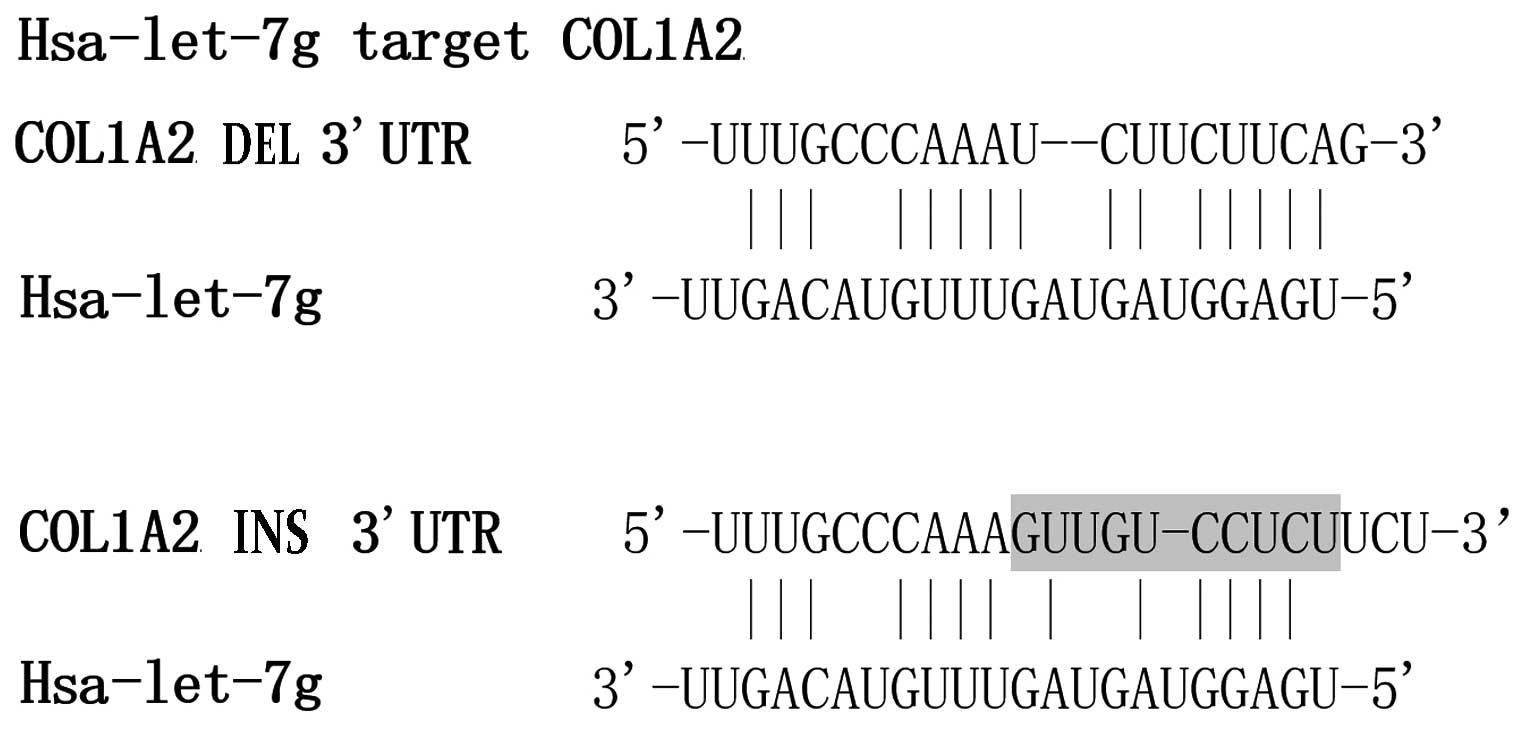
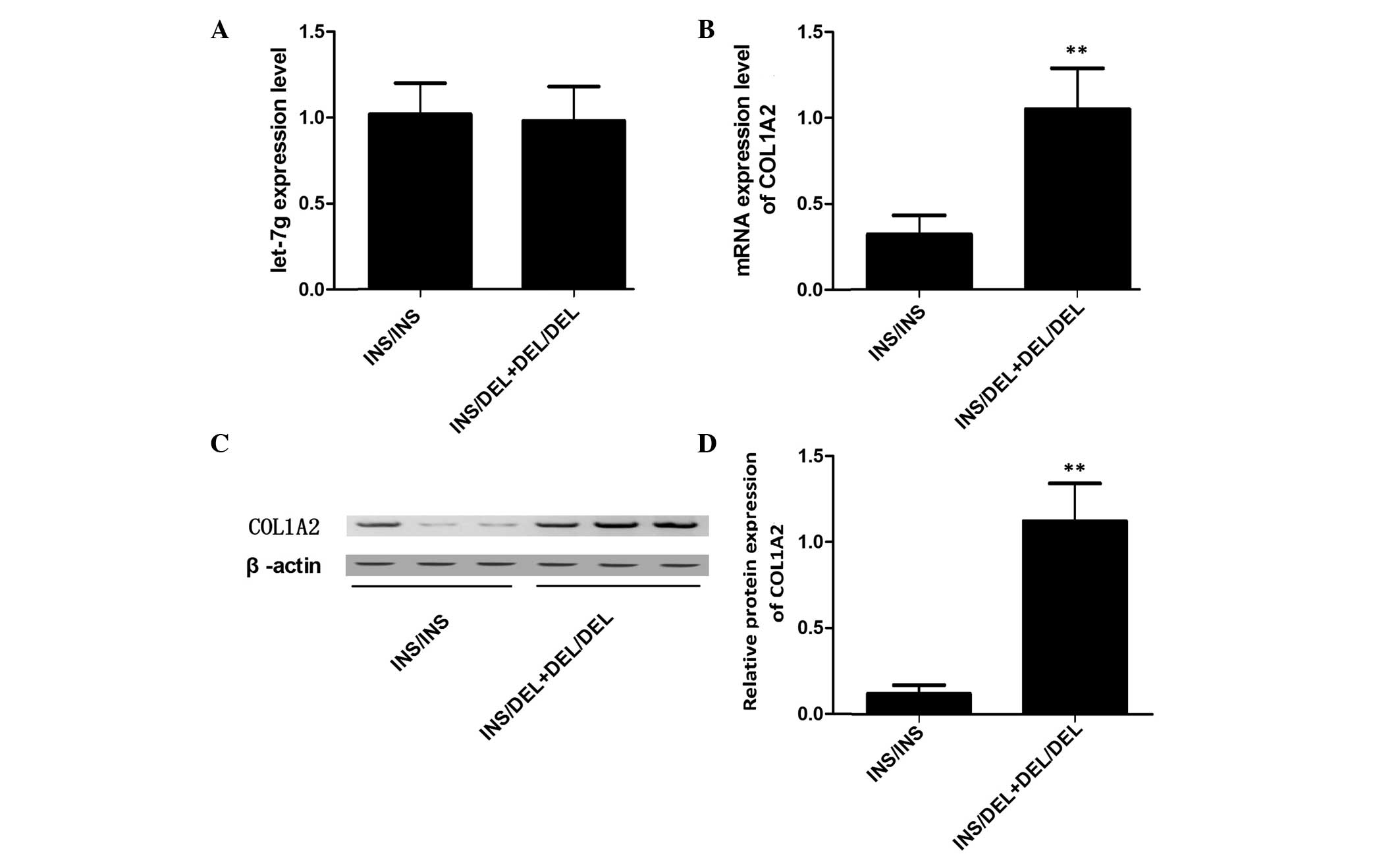
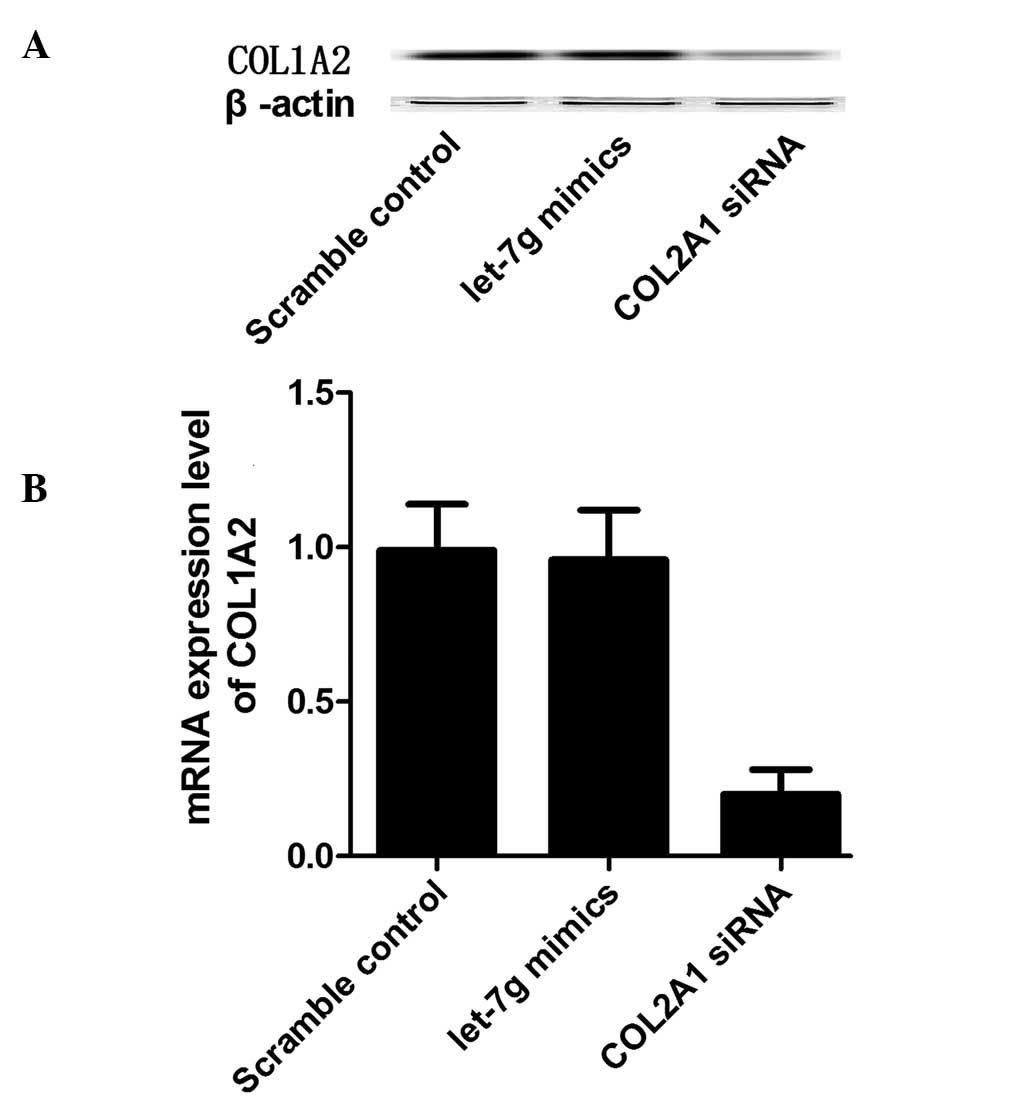
|
1
|
Kanis JA, Melton LJ III, Christiansen C,
Johnston CC and Khaltaev N: The diagnosis of osteoporosis. J Bone
Miner Res. 9:1137–1141. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guéguen R, Jouanny P, Guillemin F, Kuntz
C, Pourel J and Siest G: Segregation analysis and variance
components analysis of bone mineral density in healthy families. J
Bone Miner Res. 10:2017–2022. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Arden NK, Baker J, Hogg C, Baan K and
Spector TD: The heritability of bone mineral density, ultrasound of
the calcaneus and hip axis length: A study of postmenopausal twins.
J Bone Miner Res. 11:530–534. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Christian JC, Yu PL, Slemenda CW and
Johnston CC Jr: Heritability of bone mass: A longitudinal study in
aging male twins. Am J Hum Genet. 44:429–433. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pocock NA, Eisman JA, Hopper JL, Yeates
MG, Sambrook PN and Eberl S: Genetic determinants of bone mass in
adults. A twin study. J Clin Invest. 80:706–710. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Slemenda CW, Christian JC, Williams CJ,
Norton JA and Johnston CC Jr: Genetic determinants of bone mass in
adult women: A reevaluation of the twin model and the potential
importance of gene interaction on heritability estimates. J Bone
Miner Res. 6:561–567. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Peacock M, Koller DL, Fishburn T, Krishnan
S, Lai D, Hui S, Johnston CC, Foroud T and Econs MJ: Sex-specific
and non-sex-specific quantitative trait loci contribute to normal
variation in bone mineral density in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab.
90:3060–3066. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xiao P, Shen H, Guo YF, Xiong DH, Liu YZ,
Liu YJ, Zhao LJ, Long JR, Guo Y, Recker RR and Deng HW: Genomic
regions identified for BMD in a large sample including epistatic
interactions and gender-specific effects. J Bone Miner Res.
21:1536–1544. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Prockop DJ and Kivirikko KI: Collagens:
Molecular biology, diseases, and potentials for therapy. Annu Rev
Biochem. 64:403–434. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mann V and Ralston SH: Meta-analysis of
COL1A1 Sp1 polymorphism in relation to bone mineral density and
osteoporotic fracture. Bone. 32:711–717. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nguyen TV, Esteban LM, White CP, Grant SF,
Center JR, Gardiner EM and Eisman JA: Contribution of the collagen
I alpha1 and vitamin D receptor genes to the risk of hip fracture
in elderly women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 90:6575–6579. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pillai RS: MicroRNA function: Multiple
mechanisms for a tiny RNA? RNA. 11:1753–1761. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wiemer EA: The role of microRNAs in
cancer: No small matter. Eur J Cancer. 43:1529–1544. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Chen K, Song F, Calin GA, Wei Q, Hao X and
Zhang W: Polymorphisms in microRNA targets: A gold mine for
molecular epidemiology. Carcinogenesis. 29:1306–1311. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nicoloso MS, Sun H, Spizzo R, Kim H,
Wickramasinghe P, Shimizu M, Wojcik SE, Ferdin J, Kunej T, Xiao L,
et al: Single-nucleotide polymorphisms inside microRNA target sites
influence tumor susceptibility. Cancer Res. 70:2789–2798. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Landi D, Gemignani F, Barale R and Landi
S: A catalog of polymorphisms falling in microRNA-binding regions
of cancer genes. DNA Cell Biol. 27:35–43. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu Z, Jiang Y, Chen S, Jia S, Gao X, Dong
D and Gao Y: An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the 3′
untranslated region of type I collagen a2 (COL1A2) is associated
with susceptibility for hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese
population. Cancer Genet. 204:265–269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zhou J, Liu J, Pan Z, Du X, Li X, Ma B,
Yao W, Li Q and Liu H: The let-7g microRNA promotes follicular
granulosa cell apoptosis by targeting transforming growth factor-β
type 1 receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 409:103–112. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stewart TL and Ralston SH: Role of genetic
factors in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis. J Endocrinol.
166:235–245. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ambros V: microRNAs: Tiny regulators with
great potential. Cell. 107:823–826. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lian JB, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ, Stein
JL, Hassan MQ, Gaur T and Zhang Y: MicroRNA control of bone
formation and homeostasis. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 8:212–227. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Miyaki S and Asahara H: Macro view of
microRNA function in osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 8:543–552.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xia Z, Chen C, Chen P, Xie H and Luo X:
MicroRNAs and their roles in osteoclast differentiation. Front Med.
5:414–419. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Goldring MB and Marcu KB: Epigenomic and
microRNA-mediated regulation in cartilage development, homeostasis,
and osteoarthritis. Trends Mol Med. 18:109–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Taipaleenmäki H, Hokland L Bjerre, Chen L,
Kauppinen S and Kassem M: Mechanisms in endocrinology: micro-RNAs:
targets for enhancing osteoblast differentiation and bone
formation. Eur J Endocrinol. 166:359–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Laine SK, Hentunen T and Laitala-Leinonen
T: Do microRNAs regulate bone marrow stem cell niche physiology?
Gene. 497:1–9. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Papaioannou G, Mirzamohammadi F and
Kobayashi T: MicroRNAs involved in bone formation. Cell Mol Life
Sci. 71:4747–4761. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ji J, Zhao L, Budhu A, Forgues M, Jia HL,
Qin LX, Ye QH, Yu J, Shi X, Tang ZY and Wang XW: Let-7g targets
collagen type I alpha2 and inhibits cell migration in
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 52:690–697. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lau EM, Choy DT, Li M, Woo J, Chung T and
Sham A: The relationship between COLI A1 polymorphisms (Sp 1) and
COLI A2 polymorphisms (Eco R1 and Puv II) with bone mineral density
in Chinese men and women. Calcif Tissue Int. 75:133–137. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lindahl K, Rubin CJ, Brändström H,
Karlsson MK, Holmberg A, Ohlsson C, Mellström D, Orwoll E, Mallmin
H, Kindmark A and Ljunggren O: Heterozygosity for a coding SNP in
COL1A2 confers a lower BMD and an increased stroke risk. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 384:501–505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Lei SF, Deng FY, Xiao SM, Chen XD and Deng
HW: Association and haplotype analyses of the COL1A2 and ER-alpha
gene polymorphisms with bone size and height in Chinese. Bone.
36:533–541. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Lei SF, Deng FY, Dvornyk V, Liu MY, Xiao
SM, Jiang DK and Deng HW: The (GT)n polymorphism and haplotype of
the COL1A2 gene, but not the (AAAG)n polymorphism of the PTHR1
gene, are associated with bone mineral density in Chinese. Hum
Genet. 116:200–207. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Escobar-García D, Mejía-Saavedra J,
Jarquín-Yáñez L, Molina-Frechero N and Pozos-Guillén A: Collagenase
1A2 (COL1A2) gene A/C polymorphism in relation to severity of
dental fluorosis. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 44:162–168. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|