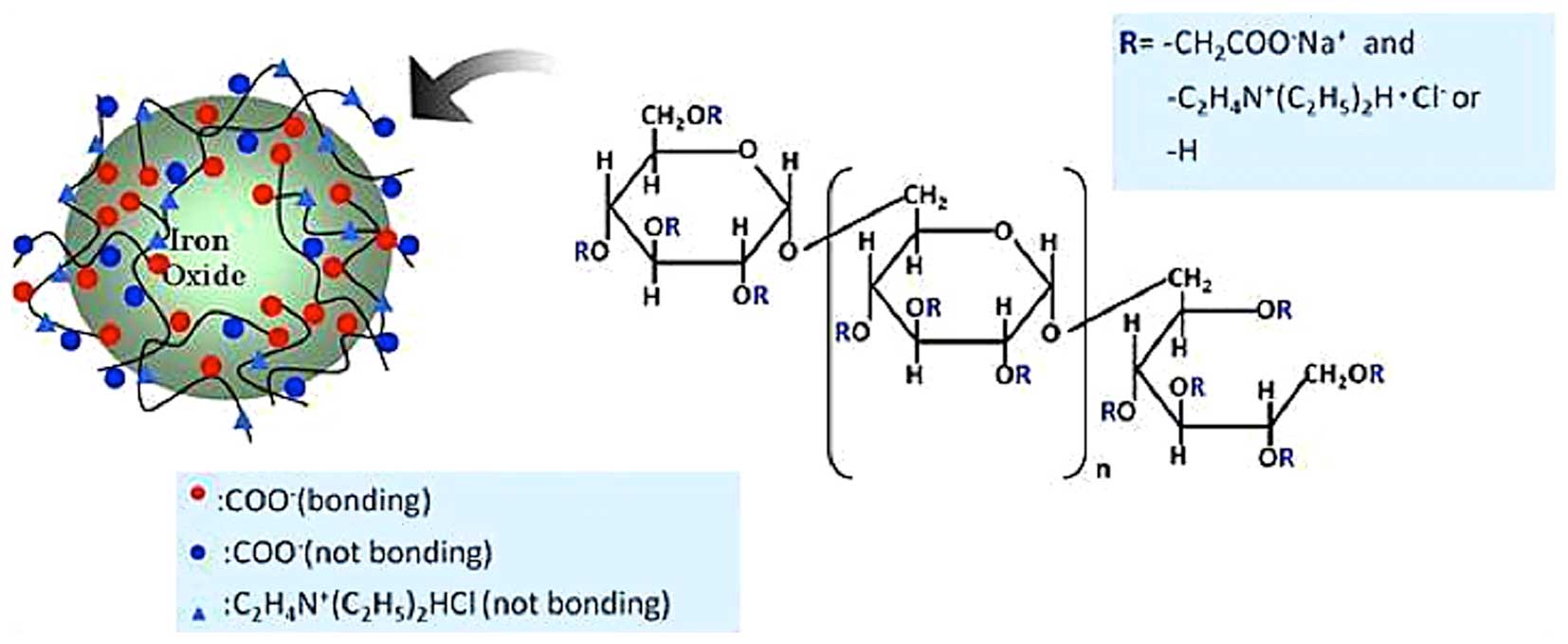
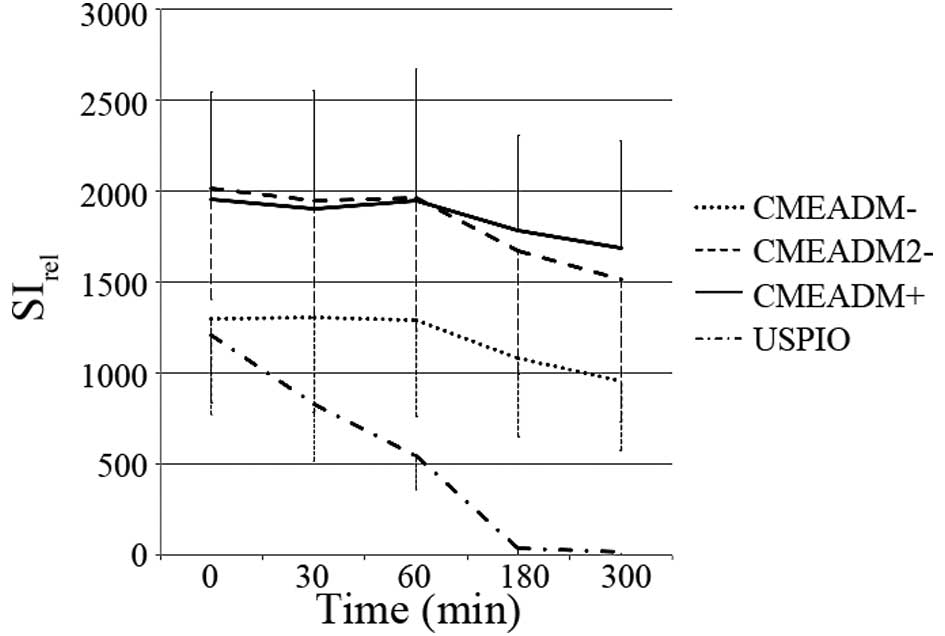
|
1
|
Allkemper T, Bremer C, Matuszewski L,
Ebert W and Reimer P: Contrast-enhanced blood-pool MR angiography
with optimized iron oxides: Effect of size and dose on vascular
contrast enhancement in rabbits. Radiology. 223:432–438. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bremerich J, Bilecen D and Reimer P: MR
angiography with blood pool contrast agents. Eur Radiol.
17:3017–3024. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Leung K: Ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron
oxide nanoparticles conjugated with
Ile-Pro-Leu-Pro-Phe-Tyr-AsnMolecular imaging and contrast agent
database (MICAD). Bethesda (MD): Fed. 23–2010
|
|
4
|
Bryson J, Reineke JW and Reineke TM:
Macromolecular imaging agents containing lanthanides: Can
conceptual promise lead to clinical potential? Macromolecules.
45:8939–8952. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Grist TM, Korosec FR, Peters DC, Witte S,
Walovitch RC, Dolan RP, Bridson WE, Yucel EK and Mistretta CA:
Steady-state and dynamic MR angiography with MS-325: Initial
experience in humans. Radiology. 207:539–544. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weller A, Barber JL and Olsen OE:
Gadolinium and nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: An update. Pediatr
Nephrol. 29:1927–1937. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Xiao W, Lin J, Li M, Ma Y, Chen Y, Zhang
C, Li D and Gu H: Prolonged in vivo circulation time by
zwitterionic modification of magnetite nanoparticles for blood pool
contrast agents. Contrast Media Mol Imaging. 7:320–327. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nitta N, Tsuchiya K, Sonoda A, Ota S,
Ushio N, Takahashi M, Murata K and Nohara S: Negatively charged
superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: A new blood-pooling
magnetic resonance contrast agent. Jpn J Radiol. 30:832–839. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tsuchiya K, Nitta N, Sonoda A, Nitta-Seko
A, Ohta S, Takahashi M, Murata K, Mukaisho K, Shiomi M, Tabata Y
and Nohara S: Evaluation of atherosclerotic lesions using dextran-
and mannan-dextran-coated USPIO: MRI analysis and pathological
findings. Int J Nanomedicine. 7:2271–2280. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tsuchiya K, Nitta N, Sonoda A, Otani H,
Takahashi M, Murata K, Shiomi M, Tabata Y and Nohara S:
Atherosclerotic imaging using 4 types of superparamagnetic iron
oxides: New possibilities for mannan-coated particles. Eur J
Radiol. 82:1919–1925. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Arbab AS, Liu W and Frank JA: Cellular
magnetic resonance imaging: Current status and future prospects.
Expert Rev Med Devices. 3:427–439. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kawaguchi T, Hanaichi T, Hasegawa M and
Maruno S: Dextran-magnetite complex: Conformation of dextran chains
and stability of solution. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 12:121–127. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Raynal I, Prigent P, Peyramaure S, Najid
A, Rebuzzi C and Corot C: Macrophage endocytosis of
superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Mechanisms and
comparison of ferumoxides and ferumoxtran-10. Invest Radiol.
39:56–63. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Neuwelt EA, Hamilton BE, Varallyay CG,
Rooney WR, Edelman RD, Jacobs PM and Watnick SG: Ultrasmall
superparamagnetic iron oxides (USPIOs): A future alternative
magnetic resonance (MR) contrast agent for patients at risk for
nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF)? Kidney Int. 75:465–474. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Corot C, Port M, Guibert I, Robert P,
Raynal I, Robic C, Raynaud JS, Prigent P, Dencausse A, et al:
Superparamagnetic contrast agents. 1st. London: CRC Press; pp.
59–84. 2007
|
|
16
|
Jo J, Aoki I and Tabata Y: Design of iron
oxide nanoparticles with different sizes and surface charges for
simple and efficient labeling of mesenchymal stem cells. J Control
Release. 142:465–473. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gaur U, Sahoo SK, De TK, Ghosh PC, Maitra
A and Ghosh PK: Biodistribution of fluoresceinated dextran using
novel nanoparticles evading reticuloendothelial system. Int J
Pharm. 202:1–10. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bulte JW and Kraitchman DL: Iron oxide MR
contrast agents for molecular and cellular imaging. NMR Biomed.
17:484–499. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Klasen J, Blondin D, Schmitt P, Bi X,
Sansone R, Wittsack HJ, Kröpil P, Quentin M, Kuhlemann J, Miese F,
et al: Nonenhanced ECG-gated quiescent-interval single-shot MRA
(QISS-MRA) of the lower extremities: Comparison with
contrast-enhanced MRA. Clin Radiol. 67:441–446. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vaage-Nilsen O: Acute, severe and
anaphylactoid reactions are very rare with low-molecular-weight
iron dextran, CosmoFer. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 23:33722008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|