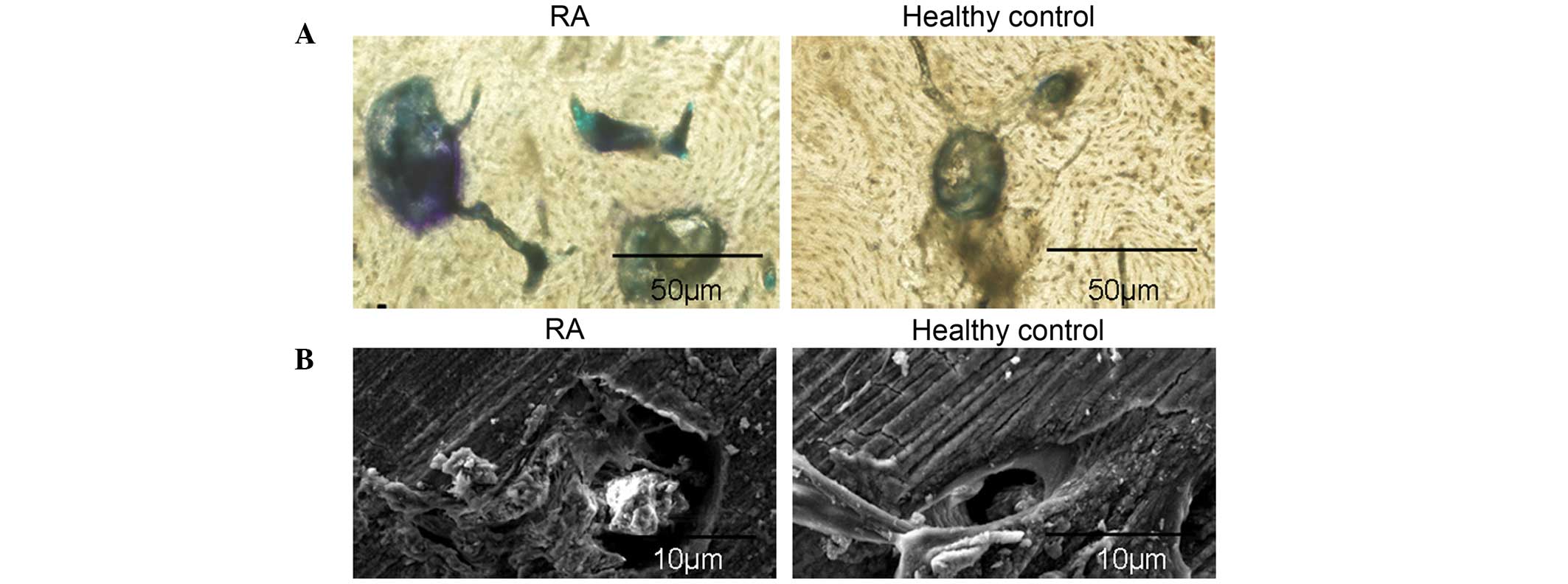
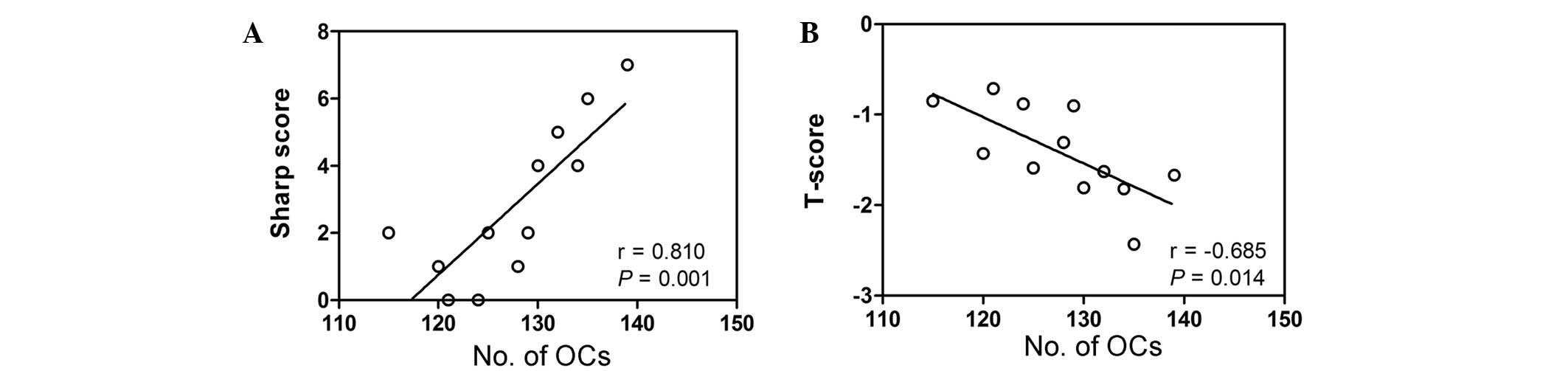
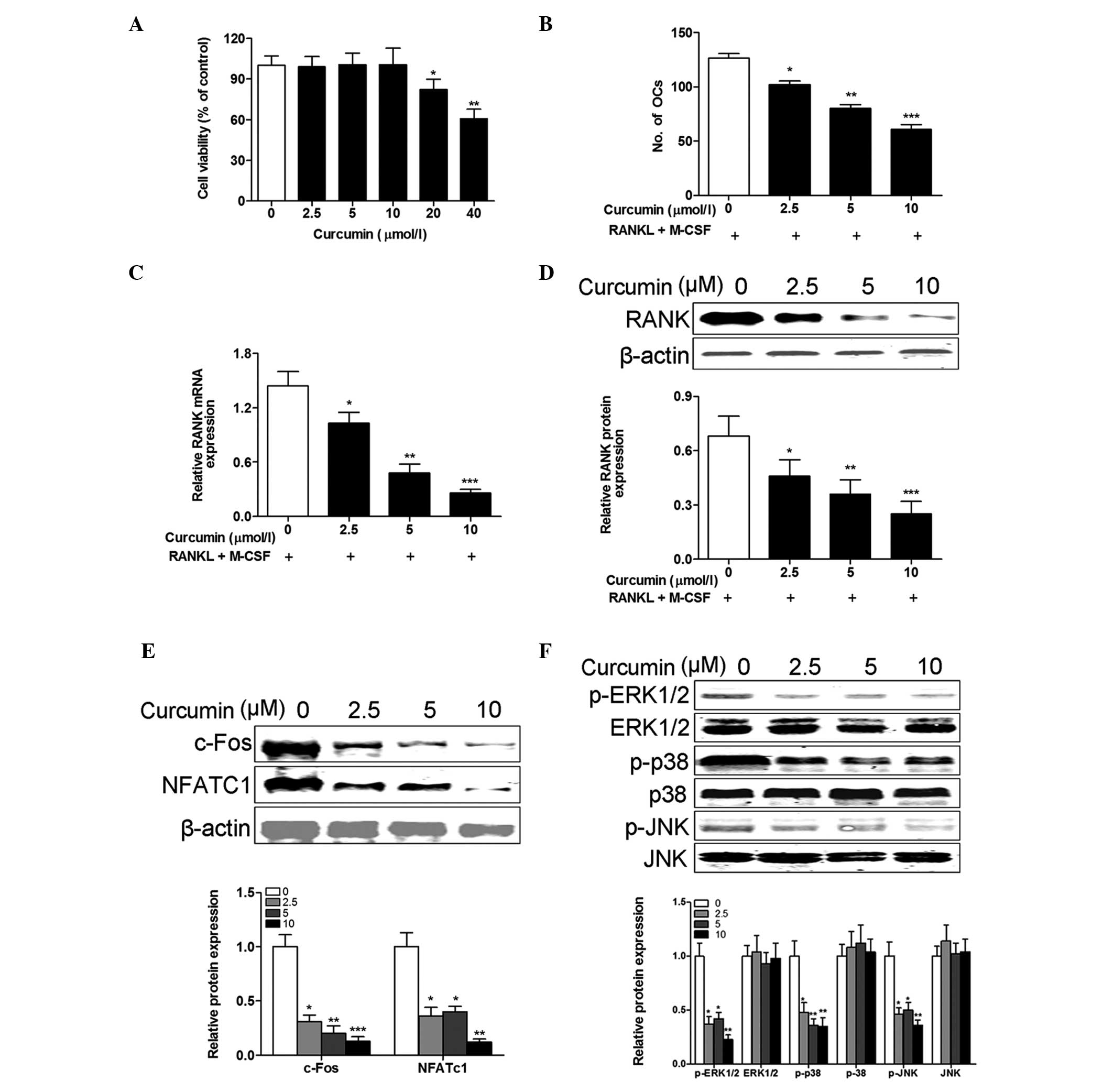
|
1
|
Wendling D, Abbas W, Godfrin-Valnet M,
Kumar A, Guillot X, Khan KA, Vidon C, Coquard L, Toussirot E, Prati
C and Herbein G: Dysregulated serum IL-23 and SIRT1 activity in
peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with rheumatoid
arthritis. PloS One. 10:e01199812015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Han M, Sung YK, Cho SK, Kim D, Won S, Choi
CB, Bang SY, Cha HS, Choe JY, Chung WT, et al: Factors associated
with the use of complementary and alternative medicine for Korean
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 42:2075–2081.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jung SM, Kim KW, Yang CW, Park SH and Ju
JH: Cytokine-mediated bone destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. J
Immunol Res. 2014:2636252014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jules J, Wang S, Shi Z, Liu J, Wei S and
Feng X: The IVVY motif and tumor necrosis factor receptor
associated factor (TRAF) sites in the cytoplasmic domain of the
receptor activator of nuclear factor κB (RANK) cooperate to induce
osteoclastogenesis. J Biol Chem. 290:23738–23750. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kong X, Yang Y, Wu W, Wan H, Li X, Zhong
M, Su X, Jia S and Lin N: Triterpenoid Saponin W3 from Anemone
flaccida suppresses osteoclast differentiation through inhibiting
activation of MAPKs and NF-κB pathways. Int J Biol Sci.
11:1204–1214. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Schulze-Koops H, Davis LS, Kavanaugh AF
and Lipsky PE: Elevated cytokine messenger RNA levels in the
peripheral blood of patients with rheumatoid arthritis suggest
different degrees of myeloid cell activation. Arthritis Rheum.
40:639–647. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ikić M, Jajić Z, Lazić E, Ivčević S,
Grubišić F, Marušić A, Kovačić N and Grčević D: Association of
systemic and intra-articular osteoclastogenic potential,
proinflammatory mediators and disease activity with the form of
inflammatory arthritis. Int Orthop. 38:183–192. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yang Y, Wu X, Wei Z, Dou Y, Zhao D, Wang
T, Bian D, Tong B, Xia Y, Xia Y and Dai Y: Oral curcumin has
anti-arthritic efficacy through somatostatin generation via
cAMP/PKA and Ca(2+)/CaMKII signaling pathways in the small
intestine. Pharmacol Res. 95–96:71–81. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kloesch B, Becker T, Dietersdorfer E,
Kiener H and Steiner G: Anti-inflammatory and apoptotic effects of
the polyphenol curcumin on human fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Int
Immunopharmacol. 15:400–405. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Huang G, Xu Z, Huang Y, Duan X, Gong W,
Zhang Y, Fan J and He F: Curcumin protects against collagen-induced
arthritis via suppression of BAFF production. J Clin Immunol.
33:550–557. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Chandran B and Goel A: A randomized, pilot
study to assess the efficacy and safety of curcumin in patients
with active rheumatoid arthritis. Phytother Res. 26:1719–1725.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Niu X, Lu C, Xiao C, Zhang Z, Jiang M, He
D, Bian Y, Zhang G, Bian Z and Lu A: The shared crosstalk of
multiple pathways involved in the inflammation between rheumatoid
arthritis and coronary artery disease based on a digital gene
expression profile. PloS One. 9:e1136592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Buhrmann C, Mobasheri A, Matis U and
Shakibaei M: Curcumin mediated suppression of nuclear factor-κB
promotes chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in
a high-density co-culture microenvironment. Arthritis Res Ther.
12:R1272010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Shakibaei M, Mobasheri A and Buhrmann C:
Curcumin synergizes with resveratrol to stimulate the MAPK
signaling pathway in human articular chondrocytes in vitro. Genes
Nutr. 6:171–179. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
von Metzler I, Krebbel H, Kuckelkorn U,
Heider U, Jakob C, Kaiser M, Fleissner C, Terpos E and Sezer O:
Curcumin diminishes human osteoclastogenesis by inhibition of the
signalosome-associated I kappaB kinase. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
135:173–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C (T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ravindran J, Cavill C, Balakrishnan C,
Jones SM, Korendowych E and McHugh NJ: A modified Sharp score
demonstrates disease progression in established psoriatic
arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 62:86–91. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen P, Miller PD, Binkley NC, Kendler DL,
Wong M and Krohn K: Use of lowest single lumbar spine vertebra bone
mineral density T-score and other T-score approaches for diagnosing
osteoporosis and relationships with vertebral fracture status. J
Clin Densitom. 11:525–531. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim JY, Min JY, Baek JM, Ahn SJ, Jun HY,
Yoon KH, Choi MK, Lee MS and Oh J: CTRP3 acts as a negative
regulator of osteoclastogenesis through AMPK-c-Fos-NFATc1 signaling
in vitro and RANKL-induced calvarial bone destruction in vivo.
Bone. 79:242–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shi C and Pamer EG: Monocyte recruitment
during infection and inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 11:762–774.
2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
McInnes IB and Schett G: The pathogenesis
of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 365:2205–2219. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Pathak JL, Bravenboer N, Verschueren P,
Lems WF, Luyten FP, Klein-Nulend J and Bakker AD: Inflammatory
factors in the circulation of patients with active rheumatoid
arthritis stimulate osteoclastogenesis via endogenous cytokine
production by osteoblasts. Osteoporos Int. 25:2453–2463. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Izawa T, Mori H, Shinohara T, Mino-Oka A,
Hutami IR, Iwasa A and Tanaka E: Rebamipide attenuates mandibular
condylar degeneration in a murine model of TMJ-OA by mediating a
chondroprotective effect and by downregulating RANKL-mediated
osteoclastogenesis. PloS One. 11:e01541072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Adamopoulos IE, Chao CC, Geissler R,
Laface D, Blumenschein W, Iwakura Y, McClanahan T and Bowman EP:
Interleukin-17A upregulates receptor activator of NF-kappaB on
osteoclast precursors. Arthritis Res Ther. 12:R292010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gravallese EM, Harada Y, Wang JT, Gorn AH,
Thornhill TS and Goldring SR: Identification of cell types
responsible for bone resorption in rheumatoid arthritis and
juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Pathol. 152:943–951.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee EG, Yun HJ, Lee SI and Yoo WH: Ethyl
acetate fraction from Cudrania tricuspidata inhibits
IL-1beta-stimulated osteoclast differentiation through
downregulation of MAPKs, c-Fos and NFATc1. Korean J Intern Med.
25:93–100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lee ZH and Kim HH: Signal transduction by
receptor activator of nuclear factor kappaB in osteoclasts. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 305:211–214. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Takayanagi H: Mechanistic insight into
osteoclast differentiation in osteoimmunology. J Mol Med (Berl).
83:170–179. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|