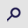
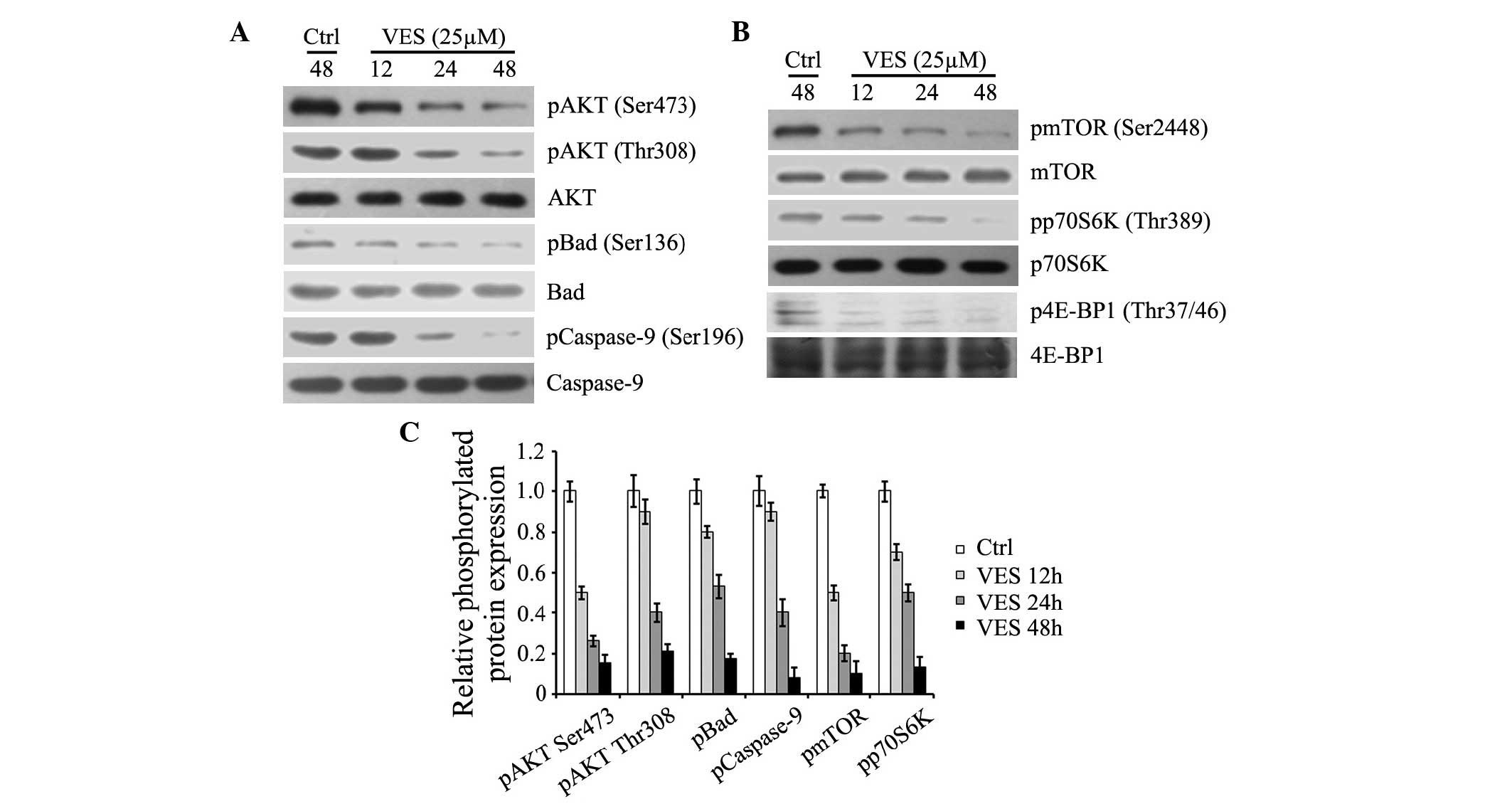
|
1
|
Montgomery EA, Bosman FT, Brennan P and
Malekzadeh R: Oesophageal cancer. World Cancer Report 2014. Stewart
BW and Wild CP: International Agency for Research on Cancer; Lyon:
pp. 528–543. 2014
|
|
2
|
Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S,
Shibuya K, Aboyans V, Abraham J, Adair T, Aggarwal R, Ahn SY, et
al: Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20
age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global
Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 380:2095–2128. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kelsen D, Daly JM, Kern SE, Levin B,
Tepper JE and Van Cutsem E: Gastrointestinal Oncology: Principles
and Practices. 2nd edition. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;
Philadelphia, PA: pp. 42007
|
|
4
|
Schottenfeld D: Cancer Epidemiology and
Prevention. 3rd edition. Oxford University Press; Oxford: pp.
6972006
|
|
5
|
Ferri FF: Esophageal Tumors. Ferri's
Clinical Advisor. 2013, Mosby (Elsevier); Maryland Heights, MO: pp.
389–391. 2012
|
|
6
|
National Cancer Institute: Cancer
Statistics: SEER stat fact sheets, esophageal cancer. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/esoph.html.
Accessed April 15, 2016.
|
|
7
|
Neuzil J, Tomasetti M, Mellick AS, Alleva
R, Salvatore BA, Birringer M and Fariss MW: Vitamin E analogues: A
new class of inducers of apoptosis with selective anti-cancer
effect. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 4:355–372. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Neuzil J, Wang XF, Dong LF, Low P and
Ralph SJ: Molecular mechanism of 'mitocan'-induced apoptosis in
cancer cells epitomizes the multiple roles of reactive oxygen
species and Bcl-2 family proteins. FEBS Lett. 580:5125–5129. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang XF, Dong L, Zhao Y, Tomasetti M, Wu K
and Neuzil J: Vitamin E analogues as anticancer agents: Lessons
from studies with alpha-tocopheryl succinate. Mol Nutr Food Res.
50:675–685. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Malafa MP and Neitzel LT: Vitamin E
succinate promotes breast cancer tumor dormancy. J Surg Res.
93:163–170. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Malafa MP, Fokum FD, Andoh J, Neitzel LT,
Bandyopadhyay S, Zhan R, Iiizumi M, Furuta E, Horvath E and Watabe
K: Vitamin E succinate suppresses prostate tumor growth by inducing
apoptosis. Int J Cancer. 118:2441–2447. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Neuzil J: Vitamin E succinate and cancer
treatment: A vitamin E prototype for selective antitumour activity.
Br J Cancer. 89:1822–1826. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Quin J, Engle D, Litwiller A, Peralta E,
Grasch A, Boley T and Hazelrigg S: Vitamin E succinate decreases
lung cancer tumor growth in mice. J Surg Res. 127:139–143. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Annovazzi L, Mellai M, Caldera V, Valente
G, Tessitore L and Schiffer D: mTOR, S6 and AKT expression
inrelation to proliferation and apoptosis/autophagy in glioma.
Anticancer Res. 29:3087–3094. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Falasca M: PI3K/Akt signaling pathway
specific inhibitors: A novel strategy to sensitize cancer cells to
anti-cancer drugs. Curr Pharm Des. 16:1410–1416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
McCubrey JA, Steelman LS, Chappell WH,
Abrams SL, Wong EW, Chang F, Lehmann B, Terrian DM, Milella M,
Tafuri A, et al: Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth,
malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1773:1263–1284. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chang F, Lee JT, Navolanic PM, Steelman
LS, Shelton JG, Blalock WL, Franklin RA and McCubrey JA:
Involvement of PI3K/Akt pathway in cell cycle progression,
apoptosis, and neoplastic transformation: A target for cancer
chemotherapy. Leukemia. 17:590–603. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H,
Gotoh Y and Greenberg ME: Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples
survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell.
91:231–241. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cardone MH, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Salvesen
GS, Franke TF, Stanbridge E, Frisch S and Reed JC: Regulation of
cell death protease caspase-9 by phosphorylation. Science.
282:1318–1321. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mabuchi S, Ohmichi M, Kimura A, Hisamoto
K, Hayakawa J, Nishio Y, Adachi K, Takahashi K, Arimoto-Ishida E,
Nakatsuji Y, et al: Inhibition of phosphorylation of BAD and Raf-1
by Akt sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to paclitaxel. J Biol
Chem. 277:33490–33500. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gibbons JJ, Abraham RT and Yu K: Mammalian
target of rapamycin: Discovery of rapamycin reveals a signaling
pathway important for normal and cancer cell growth. Semin Oncol.
36(Suppl 3): S3–S17. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kline K, Yu W and Sanders BG: Vitamin E
and breast cancer. J Nutr. 134(Suppl 12): S3458–S3462. 2004.
|
|
23
|
Yu W, Sanders BG and Kline K:
RRR-alpha-tocopheryl succinate induction of DNA synthesis arrest of
human MDA-MB-435 cells involves TGF-beta-independent activation of
p21Waf1/Cip1. Nutr Cancer. 43:227–236. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wan X, Harkavy B, Shen N, Grohar P and
Helman LJ: Rapamycin induces feedback activation of Akt signaling
through an IGF-1R-dependent mechanism. Oncogene. 26:1932–1940.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Jiang X, Sinnett-Smith J and Rozengurt E:
Carbachol induces p70S6K1 activation through an ERK-dependent but
Akt-independent pathway in human colonic epithelial cells. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 387:521–524. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Asanuma K, Moriai R, Yajima T, Yagihashi
A, Yamada M, Kobayashi D and Watanabe N: Survivin as a
radioresistance factor in pancreatic cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res.
91:1204–1209. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Chawla-Sarkar M, Bae SI, Reu FJ, Jacobs
BS, Lindner DJ and Borden EC: Downregulation of Bcl-2, FLIP or IAPs
(XIAP and survivin) by siRNAs sensitizes resistant melanoma cells
to Apo2L/TRAIL-induced apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 11:915–923.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, Scudiero DA,
Vigna N, Oltersdorf T and Reed JC: IAP-family protein survivin
inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD95), Bax,
caspases, and anticancer drugs. Cancer Res. 58:5315–5320.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yu W, Shun MC, Anderson K, Chen H, Sanders
BG and Kline K: alpha-TEA inhibits survival and enhances death
pathways in cisplatin sensitive and resistant human ovarian cancer
cells. Apoptosis. 11:1813–1823. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shun MC, Yu W, Park SK, Sanders BG and
Kline K: Downregulation of epidermal growth factor receptor
expression contributes to alpha-TEA's proapoptotic effects in human
ovarian cancer cell lines. J Oncol. 2010:8245712010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Datta SR, Katsov A, Hu L, Petros A, Fesik
SW, Yaffe MB and Greenberg ME: 14-3-3 proteins and survival kinases
cooperate to inactivate BAD by BH3 domain phosphorylation. Mol
Cell. 6:41–51. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Hayakawa J, Ohmichi M, Kurachi H, Kanda Y,
Hisamoto K, Nishio Y, Adachi K, Tasaka K, Kanzaki T and Murata Y:
Inhibition of BAD phosphorylation either at serine 112 via
extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase cascade or at serine
136 via Akt cascade sensitizes human ovarian cancer cells to
cisplatin. Cancer Res. 60:5988–5994. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I,
Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES and Wang X: Cytochrome c and
dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an
apoptotic protease cascade. Cell. 91:479–489. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Chan S: Targeting the mammalian target of
rapamycin (mTOR): A new approach to treating cancer. Br J Cancer.
91:1420–1424. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vignot S, Faivre S, Aguirre D and Raymond
E: mTOR-targeted therapy of cancer with rapamycin derivatives. Ann
Oncol. 16:525–537. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|