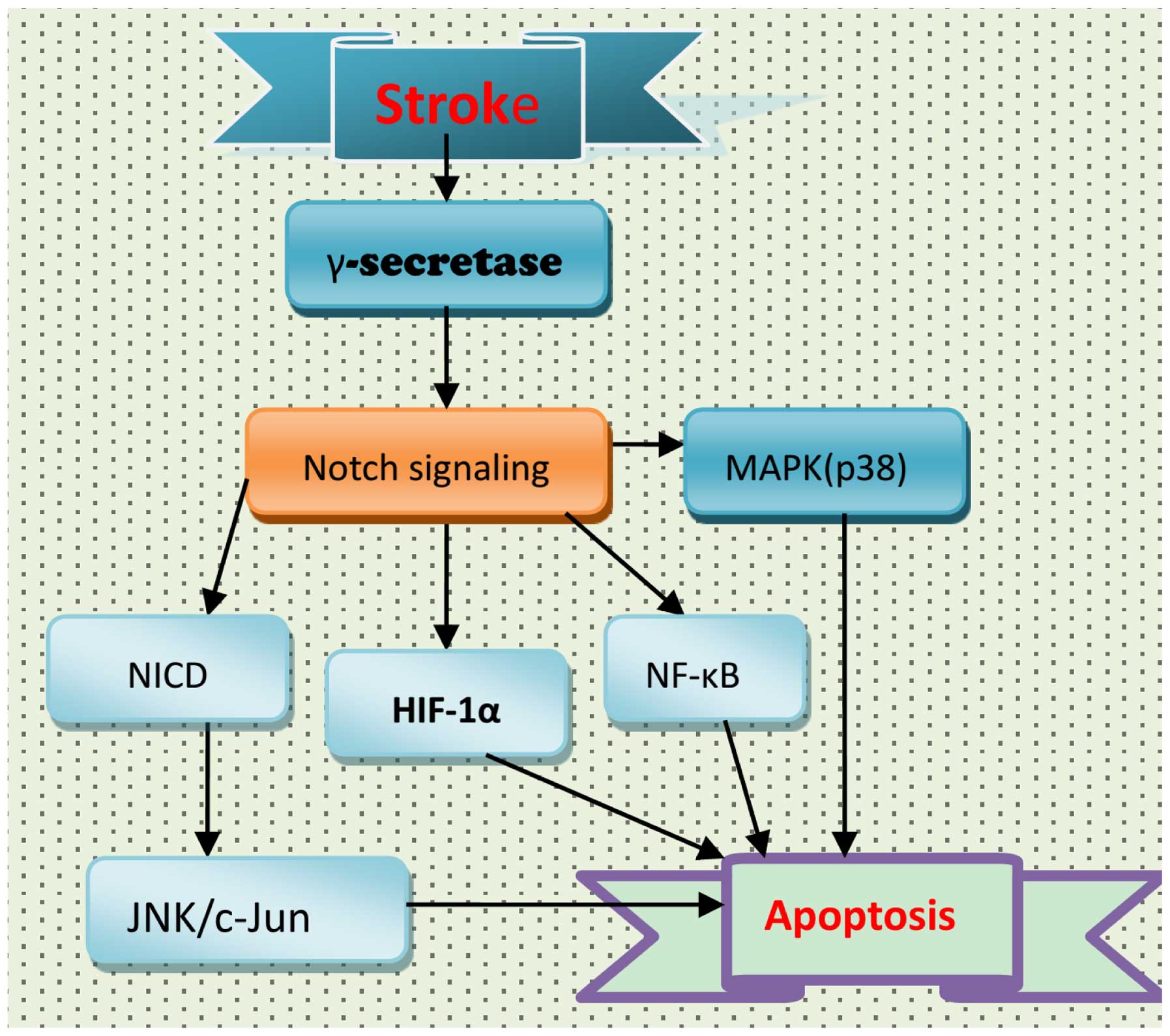
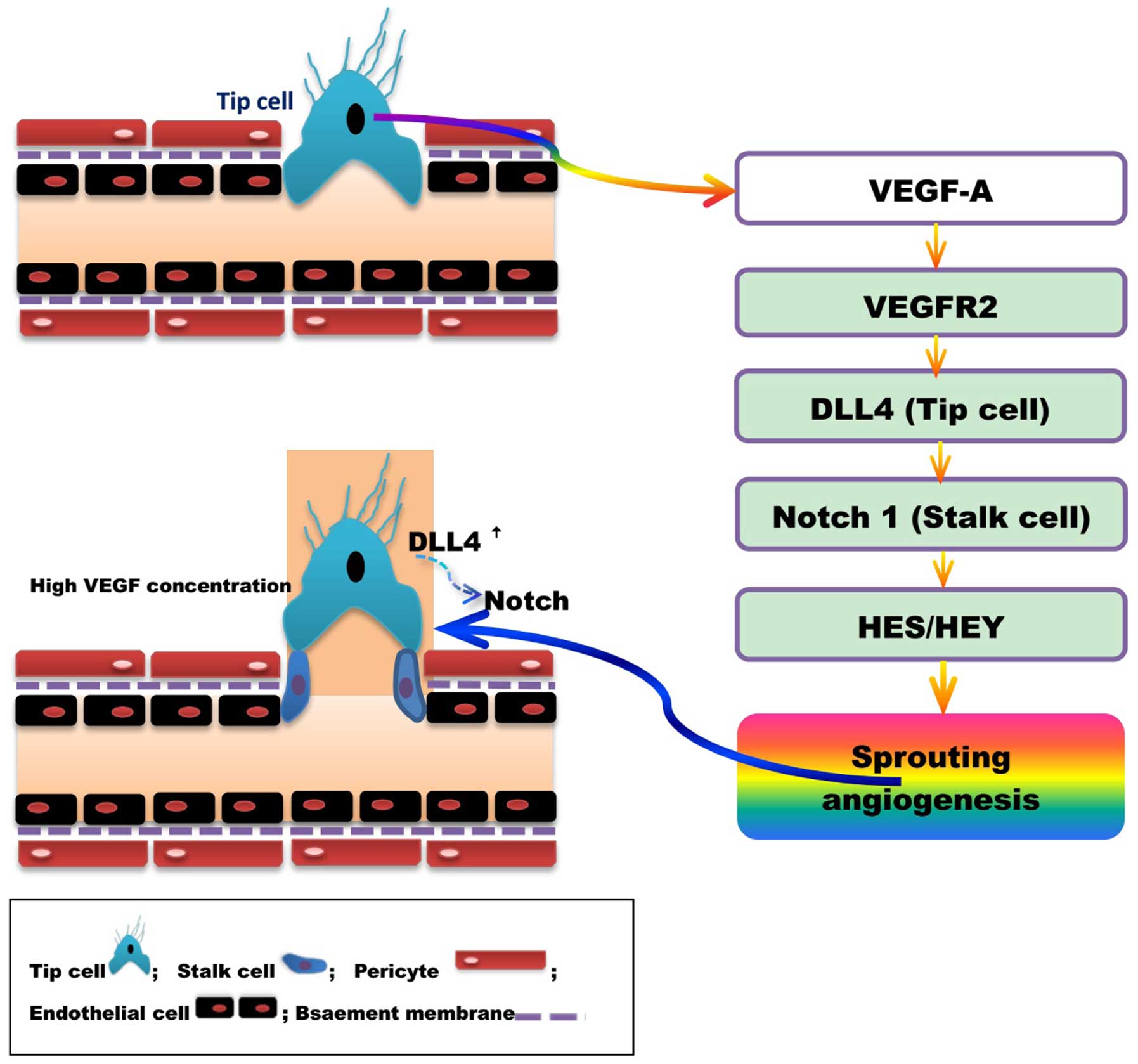
|
1
|
Lama S, Dolati P and Sutherland GR:
Controversy in the management of lenticulostriate artery dissecting
aneurysm: A case report and review of the literature. World
Neurosurg. 81:441.e1–e7. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dezmalj-Grbelja L, Bosnjak J,
Lovrencić-Huzjan A, Ivica M and Demarin V: Moyamoya disease in a
patient with brain tumor: Case report. Acta Clin Croat. 49:459–463.
2010.
|
|
3
|
Sharfstein SR, Ahmed S, Islam MQ, Najjar
MI and Ratushny V: Case of moyamoya disease in a patient with
advanced acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Stroke Cerebrovasc
Dis. 16:268–272. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Squizzato A, Gerdes VE, Brandjes DP,
Büller HR and Stam J: Thyroid diseases and cerebrovascular disease.
Stroke. 36:2302–2310. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Vetrano DL, Landi F, De Buyser SL, Carfi
A, Zuccalà G, Petrovic M, Volpato S, Cherubini A, Corsonello A,
Bernabei R and Onder G: Predictors of length of hospital stay among
older adults admitted to acute care wards: A multicentre
observational study. Eur J Intern Med. 25:56–62. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Cicconetti P, Riolo N, Priami C, Tafaro L
and Ettore E: Risk factors for cognitive impairment. Recenti Prog
Med. 95:535–545. 2004.In Italian. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Elkind MS: Epidemiology and risk factors.
Continuum (Minneap Minn). 17:1213–1232. 2011.
|
|
8
|
Jia Q, Liu LP and Wang YJ: Stroke in
China. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 37:259–264. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bhoopathi P, Chetty C, Dontula R, Gujrati
M, Dinh DH, Rao JS and Lakka SS: SPARC stimulates neuronal
differentiation of medulloblastoma cells via the Notch1/STAT3
pathway. Cancer Res. 71:4908–4919. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yuan TM and Yu HM: Notch signaling: Key
role in intrauterine infection/inflammation, embryonic development,
and white matter damage? J Neurosci Res. 88:461–468. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Veenendaal LM, Kranenburg O, Smakman N,
Klomp A, Borel Rinkes IH and van Diest PJ: Differential Notch and
TGFbeta signaling in primary colorectal tumors and their
corresponding metastases. Cell Oncol. 30:1–11. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Givogri MI, de Planell M, Galbiati F,
Superchi D, Gritti A, Vescovi A, de Vellis J and Bongarzone ER:
Notch signaling in astrocytes and neuroblasts of the adult
subventricular zone in health and after cortical injury. Dev
Neurosci. 28:81–91. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Quillard T and Charreau B: Impact of notch
signaling on inflammatory responses in cardiovascular disorders.
Int J Mol Sci. 14:6863–6888. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li F, Lan Y, Wang Y, Wang J, Yang G, Meng
F, Han H, Meng A and Yang X: Endothelial Smad4 maintains
cerebrovascular integrity by activating N-cadherin through
cooperation with Notch. Dev Cell. 20:291–302. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dichgans M: Genetics of ischaemic stroke.
Lancet Neurol. 6:149–161. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yuan Y, Rangarajan P, Kan EM, Wu Y, Wu C
and Ling EA: Scutellarin regulates the Notch pathway and affects
the migration and morphological transformation of activated
microglia in experimentally induced cerebral ischemia in rats and
in activated BV-2 microglia. J Neuroinflammation. 12:112015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cheng YL, Choi Y, Sobey CG, Arumugam TV
and Jo DG: Emerging roles of the γ-secretase-notch axis in
inflammation. Pharmacol Ther. 147:80–90. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Z, Huang W and Zuo Z: Perioperative
aspirin improves neurological outcome after focal brain ischemia
possibly via inhibition of Notch 1 in rat. J Neuroinflammation.
11:562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Li S, Zyang X, Wang Y, Ji H, Du Y and Liu
H: DAPT protects brain against cerebral ischemia by down-regulating
the expression of Notch 1 and nuclear factor κB in rats. Neurol
Sci. 33:1257–1264. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Cheng YL, Park JS, Manzanero S, Choi Y,
Baik SH, Okun E, Gelderblom M, Fann DY, Magnus T, Launikonis BS, et
al: Evidence that collaboration between HIF-1α and Notch-1 promotes
neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke. Neurobiol Dis. 62:286–295.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Wang L, Chopp M, Zhang RL, Zhang L,
Letourneau Y, Feng YF, Jiang A, Morris DC and Zhang ZG: The Notch
pathway mediates expansion of a progenitor pool and neuronal
differentiation in adult neural progenitor cells after stroke.
Neuroscience. 158:1356–1363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
22
|
Wei Z, Chigurupati S, Arumugam TV, Jo DG,
Li H and Chan SL: Notch activation enhances the microglia-mediated
inflammatory response associated with focal cerebral ischemia.
Stroke. 42:2589–2594. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Morgan TH: The theory of the gene. Am
Naturalist. 51:513–544. 1917. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Becker S, Oelschlaeger TA, Wullaert A,
Vlantis K, Pasparakis M, Wehkamp J, Stange EF and Gersemann M:
Bacteria regulate intestinal epithelial cell differentiation
factors both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One. 8:e556202013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Maier D, Kurth P, Schulz A, Russell A,
Yuan Z, Gruber K, Kovall RA and Preiss A: Structural and functional
analysis of the repressor complex in the Notch signaling pathway of
Drosophila melanogaster. Mol Biol Cell. 22:3242–3252. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Braune EB and Lendahl U: Notch-a
goldilocks signaling pathway in disease and cancer therapy. Discov
Med. 21:189–196. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Del Bianco C, Vedenko A, Choi SH, Berger
MF, Shokri L, Bulyk ML and Blacklow SC: Notch and MAML-1
complexation do not detectably alter the DNA binding specificity of
the transcription factor CSL. PLoS One. 5:e150342010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Faux CH, Turnley AM, Epa R, Cappai R and
Bartlett PF: Interactions between fbroblast growth factors and
Notch regulate neuronal differentiation. J Neurosci. 21:5587–5596.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shimizu K, Chiba S, Kumano K, Hosoya N,
Takahashi T, Kanda Y, Hamada Y, Yazaki Y and Hirai H: Mouse jagged1
physically interacts with notch2 and other notch receptors.
Assessment by quantitative methods. J Biol Chem. 274:32961–32969.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang S, Chung WC, Wu G, Egan SE and Xu K:
Tumor-suppressive activity of Lunatic Fringe in prostate through
differential modulation of Notch receptor activation. Neoplasia.
16:158–167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bresnick EH, Chu J, Christensen HM, Lin B
and Norton J: Linking Notch signaling, chromatin remodeling, and
T-cell leukemogenesis. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 35(Suppl): S46–S53.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Nam Y, Weng AP, Aster JC and Blacklow SC:
Structural requirements for assembly of the CSL. Intracellular
Notch1. Mastermind-like 1 transcriptional activation complex. J
Biol Chem. 278:21232–21239. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Portin P: General outlines of the
molecular genetics of the Notch signalling pathway in Drosophila
melanogaster. A review Hereditas. 136:89–96. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Li Y and Baker NE: Proneural enhancement
by Notch overcomes Suppressor-of-Hairless repressor function in the
developing Drosophila eye. Curr Biol. 11:330–338. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang J, Ye Z, Zheng S, Chen L, Wan Y, Deng
Y and Yang R: Lingo-1 shRNA and Notch signaling inhibitor DAPT
promote differentiation of neural stem/progenitor cells into.
neurons Brain Res. 1634:34–44. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Cardano M, Diaferia GR, Cattaneo M, Dessí
SS, Long Q, Conti L, Deblasio P, Cattaneo E and Biunno I: mSEL-1L
(Suppressor/enhancer Lin12-like) protein levels influence murine
neural stem cell self-renewal and lineage commitment. J Biol Chem.
286:18708–18719. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Berezovska O, Xia MQ and Hyman BT: Notch
is expressed in adult brain, is coexpressed with presenilin-1, and
is altered in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol.
57:738–745. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Nagarsheth MH, Viehman A, Lippa SM and
Lippa CF: Notch-1 immunoexpression is increased in Alzheimer's and
Pick's disease. J Neurol Sci. 244:111–116. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Cairney CJ, Sanguinetti G, Ranghini E,
Chantry AD, Nostro MC, Bhattacharyya A, Svendsen CN, Keith WN and
Bellantuono I: A systems biology approach to Down syndrome:
Identification of Notch/Wnt dysregulation in a model of stem cells
aging. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1792:353–363. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Fernandez-Martinez J, Vela EM,
Tora-Ponsioen M, Ocaña OH, Nieto MA and Galceran J: Attenuation of
Notch signalling by the Down-syndrome-associated kinase DYRK1A. J
Cell Sci. 122:1574–1583. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
García-Estévez DA, Barros-Angueira F and
Navarro C: CADASIL: Brief report on a family with a new p.G296C
mutation in exon 6 of the Notch-3 gene. Rev Neurol. 51:729–732.
2010.In Spanish.
|
|
42
|
Tang SC, Jeng JS, Lee MJ and Yip PK: Notch
signaling and CADASIL. Acta Neurol Taiwan. 18:81–90.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Louvi A, Arboleda-Velasquez JF and
Artavanis-Tsakonas S: CADASIL: A critical look at a Notch disease.
Dev Neurosci. 28:5–12. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Tan ZX, Li FF, Qu YY, Liu J, Liu GR, Zhou
J, Zhu YL and Liu SL: Identification of a known mutation in Notch 3
in familiar CADASIL in China. PLoS One. 7:e365902012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Posada-Duque RA, Barreto GE and
Cardona-Gomez GP: Protection after stroke: Cellular effectors of
neurovascular unit integrity. Front Cell Neurosci. 8:2312014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cotena S, Piazza O and Tufano R: The use
of erythtropoietin in cerebral diseases. Panminerva Med.
50:185–192. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Lou YL, Guo F, Liu F, Gao FL, Zhang PQ,
Niu X, Guo SC, Yin JH, Wang Y and Deng ZF: miR-210 activates notch
signaling pathway in angiogenesis induced by cerebral ischemia. Mol
Cell Biochem. 370:45–51. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Corada M, Morini MF and Dejana E:
Signaling pathways in the specifcation of arteries and veins.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 34:2372–2377. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Grieskamp T, Rudat C, Lüdtke TH, Norden J
and Kispert A: Notch signaling regulates smooth muscle
differentiation of epicardium-derived cells. Circ Res. 108:813–823.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
del Monte G, Casanova JC, Guadix JA,
MacGrogan D, Burch JB, Pérez-Pomares JM and de la Pompa JL:
Differential Notch signaling in the epicardium is required for
cardiac inflow development and coronary vessel morphogenesis. Circ
Res. 108:824–836. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Proweller A, Wright AC, Horng D, Cheng L,
Lu MM, Lepore JJ, Pear WS and Parmacek MS: Notch signaling in
vascular smooth muscle cells is required to pattern the cerebral
vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:16275–16280. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Koga J, Nakano T, Dahlman JE, Figueiredo
JL, Zhang H, Decano J, Khan OF, Niida T, Iwata H, Aster JC, et al:
Macrophage Notch Ligand Delta-Like 4 Promotes Vein Graft Lesion
Development: Implications for the Treatment of Vein Graft Failure.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:2343–2353. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Quillien A, Moore JC, Shin M, Siekmann AF,
Smith T, Pan L, Moens CB, Parsons MJ and Lawson ND: Distinct Notch
signaling outputs pattern the developing arterial system.
Development. 141:1544–1552. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Zacharek A, Chen J, Cui X, Yang Y and
Chopp M: Simvastatin increases notch signaling activity and
promotes arteriogenesis after stroke. Stroke. 40:254–260. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chen J, Cui X, Zacharek A, Ding GL,
Shehadah A, Jiang Q, Lu M and Chopp M: Niaspan treatment increases
tumor necrosis factor-alpha-converting enzyme and promotes
arteriogenesis after stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 29:911–920.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Di Napoli M and Shah IM: Neuroinflammation
and cerebrovascular disease in old age: A translational medicine
perspective. J Aging Res. 2011:8574842011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Felsky D, De Jager PL, Schneider JA,
Arfanakis K, Fleischman DA, Arvanitakis Z, Honer WG, Pouget JG,
Mizrahi R, Pollock BG, et al: Cerebrovascular and microglial states
are not altered by functional neuroinflammatory gene variant. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 36:819–830. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Cacabelos R, Torrellas C, Fernández-Novoa
L and Aliev G: Neuroimmune Crosstalk in CNS Disorders: The
Histamine Connection. Curr Pharm Des. 22:819–848. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Silva J, Polesskaya O, Knight W, Zheng JT,
Granger M, Lopez T, Ontiveros F, Feng C, Yan C, Kasischke KA and
Dewhurst S: Transient hypercapnia reveals an underlying
cerebrovascular pathology in a murine model for HIV-1 associated
neuroinflammation: Role of NO-cGMP signaling and normalization by
inhibition of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase-5. J
Neuroinflammation. 9:2532012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Meschia JF and Worrall BB: New advances in
identifying genetic anomalies in stroke-prone probands. Curr
Atheroscler Rep. 5:317–323. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Heo R, Park JS, Jang HJ, Kim SH, Shin JM,
Suh YD, Jeong JH, Jo DG and Park JH: Hyaluronan nanoparticles
bearing γ-secretase inhibitor: In vivo therapeutic effects on
rheumatoid arthritis. J Control Release. 192:295–300. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Lucitti JL, Mackey JK, Morrison JC, Haigh
JJ, Adams RH and Faber JE: Formation of the collateral circulation
is regulated by vascular endothelial growth factor-A and a
disintegrin and metal-loprotease family members 10 and 17. Circ
Res. 111:1539–1550. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Brifault C, Gras M, Liot D, May V, Vaudry
D and Wurtz O: Delayed pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating
polypeptide delivery after brain stroke improves functional
recovery by inducing m2 microglia/macrophage polarization. Stroke.
46:520–528. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Holden JA, Attard TJ, Laughton KM, Mansell
A, O'Brien-Simpson NM and Reynolds EC: Porphyromonas gingivalis
lipopolysaccharide weakly activates M1 and M2 polarized mouse
macrophages but induces inflammatory cytokines. Infect Immun.
82:4190–4203. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Zhang Y, He K, Wang F, Li X and Liu D:
Notch-1 signaling regulates astrocytic proliferation and activation
after hypoxia exposure. Neurosci Lett. 603:12–18. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Meschia JF and Worrall BB: New advances in
identifying genetic anomalies in stroke-prone probands. Curr Neurol
Neurosci Rep. 4:420–426. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Xu J, Chi F, Guo T, Punj V, Lee WN, French
SW and Tsukamoto H: NOTCH reprograms mitochondrial metabolism for
proinflammatory macrophage activation. J Clin Invest.
125:1579–1590. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Pei H, Song X, Peng C, Tan Y, Li Y, Li X,
Ma S, Wang Q, Huang R, Yang D, et al: TNF-α inhibitor protects
against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via Notch1-mediated
suppression of oxidative/nitrative stress. Free Radic Biol Med.
82:114–121. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Qin WD, Zhang F, Qin XJ, Wang J, Meng X,
Wang H, Guo HP, Wu QZ, Wu DW and Zhang MX: Notch1 inhibition
reduces low shear stress-induced plaque formation. Int J Biochem
Cell Biol. 72:63–72. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Palaga T, Buranaruk C, Rengpipat S, Fauq
AH, Golde TE, Kaufmann SH and Osborne BA: Notch signaling is
activated by TLR stimulation and regulates macrophage functions.
Eur J Immunol. 38:174–183. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Cao Q, Kaur C, Wu CY, Lu J and Ling EA:
Nuclear factor-kappa β regulates Notch signaling in production of
proinflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide in murine BV-2
microglial cells. Neuroscience. 192:140–154. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Fang M, Yuan Y, Rangarajan P, Lu J, Wu Y,
Wang H, Wu C and Ling EA: Scutellarin regulates microglia-mediated
TNC1 astrocytic reaction and astrogliosis in cerebral ischemia in
the adult rats. BMC Neurosci. 16:842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Zhou D, Huang C, Lin Z, Zhan S, Kong L,
Fang C and Li J: Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis
on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular
signaling pathways. Cell Signal. 26:192–197. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Qiu Y, Du B, Xie F, Cai W, Liu Y, Li Y,
Feng L and Qiu L: Vaccarin attenuates high glucose-induced human
EA•hy926 endothelial cell injury through inhibition of Notch
signaling. Mol Med Rep. 13:2143–2150. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Henshall TL, Keller A, He L, Johansson BR,
Wallgard E, Raschperger E, Mäe MA, Jin S, Betsholtz C and Lendahl
U: Notch3 is necessary for blood vessel integrity in the central
nervous system. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 35:409–420. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
76
|
Yu LM, Chen DX, Zhou QX, Fang N and Liu
ZL: Effects of histamine on immunophenotype and notch signaling in
human HL-60 leukemia cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 231:1633–1637.
2006.
|
|
77
|
Boulos N, Helle F, Dussaule JC, Placier S,
Milliez P, Djudjaj S, Guerrot D, Joutel A, Ronco P, Boffa JJ and
Chatziantoniou C: Notch3 is essential for regulation of the renal
vascular tone. Hypertension. 57:1176–1182. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Fischer AJ, Zelinka C, Gallina D, Scott MA
and Todd L: Reactive microglia and macrophage facilitate the
formation of Müller glia-derived retinal progenitors. Glia.
62:1608–1628. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Shipp LE, Hill RZ, Moy GW, Gokirmak T and
Hamdoun A: ABCC5 is required for cAMP-mediated hindgut invagination
in sea urchin embryos. Development. 142:3537–3548. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Bartosh TJ, Ylostalo JH, Bazhanov N,
Kuhlman J and Prockop DJ: Dynamic compaction of human mesenchymal
stem/precursor cells into spheres self-activates caspase-dependent
IL1 signaling to enhance secretion of modulators of inflammation
and immunity (PGE2, TSG6, and STC1). Stem Cells. 31:2443–2456.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Clement N, Gueguen M, Glorian M, Blaise R,
Andréani M, Brou C, Bausero P and Limon I: Notch3 and IL-1beta
exert opposing effects on a vascular smooth muscle cell
inflammatory pathway in which NF-kappaB drives crosstalk. J Cell
Sci. 120:3352–3361. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Ali M, Heyob K and Rogers LK: DHA
suppresses primary macrophage inflammatory responses via Notch
1/Jagged 1 signaling. Sci Rep. 6:222762016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
83
|
Yin J, Li H, Feng C and Zuo Z: Inhibition
of brain ischemia-caused notch activation in microglia may
contribute to isoflurane postconditioning-induced neuroprotection
in male rats. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 13:718–732. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Liu Q, Fan X, Zhu J, Xu G, Li Y and Liu X:
Co-culturing improves the OGD-injured neuron repairing and NSCs
differentiation via Notch pathway activation. Neurosci Lett.
559:1–6. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
85
|
Albéri L, Chi Z, Kadam SD, Mulholland JD,
Dawson VL, Gaiano N and Comi AM: Neonatal stroke in mice causes
long-term changes in neuronal Notch-2 expression that may
contribute to prolonged injury. Stroke. 41(Suppl 10): S64–S71.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Lipsey CC, Harbuzariu A, Daley-Brown D and
Gonzalez-Perez RR: Oncogenic role of leptin and Notch interleukin-1
leptin crosstalk outcome in cancer. World J Methodol. 6:43–55.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Grill M, Syme TE, Nocon AL, Lu AZ, Hancock
D, Rose-John S and Campbell IL: Strawberry notch homolog 2 is a
novel inflammatory response factor predominantly but not
exclusively expressed by astrocytes in the central nervous system.
Glia. 63:1738–1752. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wang H, Tian Y, Wang J, Phillips KL, Binch
AL, Dunn S, Cross A, Chiverton N, Zheng Z, Shapiro IM, et al:
Inflammatory cytokines induce NOTCH signaling in nucleus pulposus
cells: Implications in intervertebral disc degeneration. J Biol
Chem. 288:16761–16774. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Keuylian Z, de Baaij JH, Gueguen M,
Glorian M, Rouxel C, Merlet E, Lipskaia L, Blaise R, Mateo V and
Limon I: The Notch pathway attenuates interleukin 1β
(IL1β)-mediated induction of adenylyl cyclase 8 (AC8) expression
during vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) trans-differentiation. J
Biol Chem. 287:24978–24989. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Mirandola L, Apicella L, Colombo M, Yu Y,
Berta DG, Platonova N, Lazzari E, Lancellotti M, Bulfamante G,
Cobos E, et al: Anti-Notch treatment prevents multiple myeloma
cells localization to the bone marrow via the chemokine system
CXCR4/SDF-1. Leukemia. 27:1558–1566. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Fukuda D, Aikawa E, Swirski FK,
Novobrantseva TI, Kotelianski V, Gorgun CZ, Chudnovskiy A, Yamazaki
H, Croce K, Weissleder R, et al: Notch ligand delta-like 4 blockade
attenuates atherosclerosis and metabolic disorders. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:E1868–E1877. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Al Haj Zen A, Oikawa A, Bazan-Peregrino M,
Meloni M, Emanueli C and Madeddu P: Inhibition of
delta-like-4-mediated signaling impairs reparative angiogenesis
after ischemia. Circ Res. 107:283–293. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Kumari B, Jain P, Das S, Ghosal S, Hazra
B, Trivedi AC, Basu A, Chakrabarti J, Vrati S and Banerjee A:
Dynamic changes in global microRNAome and transcriptome reveal
complex miRNA-mRNA regulated host response to Japanese Encephalitis
Virus in microglial cells. Sci Rep. 6:202632016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Yao L, Cao Q, Wu C, Kaur C, Hao A and Ling
EA: Notch signaling in the central nervous system with special
reference to its expression in microglia. CNS Neurol Disord Drug
Targets. 12:807–814. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Salta E, Lau P, Sala Frigerio C, Coolen M,
Bally-Cuif L and De Strooper B: A self-organizing miR-132/Ctbp2
circuit regulates bimodal notch signals and glial progenitor fate
choice during spinal cord maturation. Dev Cell. 30:423–436. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Grandbarbe L, Michelucci A, Heurtaux T,
Hemmer K, Morga E and Heuschling P: Notch signaling modulates the
activation of microglial cells. Glia. 55:1519–1530. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Morgan SC, Taylor DL and Pocock JM:
Microglia release activators of neuronal proliferation mediated by
activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase,
phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Akt and delta-Notch signalling
cascades. J Neurochem. 90:89–101. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Arumugam TV, Chan SL, Jo DG, Yilmaz G,
Tang SC, Cheng A, Gleichmann M, Okun E, Dixit VD, Chigurupati S, et
al: Gamma secretase-mediated Notch signaling worsens brain damage
and functional outcome in ischemic stroke. Nat Med. 12:621–623.
2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
99
|
Liu HC, Zheng MH, Du YL, Wang L, Kuang F,
Qin HY, Zhang BF and Han H: N9 microglial cells polarized by LPS
and IL4 show differential responses to secondary environmental
stimuli. Cell Immunol. 278:84–90. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Yao L, Kan EM, Kaur C, Dheen ST, Hao A, Lu
J and Ling EA: Notch-1 signaling regulates microglia activation via
NF-κB pathway after hypoxic exposure in vivo and in vitro. PLoS
One. 8:e784392013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
101
|
Cao Q, Lu J, Kaur C, Sivakumar V, Li F,
Cheah PS, Dheen ST and Ling EA: Expression of Notch-1 receptor and
its ligands Jagged-1 and Delta-1 in amoeboid microglia in postnatal
rat brain and murine BV-2 cells. Glia. 56:1224–1237. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Morga E, Mouad-Amazzal L, Felten P,
Heurtaux T, Moro M, Michelucci A, Gabel S, Grandbarbe L and
Heuschling P: Jagged1 regulates the activation of astrocytes via
modulation of NFkappaB and JAK/STAT/SOCS pathways. Glia.
57:1741–1753. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Nardai S, Dobolyi A, Pál G, Skopál J,
Pintér N, Lakatos K, Merkely B and Nagy Z: Selegiline promotes
NOTCH-JAGGED signaling in astrocytes of the peri-infarct region and
improves the functional integrity of the neurovascular unit in a
rat model of focal ischemia. Restor Neurol Neurosci. 33:1–14.
2015.
|
|
104
|
Monsalve E, Ruiz-García A, Baladrón V,
Ruiz-Hidalgo MJ, Sánchez-Solana B, Rivero S, García-Ramírez JJ,
Rubio A, Laborda J and Díaz-Guerra MJ: Notch1 upregulates
LPS-induced macrophage activation by increasing NF-kappaB activity.
Eur J Immunol. 39:2556–2570. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Jones DP: Extracellular redox state:
Refining the definition of oxidative stress in aging. Rejuvenation
Res. 9:169–181. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Darley-Usmar V and Halliwell B: Blood
radicals: Reactive nitrogen species, reactive oxygen species,
transition metal ions, and the vascular system. Pharm Res.
13:649–662. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
107
|
Wu JQ, Kosten TR and Zhang XY: Free
radicals, antioxidant defense systems, and schizophrenia. Prog
Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 46:200–206. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
108
|
Catarino MD, Alves-Silva JM, Pereira OR
and Cardoso SM: Antioxidant capacities of favones and benefts in
oxidative-stress related diseases. Curr Top Med Chem. 15:105–119.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
109
|
Lee JC and Won MH: Neuroprotection of
antioxidant enzymes against transient global cerebral ischemia in
gerbils. Anat Cell Biol. 47:149–156. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Valko M, Morris H and Cronin MT: Metals,
toxicity and oxidative stress. Curr Med Chem. 12:1161–1208. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Wu D and Yotnda P: Production and
detection of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cancers. J Vis Exp.
pii: 3357. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Reiter RJ, Tan DX, Manchester LC and Qi W:
Biochemical reactivity of melatonin with reactive oxygen and
nitrogen species: A review of the evidence. Cell Biochem Biophys.
34:237–256. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
113
|
Reiter RJ, Acuña-Castroviejo D, Tan DX and
Burkhardt S: Free radical-mediated molecular damage. Mechanisms for
the protective actions of melatonin in the central nervous system.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 939:200–215. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Hemnani T and Parihar MS: Reactive oxygen
species and oxidative DNA damage. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol.
42:440–452. 1998.
|
|
115
|
Rodrigo R, Fernández-Gajardo R, Gutiérrez
R, Matamala JM, Carrasco R, Miranda-Merchak A and Feuerhake W:
Oxidative stress and pathophysiology of ischemic stroke: Novel
therapeutic opportunities. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets.
12:698–714. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Oprea E, Berteanu M, Cintezã D and
Manolescu BN: The effect of the ALAnerv nutritional supplement on
some oxidative stress markers in postacute stroke patients
undergoing rehabilitation. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 38:613–620.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Liang H, Zhang Y, Shi X, Wei T and Lou J:
Role of Notch-1 signaling pathway in PC12 cell apoptosis induced by
amyloid beta-peptide (25–35). Neural Regen Res. 9:1297–1302. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Braidy N, Jayasena T, Poljak A and Sachdev
PS: Sirtuins in cognitive ageing and Alzheimer's disease. Curr Opin
Psychiatry. 25:226–230. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Nakane H, Kamouchi M, Hata J, Ibayashi S,
Kusuda K, Omae T, Nagao T, Ago T and Kitazono T; EMINENT Study
Investigators: Effects of hydrochlorothiazide on oxidative stress
and pulse pressure in hypertensive patients with chronic stroke:
The EMINENT study. Intern Med. 54:573–577. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Nakagawa T, Hasegawa Y, Uekawa K, Ma M,
Katayama T, Sueta D, Toyama K, Kataoka K, Koibuchi N, Maeda M, et
al: Renal denervation prevents stroke and brain injury via
attenuation of oxidative stress in hypertensive rats. J Am Heart
Assoc. 2:e0003752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Das UN: Can free radicals induce coronary
vasospasm and acute myocardial infarction? Med Hypotheses.
39:90–94. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Manzanero S, Santro T and Arumugam TV:
Neuronal oxidative stress in acute ischemic stroke: Sources and
contribution to cell injury. Neurochem Int. 62:712–718. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
123
|
Cojocaru IM, Cojocaru M, Sapira V and
Ionescu A: Evaluation of oxidative stress in patients with acute
ischemic stroke. Rom J Intern Med. 51:97–106. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Icme F, Erel Ö, Avci A, Satar S, Gülen M
and Acehan S: The relation between oxidative stress parameters,
ischemic stroke, and hemorrhagic stroke. Turk J Med Sci.
45:947–953. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Simão AN, Lehmann MF, Alferi DF, Meloni
MZ, Flauzino T, Scavuzzi BM, de Oliveira SR, Lozovoy MA, Dichi I
and Reiche EM: Metabolic syndrome increases oxidative stress but
does not influence disability and short-time outcome in acute
ischemic stroke patients. Metab Brain Dis. 30:1409–1416. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
126
|
Tsai NW, Chang YT, Huang CR, Lin YJ, Lin
WC, Cheng BC, Su CM, Chiang YF, Chen SF, Huang CC, et al:
Association between oxidative stress and outcome in different
subtypes of acute ischemic stroke. Biomed Res Int. 2014:2568792014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
127
|
Pantcheva P, Elias M, Duncan K, Borlongan
CV, Tajiri N and Kaneko Y: The role of DJ-1 in the oxidative stress
cell death cascade after stroke. Neural Regen Res. 9:1430–1433.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
128
|
Nabavi SF, Dean OM, Turner A, Sureda A,
Daglia M and Nabavi SM: Oxidative stress and post-stroke
depression: Possible therapeutic role of polyphenols? Curr Med
Chem. 22:343–351. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
129
|
Gonullu H, Aslan M, Karadas S, Kati C,
Duran L, Milanlioglu A, Aydin MN and Demir H: Serum prolidase
enzyme activity and oxidative stress levels in patients with acute
hemorrhagic stroke. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 74:199–205. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
130
|
El Kossi MM and Zakhary MM: Oxidative
stress in the context of acute cerebrovascular stroke. Stroke.
31:1889–1892. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
131
|
Milanlioglu A, Aslan M, Ozkol H, Çilingir
V, Nuri Aydin M and Karadas S: Serum antioxidant enzymes activities
and oxidative stress levels in patients with acute ischemic stroke:
Influence on neurological status and outcome. Wien Klin Wochenschr.
128:169–174. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
132
|
Newton DF, Naiberg MR and Goldstein BI:
Oxidative stress and cognition amongst adults without dementia or
stroke: Implications for mechanistic and therapeutic research in
psychiatric disorders. Psychiatry Res. 227:127–134. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
133
|
Nakajima H, Kubo T, Ihara H, Hikida T,
Danjo T, Nakatsuji M, Shahani N, Itakura M, Ono Y, Azuma YT, et al:
Nuclear-translocated Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
promotes poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation during
Oxidative/Nitrosative stress in stroke. J Biol Chem.
290:14493–14503. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
134
|
Kotur-Stevuljevic J, Bogavac-Stanojevic N,
Jelic-Ivanovic Z, Stefanovic A, Gojkovic T, Joksic J, Sopic M,
Gulan B, Janac J and Milosevic S: Oxidative stress and paraoxonase
1 status in acute ischemic stroke patients. Atherosclerosis.
241:192–198. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
135
|
Han Z, Shen F, He Y, Degos V, Camus M,
Maze M, Young WL and Su H: Activation of α-7 nicotinic
acetylcholine receptor reduces ischemic stroke injury through
reduction of pro-inflammatory macrophages and oxidative stress.
PLoS One. 9:e1057112014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
136
|
Lagowska-Lenard M, Bielewicz J, Raszewski
G, Stelmasiak Z and Bartosik-Psujek H: Oxidative stress in cerebral
stroke. Pol Merkur Lekarski. 25:205–208. 2008.In Polish.
|
|
137
|
Takemori K, Murakami T, Kometani T and Ito
H: Possible involvement of oxidative stress as a causative factor
in blood-brain barrier dysfunction in stroke-prone spontaneously
hypertensive rats. Microvasc Res. 90:169–172. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
138
|
Hung LM, Huang JP, Liao JM, Yang MH, Li
DE, Day YJ and Huang SS: Insulin renders diabetic rats resistant to
acute ischemic stroke by arresting nitric oxide reaction with
superoxide to form peroxynitrite. J Biomed Sci. 21:922014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
139
|
Fabian RH and Kent TA: Hyperglycemia
accentuates persistent 'functional uncoupling' of cerebral
microvascular nitric oxide and superoxide following focal
ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Transl Stroke Res. 3:482–490. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
140
|
Fabian RH, Perez-Polo JR and Kent TA:
Perivascular nitric oxide and superoxide in neonatal cerebral
hypoxia-ischemia. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 295:H1809–H1814.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
141
|
Gümüştaş K, Meta Güzeyli FM, Atükeren P,
Sanus GZ, Kemerdere R, Tanriverdi T and Kaynar MY: The effects of
vitamin E on lipid peroxidation, nitric oxide production and
superoxide dismutase expression in hyperglycemic rats with cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Turk Neurosurg. 17:78–82. 2007.
|
|
142
|
Forman LJ, Liu P, Nagele RG, Yin K and
Wong PY: Augmentation of nitric oxide, superoxide, and
peroxynitrite production during cerebral ischemia and reperfusion
in the rat. Neurochem Res. 23:141–148. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
143
|
Brosnan MJ, Hamilton CA, Graham D, Lygate
CA, Jardine E and Dominiczak AF: Irbesartan lowers superoxide
levels and increases nitric oxide bioavailability in blood vessels
from spontaneously hypertensive stroke-prone rats. J Hypertens.
20:281–286. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
144
|
Baumeister P, Huebner T, Reiter M,
Schwenk-Zieger S and Harréus U: Reduction of oxidative DNA
fragmentation by ascorbic acid, zinc and N-acetylcysteine in nasal
mucosa tissue cultures. Anticancer Res. 29:4571–4574.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
145
|
Mikhaĭlov VF, Mazurik VK and Burlakova EB:
Signal function of the reactive oxygen species in regulatory
networks of the cell reaction to damaging effects: Contribution of
radiosensitivity and genome instability. Radiats Biol Radioecol.
43:5–18. 2003.In Russian.
|
|
146
|
Fischer-Nielsen A, Corcoran GB, Poulsen
HE, Kamendulis LM and Loft S: Menadione-induced DNA fragmentation
without 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine formation in isolated rat
hepatocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 49:1469–1474. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
147
|
Zhou T, He Q, Tong Y, Zhan R, Xu F, Fan D,
Guo X, Han H, Qin S and Chui D: Phospholipid transfer protein
(PLTP) deficiency impaired blood-brain barrier integrity by
increasing cerebrovascular oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 445:352–356. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
148
|
Tóth AE, Walter FR, Bocsik A, Sántha P,
Veszelka S, Nagy L, Puskás LG, Couraud PO, Takata F, Dohgu S, et
al: Edaravone protects against methylglyoxal-induced barrier damage
in human brain endothelial cells. PLoS One. 9:e1001522014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
149
|
Elmorsy E, Elzalabany LM, Elsheikha HM and
Smith PA: Adverse effects of antipsychotics on micro-vascular
endothelial cells of the human blood-brain barrier. Brain Res.
1583:255–268. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
150
|
Sathanoori R, Swärd K, Olde B and Erlinge
D: The ATP Receptors P2X7 and P2X4 modulate high glucose and
Palmitate-Induced inflammatory responses in endothelial cells. PLoS
One. 10:e01251112015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
151
|
Okada R, Wu Z, Zhu A, Ni J, Zhang J,
Yoshimine Y, Peters C, Saftig P and Nakanishi H: Cathepsin D
deficiency induces oxidative damage in brain pericytes and impairs
the blood-brain barrier. Mol Cell Neurosci. 64:51–60. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
152
|
Abdul-Muneer PM, Chandra N and Haorah J:
Interactions of oxidative stress and neurovascular infammation in
the pathogenesis of traumatic brain injury. Mol Neurobiol.
51:966–979. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
153
|
Ste-Marie L, Hazell AS, Bémeur C,
Butterworth R and Montgomery J: Immunohistochemical detection of
inducible nitric oxide synthase, nitrotyrosine and manganese
superoxide dismutase following hyperglycemic focal cerebral
ischemia. Brain Res. 918:10–19. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
154
|
Kumura E, Yoshimine T, Kubo S, Tanaka S,
Hayakawa T, Shiga T and Kosaka H: Effects of superoxide dismutase
on nitric oxide production during reperfusion after focal cerebral
ischemia is rats. Neurosci Lett. 200:137–140. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
155
|
Al-Maghrebi M and Renno WM: Genistein
alleviates testicular ischemia and reperfusion injury-induced
sper-matogenic damage and oxidative stress by suppressing abnormal
testicular matrix metalloproteinase system via the Notch 2/Jagged
1/Hes-1 and caspase-8 pathways. J Physiol Pharmacol. 67:129–137.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
156
|
Xie H, Sun J, Chen Y, Zong M, Li S and
Wang Y: EGCG attenuates uric Acid-Induced inflammatory and
oxidative stress responses by medicating the NOTCH pathway. Oxid
Med Cell Longev. 2015:2148362015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
157
|
Xie F, Cai W, Liu Y, Li Y, Du B, Feng L
and Qiu L: Vaccarin attenuates the human EA.hy926 endothelial cell
oxidative stress injury through inhibition of Notch signaling. Int
J Mol Med. 35:135–142. 2015.
|
|
158
|
Yang Y, Duan W, Liang Z, Yi W, Yan J, Wang
N, Li Y, Chen W, Yu S, Jin Z and Yi D: Curcumin attenuates
endothelial cell oxidative stress injury through Notch signaling
inhibition. Cell Signal. 25:615–629. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
159
|
Li M, Chen F, Clifton N, Sullivan DM,
Dalton WS, Gabrilovich DI and Nefedova Y: Combined inhibition of
Notch signaling and Bcl-2/Bcl-xL results in synergistic antimyeloma
effect. Mol Cancer Ther. 9:3200–3209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
160
|
Chen C, Cui H, Li Z, Wang R and Zhou C:
Normobaric oxygen for cerebral ischemic injury. Neural Regen Res.
8:2885–2894. 2013.
|
|
161
|
Zhu B, Yang P, Mammat N, Ding H, He J,
Qian Y, Fei J and Abdukerim K: Aiweixin, a traditional Uyghur
medicinal formula, protects against chromium toxicity in
Caenorhabditis elegans. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:2852015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
162
|
Finsterer J: Neuromuscular implications in
CADASIL. Cerebrovasc Dis. 24:401–404. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
163
|
Santoni M, Pantano F, Amantini C, Nabissi
M, Conti A, Burattini L, Zoccoli A, Berardi R, Santoni G, Tonini G,
et al: Emerging strategies to overcome the resistance to current
mTOR inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1845:221–231. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
164
|
Pei H, Yu Q, Xue Q, Guo Y, Sun L, Hong Z,
Han H, Gao E, Qu Y and Tao L: Notch1 cardioprotection in myocardial
ischemia/reperfusion involves reduction of oxidative/nitrative
stress. Basic Res Cardiol. 108:3732013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
165
|
Simón R, Aparicio R, Housden BE, Bray S
and Busturia A: Drosophila p53 controls Notch expression and
balances apoptosis and proliferation. Apoptosis. 19:1430–1443.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
166
|
Zheng WX, Cao XL, Wang F, Wang J, Ying TZ,
Xiao W, Zhang Y, Xing H, Dong W, Xu SQ, et al: Baicalin inhibiting
cerebral ischemia/hypoxia-induced neuronal apoptosis via
MRTF-A-mediated transactivity. Eur J Pharmacol. 767:201–210. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
167
|
Baroja-Mazo A, Martín-Sánchez F, Gomez AI,
Martínez CM, Amores-Iniesta J, Compan V, Barberà-Cremades M, Yagüe
J, Ruiz-Ortiz E, Antón J, et al: The NLRP3 inflammasome is released
as a particulate danger signal that amplifes the inflammatory
response. Nat Immunol. 15:738–748. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
168
|
Yang RY and Liu FT: Galectins in cell
growth and apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 60:267–276. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
169
|
Bao JX, Su YT, Cheng YP, Zhang HJ, Xie XP
and Chang YM: Vascular sphingolipids in physiological and
pathological adaptation. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 21:1168–1186.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
170
|
Kagiya G, Ogawa R, Tabuchi Y, Feril LB Jr,
Nozaki T, Fukuda S, Yamamoto K and Kondo T: Expression of heme
oxygenase-1 due to intracellular reactive oxygen species induced by
ultrasound. Ultrason Sonochem. 13:388–396. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
171
|
Santiago B, Galindo M, Palao G and Pablos
JL: Intracellular regulation of Fas-induced apoptosis in human
fibroblasts by extracellular factors and cycloheximide. J Immunol.
172:560–566. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
172
|
Wang L, Song G, Liu M, Chen B, Chen Y,
Shen Y, Zhu J and Zhou X: MicroRNA-375 overexpression influences
P19 cell proliferation, apoptosis and differentiation through the
Notch signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med. 37:47–55. 2016.
|
|
173
|
Aboutaleb N, Shamsaei N, Khaksari M,
Erfani S, Rajabi H and Nikbakht F: Pre-ischemic exercise reduces
apoptosis in hippocampal CA3 cells after cerebral ischemia by
modulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 proteins ratio and prevention of
caspase-3 activation. J Physiol Sci. 65:435–443. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
174
|
Zhang JF, Shi LL, Zhang L, Zhao ZH, Liang
F, Xu X, Zhao LY, Yang PB, Zhang JS and Tian YF: MicroRNA-25
negatively regulates cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury-Induced
cell apoptosis through Fas/FasL pathway. J Mol Neurosci.
58:507–516. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
175
|
Xue R, Wu G, Wei X, Lv J, Fu R, Lei X,
Zhang Z, Li W, He J, Zhao H, et al: Tea polyphenols may attenuate
the neurocognitive impairment caused by global cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury via anti-apoptosis. Nutr Neurosci.
19:63–69. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
176
|
Yang Y, Gao K, Hu Z, Li W, Davies H, Ling
S, Rudd JA and Fang M: Autophagy upregulation and apoptosis
downregulation in DAHP and triptolide treated cerebral ischemia.
Mediators Inflamm. 2015:1201982015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
177
|
Wu L, Zhao QS, Li TW, Li HY, Wang QB, Bi
XY, Cai XK and Tang N: Yifei Xuanfei Jiangzhuo formula, a Chinese
herbal decoction, improves memory impairment through inhibiting
apoptosis and enhancing PKA/CREB signal transduction in rats with
cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Med Rep. 12:4273–4283.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
178
|
Saad MA, Abdelsalam RM, Kenawy SA and
Attia AS: Ischemic preconditioning and postconditioning alleviates
hippocampal tissue damage through abrogation of apoptosis modulated
by oxidative stress and inflammation during transient global
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Chem Biol Interact.
232:21–29. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
179
|
Fan M, Jin W, Zhao H, Xiao Y, Jia Y, Yin
Y, Jiang X, Xu J, Meng N and Lv P: Lithium chloride administration
prevents spatial learning and memory impairment in repeated
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion mice by depressing apoptosis and
increasing BDNF expression in hippocampus. Behav Brain Res.
291:399–406. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
180
|
Garrigue P, Giacomino L, Bucci C, Muzio V,
Filannino MA, Sabatier F, Dignat-George F, Pisano P and Guillet B:
Single photon emission computed tomography imaging of cerebral
blood flow, blood-brain barrier disruption, and apoptosis time
course after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Int J Stroke.
11:117–126. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
181
|
Cao G, Zhou H, Jiang N, Han Y, Hu Y, Zhang
Y, Qi J, Kou J and Yu B: YiQiFuMai powder injection ameliorates
cerebral ischemia by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum
Stress-Mediated neuronal apoptosis. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2016:54932792016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
182
|
Yan XG, Cheng BH, Wang X, Ding LC, Liu HQ,
Chen J and Bai B: Lateral intracerebroventricular injection of
Apelin-13 inhibits apoptosis after cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Neural Regen Res. 10:766–771. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
183
|
Saad MA, Abdel Salam RM, Kenawy SA and
Attia AS: Pinocembrin attenuates hippocampal inflammation,
oxidative perturbations and apoptosis in a rat model of global
cerebral ischemia reperfusion. Pharmacol Rep. 67:115–122. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
184
|
Jiang Y, Li L, Tan X, Liu B, Zhang Y and
Li C: miR-210 mediates vagus nerve stimulation-induced antioxidant
stress and anti-apoptosis reactions following cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. J Neurochem. 134:173–181.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
185
|
Chopp M and Li Y: Apoptosis in focal
cerebral ischemia. Acta Neurochir Suppl. 66:21–26. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
186
|
Wu X, Li L, Zhang L, Wu J, Zhou Y, Zhou Y,
Zhao Y and Zhao J: Inhibition of thioredoxin-1 with siRNA
exacerbates apoptosis by activating the ASK1-JNK/p38 pathway in
brain of a stroke model rats. Brain Res. 1599:20–31. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
187
|
Baregamian N, Song J, Bailey CE,
Papaconstantinou J, Evers BM and Chung DH: Tumor necrosis
factor-alpha and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 control
reactive oxygen species release, mitochondrial autophagy, and c-Jun
N-terminal kinase/p38 phosphorylation during necrotizing
enterocolitis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2:297–306. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
188
|
Bedogni B, Warneke JA, Nickoloff BJ,
Giaccia AJ and Powell MB: Notch1 is an effector of Akt and hypoxia
in melanoma development. J Clin Invest. 118:3660–3670. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
189
|
Petit A, Bihel F, Alvès da Costa C,
Pourquié O, Checler F and Kraus JL: New protease inhibitors prevent
gamma-secretase-mediated production of Abeta40/42 without affecting
Notch cleavage. Nat Cell Biol. 3:507–511. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
190
|
Okochi M, Steiner H, Fukumori A, Tanii H,
Tomita T, Tanaka T, Iwatsubo T, Kudo T, Takeda M and Haass C:
Presenilins mediate a dual intramembranous gamma-secretase cleavage
of Notch-1. EMBO J. 21:5408–5416. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
191
|
Ikeuchi T and Sisodia SS: The Notch
ligands, Delta1 and Jagged2, are substrates for
presenilin-dependent 'gamma-secretase' cleavage. J Biol Chem.
278:7751–7754. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
192
|
Yang G, Gong Y, Wang Q, Wang Y and Zhang
X: The role of miR-100-mediated Notch pathway in apoptosis of
gastric tumor cells. Cell Signal. 27:1087–1101. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
193
|
Liu XD, Zhang LY, Zhu TC, Zhang RF, Wang
SL and Bao Y: Overexpression of miR-34c inhibits high
glucose-induced apoptosis in podocytes by targeting Notch signaling
pathways. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:4525–4534. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
194
|
Wang XM, Yao M, Liu SX, Hao J, Liu QJ and
Gao F: Interplay between the Notch and PI3K/Akt pathways in high
glucose-induced podocyte apoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.
306:F205–F213. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
195
|
Gao F, Yao M, Shi Y, Hao J, Ren Y, Liu Q,
Wang X and Duan H: Notch pathway is involved in high
glucose-induced apoptosis in podocytes via Bcl-2 and p53 pathways.
J Cell Biochem. 114:1029–1038. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
196
|
Yang Y, Li X, Zhang L, Liu L, Jing G and
Cai H: Ginsenoside Rg1 suppressed infammation and neuron apoptosis
by activating PPAR γ/HO-1 in hippocampus in rat model of cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2484–2494.
2015.
|
|
197
|
Zhao Y, Deng B, Li Y, Zhou L, Yang L, Gou
X, Wang Q, Chen G, Xu H and Xu L: Electroacupuncture pretreatment
attenuates cerebral ischemic injury via Notch Pathway-Mediated
Up-Regulation of hypoxia inducible Factor-1α in Rats. Cell Mol
Neurobiol. 35:1093–1103. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
198
|
Cheng YL, Choi Y, Seow WL, Manzanero S,
Sobey CG, Jo DG and Arumugam TV: Evidence that neuronal Notch-1
promotes JNK/c-Jun activation and cell death following ischemic
stress. Brain Res. 1586:193–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
199
|
Meng S, Su Z, Liu Z, Wang N and Wang Z:
Rac1 contributes to cerebral ischemia reperfusion-induced injury in
mice by regulation of Notch2. Neuroscience. 306:100–114. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
200
|
Ma M, Wang X, Ding X, Teng J, Shao F and
Zhang J: Numb/Notch signaling plays an important role in cerebral
ischemia-induced apoptosis. Neurochem Res. 38:254–261. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
201
|
Sun J, Ling Z, Wang F, Chen W, Li H, Jin
J, Zhang H, Pang M, Yu J and Liu J: Clostridium butyricum
pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury in
mice via anti-oxidation and anti-apoptosis. Neurosci Lett.
613:30–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
202
|
Arumugam TV, Cheng YL, Choi Y, Choi YH,
Yang S, Yun YK, Park JS, Yang DK, Thundyil J, Gelderblom M, et al:
Evidence that gamma-secretase-mediated Notch signaling induces
neuronal cell death via the nuclear factor-kappaB-Bcl-2-interacting
mediator of cell death pathway in ischemic stroke. Mol Pharmacol.
80:23–31. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
203
|
Park JS, Manzanero S, Chang JW, Choi Y,
Baik SH, Cheng YL, Li YI, Gwon AR, Woo HN, Jang J, et al:
Calsenilin contributes to neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke.
Brain Pathol. 23:402–412. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
204
|
Baik SH, Fane M, Park JH, Cheng YL,
Yang-Wei Fann D, Yun UJ, Choi Y, Park JS, Chai BH, Back SH, et al:
Pin1 promotes neuronal death in stroke by stabilizing Notch
intracellular domain. Ann Neurol. 77:504–516. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
205
|
Viswanathan A, Gray F, Bousser MG,
Baudrimont M and Chabriat H: Cortical neuronal apoptosis in
CADASIL. Stroke. 37:2690–2695. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
206
|
Kalimo H, Ruchoux MM, Viitanen M and
Kalaria RN: CADASIL: A common form of hereditary arteriopathy
causing brain infarcts and dementia. Brain Pathol. 12:371–384.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
207
|
Liu XY, Gonzalez-Toledo ME, Fagan A, Duan
WM, Liu Y, Zhang S, Li B, Piao CS, Nelson L and Zhao LR: Stem cell
factor and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor exhibit
therapeutic effects in a mouse model of CADASIL. Neurobiol Dis.
73:189–203. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
208
|
Wang S, Yuan Y, Xia W, Li F, Huang Y, Zhou
Y and Guo Y: Neuronal apoptosis and synaptic density in the dentate
gyrus of ischemic rats' response to chronic mild stress and the
effects of Notch signaling. PLoS One. 7:e428282012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
209
|
Zhang HP, Sun YY, Chen XM, Yuan LB, Su BX,
Ma R, Zhao RN, Dong HL and Xiong L: The neuroprotective effects of
isofurane preconditioning in a murine transient global cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion model: The role of the Notch signaling
pathway. Neuromolecular Med. 16:191–204. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
210
|
Yang Q, Yan W, Li X, Hou L, Dong H, Wang
Q, Wang S, Zhang X and Xiong L: Activation of canonical notch
signaling pathway is involved in the ischemic tolerance induced by
sevo-flurane preconditioning in mice. Anesthesiology. 117:996–1005.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
211
|
Yao J and Qian C: Over-activated Notch-1
protects gastric carcinoma BGC-823 cells from TNFalpha-induced
apoptosis. Dig Liver Dis. 41:867–874. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
212
|
Yang X, Klein R, Tian X, Cheng HT, Kopan R
and Shen J: Notch activation induces apoptosis in neural progenitor
cells through a p53-dependent pathway. Dev Biol. 269:81–94. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
213
|
de Antonellis P, Medaglia C, Cusanelli E,
Andolfo I, Liguori L, De Vita G, Carotenuto M, Bello A, Formiggini
F, Galeone A, et al: MiR-34a targeting of Notch ligand delta-like 1
impairs CD15+/CD133+ tumor-propagating cells and supports neural
differentiation in medulloblastoma. PLoS One. 6:e245842011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
214
|
Sionov RV, Kfr-Erenfeld S, Spokoini R and
Yefenof E: A role for bcl-2 in notch1-dependent transcription in
thymic lymphoma cells. Adv Hematol. 2012:4352412012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
215
|
Ye QF, Zhang YC, Peng XQ, Long Z, Ming YZ
and He LY: Silencing Notch-1 induces apoptosis and increases the
chemo-sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to docetaxel through
Bcl-2 and Bax. Oncol Lett. 3:879–884. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
216
|
Cao H, Hu Y, Wang P, Zhou J, Deng Z and
Wen J: Down-regulation of Notch receptor signaling pathway induces
caspase-dependent and caspase-independent apoptosis in lung
squamous cell carcinoma cells. APMIS. 120:441–450. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
217
|
Brockhaus M, Grünberg J, Röhrig S,
Loetscher H, Wittenburg N, Baumeister R, Jacobsen H and Haass C:
Caspase-mediated cleavage is not required for the activity of
presenilins in amyloidogenesis and NOTCH signaling. Neuroreport.
9:1481–1486. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
218
|
Wu K, Hu L and Hou J: Selective
suppression of Notch1 inhibits proliferation of renal cell
carcinoma cells through JNK/p38 pathway. Oncol Rep. 35:2795–2800.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
219
|
Smith KA, Voiriot G, Tang H, Fraidenburg
DR, Song S, Yamamura H, Yamamura A, Guo Q, Wan J, Pohl NM, et al:
Notch activation of Ca(2+) signaling in the development of hypoxic
pulmonary vasoconstriction and pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir
Cell Mol Biol. 53:355–367. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
220
|
Rothschild SC, Lahvic J, Francescatto L,
McLeod JJ, Burgess SM and Tombes RM: CaMK-II activation is
essential for zebrafsh inner ear development and acts through
Delta-Notch signaling. Dev Biol. 381:179–188. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
221
|
Kim SK, Park HJ, Hong HS, Baik EJ, Jung MW
and Mook-Jung I: ERK1/2 is an endogenous negative regulator of the
gamma-secretase activity. FASEB J. 20:157–159. 2006.
|
|
222
|
Servín-González LS, Granados-López AJ and
López JA: Families of microRNAs expressed in clusters regulate cell
signaling in cervical cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 16:12773–12790. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
223
|
Aguirre A, Rubio ME and Gallo V: Notch and
EGFR pathway interaction regulates neural stem cell number and
self-renewal. Nature. 467:323–327. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
224
|
Nagaraj R and Banerjee U: Regulation of
Notch and Wingless signalling by phyllopod, a transcriptional
target of the EGFR pathway. EMBO J. 28:337–346. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
225
|
Elmadhun NY, Sabe AA, Lassaletta AD, Chu
LM, Kondra K, Sturek M and Sellke FW: Metabolic syndrome impairs
notch signaling and promotes apoptosis in chronically ischemic
myocardium. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 148:1048–1055. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
226
|
Guo D, Ye J, Dai J, Li L, Chen F, Ma D and
Ji C: Notch-1 regulates Akt signaling pathway and the expression of
cell cycle regulatory proteins cyclin D1, CDK2 and p21 in T-ALL
cell lines. Leuk Res. 33:678–685. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
227
|
Sweetwyne MT, Gruenwald A, Niranjan T,
Nishinakamura R, Strobl LJ and Susztak K: Notch1 and Notch2 in
podocytes play differential roles during diabetic nephropathy
development. Diabetes. 64:4099–4111. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
228
|
Bheeshmachar G, Purushotaman D, Sade H,
Gunasekharan V, Rangarajan A and Sarin A: Evidence for a role for
notch signaling in the cytokine-dependent survival of activated T
cells. J Immunol. 177:5041–5050. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
229
|
Sholler GS, Currier EA, Dutta A, Slavik
MA, Illenye SA, Mendonca MC, Dragon J, Roberts SS and Bond JP:
PCI-24781 (abexinostat), a novel histone deacetylase inhibitor,
induces reactive oxygen species-dependent apoptosis and is
synergistic with bortezomib in neuroblastoma. J Cancer Ther Res.
2:212013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
230
|
Yu HC, Bai L, Yue SQ, Wang DS, Wang L, Han
H and Dou KF: Notch signal protects non-parenchymal cells from
ischemia/reperfusion injury in vitro by repressing ROS. Ann
Hepatol. 12:815–821. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
231
|
Naik S, MacFarlane M and Sarin A: Notch4
signaling confers susceptibility to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
breast cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 116:1371–1380. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
232
|
Wang C, Qi R, Li N, Wang Z, An H, Zhang Q,
Yu Y and Cao X: Notch1 signaling sensitizes tumor necrosis
factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by inhibiting Akt/Hdm2-mediated p53
degradation and up-regulating p53-dependent DR5 expression. J Biol
Chem. 284:16183–16190. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
233
|
Chung AS, Lee J and Ferrara N: Targeting
the tumour vascu-lature: Insights from physiological angiogenesis.
Nat Rev Cancer. 10:505–514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
234
|
Carmeliet P, Moons L, Dewerchin M, Mackman
N, Luther T, Breier G, Ploplis V, Müller M, Nagy A, Plow E, et al:
Insights in vessel development and vascular disorders using
targeted inactivation and transfer of vascular endothelial growth
factor, the tissue factor receptor and the plasminogen system. Ann
N Y Acad Sci. 811:191–206. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
235
|
Lymboussaki A, Olofsson B, Eriksson U and
Alitalo K: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and VEGF-C
show overlapping binding sites in embryonic endothelia and distinct
sites in differentiated adult endothelia. Circ Res. 85:992–999.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
236
|
McColl BK, Stacker SA and Achen MG:
Molecular regulation of the VEGF family-inducers of angiogenesis
and lymphangiogenesis. APMIS. 112:463–480. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
237
|
Przybylski M: A review of the current
research on the role of bFGF and VEGF in angiogenesis. J Wound
Care. 18:516–519. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
238
|
Li JL and Harris AL: Crosstalk of VEGF and
Notch pathways in tumour angiogenesis: Therapeutic implications.
Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 14:3094–3110. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
239
|
Dimova I, Popivanov G and Djonov V:
Angiogenesis in cancer-general pathways and their therapeutic
implications. J BUON. 19:15–21. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
240
|
Phng LK and Gerhardt H: Angiogenesis: A
team effort coordinated by notch. Dev Cell. 16:196–208. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
241
|
Benedito R, Roca C, Sörensen I, Adams S,
Gossler A, Fruttiger M and Adams RH: The notch ligands Dll4 and
Jagged1 have opposing effects on angiogenesis. Cell. 137:1124–1135.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
242
|
Boas SE and Merks RM: Tip cell overtaking
occurs as a side effect of sprouting in computational models of
angiogenesis. BMC Syst Biol. 9:862015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
243
|
Garcia-Pascual CM, Zimmermann RC, Ferrero
H, Shawber CJ, Kitajewski J, Simón C, Pellicer A and Gomez R:
Delta-like ligand 4 regulates vascular endothelial growth factor
receptor 2-driven luteal angiogenesis through induction of a
tip/stalk phenotype in proliferating endothelial cells. Fertil
Steril. 100:1768–1776.e1. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
244
|
Brzozowa M, Wojnicz R, Kowalczyk-Ziomek G
and Helewski K: The Notch ligand Delta-like 4 (DLL4) as a target in
angiogenesis-based cancer therapy? Contemp Oncol (Pozn).
17:234–237. 2013.
|
|
245
|
Fukuhara S, Sako K, Noda K, Zhang J,
Minami M and Mochizuki N: Angiopoietin-1/Tie2 receptor signaling in
vascular quiescence and angiogenesis. Histol Histopathol.
25:387–396. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
246
|
Cao Y, Cao R and Hedlund EM: R Regulation
of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis by FGF and PDGF signaling
pathways. J Mol Med (Berl). 86:785–789. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
247
|
van Meeteren LA, Goumans MJ and ten Dijke
P: TGF-β receptor signaling pathways in angiogenesis; emerging
targets for anti-angiogenesis therapy. Curr Pharm Biotechnol.
12:2108–2120. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
248
|
Orlova VV, Liu Z, Goumans MJ and ten Dijke
P: Controlling angiogenesis by two unique TGF-β type I receptor
signaling pathways. Histol Histopathol. 26:1219–1230.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
249
|
Taniyama Y, Morishita R, Aoki M, Nakagami
H, Yamamoto K, Yamazaki K, Matsumoto K, Nakamura T, Kaneda Y and
Ogihara T: Therapeutic angiogenesis induced by human hepatocyte
growth factor gene in rat and rabbit hindlimb ischemia models:
Preclinical study for treatment of peripheral arterial disease.
Gene Ther. 8:181–189. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
250
|
Wu L, Fu Z, Zhou S, Gong J, Liu CA, Qiao Z
and Li S: HIF-12α and HIF-22α: Siblings in promoting angiogenesis
of residual hepatocellular carcinoma after high-intensity focused
ultrasound ablation. PLoS One. 9:e889132014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
251
|
Hayashi H and Kume T: Foxc transcription
factors directly regulate Dll4 and Hey2 expression by interacting
with the VEGF-Notch signaling pathways in endothelial cells. PLoS
One. 3:e24012008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
252
|
Mitsuhashi N, Shimizu H, Ohtsuka M,
Wakabayashi Y, Ito H, Kimura F, Yoshidome H, Kato A, Nukui Y and
Miyazaki M: Angiopoietins and Tie-2 expression in angiogenesis and
proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology.
37:1105–1113. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
253
|
Wulff C, Wilson H, Largue P, Duncan WC,
Armstrong DG and Fraser HM: Angiogenesis in the human corpus
luteum: Localization and changes in angiopoietins, tie-2 and
vascular endothelial growth factor messenger ribonucleic acid. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 85:4302–4309. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
254
|
Weinmaster G: Notch signaling: Direct or
what? Curr Opin Genet Dev. 8:436–442. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
255
|
Reizis B and Leder P: Direct induction of
T lymphocyte-specific gene expression by the mammalian Notch
signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 16:295–300. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
256
|
Nakano N, Nishiyama C, Yagita H, Hara M,
Motomura Y, Kubo M, Okumura K and Ogawa H: Notch signaling enhances
FcεRI-mediated cytokine production by mast cells through direct and
indirect mechanisms. J Immunol. 194:4535–4544. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
257
|
Wüstehube J, Bartol A, Liebler SS, Brütsch
R, Zhu Y, Felbor U, Sure U, Augustin HG and Fischer A: Cerebral
cavernous malformation protein CCM1 inhibits sprouting angiogenesis
by activating DELTA-NOTCH signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
107:12640–12645. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
258
|
You C, Sandalcioglu IE, Dammann P, Felbor
U, Sure U and Zhu Y: Loss of CCM3 impairs DLL4-Notch signalling:
Implication in endothelial angiogenesis and in inherited cerebral
cavernous malformations. J Cell Mol Med. 17:407–418. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
259
|
Patel NS, Li JL, Generali D, Poulsom R,
Cranston DW and Harris AL: Up-regulation of delta-like 4 ligand in
human tumor vasculature and the role of basal expression in
endothelial cell function. Cancer Res. 65:8690–8697. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
260
|
Rath S, Liebl J, Furst R, Vollmar AM and
Zahler S: Regulation of endothelial signaling and migration by
v-ATPase. Angiogenesis. 17:587–601. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
261
|
Hernandez SL, Banerjee D, Garcia A,
Kangsamaksin T, Cheng WY, Anastassiou D, Funahashi Y,
Kadenhe-Chiweshe A, Shawber CJ, Kitajewski JK, et al: Notch and
VEGF pathways play distinct but complementary roles in tumor
angiogenesis. Vasc Cell. 5:172013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
262
|
Jin Y, Kaluza D and Jakobsson L: VEGF,
Notch and TGFβ/BM Ps in regulation of sprouting angiogenesis and
vascular patterning. Biochem Soc Trans. 42:1576–1583. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
263
|
Chintala H, Krupska I, Yan L, Lau L, Grant
M and Chaqour B: The matricellular protein CCN1 controls retinal
angiogenesis by targeting VEGF, Src homology 2 domain phosphatase-1
and Notch signaling. Development. 142:2364–2374. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
264
|
Kiec-Wilk B, Grzybowska-Galuszka J, Polus
A, Pryjma J, Knapp A and Kristiansen K: The MAPK-dependent
regulation of the Jagged/Notch gene expression by VEGF, bFGF or
PPAR gamma mediated angiogenesis in HUVEC. J Physiol Pharmacol.
61:217–225. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
265
|
Cao L, Arany PR, Wang YS and Mooney DJ:
Promoting angio-genesis via manipulation of VEGF responsiveness
with notch signaling. Biomaterials. 30:4085–4093. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
266
|
Thurston G and Kitajewski J: VEGF and
Delta-Notch: Interacting signalling pathways in tumour
angiogenesis. Br J Cancer. 99:1204–1209. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
267
|
Zechariah A, ElAli A, Doeppner TR, Jin F,
Hasan MR, Helfrich I, Mies G and Hermann DM: Vascular endothelial
growth factor promotes pericyte coverage of brain capillaries,
improves cerebral blood flow during subsequent focal cerebral
ischemia, and preserves the metabolic penumbra. Stroke.
44:1690–1697. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
268
|
Yang JP, Liu HJ and Liu XF: VEGF promotes
angiogenesis and functional recovery in stroke rats. J Invest Surg.
23:149–155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
269
|
Dzietko M, Derugin N, Wendland MF, Vexler
ZS and Ferriero DM: Delayed VEGF treatment enhances angiogenesis
and recovery after neonatal focal rodent stroke. Transl Stroke Res.
4:189–200. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
270
|
Lee HJ, Kim KS, Park IH and Kim SU: Human
neural stem cells over-expressing VEGF provide neuroprotection,
angiogenesis and functional recovery in mouse stroke model. PLoS
One. 2:e1562007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
271
|
Esposito E, Hayakawa K, Maki T, Arai K and
Lo EH: Effects of postconditioning on neurogenesis and angiogenesis
during the recovery phase after focal cerebral ischemia. Stroke.
46:2691–2694. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
272
|
Oh TW, Park KH, Jung HW and Park YK:
Neuroprotective effect of the hairy root extract of Angelica gigas
NAKAI on transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats through the
regulation of angiogenesis. BMC Complement Altern Med. 15:1012015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
273
|
Duan S, Shao G, Yu L and Ren C:
Angiogenesis contributes to the neuroprotection induced by
hyperbaric oxygen preconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia
in rats. Int J Neurosci. 125:625–634. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
274
|
Hayward NM, Yanev P, Haapasalo A,
Miettinen R, Hiltunen M, Grohn O and Jolkkonen J: Chronic
hyperperfusion and angiogenesis follow subacute hypoperfusion in
the thalamus of rats with focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 31:1119–1132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
275
|
Guo F, Lv S, Lou Y, Tu W, Liao W, Wang Y
and Deng Z: Bone marrow stromal cells enhance the angiogenesis in
ischaemic cortex after stroke: Involvement of notch signalling.
Cell Biol Int. 36:997–1004. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
276
|
Dao M, Tate CC, McGrogan M and Case CC:
Comparing the angiogenic potency of naïve marrow stromal cells and
Notch-transfected marrow stromal cells. J Transl Med. 11:812013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
277
|
Lähteenvuo JE, Lähteenvuo MT, Kivelä A,
Rosenlew C, Falkevall A, Klar J, Heikura T, Rissanen TT, Vähakängas
E, Korpisalo P, et al: Vascular endothelial growth factor-B induces
myocardium-specific angiogenesis and arteriogenesis via vascular
endothelial growth factor receptor-1- and neuropilin
receptor-1-dependent mechanisms. Circulation. 119:845–856. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
278
|
Semenza GL: Vasculogenesis, angiogenesis,
and arteriogenesis: Mechanisms of blood vessel formation and
remodeling. J Cell Biochem. 102:840–847. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
279
|
Carmeliet P: Mechanisms of angiogenesis
and arteriogenesis. Nat Med. 6:389–395. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
280
|
Buschmann I and Schaper W: Arteriogenesis
Versus Angiogenesis: Two Mechanisms of Vessel Growth. News Physiol
Sci. 14:121–125. 1999.
|
|
281
|
Rangarajan A, Talora C, Okuyama R, Nicolas
M, Mammucari C, Oh H, Aster JC, Krishna S, Metzger D, Chambon P, et
al: Notch signaling is a direct determinant of keratinocyte growth
arrest and entry into differentiation. EMBO J. 20:3427–3436. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
282
|
Gunaratne A, Chan E, El-Chabib TH, Carter
D and Di Guglielmo GM: aPKC alters the TGFβ response in NSCLC cells
through both Smad-dependent and Smad-independent pathways. J Cell
Sci. 128:487–498. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
283
|
Wang Y, Pan L, Moens CB and Appel B:
Notch3 establishes brain vascular integrity by regulating pericyte
number. Development. 141:307–317. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
284
|
Blasi F, Wei Y, Balkaya M, Tikka S,
Mandeville JB, Waeber C, Ayata C and Moskowitz MA: Recognition
memory impairments after subcortical white matter stroke in mice.
Stroke. 45:1468–1473. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
285
|
Yao H, Duan M, Hu G and Buch S:
Platelet-derived growth factor B chain is a novel target gene of
cocaine-mediated Notch1 signaling: Implications for HIV-associated
neurological disorders. J Neurosci. 31:12449–12454. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
286
|
Manda VK, Mittapalli RK, Geldenhuys WJ and
Lockman PR: Chronic exposure to nicotine and saquinavir decreases
endothelial Notch-4 expression and disrupts blood-brain barrier
integrity. J Neurochem. 115:515–525. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
287
|
Nakatsu MN, Sainson RC, Aoto JN, Taylor
KL, Aitkenhead M, Pérez-del-Pulgar S, Carpenter PM and Hughes CC:
Angiogenic sprouting and capillary lumen formation modeled by human
umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) in fibrin gels: The role
of fibroblasts and Angiopoietin-1. Microvasc Res. 66:102–112. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
288
|
Li Z, Wang J, Zhao C, Ren K, Xia Z, Yu H
and Jiang K: Acute Blockage of Notch signaling by DAPT induces
neuroprotection and Neurogenesis in the Neonatal rat brain after
stroke. Transl Stroke Res. 7:132–140. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
289
|
Marumo T, Takagi Y, Muraki K, Hashimoto N,
Miyamoto S and Tanigaki K: Notch signaling regulates
nucleocytoplasmic Olig2 translocation in reactive astrocytes
differentiation after ischemic stroke. Neurosci Res. 75:204–209.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
290
|
Shimada IS, Borders A, Aronshtam A and
Spees JL: Proliferating reactive astrocytes are regulated by
Notch-1 in the peri-infarct area after stroke. Stroke.
42:3231–3237. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
291
|
Uyttendaele H, Closson V, Wu G, Roux F,
Weinmaster G and Kitajewski J: Notch4 and Jagged-1 induce
microvessel differentiation of rat brain endothelial cells.
Microvasc Res. 60:91–103. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
292
|
Xiao MJ, Han Z, Shao B and Jin K: Notch
signaling and neuro-genesis in normal and stroke brain. Int J
Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 1:192–202. 2009.
|
|
293
|
Carlén M, Meletis K, Göritz C, Darsalia V,
Evergren E, Tanigaki K, Amendola M, Barnabe-Heider F, Yeung MS,
Naldini L, et al: Forebrain ependymal cells are Notch-dependent and
generate neuroblasts and astrocytes after stroke. Nat Neurosci.
12:259–267. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
294
|
Yang T, Liu LY, Ma YY and Zhang W: Notch
signaling-mediated neural lineage selection facilitates
intrastriatal transplantation therapy for ischemic stroke by
promoting endogenous regeneration in the hippocampus. Cell
Transplant. 23:221–238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
295
|
Yasuhara T, Matsukawa N, Hara K, Maki M,
Ali MM, Yu SJ, Bae E, Yu G, Xu L, McGrogan M, et al: Notch-induced
rat and human bone marrow stromal cell grafts reduce ischemic cell
loss and ameliorate behavioral deficits in chronic stroke animals.
Stem Cells Dev. 18:1501–1514. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|