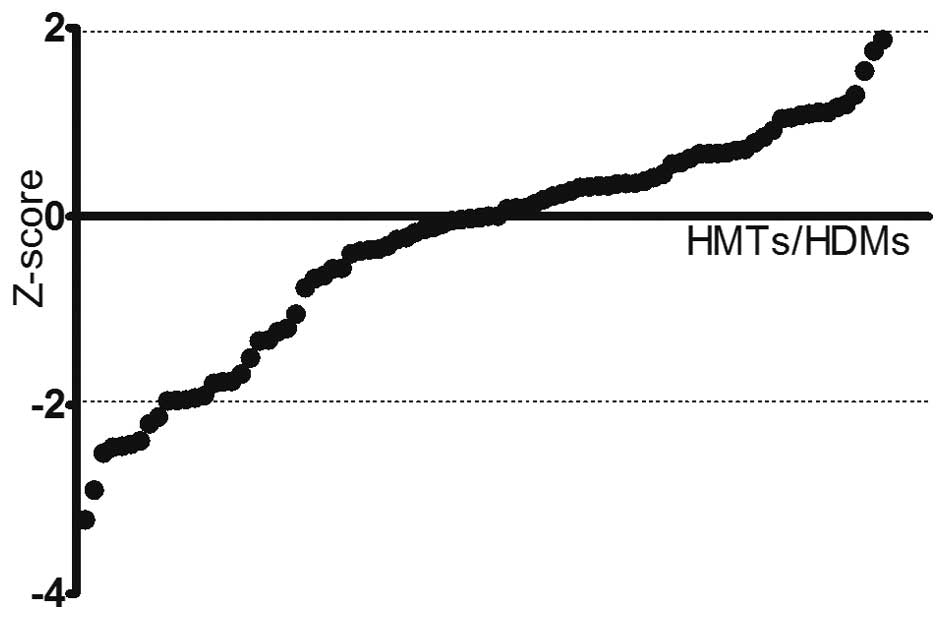
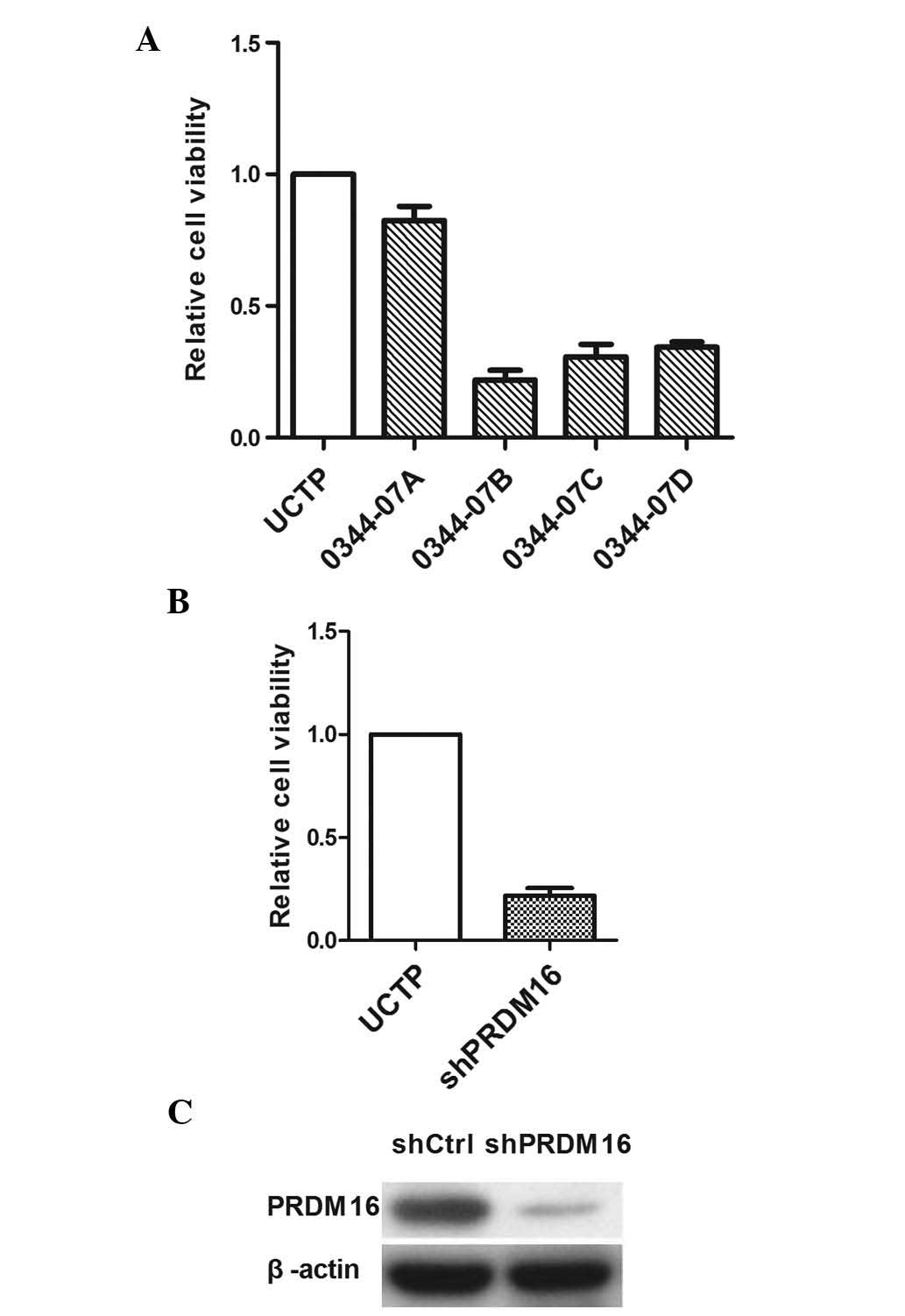
|
1
|
Siegel RL, Miller KD and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 65:5–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bert SA, Robinson MD, Strbenac D, Statham
AL, Song JZ, Hulf T, Sutherland RL, Coolen MW, Stirzaker C and
Clark SJ: Regional activation of the cancer genome by long-range
epigenetic remodeling. Cancer Cell. 23:9–22. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Coolen MW, Stirzaker C, Song JZ, Statham
AL, Kassir Z, Moreno CS, Young AN, Varma V, Speed TP, Cowley M, et
al: Consolidation of the cancer genome into domains of repressive
chromatin by long-range epigenetic silencing (LRES) reduces
transcriptional plasticity. Nat Cell Biol. 12:235–246.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Crea F, Sun L, Mai A, Chiang YT, Farrar
WL, Danesi R and Helgason CD: The emerging role of histone lysine
demethylases in prostate cancer. Mol Cancer. 11:522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Albert M and Helin K: Histone
methyltransferases in cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 21:209–220.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Shi Y, Lan F, Matson C, et al: Histone
Demethylation Mediated by the Nuclear Amine Oxidase Homolog LSD1.
Cell. 119:941–953. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Metzger E, Wissmann M, Yin N, Müller JM,
Schneider R, Peters AH, Günther T, Buettner R and Schüle R: LSD1
demethylates repressive histone marks to promote
androgen-receptor-dependent transcription. Nature. 437:436–439.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Duan S, Cermak L, Pagan JK, Rossi M,
Martinengo C, di Celle PF, Chapuy B, Shipp M, Chiarle R and Pagano
M: FBXO11 targets BCL6 for degradation and is inactivated in
diffuse large B-cell lymphomas. Nature. 481:90–93. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Baldwin RM, Morettin A, Paris G, Goulet I
and Côté J: Alternatively spliced protein arginine
methyltransferase 1 isoform PRMT1v2 promotes the survival and
invasiveness of breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 11:4597–4612.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Paris PL, Sridharan S, Hittelman AB,
Kobayashi Y, Perner S, Huang G, Simko J, Carroll P, Rubin MA and
Collins C: An oncogenic role for the multiple endocrine neoplasia
type 1 gene in prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
12:184–191. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Angelova S, Jordanova M, Spassov B,
Shivarov V, Simeonova M, Christov I, Angelova P, Alexandrova K,
Stoimenov A, Nikolova V, et al: Amplification of c-MYC and MLL
genes as a marker of clonal cell progression in patients with
myeloid malignancy and trisomy of chromosomes 8 or 11. Balkan J Med
Genet. 14:17–24. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Duhoux FP, Ameye G, Montano-Almendras CP,
et al: PRDM16 (1p36) translocations define a distinct entity of
myeloid malignancies with poor prognosis but may also occur in
lymphoid malignancies. Br J Haematol. 156:76–88. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Faria JA, Corrêa NC, de Andrade C, et al:
SET domain-containing protein 4 (SETD4) is a newly identified
cytosolic and nuclear lysine methyltransferase involved in breast
cancer cell proliferation. J Cancer Sci Ther. 5:58–65.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Berry WL and Janknecht R: KDM4/JMJD2
histone demethylases: Epigenetic regulators in cancer cells. Cancer
Res. 73:2936–2942. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Pinheiro I, Margueron R, Shukeir N, Eisold
M, Fritzsch C, Richter FM, Mittler G, Genoud C, Goyama S, Kurokawa
M, et al: Prdm3 and Prdm16 are H3K9me1 methyltransferases required
for mammalian heterochromatin integrity. Cell. 150:948–960. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoshida M, Nosaka K, Yasunaga J, Nishikata
I, Morishita K and Matsuoka M: Aberrant expression of the MEL1S
gene identified in association with hypomethylation in adult T-cell
leukemia cells. Blood. 103:2753–2760. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Takahata M, Inoue Y, Tsuda H, Imoto I,
Koinuma D, Hayashi M, Ichikura T, Yamori T, Nagasaki K, Yoshida M,
et al: SKI and MEL1 cooperate to inhibit transforming growth
factor-beta signal in gastric cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
284:3334–3344. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|