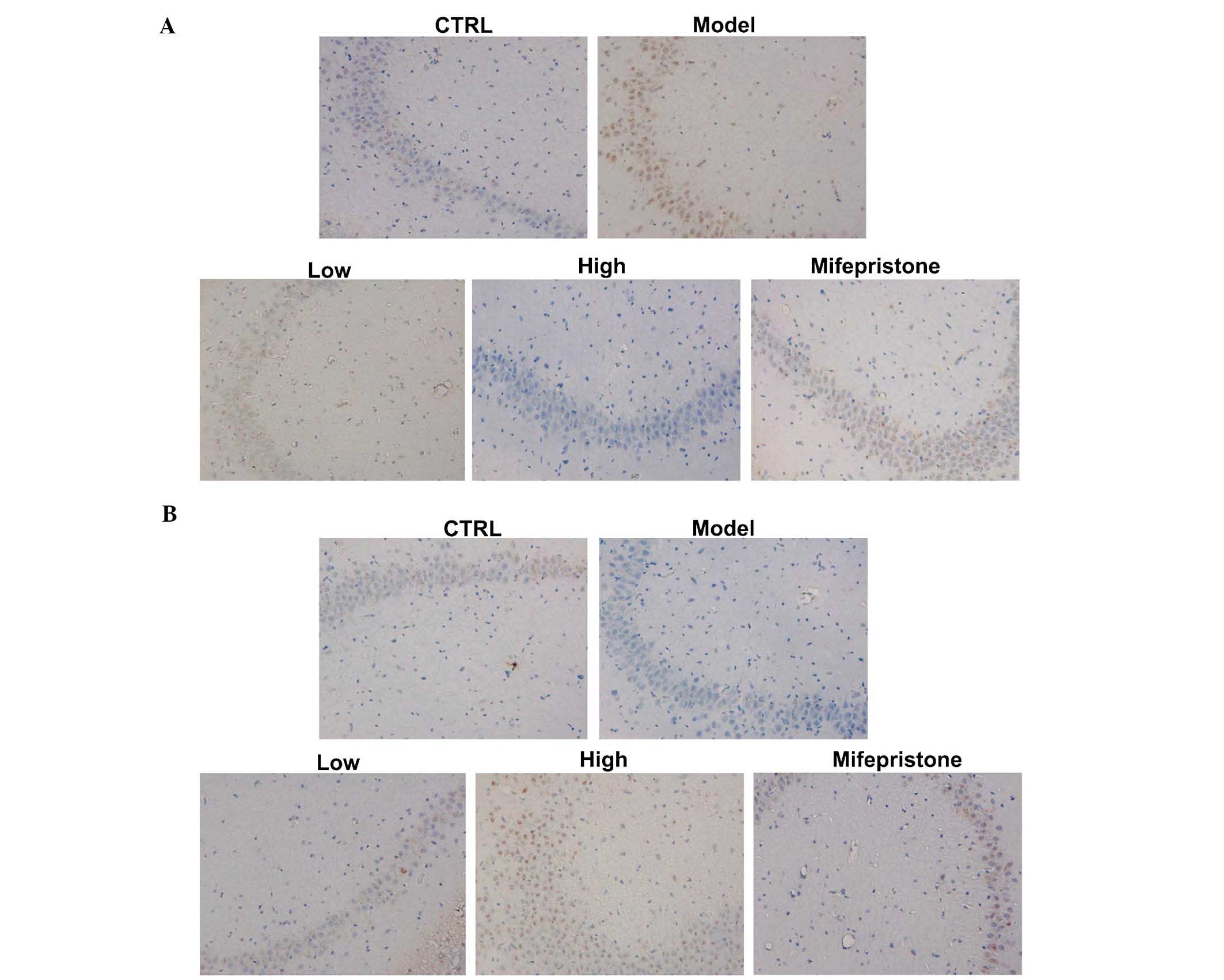
|
1
|
Demyttenaere K, Bruffaerts R, Posada-Villa
J, Gasquet I, Kovess V, Lepine JP, Angermeyer MC, Bernert S, de
Girolamo G, Morosini P, et al: Prevalence, severity, and unmet need
for treatment of mental disorders in the World Health Organization
World Mental Health Surveys. JAMA. 291:2581–2590. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hettema JM, Neale MC and Kendler KS: A
review and meta-analysis of the genetic epidemiology of anxiety
disorders. Am J Psychiatry. 158:1568–1578. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sachser N and Lesch KP: The interplay of
genotype and environment in the development of fear and anxiety.
e-Neuroforum. 4:57–62. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bandelow B, Sher L, Bunevicius R,
Hollander E, Kasper S, Zohar J and Möller HJ; WFSBP Task Force on
Mental Disorders in Primary Care; WFSBP Task Force on Anxiety
Disorders, OCD and PTSD: Guidelines for the pharmacological
treatment of anxiety disorders, obsessive-compulsive disorder and
post-traumatic stress disorder in primary care. Int J Psychiatry
Clin Pract. 16:77–84. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Farach FJ, Pruitt LD, Jun JJ, Jerud AB,
Zoellner LA and Roy-Byrne PP: Pharmacological treatment of anxiety
disorders: Current treatments and future directions. J Anxiety
Disorders. 26:833–843. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Bystritsky A, Hovav S, Sherbourne C, Stein
MB, Rose RD, Campbell-Sills L, Golinelli D, Sullivan G, Craske MG
and Roy-Byrne PP: Use of complementary and alternative medicine in
a large sample of anxiety patients. Psychosomatics. 53:266–272.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sarris J, McIntyre E and Camfield DA:
Plant-based medicines for anxiety disorders, part 2: A review of
clinical studies with supporting preclinical evidence. CNS Drugs.
27:301–319. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen WF, Xu L, Yu CH, Ho CK, Wu K, Leung
GC and Wong MS: The in vivo therapeutic effect of free wanderer
powder (xiāo yáo sǎn, Xiaoyaosan) on mice with 4T1 cell induced
breast cancer model. J Tradit Complement Med. 2:67–75.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Qin F, Wu XA, Tang Y, Huang Q, Zhang ZJ
and Yuan JH: Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials to
assess the effectiveness and safety of free and easy wanderer plus,
a poly-herbal preparation for depressive disorders. J Psychiatr
Res. 45:1518–1524. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fratkin JP and Dharmananda S: Chinese
herbal patent medicines: The clinical desk reference. Shya
Publications; Boulder, CO: 2001
|
|
11
|
Chien SC, Chang WC, Lin PH, Chang WP, Hsu
SC, Chang JC, Wu YC, Pei JK and Lin CH: A Chinese herbal medicine,
Jia-Wei-Xiao-Yao-San, prevents dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic
fibrosis in rats. Scientific World Journal. 2014:2175252014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Y, Han M, Liu Z, Wang J, He Q and
Liu J: Chinese herbal formula Xiao yao san for treatment of
depression: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials.
Evid Based Complement and Alternat Med. 2012:9316362012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Mizowaki M, Toriizuka K and Hanawa T:
Anxiolytic effect of Kami-Shoyo-San (TJ-24) in mice: Possible
mediation of neurosteroid synthesis. Life Sci. 69:2167–2177. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Campos AC, Fogaca MV, Aguiar DC and
Guimarães FS: Animal models of anxiety disorders and stress. Rev
Bras Psiquiatr. 35(Suppl 2): S101–S111. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Walf AA and Frye CA: The use of the
elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in
rodents. Nat Protoc. 2:322–328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Volk H, Potschka H and Löscher W:
Immunohistochemical localization of P-glycoprotein in rat brain and
detection of its increased expression by seizures are sensitive to
fixation and staining variables. J Histochem Cytochem. 53:517–531.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen HY, Lin YH, Wu JC, Chen YC, Yang SH,
Chen JL and Chen TJ: Prescription patterns of Chinese herbal
products for menopausal syndrome: Analysis of a nationwide
prescription database. J Ethnopharmacol. 137:1261–1266. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yeung WF, Chung KF, Poon MM, Ho FY, Zhang
SP, Zhang ZJ, Ziea ET and Wong Taam V: Prescription of chinese
herbal medicine and selection of acupoints in pattern-based
traditional chinese medicine treatment for insomnia: A systematic
review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:9025782012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yeung WF, Chung KF, Ng KY, Yu YM, Ziea ET
and Ng BF: A systematic review on the efficacy, safety and types of
Chinese herbal medicine for depression. J Psychiatr Res.
57:165–175. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
McEwen BS: Central effects of stress
hormones in health and disease: Understanding the protective and
damaging effects of stress and stress mediators. Eur J Pharmacol.
583:174–185. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Saavedra JM, Sánchez-Lemus E and Benicky
J: Blockade of brain angiotensin II A T1 receptors ameliorates
stress, anxiety, brain inflammation and ischemia: Therapeutic
implications. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 36:1–18. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Djamshidian A and Lees AJ: Can stress
trigger Parkinson's disease? J Neurosurg Psychiatry. 85:878–881.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Heim C and Nemeroff CB: The impact of
early adverse experiences on brain systems involved in the
pathophysiology of anxiety and affective disorders. Biol
Psychiatry. 46:1509–1522. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Adriaan Bouwknecht J, Olivier B and Paylor
RE: The stress-induced hyperthermia paradigm as a physiological
animal model for anxiety: A review of pharmacological and genetic
studies in the mouse. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 31:41–59. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Haller J and Alicki M: Current animal
models of anxiety, anxiety disorders, and anxiolytic drugs. Curr
Opin Psychiatry. 25:59–64. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jaggi AS, Bhatia N, Kumar N, Singh N,
Anand P and Dhawan R: A review on animal models for screening
potential anti-stress agents. Neurol Sci. 32:993–1005. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
DeBattista C and Belanoff J: The use of
mifepristone in the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 17:117–121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Leentjens AF, Dujardin K, Marsh L,
Martinez-Martin P, Richard IH and Starkstein SE: Anxiety and motor
fluctuations in Parkinson's disease: A cross-sectional
observational study. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 18:1084–1088. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gallagher D, Coen R, Kilroy D, Belinski K,
Bruce I, Coakley D, Walsh B, Cunningham C and Lawlor BA: Anxiety
and behavioural disturbance as markers of prodromal Alzheimer's
disease in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Int J Geriatr
Psychiatry. 26:166–172. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Radley JJ and Morrison JH: Repeated stress
and structural plasticity in the brain. Ageing Res Rev. 4:271–287.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Goedert M: Alpha-synuclein and
neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2:492–501. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Morris EP, Stewart SH and Ham LS: The
relationship between social anxiety disorder and alcohol use
disorders: A critical review. Clin Psychol Rev. 25:734–760. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ramos A, Moisan MP, Chaouloff F, Mormede C
and Mormède P: Identification of female-specific QTLs affecting an
emotionality-related behavior in rats. Mol Psychiatry. 4:453–462.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chiavegatto S, Izidio GS, Mendes-Lana A,
Aneas I, Freitas TA, Torrão AS, Conceição IM, Britto LR and Ramos
A: Expression of alpha-synuclein is increased in the hippocampus of
rats with high levels of innate anxiety. Mol Psychiatry.
14:894–905. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Liu Y, Shepherd EG and Nelin LD: MAPK
phosphatases-regulating the immune response. Nat Rev Immunol.
7:202–212. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Toska K, Kleppe R, Armstrong CG, Morrice
NA, Cohen P and Haavik J: Regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase by
stress-activated protein kinases. J Neurochem. 83:775–783. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wu J, Lou H, Alerte TN, Stachowski EK,
Chen J, Singleton AB, Hamilton RL and Perez RG: Lewy-like
aggregation of α-synuclein reduces protein phosphatase 2A activity
in vitro and invivo. Neuroscience. 207:288–297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wittmann W, Schunk E, Rosskothen I,
Gaburro S, Singewald N, Herzog H and Schwarzer C:
Prodynorphin-derived peptides are critical modulators of anxiety
and regulate neurochemistry and corticosterone.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 34:775–785. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Shepard JD, Barron KW and Myers DA:
Corticosterone delivery to the amygdala increases
corticotropin-releasing factor mRNA in the central amygdaloid
nucleus and anxiety-like behavior. Brain Res. 861:288–295. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Vallée M, Mayo W, Dellu F, Le Moal M,
Simon H and Maccari S: Prenatal stress induces high anxiety and
postnatal handling induces low anxiety in adult offspring:
Correlation with stress-induced corticosterone secretion. J
Neurosci. 17:2626–2636. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mitra R and Sapolsky RM: Acute
corticosterone treatment is sufficient to induce anxiety and
amygdaloid dendritic hypertrophy. Proc Nat Acad Sci. 105:5573–5578.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|