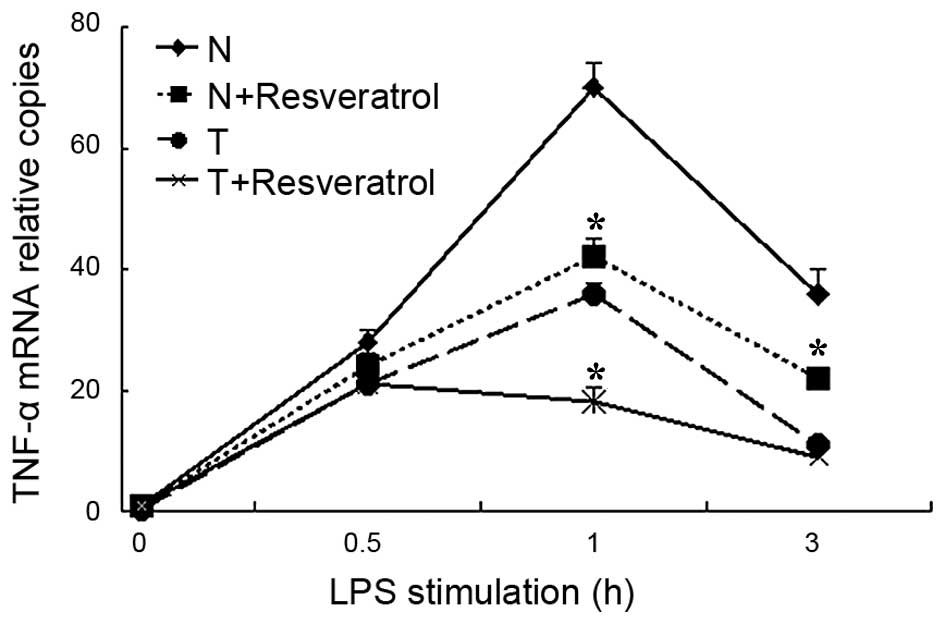
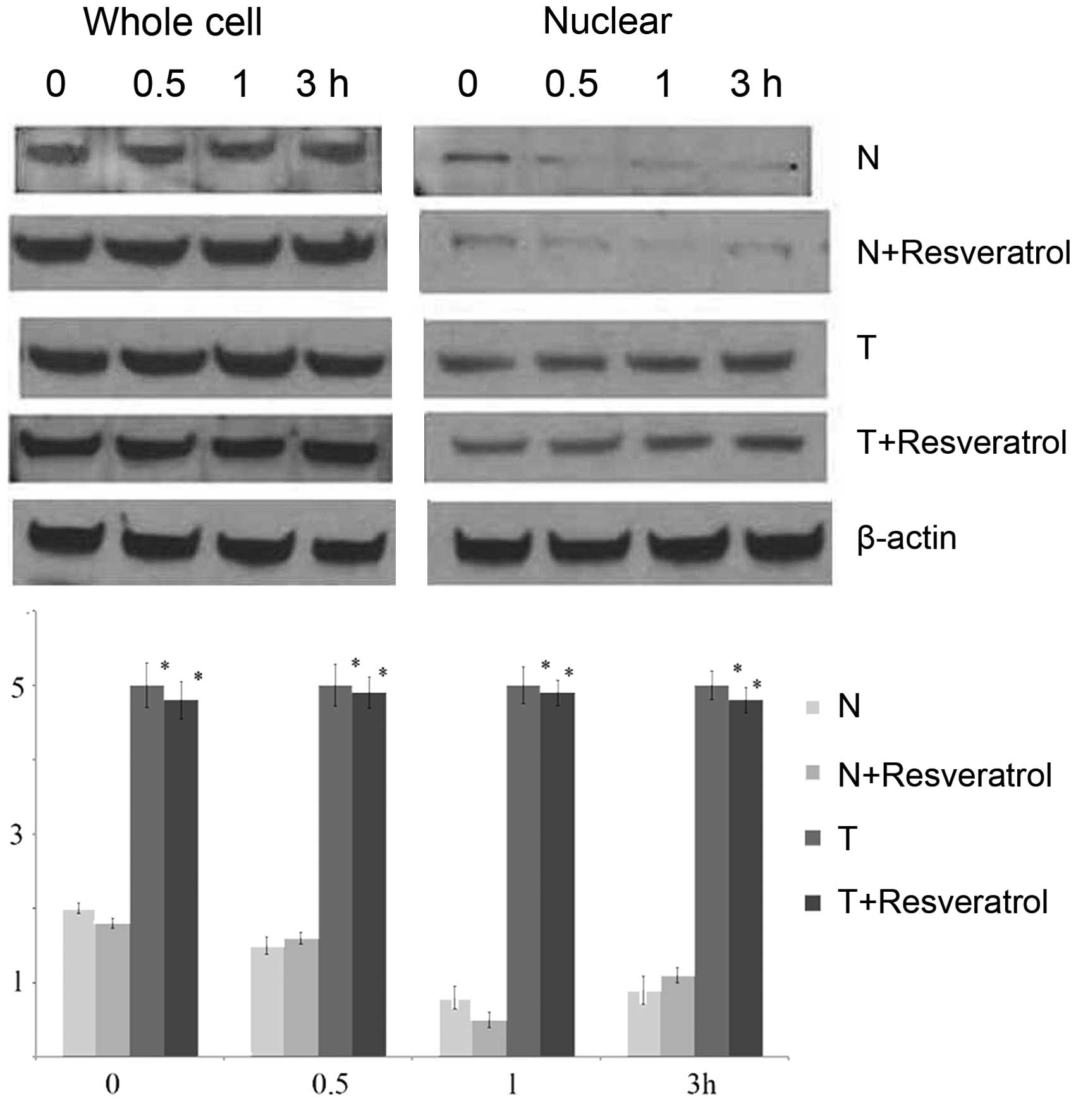
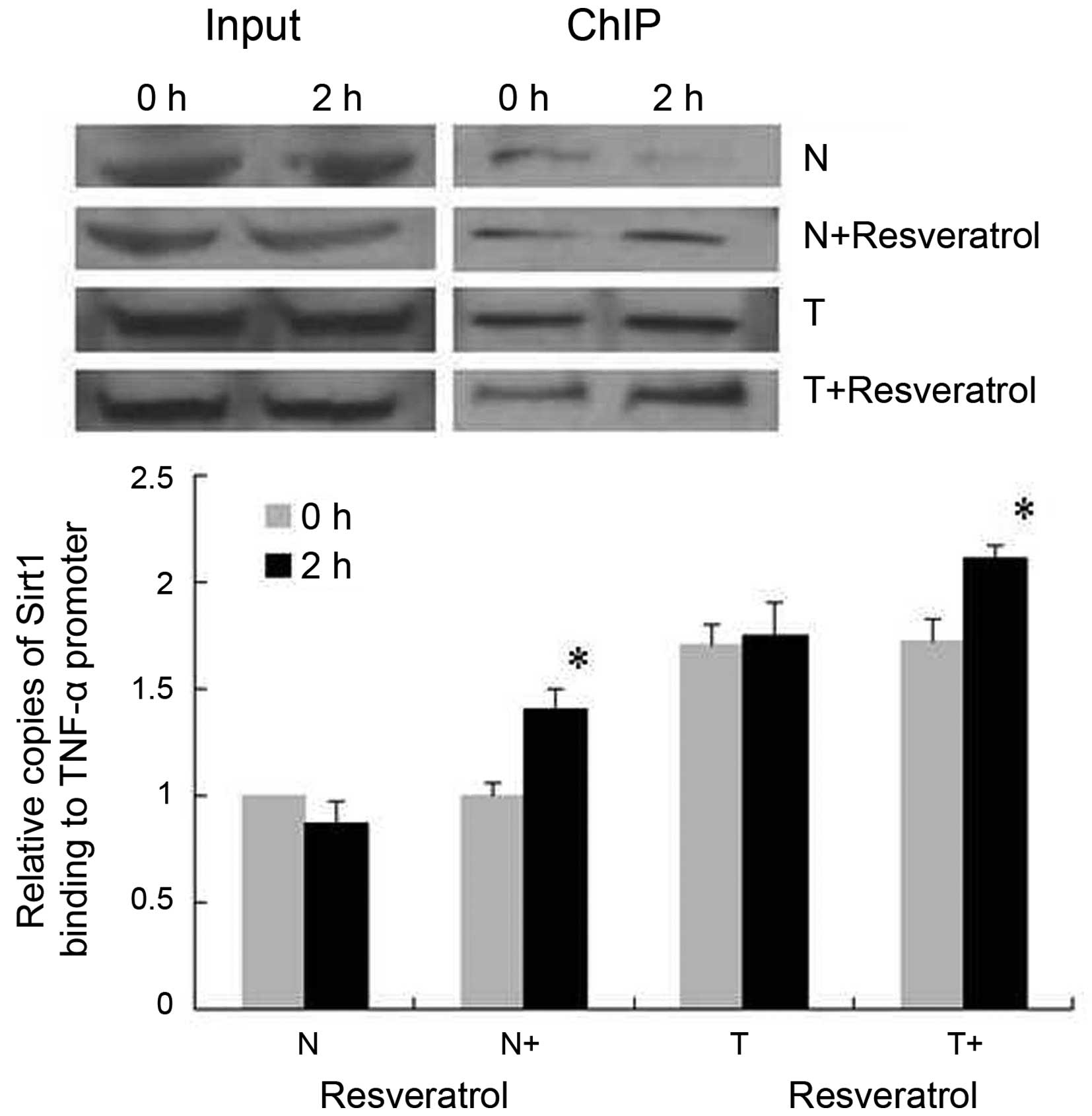
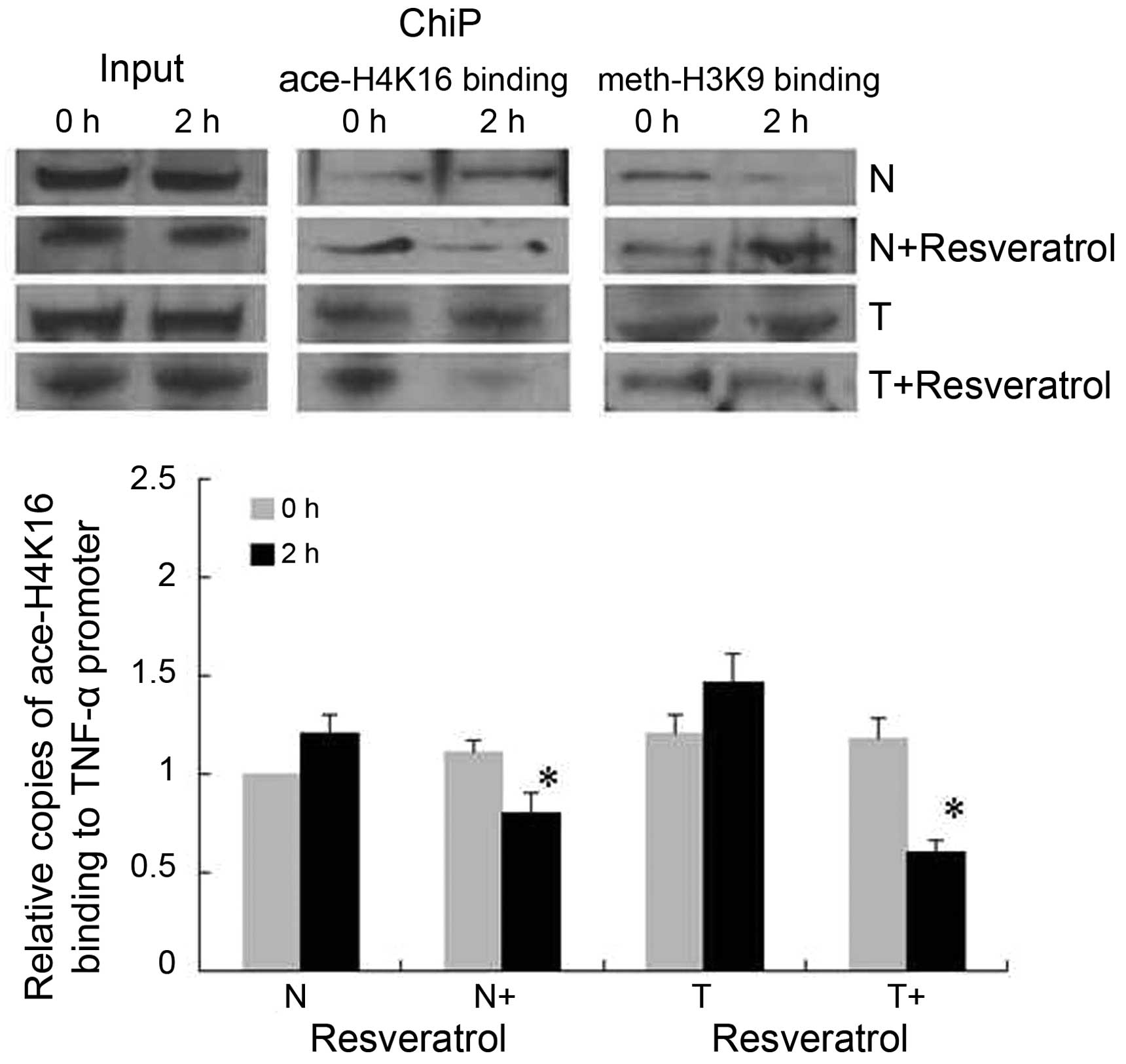
|
1
|
Stearns-Kurosawa DJ, Osuchowski MF,
Valentine C, Kurosawa S and Remick DG: The pathogenesis of sepsis.
Annu Rev Pathol. 6:19–48. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cai B, Deitch EA and Ulloa L: Novel
insights for systemic inflammation in sepsis and hemorrhage.
Mediators Inflamm. 2010:6424622010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Russell JA: Management of sepsis. N Engl J
Med. 355:1699–1713. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Matsuda A, Jacob A, Wu R, Aziz M, Yang WL,
Matsutani T, Suzuki H, Furukawa K, Uchida E and Wang P: Novel
therapeutic targets for sepsis: Regulation of exaggerated
inflammatory responses. J Nippon Med Sch. 79:4–18. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nolan A, Weiden M, Kelly A, Hoshino Y,
Hoshino S, Mehta N and Gold JA: CD40 and CD80/86 act
synergistically to regulate inflammation and mortality in
polymicrobial sepsis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 177:301–308. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Flohé SB, Agrawal H, Schmitz D, Gertz M,
Flohé S and Schade FU: Dendritic cells during polymicrobial sepsis
rapidly mature but fail to initiate a protective Th1-type immune
response. J Leukoc Biol. 79:473–481. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Roger PM, Hyvernat H, Ticchioni M, Kumar
G, Dellamonica J and Bernardin G: The early phase of human sepsis
is characterized by a combination of apoptosis and proliferation of
T cells. J Crit Care. 27:384–393. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paunel-Görgülü A, Kirichevska T, Lögters
T, Windolf J and Flohé S: Molecular mechanisms underlying delayed
apoptosis in neutrophils from multiple trauma patients with and
without sepsis. Mol Med. 18:325–335. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Russell JA, Boyd J, Nakada T, Thair S and
Walley KR: Molecular mechanisms of sepsis. Contrib Microbiol.
17:48–85. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Simmons GE Jr, Pruitt WM and Pruitt K:
Diverse roles of SIRT1 in cancer biology and lipid metabolism. Int
J Mol Sci. 16:950–965. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Giblin W, Skinner ME and Lombard DB:
Sirtuins: Guardians of mammalian healthspan. Trends Genet.
30:271–286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Liu TF, Vachharajani V, Millet P,
Bharadwaj MS, Molina AJ and McCall CE: Sequential actions of
SIRT1-RELB-SIRT3 coordinate nuclear-mitochondrial communication
during immunometabolic adaptation to acute inflammation and sepsis.
J Biol Chem. 290:396–408. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xu W, Lu Y, Yao J, Li Z, Chen Z, Wang G,
Jing H, Zhang X, Li M, Peng J and Tian X: Novel role of
resveratrol: Suppression of high-mobility group protein box 1
nucleocytoplasmic translocation by the upregulation of sirtuin 1 in
sepsis-induced liver injury. Shock. 42:440–447. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jia Y, Zheng Z, Wang Y, Zhou Q, Cai W, Jia
W, Yang L, Dong M, Zhu X, Su L and Hu D: SIRT1 is a regulator in
high glucose-induced inflammatory response in RAW264.7 cells. PLoS
One. 10:e01208492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Gao R, Ma Z, Hu Y, Chen J, Shetty S and Fu
J: SirT1 restrains lung inflammasome activation in a murine model
of sepsis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 308:L847–L853. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schug TT, Xu Q, Gao H, Peres-da-Silva A,
Draper DW, Fessler MB, Purushotham A and Li X: Myeloid deletion of
SIRT1 induces inflammatory signaling in response to environmental
stress. Mol Cell Biol. 30:4712–4721. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang Z, Kahn BB, Shi H and Xue BZ:
Macrophage alpha1 AMP-activated protein kinase (alpha1AMPK)
antagonizes fatty acid-induced inflammation through SIRT1. J Biol
Chem. 285:19051–19059. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Imai S, Armstrong CM, Kaeberlein M and
Guarente L: Transcriptional silencing and longevity protein Sir2 is
an NAD-dependent histone deacetylase. Nature. 403:795–800. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Vaquero A, Scher M, Lee D,
Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P and Reinberg D: Human SirT1 interacts
with histone H1 and promotes formation of facultative
heterochromatin. Mol Cell. 16:93–105. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu TF, Yoza BK, El Gazzar M, Vachharajani
VT and McCall CE: NAD+-dependent SIRT1 deacetylase
participates in epigenetic reprogramming during endotoxin
tolerance. J Biol Chem. 286:9856–9864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chen X, Yoza BK, El Gazzar M, Hu JY,
Cousart SL and McCall CE: RelB sustains IkappaBalpha expression
during endotoxin tolerance. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 16:104–110. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li J, Qu X, Ricardo SD, Bertram JF and
Nikolic-Paterson DJ: Resveratrol inhibits renal fibrosis in the
obstructed kidney: Potential role in deacetylation of Smad3. Am J
Pathol. 177:1065–1071. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
El Gazzar M, Yoza BK, Chen X, Hu J,
Hawkins GA and McCall CE: G9a and HP1 couple histone and DNA
methylation to TNFalpha transcription silencing during endotoxin
tolerance. J Biol Chem. 283:32198–32208. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hou J, Chong ZZ, Shang YC and Maiese K:
Early apoptotic vascular signaling is determined by SirT1 through
nuclear shuttling, forkhead trafficking, bad, and mitochondrial
caspase activation. Curr Neurovasc Res. 7:95–112. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Autiero I, Costantini S and Colonna G:
Human Sirt-1: Molecular modeling and structure-function
relationships of an unordered protein. PLoS One. 4:e73502008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sharma A, Gautam V, Costantini S, Paladino
A and Colonna G: Interactomic and pharmacological insights on human
Sirt-1. Front Pharmacol. 3:402012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kim EJ, Kho JH, Kang MR and Um SJ: Active
regulator of SIRT1 cooperates with SIRT1 and facilitates
suppression of p53 activity. Mol Cell. 28:277–290. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Li T, Zhang J, Feng J, Li Q, Wu L, Ye Q,
Sun J, Lin Y, Zhang M, Huang R, et al: Resveratrol reduces acute
lung injury in a LPS-induced sepsis mouse model via activation of
SirT1. Mol Med Rep. 7:1889–1895. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Franco JG, de Moura EG, Koury JC, Trotta
PA, Cordeiro A, Souza LL, Almeida NA, Lima Nda S, Pazos-Moura CC,
Lisboa PC and Passos MC: Resveratrol reduces lipid peroxidation and
increases sirtuin 1 expression in adult animals programmed by
neonatal protein restriction. J Endocrinol. 207:319–328. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Chen X, El Gazzar M, Yoza BK and McCall
CE: The NF-kappaB factor RelB and histone H3 lysine
methyltransferase G9a directly interact to generate epigenetic
silencing in endotoxin tolerance. J Biol Chem. 284:27857–27865.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
El Gazzar M, Yoza BK, Chen X, Garcia BA,
Young NL and McCall CE: Chromatin-specific remodeling by HMGB1 and
linker histone H1 silences proinflammatory genes during endotoxin
tolerance. Mol Cell Biol. 29:1959–1971. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|