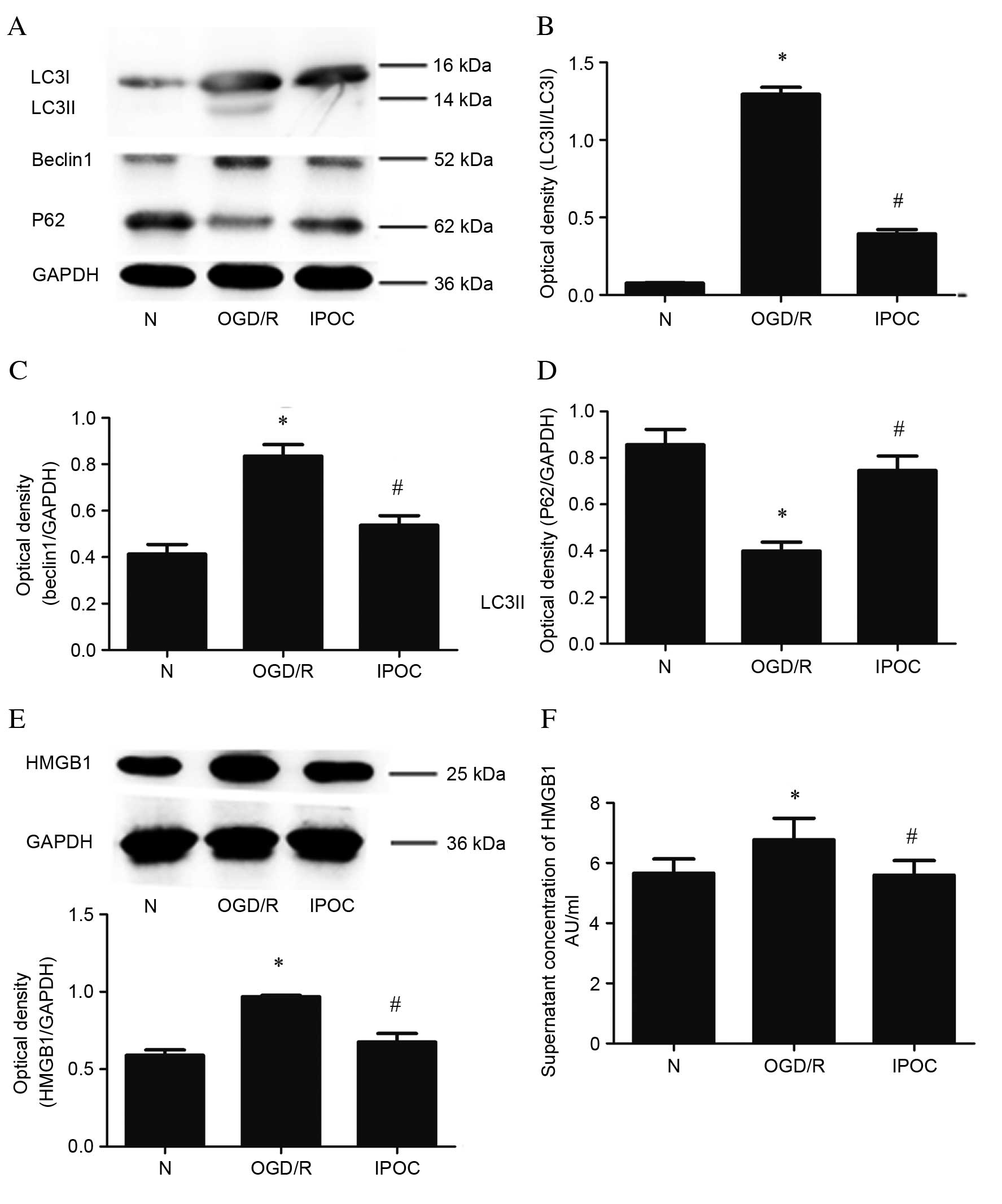
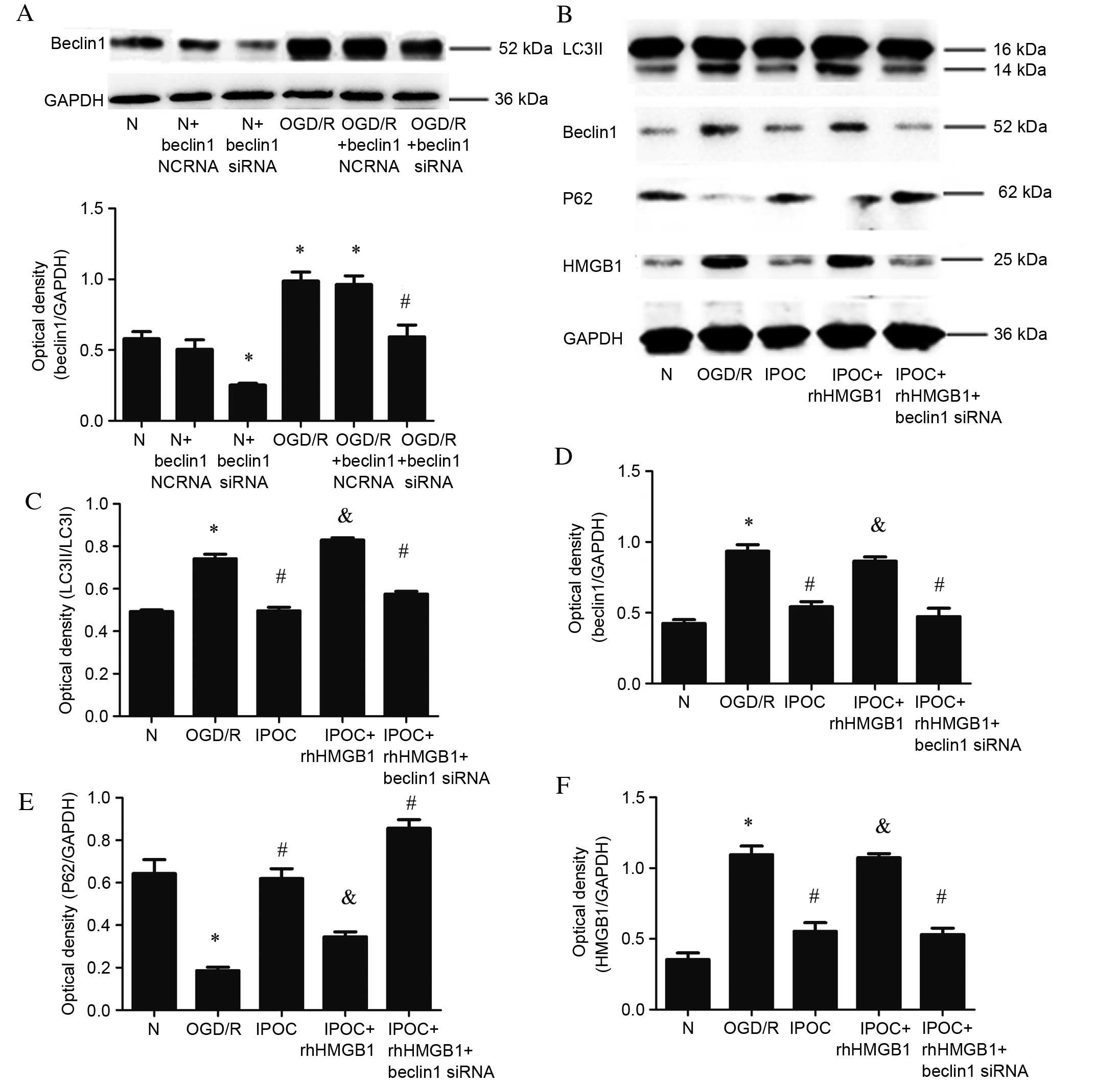
|
1
|
Writing Group Members, ; Mozaffarian D,
Benjamin EJ, Go AS, Arnett DK, Blaha MJ, Cushman M, Das SR, de
Ferranti S, Després JP, et al: Executive summary: Heart disease and
stroke statistics-2016 update: A report from the American heart
association. Circulation. 133:447–454. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao H: Ischemic postconditioning as a
novel avenue to protect against brain injury after stroke. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 29:873–885. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Duanmu WS, Cao L, Chen JY, Ge HF, Hu R and
Feng H: Ischemic postconditioning protects against ischemic brain
injury by up-regulation of acid-sensing ion channel 2a. Neural
Regen Res. 11:641–645. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Han D, Zhang S, Fan B, Wen LL, Sun M,
Zhang H and Feng J: Ischemic postconditioning protects the
neurovascular unit after focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury. J Mol Neurosci. 53:50–58. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yuan Y, Guo Q, Ye Z, Pingping X, Wang N
and Song Z: Ischemic postconditioning protects brain from
ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating endoplasmic reticulum
stress-induced apoptosis through PI3K-Akt pathway. Brain Res.
1367:85–93. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhu C, Xu F, Wang X, Shibata M, Uchiyama
Y, Blomgren K and Hagberg H: Different apoptotic mechanisms are
activated in male and female brains after neonatal
hypoxia-ischaemia. J Neurochem. 96:1016–1027. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li J, Han B, Ma X and Qi S: The effects of
propofol on hippocampal caspase-3 and Bcl-2 expression following
forebrain ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Brain Res. 1356:11–23.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bowen ID, Mullarkey K and Margen SM:
Programmed cell death during meta-morphosis in the blow-fly
Calliphora vormitoria. Microsc Res Tech. 34:202–217. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wen YD, Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Zhang X,
Zhang XD, Han F, Fukunaga K and Qin ZH: Neuronal injury in rat
model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia is associated with
activation of autophagic and lysosomal pathways. Autophagy.
4:762–769. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Koike M, Shibata M, Tadakoshi M, Gotoh K,
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Kawahara N, Kuida K, Nagata S, Kominami E, et
al: Inhibition of autophagy prevents hippocampal pyramidal neuron
death after hypoxic-ischemic injury. Am J Pathol. 172:454–469.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gao L, Jiang T, Guo J, Liu Y, Cui G, Gu L,
Su L and Zhang Y: Inhibition of autophagy contributes to ischemic
postconditioning-induced neuroprotection against focal cerebral
ischemia in rats. PLoS One. 7:e460922012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chakrabarti L, Eng J, Ivanov N, Garden GA
and La Spada AR: Autophagy activation and enhanced mitophagy
characterize the Purkinje cells of pcd mice prior to neuronal
death. Mol Brain. 2:242009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Erlich S, Shohami E and Pinkas-Kramarski
R: Neurodegeneration induces upregulation of Beclin 1. Autophagy.
2:49–51. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Goodwin GH, Sanders C and Johns EW: A new
group of chromatin associated proteins with a high content of
acidic and basic amino acids. Eur J Biochem. 38:14–19. 1973.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM,
Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, et
al: HMGB-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice.
Science. 285:248–251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang QW, Wang JZ, Li JC, Zhou Y, Zhong Q,
Lu FL and Xiang J: High-mobility group protein box-1 and its
relevance to cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
30:243–254. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Huang JM, Hu J, Chen N and Hu ML:
Relationship between plasma high-mobility group box-1 levels and
clinical outcomes of ischemic stroke. J Crit Care. 28:792–797.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Rickenbacher A, Jang JH, Limani P,
Ungethüm U, Lehmann K, Oberkofler CE, Weber A, Graf R, Humar B and
Clavien PA: Fasting protects liver from ischemic injury through
sirt1-mediated downregulation of circulating HMGB1 in mice. J
Hepatol. 61:301–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Nakamura T, Yamada S and Yoshioka T: Brain
hypothermic therapy dramatically decreases elevated blood
concentrations of high mobility group box 1 in neonates with
hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Dis Markers. 35:327–330. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Q, Wang F, Li X, Yang Q, Li X, Xu N,
Huang Y, Zhang Q, Gou X, Chen S and Xiong L: Electroacupuncture
pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemic injury through α7
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated inhibition of
high-mobility group box 1 release in rats. J Neuroinflammation.
9:242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kang R, Zeh HJ, Lotze MT and Tang D: The
Beclin 1 network regulates autophagy and apoptosis. Cell Death
Differ. 18:571–580. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Thorburn J, Frankel AE and Thorburn A:
Regulation of HMGB1 release by autophagy. Autophagy. 5:247–249.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang D, Kang R, Livesey KM, Kroemer G,
Billiar TR, Van Houten B, Zeh HJ III and Lotze MT: High-mobility
group box 1 is essential for mitochondrial quality control. Cell
Metab. 13:701–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tang D, Kang R, Livesey KM, Cheh CW,
Farkas A, Loughran P, Hoppe G, Bianchi ME, Tracey KJ, Zeh HJ III
and Lotze MT: Endogenous HMGB1 regulates autophagy. J Cell Biol.
190:881–892. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tang D, Kang R, Cheh CW, Livesey KM, Liang
X, Schapiro NE, Benschop R, Sparvero LJ, Amoscato AA, Tracey KJ, et
al: HMGB1 release and redox regulates autophagy and apoptosis in
cancer cells. Oncogene. 29:5299–5310. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Juhaszova M, Zorov DB, Yaniv Y, Nuss HB,
Wang S and Sollott SJ: Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3beta in
cardioprotection. Circ Res. 104:1240–1252. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cuervo AM: Autophagy: In sickness and in
health. Trends Cell Biol. 14:70–77. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Liu XQ, Gao B
and Qin ZH: Autophagy activation is associated with neuroprotection
in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemic preconditioning.
Autophagy. 6:482–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Su J, Zhang T, Wang K, Zhu T and Li X:
Autophagy activation contributes to the neuroprotection of remote
ischemic perconditioning against focal cerebral ischemia in rats.
Neurochem Res. 39:2068–2077. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang JY, Xia Q, Chu KT, Pan J, Sun LN,
Zeng B, Zhu YJ, Wang Q, Wang K and Luo BY: Severe global cerebral
ischemia-induced programmed necrosis of hippocampal CA1 neurons in
rat is prevented by 3-methyladenine: A widely used inhibitor of
autophagy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 70:314–322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu XP, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Funderburk SF, Wang QJ and Yue Z: The
Beclin 1-VPS34 complex-at the crossroads of autophagy and beyond.
Trends Cell Biol. 20:355–362. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Cui D, Wang L, Qi A, Zhou Q, Zhang X and
Jiang W: Propofol prevents autophagic cell death following oxygen
and glucose deprivation in PC12 cells and cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS One. 7:e353242012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Wang J, Han D, Sun M and Feng J: A
combination of remote ischemic perconditioning and cerebral
ischemic postconditioning inhibits autophagy to attenuate plasma
HMGB1 and induce neuroprotection against stroke in rat. J Mol
Neurosci. 58:424–431. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhang CC, Krieg S and Shapiro DJ: HMG-1
stimulates estrogen response element binding by estrogen receptor
from stably transfected HeLa cells. Mol Endocrinol. 13:632–643.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM,
Ombrellino M, Che J, Frazier A, Yang H, Ivanova S, Borovikova L, et
al: HMG1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice.
Science. 285:248–251. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hayakawa K, Mishima K, Nozako M, Hazekawa
M, Mishima S, Fujioka M, Orito K, Egashira N, Iwasaki K and
Fujiwara M: Delayed treatment with minocycline ameliorates
neurologic impairment through activated microglia expressing a
high-mobility group box 1-inhibiting mechanism. Stroke. 39:951–958.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Qiu J, Nishimura M, Wang Y, Sims JR, Qiu
S, Savitz SI, Salomone S and Moskowitz MA: Early release of HMGB-1
from neurons after the onset of brain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow
Metab. 28:927–938. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Nakahara T, Tsuruta R, Kaneko T, Yamashita
S, Fujita M, Kasaoka S, Hashiguchi T, Suzuki M, Maruyama I and
Maekawa T: High-mobility group box 1 protein in CSF of patients
with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurocrit Care. 11:362–368. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|