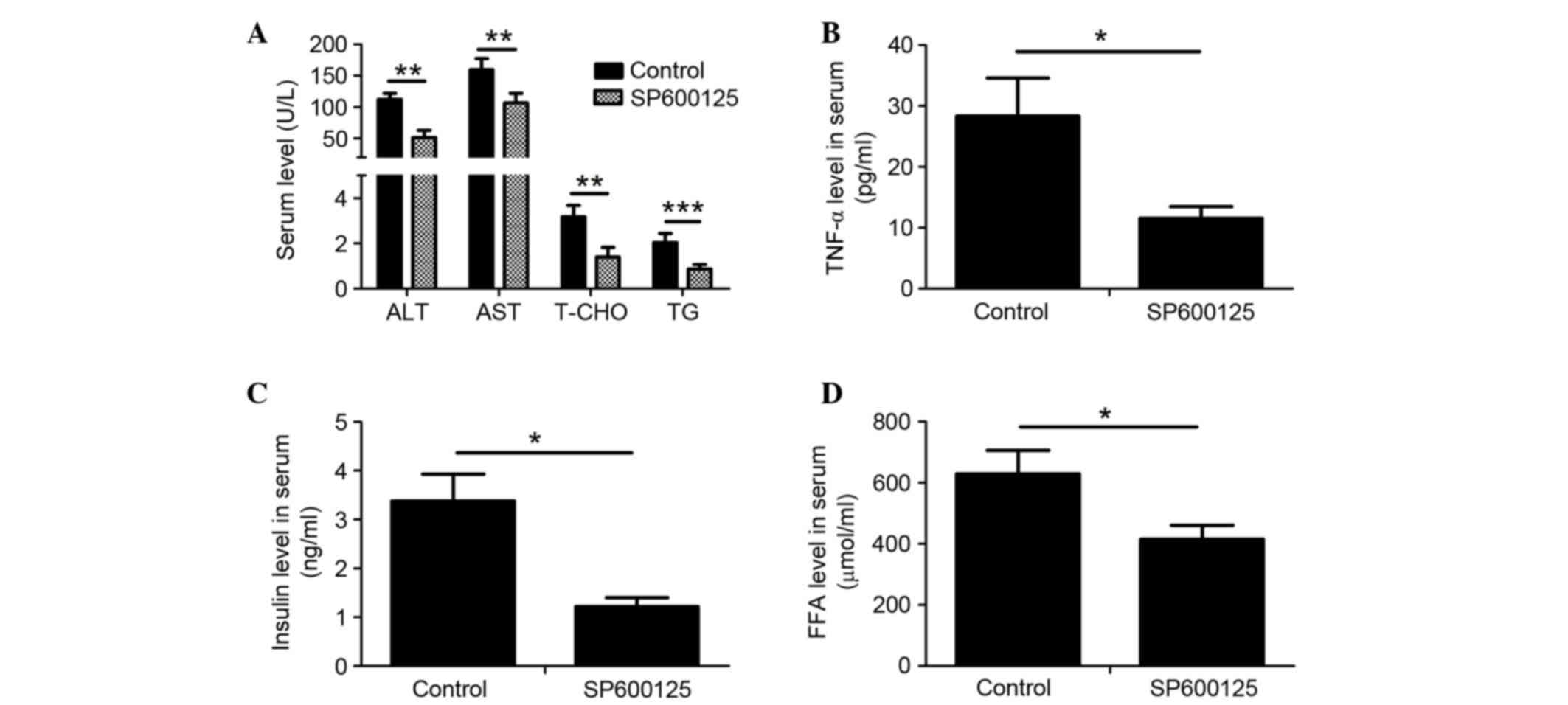
|
1
|
Chang E, Park CY and Park SW: Role of
thiazolidinediones, insulin sensitizers, in non-alcoholic fatty
liver disease. J Diabetes Investig. 4:517–524. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, Görgün CZ,
Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M and Hotamisligil GS: A central role for
JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature. 420:333–336. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Brännmark C, Nyman E, Fagerholm S,
Bergenholm L, Ekstrand EM, Cedersund G and Strålfors P: Insulin
signaling in type 2 diabetes: Experimental and modeling analyses
reveal mechanisms of insulin resistance in human adipocytes. J Biol
Chem. 288:9867–9880. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sethi JK and Hotamisligil GS: The role of
TNF alpha in adipocyte metabolism. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 10:19–29.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boden G: Role of fatty acids in the
pathogenesis of insulin resistance and NIDDM. Diabetes. 46:3–10.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schattenberg JM, Singh R, Wang Y,
Lefkowitch JH, Rigoli RM, Scherer PE and Czaja MJ: JNK1 but not
JNK2 promotes the development of steatohepatitis in mice.
Hepatology. 43:163–172. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hiratani K, Haruta T, Tani A, Kawahara J,
Usui I and Kobayashi M: Roles of mTOR and JNK in serine
phosphorylation, translocation and degradation of IRS-1. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 335:836–842. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun RQ, Wang H, Zeng XY, Chan SM, Li SP,
Jo E, Leung SL, Molero JC and Ye JM: IRE1 impairs insulin signaling
transduction of fructose-fed mice via JNK independent of excess
lipid. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1852:156–165. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li DD, Wang LL, Deng R, Tang J, Shen Y,
Guo JF, Wang Y, Xia LP, Feng GK, Liu QQ, et al: The pivotal role of
c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase-mediated Beclin 1 expression during
anticancer agents-induced autophagy in cancer cells. Oncogene.
28:886–898. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kluwe J, Pradere JP, Gwak GY, Mencin A, De
Minicis S, Osterreicher CH, Colmenero J, Bataller R and Schwabe RF:
Modulation of hepatic fibrosis by c-Jun-N-terminal kinase
inhibition. Gastroenterology. 138:347–359. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Novak
I, Komatsu M, Tanaka K, Cuervo AM and Czaja MJ: Autophagy regulates
lipid metabolism. Nature. 458:1131–1135. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim KH, Jeong YT, Oh H, Kim SH, Cho JM,
Kim YN, Kim SS, Kim do H, Hur KY, Kim HK, et al: Autophagy
deficiency leads to protection from obesity and insulin resistance
by inducing Fgf21 as a mitokine. Nat Med. 19:83–92. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Rautou PE, Mansouri A, Lebrec D, Durand F,
Valla D and Moreau R: Autophagy in liver diseases. J Hepatol.
53:1123–1134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ma D, Molusky MM, Song J, Hu CR, Fang F,
Rui C, Mathew AV, Pennathur S, Liu F, Cheng JX, et al: Autophagy
deficiency by hepatic FIP200 deletion uncouples steatosis from
liver injury in NAFLD. Mol Endocrinol. 27:1643–1654. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li L, Hai J, Li Z, Zhang Y, Peng H, Li K
and Weng X: Resveratrol modulates autophagy and NF-κB activity in a
murine model for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Food
Chem Toxicol. 63:166–173. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Christian P, Sacco J and Adeli K:
Autophagy: Emerging roles in lipid homeostasis and metabolic
control. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1831:819–824. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Gonzalez-Rodriguez A, Mayoral R, Agra N,
Valdecantos MP, Pardo V, Miquilena-Colina ME, Vargas-Castrillón J,
Lo Iacono O, Corazzari M, Fimia GM, et al: Impaired autophagic flux
is associated with increased endoplasmic reticulum stress during
the development of NAFLD. Cell Death Dis. 5:e11792014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang L, Li P, Fu S, Calay ES and
Hotamisligil GS: Defective hepatic autophagy in obesity promotes ER
stress and causes insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 11:467–478. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shibata M, Yoshimura K, Furuya N, Koike M,
Ueno T, Komatsu M, Arai H, Tanaka K, Kominami E and Uchiyama Y: The
MAP1-LC3 conjugation system is involved in lipid droplet formation.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 382:419–423. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shimizu S, Konishi A, Nishida Y, Mizuta T,
Nishina H, Yamamoto A and Tsujimoto Y: Involvement of JNK in the
regulation of autophagic cell death. Oncogene. 29:2070–2082. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wei Y, Pattingre S, Sinha S, Bassik M and
Levine B: JNK1-mediated phosphorylation of Bcl-2 regulates
starvation-induced autophagy. Mol Cell. 30:678–688. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Komiya K, Uchida T, Ueno T, Koike M, Abe
H, Hirose T, Kawamori R, Uchiyama Y, Kominami E, Fujitani Y and
Watada H: Free fatty acids stimulate autophagy in pancreatic
β-cells via JNK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 401:561–567.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhou L, Zhang J, Fang Q, Liu M, Liu X, Jia
W, Dong LQ and Liu F: Autophagy-mediated insulin receptor
down-regulation contributes to endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced
insulin resistance. Mol Pharmacol. 76:596–603. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
D'Adamo E, Cali AM, Weiss R, Santoro N,
Pierpont B, Northrup V and Caprio S: Central role of fatty liver in
the pathogenesis of insulin resistance in obese adolescents.
Diabetes Care. 33:1817–1822. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kodama Y and Brenner DA: c-Jun N-terminal
kinase signaling in the pathogenesis of nonalcoholic fatty liver
disease: Multiple roles in multiple steps. Hepatology. 49:6–8.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Solinas G and Karin M: JNK1 and IKK beta:
Molecular links between obesity and metabolic dysfunction. FASEB J.
24:2596–2611. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Singh R, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Tanaka KE,
Gaarde WA and Czaja MJ: Differential effects of JNK1 and JNK2
inhibition on murine steatohepatitis and insulin resistance.
Hepatology. 49:87–96. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Özcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi
NN, Ozdelen E, Tuncman G, Görgün C, Glimcher LH and Hotamisligil
GS: Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action and
type 2 diabetes. Science. 306:457–461. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Amir M and Czaƒja MJ: Autophagy in
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
5:159–166. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kovsan J, Blüher M, Tarnovscki T, Klöting
N, Kirshtein B, Madar L, Shai I, Golan R, Harman-Boehm I, Schön MR,
et al: Altered autophagy in human adipose tissues in obesity. J
Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E268–E277. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Zhang Y, Goldman S, Baerga R, Zhao Y,
Komatsu M and Jin S: Adipose-specific deletion of autophagy-related
gene 7 (atg7) in mice reveals a role in adipogenesis. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 106:19860–19865. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Khamzina L, Veilleux A, Bergeron S and
Marette A: Increased activation of the mammalian target of
rapamycin pathway in liver and skeletal muscle of obese rats:
Possible involvement in obesity-linked insulin resistance.
Endocrinology. 146:1473–1481. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lou J, Wang Y, Wang X and Jiang Y:
Uncoupling protein 2 regulates palmitic acid-induced hepatoma cell
autophagy. Biomed Res Int. 2014:8104012014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Sekine Y, Takeda K and Ichijo H: The
ASK1-MAP kinase signaling in ER stress and neurodegenerative
diseases. Curr Mol Med. 6:87–97. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|