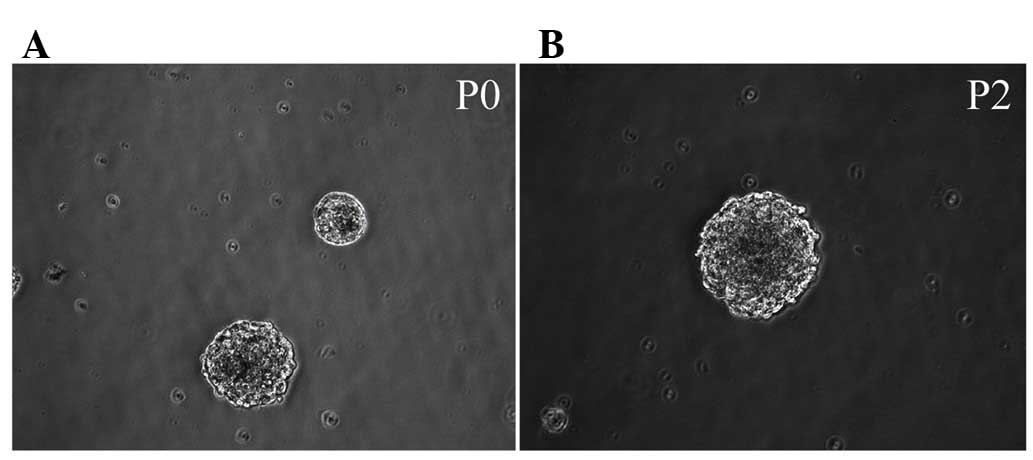
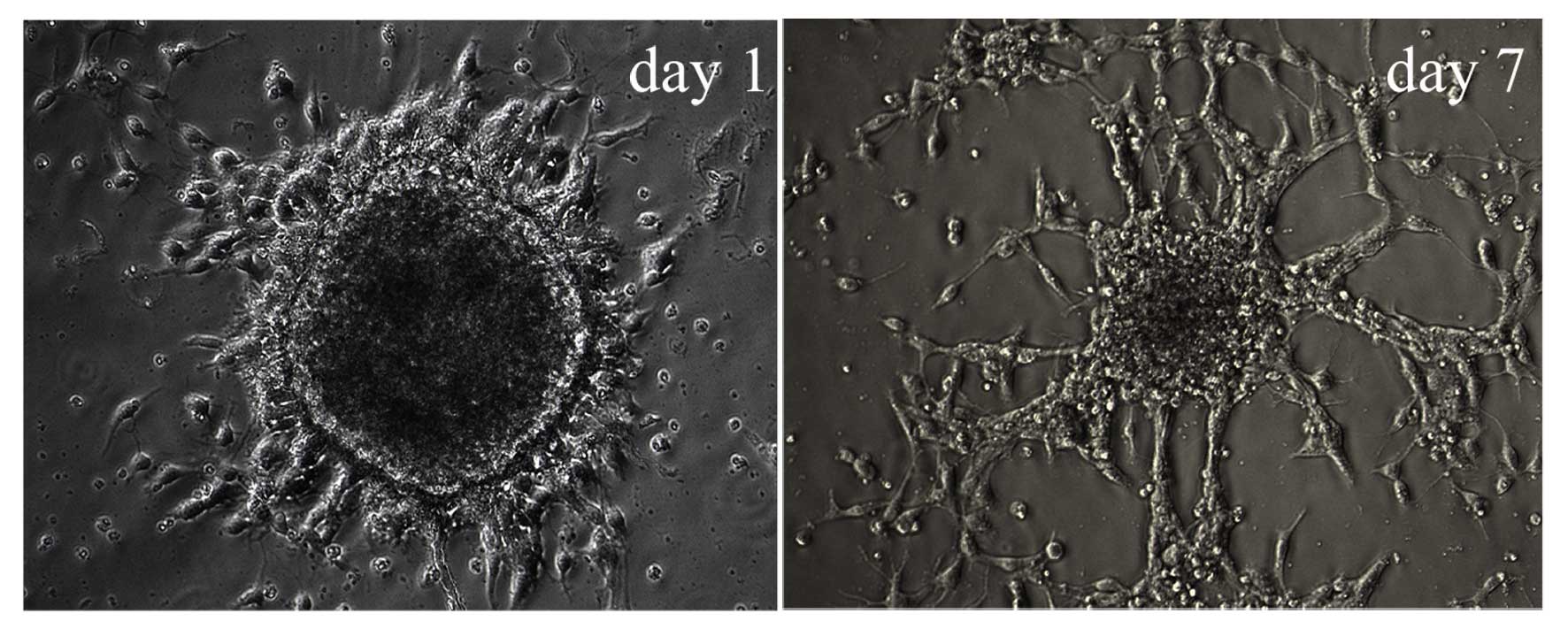
|
1
|
Yacoubian TA and Standaert DG: Targets for
neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1792:676–687. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Braak H, Bohl JR, Müller CM, Rüb U, de Vos
RA and Del Tredici K: Stanley fahn lecture 2005: The staging
procedure for the inclusion body pathology associated with sporadic
Parkinson's disease reconsidered. Mov Disord. 21:2042–2051. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Diaz NL and Waters CH: Current strategies
in the treatment of Parkinson's disease and a personized approach
to management. Expert Rev Neurother. 9:1781–1789. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reichmann H: New prospects for therapy in
Parkinson's disease. Drug Res (Stuttg). 63(Suppl 1): S232013.
|
|
5
|
Ding YX, Wei LC, Wang YZ, Cao R, Wang X
and Chen LW: Molecular manipulation targeting regulation of
dopaminergic differentiation and proliferation of neural stem cells
or pluripotent stem cells. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.
10:517–528. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lim MS, Chang MY, Kim SM, Yi SH, Suh-Kim
H, Jung SJ, Kim MJ, Kim JH, Lee YS, Lee SY, et al: Generation of
dopamine neurons from rodent fibroblasts through the expandable
neural precursor cell stage. J Biol Chem. 290:17401–17414. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Gyárfás T, Knuuttila J, Lindholm P,
Rantamäki T and Castrén E: Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic
factor (BDNF) and cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor (CDNF) by
anti-parkinsonian drug therapy in vivo. Cell Mol Neurobiol.
30:361–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Hauser DN and Cookson MR: Astrocytes in
Parkinson's disease and DJ-1. J Neurochem. 117:357–358. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang YH, Yu HT, Pu XP and Du GH: Baicalein
prevents 6-hydroxydopamine-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in
SH-SY5Y cells via inhibition of mitochondrial oxidation and
up-regulation of DJ-1 protein expression. Molecules.
18:14726–14738. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Okano H and Sawamoto K: Neural stem cells:
Involvement in adult neurogenesis and CNS repair. Philos Trans R
Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 363:2111–2122. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Muramatsu S, Okuno T, Suzuki Y, Nakayama
T, Kakiuchi T, Takino N, Iida A, Ono F, Terao K, Inoue N, et al:
Multitracer assessment of dopamine function after transplantation
of embryonic stem cell-derived neural stem cells in a primate model
of Parkinson's disease. Synapse. 63:541–548. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Williams CJ and Dexter DT: Neuroprotective
and symptomatic effects of targeting group III mGlu receptors in
neurodegenerative disease. J Neurochem. 129:4–20. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Richardson JR and Hossain MM: Microglial
ion channels as potential targets for neuroprotection in
Parkinson's disease. Neural Plast. 2013:5874182013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wei LC, Ding YX, Liu YH, Duan L, Bai Y,
Shi M and Chen LW: Low-dose radiation stimulates Wnt/β-catenin
signaling, neural stem cell proliferation and neurogenesis of the
mouse hippocampus in vitro and in vivo. Curr Alzheimer Res.
9:278–289. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kishi Y, Takahashi J, Koyanagi M, Morizane
A, Okamoto Y, Horiguchi S, Tashiro K, Honjo T, Fujii S and
Hashimoto N: Estrogen promotes differentiation and survival of
dopaminergic neurons derived from human neural stem cells. J
Neurosci Res. 79:279–286. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zuo FX, Bao XJ, Sun XC, Wu J, Bai QR, Chen
G, Li XY, Zhou QY, Yang YF, Shen Q and Wang RZ: Transplantation of
human neural stem cells in a Parkinsonian model exerts
neuroprotection via regulation of the host microenvironment. Int J
Mol Sci. 16:26473–26492. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cave JW, Wang M and Baker H: Adult
subventricular zone neural stem cells as a potential source of
dopaminergic replacement neurons. Front Neurosci. 8:162014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yamashita T and Abe K: Direct reprogrammed
neuronal cells as a novel resource for cell transplantation
therapy. Cell Transplant. 23:435–439. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Trueman RC, Klein A, Lindgren HS, Lelos MJ
and Dunnett SB: Repair of the CNS using endogenous and transplanted
neural stem cells. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 15:357–398. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Buttery PC and Barker RA: Treating
Parkinson's disease in the 21st century: Can stem cell
transplantation compete? J Comp Neurol. 522:2802–2816. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sadan O, Bahat-Stromza M, Barhum Y, Levy
YS, Pisnevsky A, Peretz H, Ilan AB, Bulvik S, Shemesh N, Krepel D,
et al: Protective effects of neurotrophic factor-secreting cells in
a 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson disease. Stem Cells Dev.
18:1179–1190. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li F, Wang M, Zhu S, Li L, Xiong Y and Gao
DS: The potential neuroprotection mechanism of GDNF in the
6-OHDA-induced cellular models of Parkinson's disease. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 33:907–919. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ren X, Zhang T, Gong X, Hu G, Ding W and
Wang X: AAV2-mediated striatum delivery of human CDNF prevents the
deterioration of midbrain dopamine neurons in a 6-hydroxydopamine
induced parkinsonian rat model. Exp Neurol. 248:148–156. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ogawa I, Saito Y, Saigoh K, Hosoi Y,
Mitsui Y, Noguchi N and Kusunoki S: The significance of oxidized
DJ-1 protein (oxDJ-1) as a biomarker for Parkinson's disease. Brain
Nerve. 66:471–477. 2014.In Japanese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kahle PJ, Waak J and Gasser T: DJ-1 and
prevention of oxidative stress in Parkinson's disease and other
age-related disorders. Free Radic Biol Med. 47:1354–1361. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hebsgaard JB, Nelander J, Sabelström H,
Jönsson ME, Stott S and Parmar M: Dopamine neuron precursors within
the developing human mesencephalon show radial glial
characteristics. Glia. 57:1648–1658. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Reynolds BA and Weiss S: Generation of
neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian
central nervous system. Science. 255:1707–1710. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ding YX, Wei LC, Wang YZ, Cao R, Wang X
and Chen LW: Molecular manipulation targeting regulation of
dopaminergic differentiation and proliferation of neural stem cells
or pluripotent stem cells. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.
10:517–528. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Carrillo-García C, Suh Y, Obernier K,
Hölzl-Wenig G, Mandl C and Ciccolini F: Multipotent precursors in
the anterior and hippocampal subventricular zone display similar
transcription factor signatures but their proliferation and
maintenance are differentially regulated. Mol Cell Neurosci.
44:318–329. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ambasudhan R, Dolatabadi N, Nutter A,
Masliah E, Mckercher SR and Lipton SA: Potential for cell therapy
in Parkinson's disease using genetically-programmed human embryonic
stem cell-derived neural progenitor cells. J Comp Neurol.
522:2845–2856. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Park CH, Lim MS, Rhee YH, Yi SH, Kim BK,
Shim JW, Kim YH, Jung SJ and Lee SH: In vitro generation of mature
dopamine neurons by decreasing and delaying the expression of
exogenous Nurr1. Development. 139:2447–2451. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lei Z, Jiang Y, Li T, Zhu J and Zeng S:
Signaling of glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor and its
receptor GFRα1 induce Nurr1 and Pitx3 to promote survival of
grafted midbrain-derived neural stem cells in a rat model of
Parkinson disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 70:736–747. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alvarez-Castelao B, Losada F, Ahicart P
and Castaño JG: The N-terminal region of Nurr1 (a.a 1-31) is
essential for its efficient degradation by the ubiquitin proteasome
pathway. PloS One. 8:e559992013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bang SY, Kwon SH, Yi SH, Yi SA, Park EK,
Lee JC, Jang CG, You JS, Lee SH and Han JW: Epigenetic activation
of the Foxa2 gene is required for maintaining the potential of
neural precursor cells to differentiate into dopaminergic neurons
after expansion. Stem Cells Dev. 24:520–533. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Moreno-Bravo JA, Martinez-Lopez JE and
Puelles E: Mesencephalic neuronal populations: New insights on the
ventral differentiation programs. Histol Histopathol. 27:1529–1538.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Barneda-Zahonero B, Servitja JM, Badiola
N, Miñano-Molina AJ, Fadó R, Saura CA and Rodríguez-Alvarez J:
Nurr1 protein is required for N-methyl-D-aspartic acid (NMDA)
receptor-mediated neuronal survival. J Biol Chem. 287:11351–11362.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Jiang C, Wan X, He Y, Pan T, Jankovic J
and Le W: Age-dependent dopaminergic dysfunction in Nurr1 knockout
mice. Exp Neurol. 191:154–162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Sonntag KC, Simantov R, Kim KS and Isacson
O: Temporally induced Nurr1 can induce a non-neuronal dopaminergic
cell type in embryonic stem celt differentiation. Eur J Nearosci.
19:1141–1152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kittappa R, Chang WW, Awatramani RB and
McKay RD: The foxa2 gene controls the birth and spontaneous
degenerate of dopamine neurons in old age. PLoS Biol. 5:e3252007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Veenvliet JV, Dos Santos MT, Kouwenhoven
WM, von Oerthel L, Lim JL, van der Linden AJ, Koerkamp MJ, Holstege
FC and Smidt MP: Specification of dopaminergic subsets involves
interplay of En1 and Pitx3. Development. 140:3373–3384. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Panman L, Papathanou M, Laguna A,
Oosterveen T, Volakakis N, Acampora D, Kurtsdotter I, Yoshitake T,
Kehr J, Joodmardi E, et al: Sox6 and Otx2 control the specification
of substantia nigra and ventral tegmental area dopamine neurons.
Cell Rep. 8:1018–1025. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|