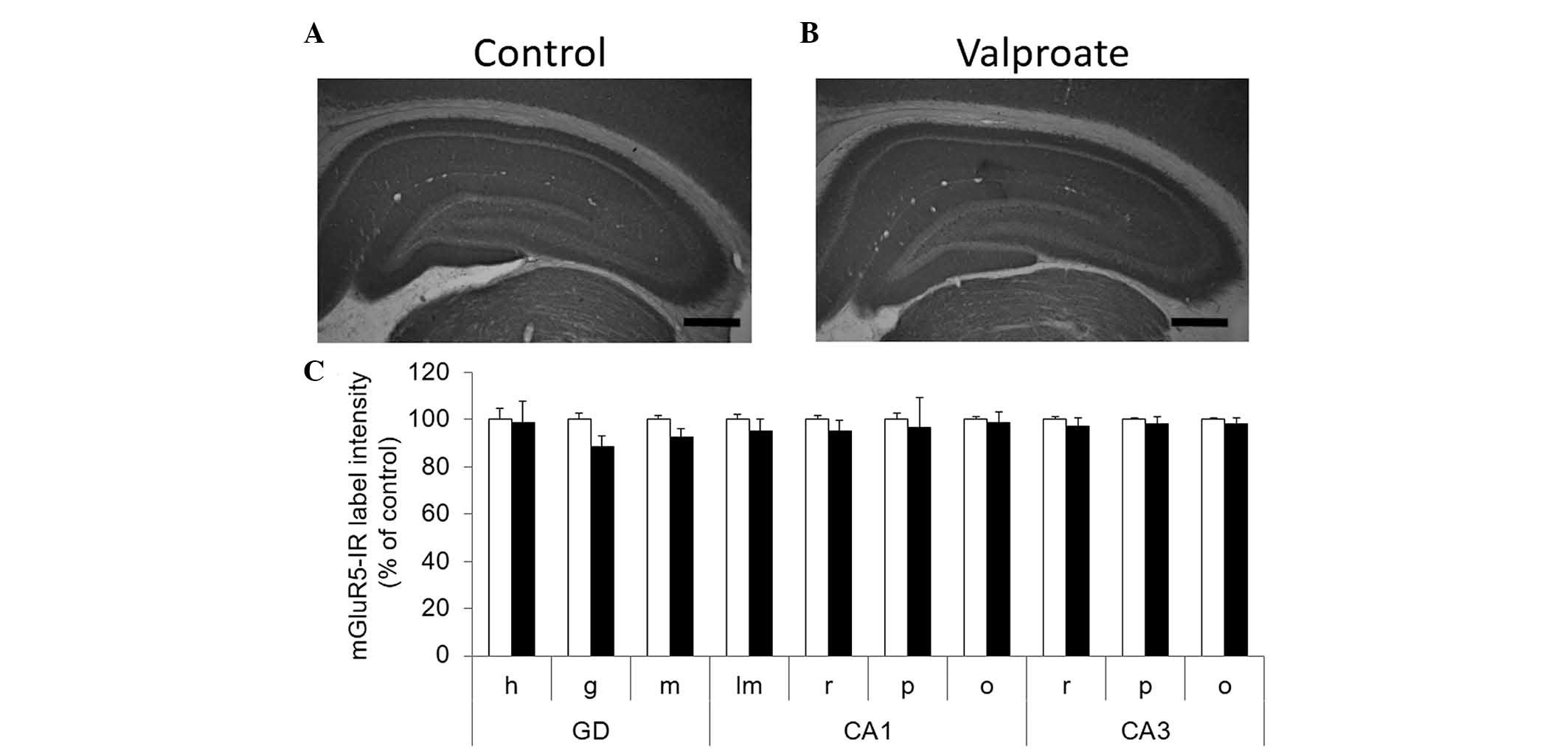
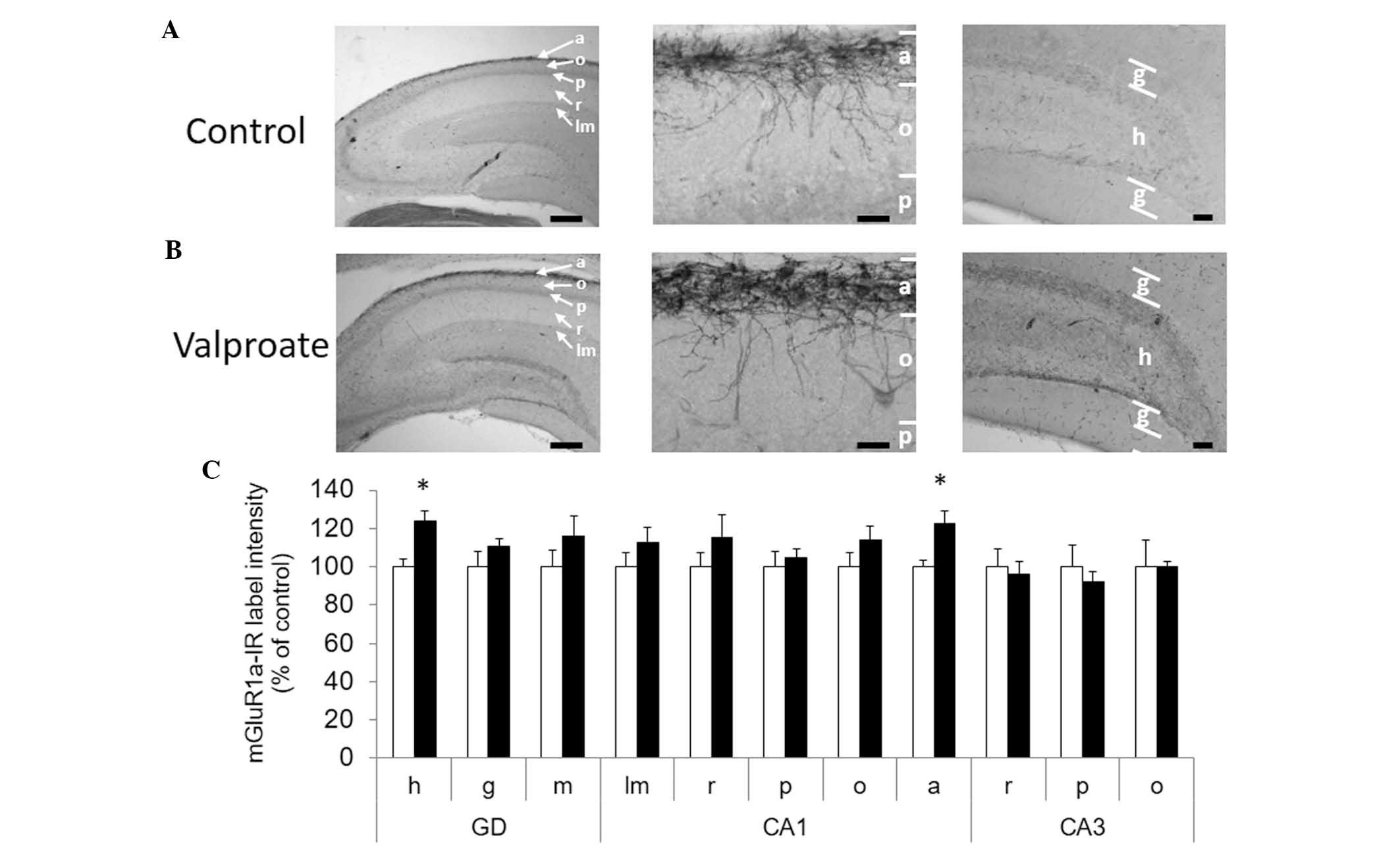
|
1
|
Frith U and Happé F: Autism spectrum
disorder. Curr Biol. 15:R786–R790. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Wass S: Distortions and disconnections:
Disrupted brain connectivity in autism. Brain Cogn. 75:18–28. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Blatt GJ: The neuropathology of autism.
Scientifica (Cairo). 2012:7036752012.
|
|
4
|
Betancur C: Etiological heterogeneity in
autism spectrum disorders: More than 100 genetic and genomic
disorders and still counting. Brain Res. 1380:42–77. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jamain S, Quach H, Betancur C, Råstam M,
Colineaux C, Gillberg IC, Soderstrom H, Giros B, Leboyer M,
Gillberg C, et al: Mutations of the X-linked genes encoding
neuroligins NLGN3 and NLGN4 are associated with autism. Nat Genet.
34:27–29. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moessner R, Marshall CR, Sutcliffe JS,
Skaug J, Pinto D, Vincent J, Zwaigenbaum L, Fernandez B, Roberts W,
Szatmari P and Scherer SW: Contribution of SHANK3 mutations to
autism spectrum disorder. Am J Hum Genet. 81:1289–1297. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Durand CM, Betancur C, Boeckers TM,
Bockmann J, Chaste P, Fauchereau F, Nygren G, Rastam M, Gillberg
IC, Anckarsäter H, et al: Mutations in the gene encoding the
synaptic scaffolding protein SHANK3 are associated with autism
spectrum disorders. Nat Genet. 39:25–27. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
8
|
Hung AY, Futai K, Sala C, Valtschanoff JG,
Ryu J, Woodworth MA, Kidd FL, Sung CC, Miyakawa T, Bear MF, et al:
Smaller dendritic spines, weaker synaptic transmission, but
enhanced spatial learning in mice lacking Shank1. J Neurosci.
28:1697–1708. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dindot SV, Antalffy BA, Bhattacharjee MB
and Beaud: The Angelman syndrome ubiquitin ligase localizes to the
synapse and nucleus and maternal deficiency results in abnormal
dendritic spine morphology. Hum Mol Genet. 17:111–118. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Kishino T, Lalande M and Wagstaff J:
UBE3A/E6-AP mutations cause Angelman syndrome. Nat Genet. 15:70–73.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sadakata T, Washida M, Iwayama Y, Shoji S,
Sato Y, Ohkura T, Katoh-Semba R, Nakajima M, Sekine Y, Tanaka M, et
al: Autistic-like phenotypes in Cadps2-knockout mice and aberrant
CADPS2 splicing in autistic patients. J Clin Invest. 117:931–943.
2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Costa-Mattioli M, Sossin WS, Klann E and
Sonenberg N: Translational control of long-lasting synaptic
plasticity and memory. Neuron. 61:10–26. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hoeffer CA and Klann E: mTOR signaling: At
the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci.
33:67–75. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
de Vries PJ and Howe CJ: The tuberous
sclerosis complex proteins-a GRIPP on cognition and
neurodevelopment. Trends Mol Med. 13:319–326. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Feng Y, Zhang F, Lokey LK, Chastain JL,
Lakkis L, Eberhart D and Warren ST: Translational suppression by
trinucleotide repeat expansion at FMR1. Science. 268:731–734. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Koekkoek SK, Yamaguchi K, Milojkovic BA,
Dortland BR, Ruigrok TJ, Maex R, De Graaf W, Smit AE, VanderWerf F,
Bakker CE, et al: Deletion of FMR1 in Purkinje cells enhances
parallel fiber LTD, enlarges spines, and attenuates cerebellar
eyelid conditioning in Fragile X syndrome. Neuron. 47:339–352.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Butler MG, Dasouki MJ, Zhou XP,
Talebizadeh Z, Brown M, Takahashi TN, Miles JH, Wang CH, Stratton
R, Pilarski R and Eng C: Subset of individuals with autism spectrum
disorders and extreme macrocephaly associated with germline PTEN
tumour suppressor gene mutations. J Med Genet. 42:318–332. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Goffin A, Hoefsloot LH, Bosgoed E, Swillen
A and Fryns JP: PTEN mutation in a family with Cowden syndrome and
autism. Am J Med Genet. 105:521–524. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zori RT, Marsh DJ, Graham GE, Marliss EB
and Eng C: Germline PTEN mutation in a family with Cowden syndrome
and Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome. Am J Med Genet. 80:399–402.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Neves-Pereira M, Müller B, Massie D,
Williams JH, O'Brien PC, Hughes A, Shen SB, Clair DS and
Miedzybrodzka Z: Deregulation of EIF4E: A novel mechanism for
autism. J Med Genet. 46:759–765. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kelleher RJ IIIrd and Bear MF: The
autistic neuron: Troubled translation? Cell. 135:401–406. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kao DI, Aldridge GM and Greenough WT:
Altered mRNA transport, docking and protein translation in neurons
lacking fragile X mental retardation protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 107:15601–15606. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Markram K, Rinaldi T, La Mendola D, Sandi
C and Markram H: Abnormal fear conditioning and amygdala processing
in an animal model of autism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 33:901–912.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Silva GT, Le Bé JV, Riachi I, Rinaldi T,
Markram K and Markram H: Enhanced long-term microcircuit plasticity
in the valproic acid animal model of autism. Front Synaptic
Neurosci. 1:12009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Rinaldi T, Perrodin C and Markram H:
Hyper-connectivity and hyper-plasticity in the medial prefrontal
cortex in the valproic acid animal model of autism. Front Neural
Circuits. 2:42008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Rinaldi T, Silberberg G and Markram H:
Hyperconnectivity of local neocortical microcircuitry induced by
prenatal exposure to valproic acid. Cereb Cortex. 18:763–770. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Rinaldi T, Kulangara K, Antoniello K and
Markram H: Elevated NMDA receptor levels and enhanced postsynaptic
long-term potentiation induced by prenatal exposure to valproic
acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:13501–13506. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mehta MV, Gandal MJ and Siegel SJ:
mGluR5-antagonist mediated reversal of elevated stereotyped,
repetitive behaviors in the VPA model of autism. PLoS One.
6:e260772011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
WalfA AA and Frye CA: The use of the
elevated plus maze as an assay of anxiety-related behavior in
rodents. Nat Protoc. 2:322–328. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Fernandes C and File SE: The influence of
open arm ledges and maze experience in the elevated plus-maze.
Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 54:31–40. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE and Briley M:
Validation of open:Closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a
measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods. 14:149–167.
1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Moy SS, Nadler JJ, Perez A, Barbaro RP,
Johns JM, Magnuson TR, Piven J and Crawley JN: Sociability and
preference for social novelty in five inbred strains: An approach
to assess autistic-like behavior in mice. Genes Brain Behav.
3:287–302. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Conrad CD, Grote KA, Hobbs RJ and
Ferayorni A: Sex differences in spatial and non-spatial Y-maze
performance after chronic stress. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 79:32–40.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Conrad CD, Galea LA, Kuroda Y and McEwen
BS: Chronic stress impairs rat spatial memory on the Y maze, and
this effect is blocked by tianeptine pretreatment. Behav Neurosci.
110:1321–1334. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Dellu F, Mayo W, Cherkaoui J, Le Moal M
and Simon H: Two-trial memory task with automated recording: Study
in young and aged rats. Brain Res. 588:132–139. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Edalatmanesh MA, Nikfarjam H, Vafaee F and
Moghadas M: Increased hippocampal cell density and enhanced spatial
memory in the valproic acid rat model of autism. Brain Res.
1526:15–25. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lapointe V, Morin F, Ratté S, Croce A,
Conquet F and Lacaille JC: Synapse-specific mGluR1-dependent
long-term potentiation in interneurones regulates mouse hippocampal
inhibition. J Physiol. 15:125–135. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Shigemoto R, Kinoshita A, Wada E, Nomura
S, Ohishi H, Takada M, Flor PJ, Neki A, Abe T, Nakanishi S and
Mizuno N: Differential presynaptic localization of metabotropic
glutamate receptor subtypes in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci.
17:7503–7522. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Patterson PH: Modeling autistic features
in animals. Pediatr Res. 69:34R–40R. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kim KC, Kim P, Go HS, Choi CS, Yang SI,
Cheong JH, Shin CY and Ko KH: The critical period of valproate
exposure to induce autistic symptoms in Sprague-Dawley rats.
Toxicol Lett. 201:137–142. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Schneider T and Przewłocki R: Behavioral
alterations in rats prenatally exposed to valproic acid: Animal
model of autism. Neuropsychopharmacology. 30:80–89. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Kim JE, Shin MS, Seo TB, Ji ES, Baek SS,
Lee SJ, Park JK and Kim CJ: Treadmill exercise ameliorates motor
disturbance through inhibition of apoptosis in the cerebellum of
valproic acid-induced autistic rat pups. Mol Med Rep. 8:327–334.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Tang G, Gudsnuk K, Kuo SH, Cotrina ML,
Rosoklija G, Sosunov A, Sonders MS, Kanter E, Castagna C, Yamamoto
A, et al: Loss of mTOR-dependent macroautophagy causes
autistic-like synaptic pruning deficits. Neuron. 83:1131–1143.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nicolini C, Ahn Y, Michalski B, Rho JM and
Fahnestock M: Decreased mTOR signaling pathway in human idiopathic
autism and in rats exposed to valproic acid. Acta Neuropathol
Commun. 3:32015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Bear MF, Huber KM and Warren ST: The mGluR
theory of fragile X mental retardation. Trends Neurosci.
27:370–377. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Osterweil EK, Krueger DD, Reinhold K and
Bear MF: Hypersensitivity to mGluR5 and ERK1/2 leads to excessive
protein synthesis in the hippocampus of a mouse model of fragile X
syndrome. J Neurosci. 30:15616–15627. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Mannaioni G, Marino MJ, Valenti O,
Traynelis SF and Conn PJ: Metabotropic glutamate receptors 1 and 5
differentially regulate CA1 pyramidal cell function. J Neurosci.
21:5925–5934. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
van Hooft JA, Giuffrida R, Blatow M and
Monyer H: Differential expression of group I metabotropic glutamate
receptors in functionally distinct hippocampal interneurons. J
Neurosci. 20:3544–3551. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Kullmann DM: Interneuron networks in the
hippocampus. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 21:709–716. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Stewart M and Fox SE: Do septal neurons
pace the hippocampal theta rhythm? Trends Neurosci. 13:163–168.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Chee SS, Menard JL and Dringenberg HC: The
lateral septum as a regulator of hippocampal theta oscillations and
defensive behavior in rats. J Neurophysiol. 113:1831–1841. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Lovett-Barron M, Kaifosh P, Kheirbek MA,
Danielson N, Zaremba JD, Reardon TR, Turi GF, Hen R, Zemelman BV
and Losonczy A: Dendritic inhibition in the hippocampus supports
fear learning. Science. 343:857–863. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Han E and Heinemann S: Distal dendritic
inputs control neuronal activity by heterosynaptic potentiation of
proximal inputs. J Neurosci. 33:1314–1325. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Scharfman HE and Myers CE: Hilar mossy
cells of the dentate gyrus: A historical perspective. Front Neural
Circuits. 6:1062013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Acsády L, Kamondi A, Sík A, Freund T and
Buzsáki G: GABAergic cells are the major postsynaptic targets of
mossy fibers in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci. 18:3386–3403.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Baude A, Nusser Z, Roberts JD, Mulvihill
E, McIlhinney RA and Somogyi P: The metabotropic glutamate receptor
(mGluR1 alpha) is concentrated at perisynaptic membrane of neuronal
subpopulations as detected by immunogold reaction. Neuron.
11:771–787. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Techlovská S, Chambers JN, Dvořáková M,
Petralia RS, Wang YX, Hájková A, Nová A, Franková D, Prezeau L and
Blahos J: Metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 splice variants mGluR1a
and mGluR1b combine in mGluR1a/b dimers in vivo. Neuropharmacology.
86:329–336. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
58
|
Sevastyanova TN and Kammermeier PJ:
Cooperative signaling between homodimers of metabotropic glutamate
receptors 1 and 5. Mol Pharmacol. 86:492–504. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|