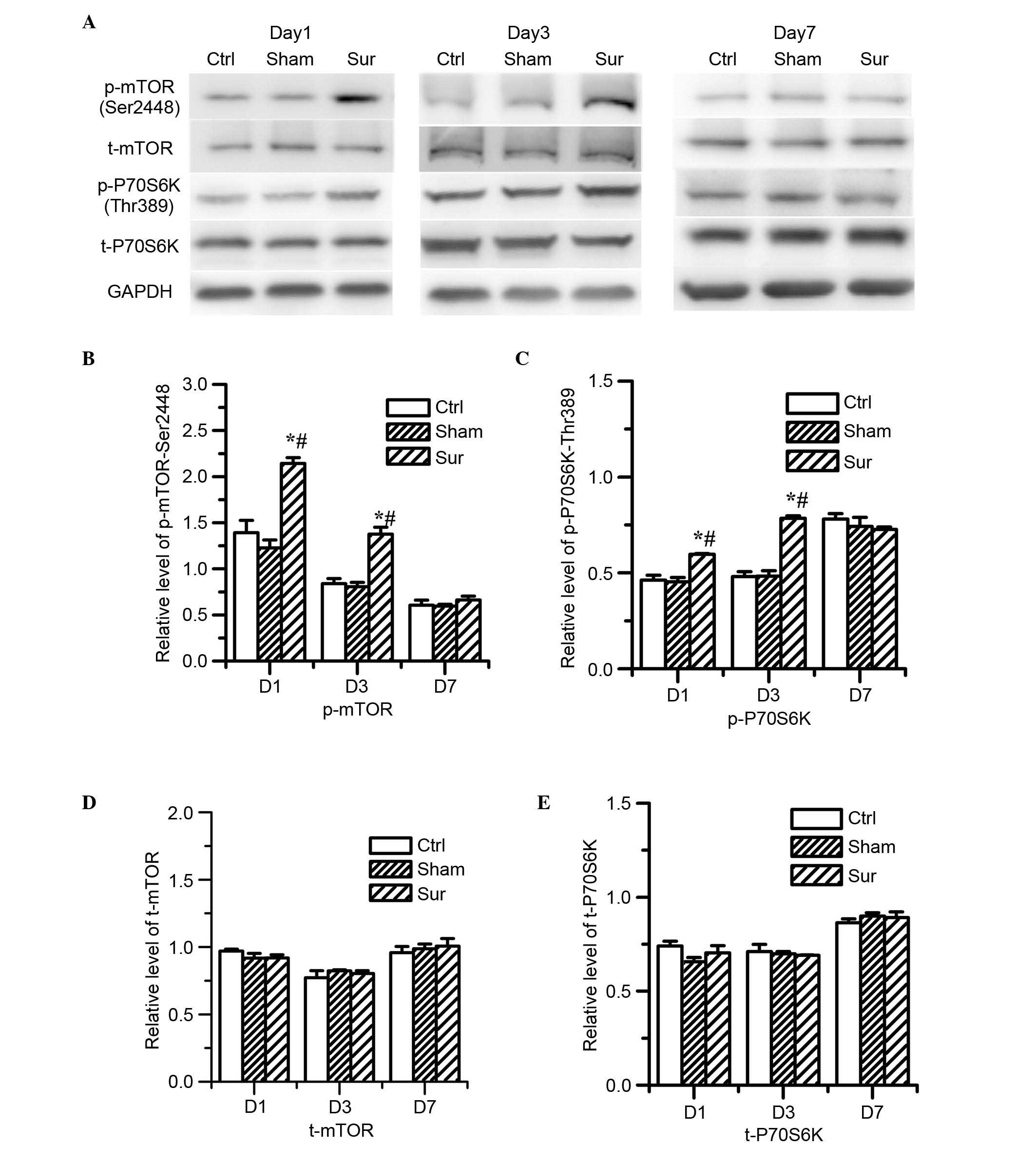
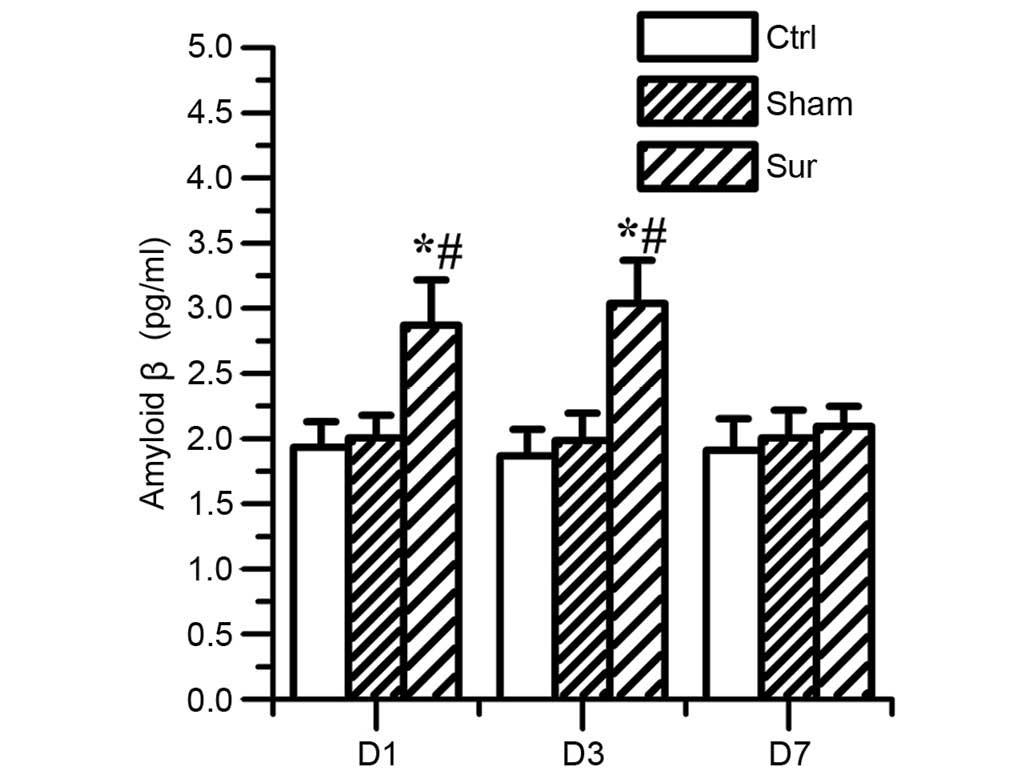
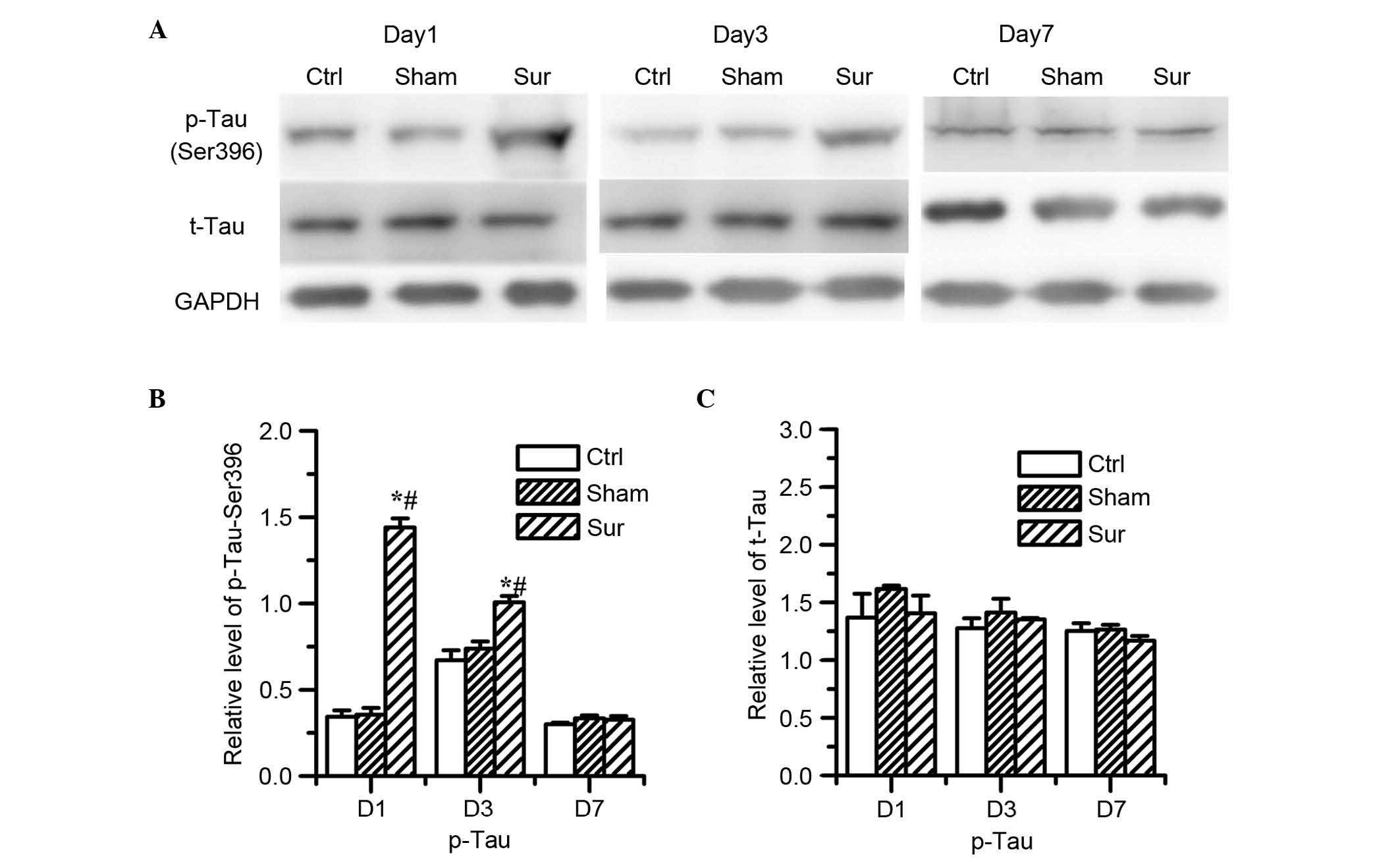
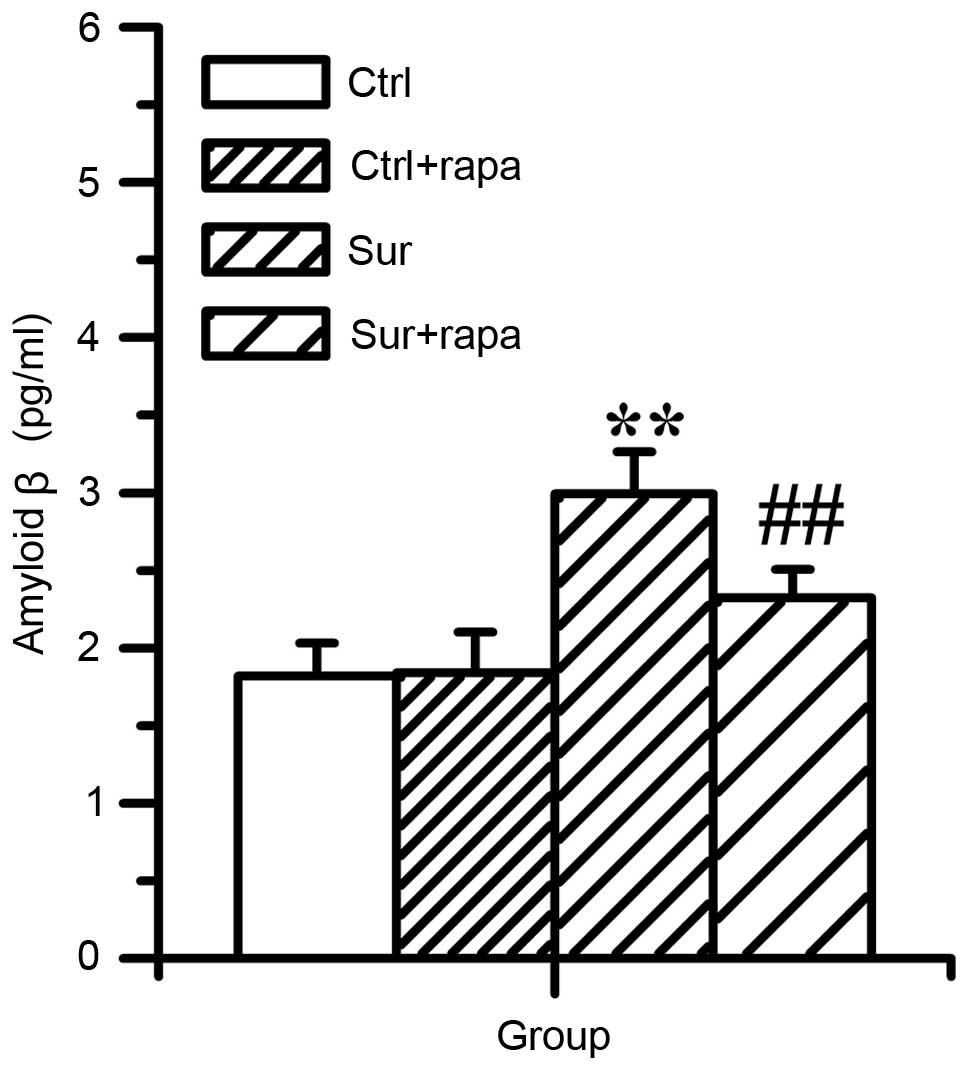
|
1
|
Moller JT, Cluitmans P, Rasmussen LS, Houx
P, Rasmussen H, Canet J, Rabbitt P, Jolles J, Larsen K, Hanning CD,
et al: Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly
ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators International Study of
Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Lancet. 351:857–861. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rubens FD, Boodhwani M and Nathan H:
Interpreting studies of cognitive function following cardiac
surgery: A guide for surgical teams. Perfusion. 22:185–192. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Newman S, Stygall J, Hirani S, Shaefi S
and Maze M: Postoperative cognitive dysfunction after noncardiac
surgery: A systematic review. Anesthesiology. 106:572–590. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vacas S, Degos V, Feng X and Maze M: The
neuroinflammatory response of postoperative cognitive decline. Br
Med Bull. 106:161–78. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Krenk L, Rasmussen LS and Kehlet H: New
insights into the pathophysiology of postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 54:951–956. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang C, Yu JT, Miao D, Wu ZC, Tan MS and
Tan L: Targeting the mTOR signaling network for Alzheimer's disease
therapy. Mol Neurobiol. 49:120–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Hoeffer CA and Klann E: mTOR signaling: At
the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci.
33:67–75. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Banko JL, Merhav M, Stern E, Sonenberg N,
Rosenblum K and Klann E: Behavioral alterations in mice lacking the
translation repressor 4E-BP2. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 87:248–256.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Ehninger D, Han S, Shilyansky C, Zhou Y,
Li W, Kwiatkowski DJ, Ramesh V and Silva AJ: Reversal of learning
deficits in a Tsc2+/− mouse model of tuberous sclerosis. Nat Med.
14:843–848. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Garelick MG and Kennedy BK: TOR on the
brain. Exp Gerontol. 46:155–163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Heras-Sandoval D, Pérez-Rojas JM,
Hernández-Damián J and Pedraza-Chaverri J: The role of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in the modulation of autophagy and the
clearance of protein aggregates in neurodegeneration. Cell Signal.
26:2694–2701. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Alafuzoff I, Soininen H, Winblad B
and Pei JJ: Levels of mTOR and its downstream targets 4E-BP1, eEF2,
and eEF2 kinase in relationships with tau in Alzheimer's disease
brain. FEBS J. 272:4211–4220. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Caccamo A, Majumder S, Richardson A,
Strong R and Oddo S: Molecular interplay between mammalian target
of rapamycin (mTOR), amyloid-beta, and Tau: Effects on cognitive
impairments. J Biol Chem. 285:13107–13120. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Spilman P, Podlutskaya N, Hart MJ, Debnath
J, Gorostiza O, Bredesen D, Richardson A, Strong R and Galvan V:
Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin abolishes cognitive deficits and
reduces amyloid-beta levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer's
disease. PLoS One. 5:e99792010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cao XZ, Ma H, Wang JK, Liu F, Wu BY, Tian
AY, Wang LL and Tan WF: Postoperative cognitive deficits and
neuroinflammation in the hippocampus triggered by surgical trauma
are exacerbated in aged rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol
Psychiatry. 34:1426–1432. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR
signaling. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 4:22012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Lee DF, Kuo HP, Chen CT, Hsu JM, Chou CK,
Wei Y, Sun HL, Li LY, Ping B, Huang WC, et al: IKK beta suppression
of TSC1 links inflammation and tumor angiogenesis via the mTOR
pathway. Cell. 130:440–455. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Degos V, Vacas S, Han Z, van Rooijen N,
Gressens P, Su H, Young WL and Maze M: Depletion of bone
marrow-derived macrophages perturbs the innate immune response to
surgery and reduces postoperative memory dysfunction.
Anesthesiology. 118:527–536. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vizcaychipi MP, Xu L, Barreto GE, Ma D,
Maze M and Giffard RG: Heat shock protein 72 overexpression
prevents early postoperative memory decline after orthopedic
surgery under general anesthesia in mice. Anesthesiology.
114:891–900. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vacas S, Degos V, Tracey KJ and Maze M:
High-mobility group box 1 protein initiates postoperative cognitive
decline by engaging bone marrow-derived macrophages.
Anesthesiology. 120:1160–1167. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
21
|
Erlich S, Alexandrovich A, Shohami E and
Pinkas-Kramarski R: Rapamycin is a neuroprotective treatment for
traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 26:86–93. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tang P, Hou H and Zhang L, Lan X, Mao Z,
Liu D, He C, Du H and Zhang L: Autophagy reduces neuronal damage
and promotes locomotor recovery via inhibition of apoptosis after
spinal cord injury in rats. Mol Neurobiol. 49:276–287. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Broadbent NJ, Squire LR and Clark RE:
Spatial memory, recognition memory, and the hippocampus. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 101:14515–14520. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maren S, Phan KL and Liberzon I: The
contextual brain: Implications for fear conditioning, extinction
and psychopathology. Nat Rev Neurosci. 14:417–428. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Cibelli M, Fidalgo AR, Terrando N, Ma D,
Monaco C, Feldmann M, Takata M, Lever IJ, Nanchahal J, Fanselow MS
and Maze M: Role of interleukin-1beta in postoperative cognitive
dysfunction. Ann Neurol. 68:360–368. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Terrando N, Eriksson LI, Ryu JK, Yang T,
Monaco C, Feldmann M, Jonsson Fagerlund M, Charo IF, Akassoglou K
and Maze M: Resolving postoperative neuroinflammation and cognitive
decline. Ann Neurol. 70:986–995. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu N, Guo D, Wang H, Xie K, Wang C, Li Y,
Wang C, Wang C, Yu Y and Wang G: Involvement of the blood-brain
barrier opening in cognitive decline in aged rats following
orthopedic surgery and high concentration of sevoflurane
inhalation. Brain Res. 1551:13–24. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Majumder S, Caccamo A, Medina DX,
Benavides AD, Javors MA, Kraig E, Strong R, Richardson A and Oddo
S: Lifelong rapamycin administration ameliorates age-dependent
cognitive deficits by reducing IL-1β and enhancing NMDA signaling.
Aging Cell. 11:326–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Caccamo A, Magri A, Medina DX, Wisely EV,
López-Aranda MF, Silva AJ and Oddo S: mTOR regulates tau
phosphorylation and degradation: Implications for Alzheimer's
disease and other tauopathies. Aging Cell. 12:370–380. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wang S, Zhou SL, Min FY, Ma JJ, Shi XJ,
Bereczki E and Wu J: mTOR-mediated hyperphosphorylation of tau in
the hippocampus is involved in cognitive deficits in
streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Metab Brain Dis. 29:729–736.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Hoeffer CA, Tang W, Wong H, Santillan A,
Patterson RJ, Martinez LA, Tejada-Simon MV, Paylor R, Hamilton SL
and Klann E: Removal of FKBP12 enhances mTOR-Raptor interactions,
LTP, memory, and perseverative/repetitive behavior. Neuron.
60:832–845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dash PK, Orsi SA and Moore AN: Spatial
memory formation and memory-enhancing effect of glucose involves
activation of the tuberous sclerosis complex-Mammalian target of
rapamycin pathway. J Neurosci. 26:8048–8056. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Schicknick H, Schott BH, Budinger E,
Smalla KH, Riedel A, Seidenbecher CI, Scheich H, Gundelfinger ED
and Tischmeyer W: Dopaminergic modulation of auditory
cortex-dependent memory consolidation through mTOR. Cereb Cortex.
18:2646–2658. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Puighermanal E, Marsicano G,
Busquets-Garcia A, Lutz B, Maldonado R and Ozaita A: Cannabinoid
modulation of hippocampal long-term memory is mediated by mTOR
signaling. Nat Neurosci. 12:1152–1158. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Halloran J, Hussong SA, Burbank R,
Podlutskaya N, Fischer KE, Sloane LB, Austad SN, Strong R,
Richardson A, Hart MJ and Galvan V: Chronic inhibition of mammalian
target of rapamycin by rapamycin modulates cognitive and
non-cognitive components of behavior throughout lifespan in mice.
Neuroscience. 223:102–113. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Braak H and Braak E: Neuropathological
stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol.
82:239–259. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Blasko I, Kemmler G, Jungwirth S, Wichart
I, Krampla W, Weissgram S, Jellinger K, Tragl KH and Fischer P:
Plasma amyloid beta-42 independently predicts both late-onset
depression and Alzheimer disease. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry.
18:973–982. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wan Y, Xu J, Meng F, Bao Y, Ge Y, Lobo N,
Vizcaychipi MP, Zhang D, Gentleman SM, Maze M and Ma D: Cognitive
decline following major surgery is associated with gliosis,
β-amyloid accumulation and tau phosphorylation in old mice. Crit
Care Med. 38:2190–2198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Reinsfelt B, Westerlind A, Blennow K,
Zetterberg H and Ricksten SE: Open-heart surgery increases
cerebrospinal fluid levels of Alzheimer-associated amyloid β. Acta
Anaesthesiol Scand. 57:82–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Ma YQ, Wu DK and Liu JK: mTOR and tau
phosphorylated proteins in the hippocampal tissue of rats with type
2 diabetes and Alzheimer's disease. Mol Med Rep. 7:623–627.
2013.
|
|
41
|
Tang Z, Bereczki E, Zhang H, Wang S, Li C,
Ji X, Branca RM, Lehtiö J, Guan Z, Filipcik P, et al: Mammalian
target of rapamycin (mTor) mediates tau protein dyshomeostasis:
Implication for Alzheimer disease. J Biol Chem. 288:15556–15570.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Lyman M, Lloyd DG, Ji X, Vizcaychipi MP
and Ma D: Neuro-inflammation: The role and consequences. Neurosci
Res. 79:1–12. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Terrando N, Monaco C, Ma D, Foxwell BM,
Feldmann M and Maze M: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha triggers a
cytokine cascade yielding postoperative cognitive decline. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:20518–20522. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhu XC, Yu JT, Jiang T and Tan L:
Autophagy modulation for Alzheimer's disease therapy. Mol
Neurobiol. 48:702–714. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|