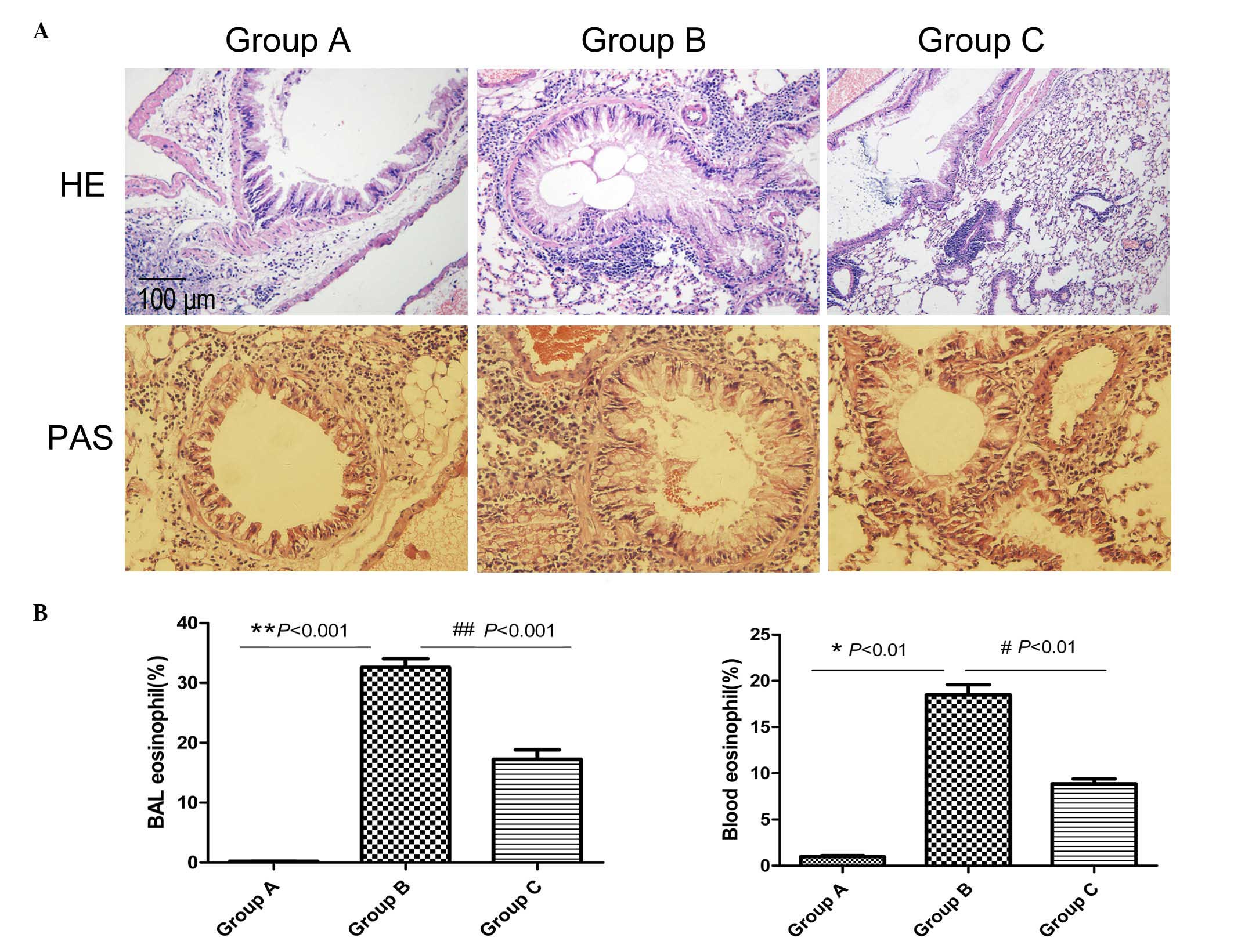
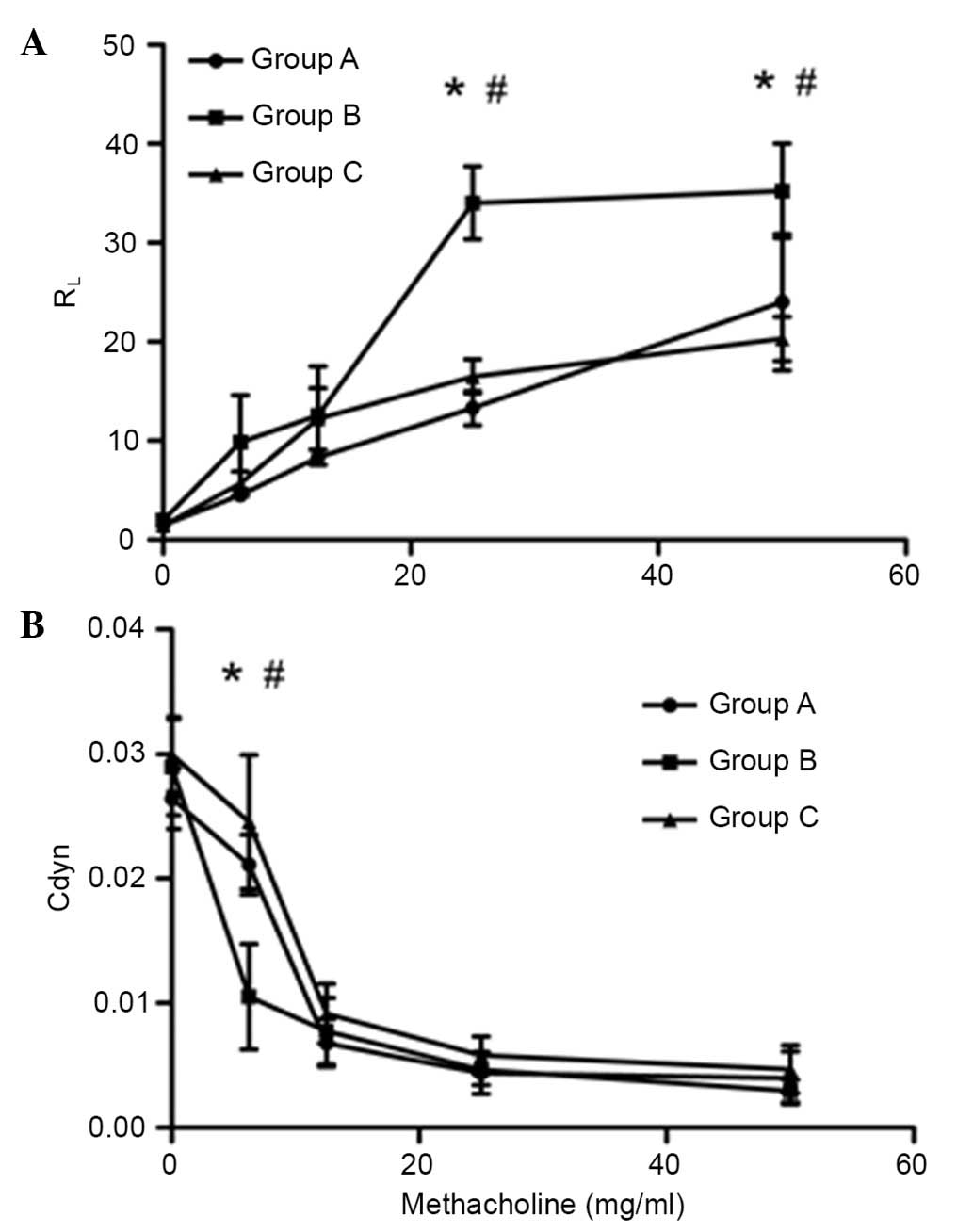
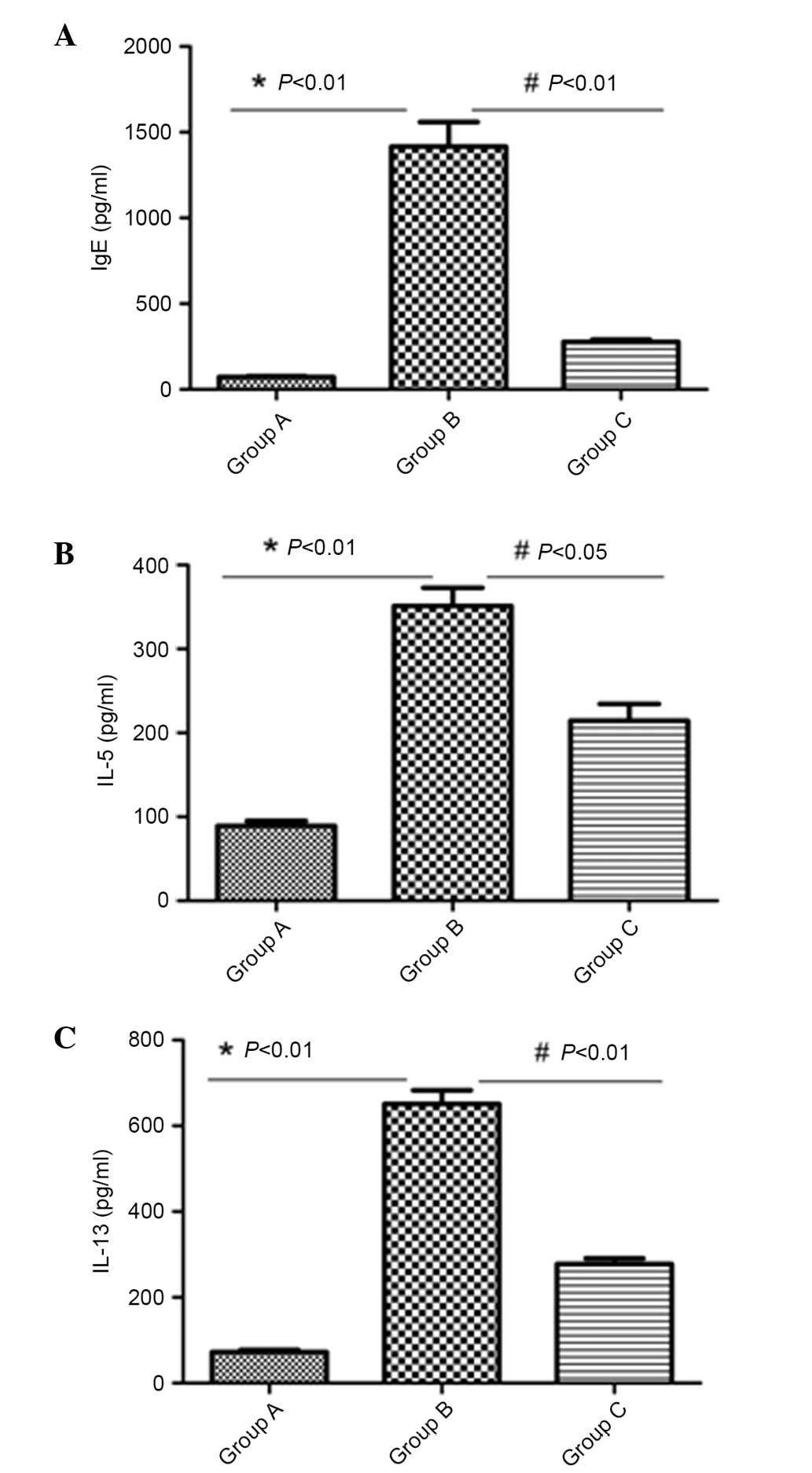
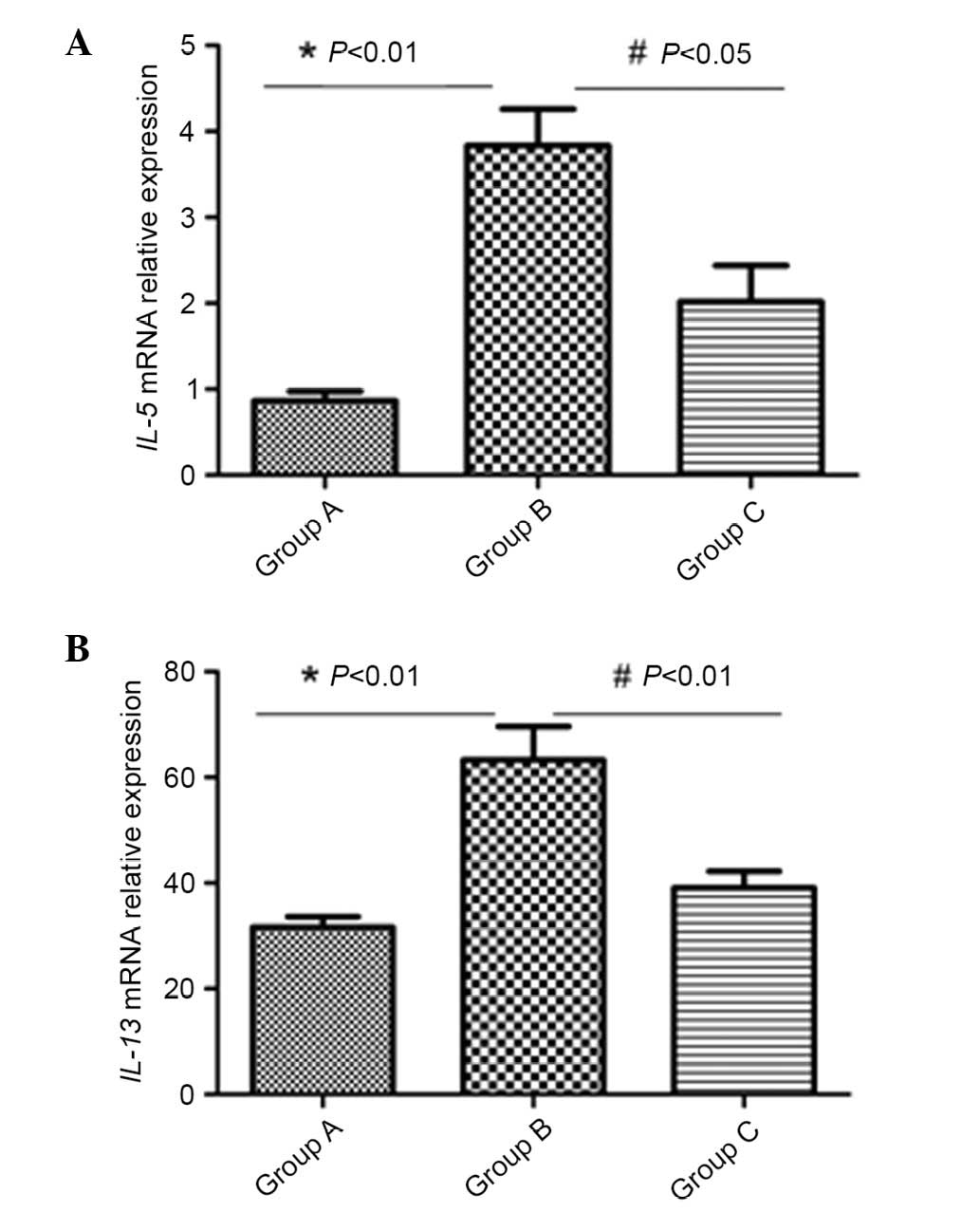
|
1
|
Krishnan V, Diette GB, Rand CS, Bilderback
AL, Merriman B, Hansel NN and Krishnan JA: Mortality in patients
hospitalized for asthma exacerbations in the United States. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 174:633–638. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bateman ED, Hurd SS, Barnes PJ, Bousquet
J, Drazen JM, FitzGerald M, Gibson P, Ohta K, O'Byrne P, Pedersen
SE, et al: Global strategy for asthma management and prevention:
GINA executive summary. Eur Respir J. 31:143–178. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Taube C, Wei X, Swasey CH, Joetham A,
Zarini S, Lively T, Takeda K, Loader J, Miyahara N, Kodama T, et
al: Mast cells, Fc epsilon RI, and IL-13 are required for
development of airway hyperresponsiveness after aerosolized
allergen exposure in the absence of adjuvant. J Immunol.
172:6398–6406. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cockcroft DW and Davis BE: Mechanisms of
airway hyperresponsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 118:551–559;
quiz 560–561. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Asquith KL, Ramshaw HS, Hansbro PM,
Beagley KW, Lopez AF and Foster PS: The IL-3/IL-5/GM-CSF common
receptor plays a pivotal role in the regulation of Th2 immunity and
allergic airway inflammation. J Immunol. 180:1199–1206. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Takatsu K and Nakajima H: IL-5 and
eosinophilia. Curr Opin Immunol. 20:288–294. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Busse WW, Ring J, Huss-Marp J and Kahn JE:
A review of treatment with mepolizumab, an anti-IL-5 mAb, in
hypereosinophilic syndromes and asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
125:803–813. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Corren J: Role of interleukin-13 in
asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 13:415–420. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
de Vries JE: The role of IL-13 and its
receptor in allergy and inflammatory responses. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 102:165–169. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
McKenzie GJ, Emson CL, Bell SE, Anderson
S, Fallon P, Zurawski G, Murray R, Grencis R and McKenzie AN:
Impaired development of Th2 cells in IL-13-deficient mice.
Immunity. 9:423–432. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Punnonen J, Aversa G, Cocks BG, McKenzie
AN, Menon S, Zurawski G, de Waal Malefyt R and de Vries JE:
Interleukin 13 induces interleukin 4-independent IgG4 and IgE
synthesis and CD23 expression by human B cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 90:3730–3734. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Horie S, Okubo Y, Hossain M, Sato E,
Nomura H, Koyama S, Suzuki J, Isobe M and Sekiguchi M:
Interleukin-13 but not interleukin-4 prolongs eosinophil survival
and induces eosinophil chemotaxis. Intern Med. 36:179–185. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Luttmann W, Knoechel B, Foerster M,
Matthys H, Virchow JC Jr and Kroegel C: Activation of human
eosinophils by IL-13. Induction of CD69 surface antigen, its
relationship to messenger RNA expression, and promotion of cellular
viability. J Immunol. 157:1678–1683. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kondo M, Tamaoki J, Takeyama K, Isono K,
Kawatani K, Izumo T and Nagai A: Elimination of IL-13 reverses
established goblet cell metaplasia into ciliated epithelia in
airway epithelial cell culture. Allergol Int. 55:329–336. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bossé Y, Thompson C, Audette K, Stankova J
and Rola-Pleszczynski M: Interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 enhance
human bronchial smooth muscle cell proliferation. Int Arch Allergy
Immunol. 146:138–148. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chiba Y, Nakazawa S, Todoroki M, Shinozaki
K, Sakai H and Misawa M: Interleukin-13 augments bronchial smooth
muscle contractility with an up-regulation of RhoA protein. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 40:159–167. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hacha J, Tomlinson K, Maertens L,
Paulissen G, Rocks N, Foidart JM, Noel A, Palframan R, Gueders M
and Cataldo DD: Nebulized anti-IL-13 monoclonal antibody Fab'
fragment reduces allergen-induced asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol
Biol. 47:709–717. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Dittrich AM, Erbacher A, Specht S, Diesner
F, Krokowski M, Avagyan A, Stock P, Ahrens B, Hoffmann WH, Hoerauf
A and Hamelmann E: Helminth infection with Litomosoides sigmodontis
induces regulatory T cells and inhibits allergic sensitization,
airway inflammation, and hyperreactivity in a murine asthma model.
J Immunol. 180:1792–1799. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Forsythe P, Inman MD and Bienenstock J:
Oral treatment with live Lactobacillus reuteri inhibits the
allergic airway response in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
175:561–569. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Karimi K, Inman MD, Bienenstock J and
Forsythe P: Lactobacillus reuteri-induced regulatory T cells
protect against an allergic airway response in mice. Am J Respir
Crit Care Med. 179:186–193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liu J, Tran V, Leung AS, Alexander DC and
Zhu B: BCG vaccines: Their mechanisms of attenuation and impact on
safety and protective efficacy. Hum Vaccin. 5:70–78. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li C, Xu Y, Zhang Z, Yang D, Liu X and
Xiong W: An experimental study of the effect of bacille
calmette-guerin vaccine on the production of a rat asthmatic model
and its relation with gamma delta T cells. Zhonghua Jie He He Hu Xi
Za Zhi. 25:162–165. 2002.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang J, Li C and Guo S: Effects of
inhaled inactivated Mycobacterium phlei on airway inflammation in
mouse asthmatic models. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv. 25:96–103.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kanehiro A, Lahn M, Mäkelä MJ, Dakhama A,
Fujita M, Joetham A, Mason RJ, Born W and Gelfand EW: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha negatively regulates airway
hyperresponsiveness through gamma-delta T cells. Am J Respir Crit
Care Med. 164:2229–2238. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hopfenspirger MT and Agrawal DK: Airway
hyperresponsiveness, late allergic response, and eosinophilia are
reversed with mycobacterial antigens in ovalbumin-presensitized
mice. J Immunol. 168:2516–2522. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bradley BL, Azzawi M, Jacobson M, Assoufi
B, Collins JV, Irani AM, Schwartz LB, Durham SR, Jeffery PK and Kay
AB: Eosinophils, T-lymphocytes, mast cells, neutrophils, and
macrophages in bronchial biopsy specimens from atopic subjects with
asthma: Comparison with biopsy specimens from atopic subjects
without asthma and normal control subjects and relationship to
bronchial hyperresponsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 88:661–674.
1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jo EJ, Kim MY, Lee SE, Lee SY, Kim MH,
Song WJ, Kim SH, Kang HR, Chang YS, Cho SH and Min KU: Eosinophilic
airway inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness according to
aeroallergen sensitization pattern in patients with lower airway
symptoms. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 6:39–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yang MS, Lee HS, Kim MH, Song WJ, Kim TW,
Kwon JW, Kim SH, Park HW, Chang YS, Cho SH and Min KU: Rhinitis
patients with sputum eosinophilia show decreased lung function in
the absence of airway hyperresponsiveness. Allergy Asthma Immunol
Res. 5:232–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Stein ML and Munitz A: Targeting
interleukin (IL) 5 for asthma and hypereosinophilic diseases.
Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov. 4:201–209. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Losol P, Kim SH, Hwang EK, Shin YS and
Park HS: IL-5 promoter polymorphism enhances IgE responses to
staphylococcal superantigens in adult asthmatics. Allergy Asthma
Immunol Res. 5:106–109. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jayaprakasam B, Yang N, Wen MC, Wang R,
Goldfarb J, Sampson H and Li XM: Constituents of the anti-asthma
herbal formula ASHMI(TM) synergistically inhibit IL-4 and IL-5
secretion by murine Th2 memory cells, and eotaxin by human lung
fibroblasts in vitro. J Integr Med. 11:195–205. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Seys SF, Grabowski M, Adriaensen W,
Decraene A, Dilissen E, Vanoirbeek JA, Dupont LJ, Ceuppens JL and
Bullens DM: Sputum cytokine mapping reveals an ‘IL-5, IL-17A,
IL-25-high’ pattern associated with poorly controlled asthma. Clin
Exp Allergy. 43:1009–1017. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Hussain S: IL-13 gene polymorphisms and
their association with atopic asthma and rhinitis in Pakistani
patients. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 13:298–299.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Utsumi Y, Sasaki N, Nagashima H, Suzuki N,
Nakamura Y, Yamashita M, Kobayashi H and Yamauchi K: Association of
IL-13 gene polymorphisms with airway hyperresponsiveness in a
Japanese adult asthmatic population. Respir Investig. 51:147–152.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Haldar P, Brightling CE, Hargadon B, Gupta
S, Monteiro W, Sousa A, Marshall RP, Bradding P, Green RH, Wardlaw
AJ and Pavord ID: Mepolizumab and exacerbations of refractory
eosinophilic asthma. N Engl J Med. 360:973–984. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Pavord ID, Korn S, Howarth P, Bleecker ER,
Buhl R, Keene ON, Ortega H and Chanez P: Mepolizumab for severe
eosinophilic asthma (DREAM): A multicentre, double-blind,
placebo-controlled trial. Lancet. 380:651–659. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nair P, Pizzichini MM, Kjarsgaard M, Inman
MD, Efthimiadis A, Pizzichini E, Hargreave FE and O'Byrne PM:
Mepolizumab for prednisone-dependent asthma with sputum
eosinophilia. N Engl J Med. 360:985–993. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Castro M, Mathur S, Hargreave F, Boulet
LP, Xie F, Young J, Wilkins HJ, Henkel T and Nair P: Res-5-0010
Study Group: Reslizumab for poorly controlled, eosinophilic asthma:
A randomized, placebo-controlled study. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.
184:1125–1132. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang Y and McCusker CT:
Interleukin-13-dependent bronchial hyper-responsiveness following
isolated upper-airway allergen challenge in a murine model of
allergic rhinitis and asthma. Clin Exp Allergy. 35:1104–1111. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Hashimoto S and Bel EH: Targeting IL-5 in
severe asthma: A DREAM come true? Lancet. 380:626–627. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mathur M, Herrmann K, Li X, Qin Y,
Weinstock J, Elliott D, Monahan J and Padrid P: TRFK-5 reverses
established airway eosinophilia but not established
hyperresponsiveness in a murine model of chronic asthma. Am J
Respir Crit Care Med. 159:580–587. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Leckie MJ, ten Brinke A, Khan J, Diamant
Z, O'Connor BJ, Walls CM, Mathur AK, Cowley HC, Chung KF,
Djukanovic R, et al: Effects of an interleukin-5 blocking
monoclonal antibody on eosinophils, airway hyper-responsiveness and
the late asthmatic response. Lancet. 356:2144–2148. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
El-Zein M, Parent ME, Benedetti A and
Rousseau MC: Does BCG vaccination protect against the development
of childhood asthma? A systematic review and meta-analysis of
epidemiological studies. Int J Epidemiol. 39:469–486. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Obihara CC, Bollen CW, Beyers N and Kimpen
JL: Mycobacterial infection and atopy in childhood: A systematic
review. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 18:551–559. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Hopfenspirger MT, Parr SK, Hopp RJ,
Townley RG and Agrawal DK: Mycobacterial antigens attenuate late
phase response, airway hyperresponsiveness, and bronchoalveolar
lavage eosinophilia in a mouse model of bronchial asthma. Int
Immunopharmacol. 1:1743–1751. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Assa'ad AH, Gupta SK, Collins MH, Thomson
M, Heath AT, Smith DA, Perschy TL, Jurgensen CH, Ortega HG and
Aceves SS: An antibody against IL-5 reduces numbers of esophageal
intraepithelial eosinophils in children with eosinophilic
esophagitis. Gastroenterology. 141:1593–1604. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Spergel JM, Rothenberg ME, Collins MH,
Furuta GT, Markowitz JE, Fuchs G III, O'Gorman MA, Abonia JP, Young
J, Henkel T, et al: Reslizumab in children and adolescents with
eosinophilic esophagitis: Results of a double-blind, randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 129:456–463,
463.e1-3. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Assa'ad AH and Rothenberg ME: Eosinophilic
asthma: Insights into the effects of reducing IL-5
receptor-positive cell levels. J Allergy Clin Immunol.
132:1097–1098. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Akira S: Pathogen recognition by innate
immunity and its signaling. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci.
85:143–156. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Reba SM, Li Q, Onwuzulike S, Ding X, Karim
AF, Hernandez Y, Fulton SA, Harding CV, Lancioni CL, Nagy N, et al:
TLR2 engagement on CD4(+) T cells enhances effector functions and
protective responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Eur J Immunol.
44:1410–1421. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Almeida PE, Roque NR, Magalhães KG, Mattos
KA, Teixeira L, Maya-Monteiro C, Almeida CJ, Castro-Faria-Neto HC,
Ryffel B, Quesniaux VF and Bozza PT: Differential TLR2 downstream
signaling regulates lipid metabolism and cytokine production
triggered by Mycobacterium bovis BCG infection. Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1841:97–107. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Chávez-Galán L, Ramon-Luing LA,
Torre-Bouscoulet L, Pérez-Padilla R and Sada-Ovalle I: Pre-exposure
of Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages to crystalline
silica impairs control of bacterial growth by deregulating the
balance between apoptosis and necrosis. PLoS One. 8:e809712013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Akdis CA, Kussebi F, Pulendran B, Akdis M,
Lauener RP, Schmidt-Weber CB, Klunker S, Isitmangil G, Hansjee N,
Wynn TA, et al: Inhibition of T helper 2-type responses, IgE
production and eosinophilia by synthetic lipopeptides. Eur J
Immunol. 33:2717–2726. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Manicassamy S and Pulendran B: Modulation
of adaptive immunity with Toll-like receptors. Semin Immunol.
21:185–193. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Cdos S Samary, Antunes MA, Silva JD, Silva
AL, Araujo CC, Bakker-Abreu I, Diaz BL, Fernezlian S, Parra ER,
Capelozzi VL, et al: Impact of bacillus Calmette-Guerin Moreau
vaccine on lung remodeling in experimental asthma. Respir Physiol
Neurobiol. 189:614–623. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Czerkinsky C, Anjuere F, McGhee JR,
George-Chandy A, Holmgren J, Kieny MP, Fujiyashi K, Mestecky JF,
Pierrefite-Carle V, Rask C and Sun JB: Mucosal immunity and
tolerance: Relevance to vaccine development. Immunol Rev.
170:197–222. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Horner AA and Raz E: Immunostimulatory
sequence oligodeoxynucleotide: A novel mucosal adjuvant. Clin
Immunol. 95:(Suppl). S19–S29. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Horner AA, Datta SK, Takabayashi K,
Belyakov IM, Hayashi T, Cinman N, Nguyen MD, Van Uden JH, Berzofsky
JA, Richman DD and Raz E: Immunostimulatory DNA-based vaccines
elicit multifaceted immune responses against HIV at systemic and
mucosal sites. J Immunol. 167:1584–1591. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Takabayashi K, Libet L, Chisholm D,
Zubeldia J and Horner AA: Intranasal immunotherapy is more
effective than intradermal immunotherapy for the induction of
airway allergen tolerance in Th2-sensitized mice. J Immunol.
170:3898–3905. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|