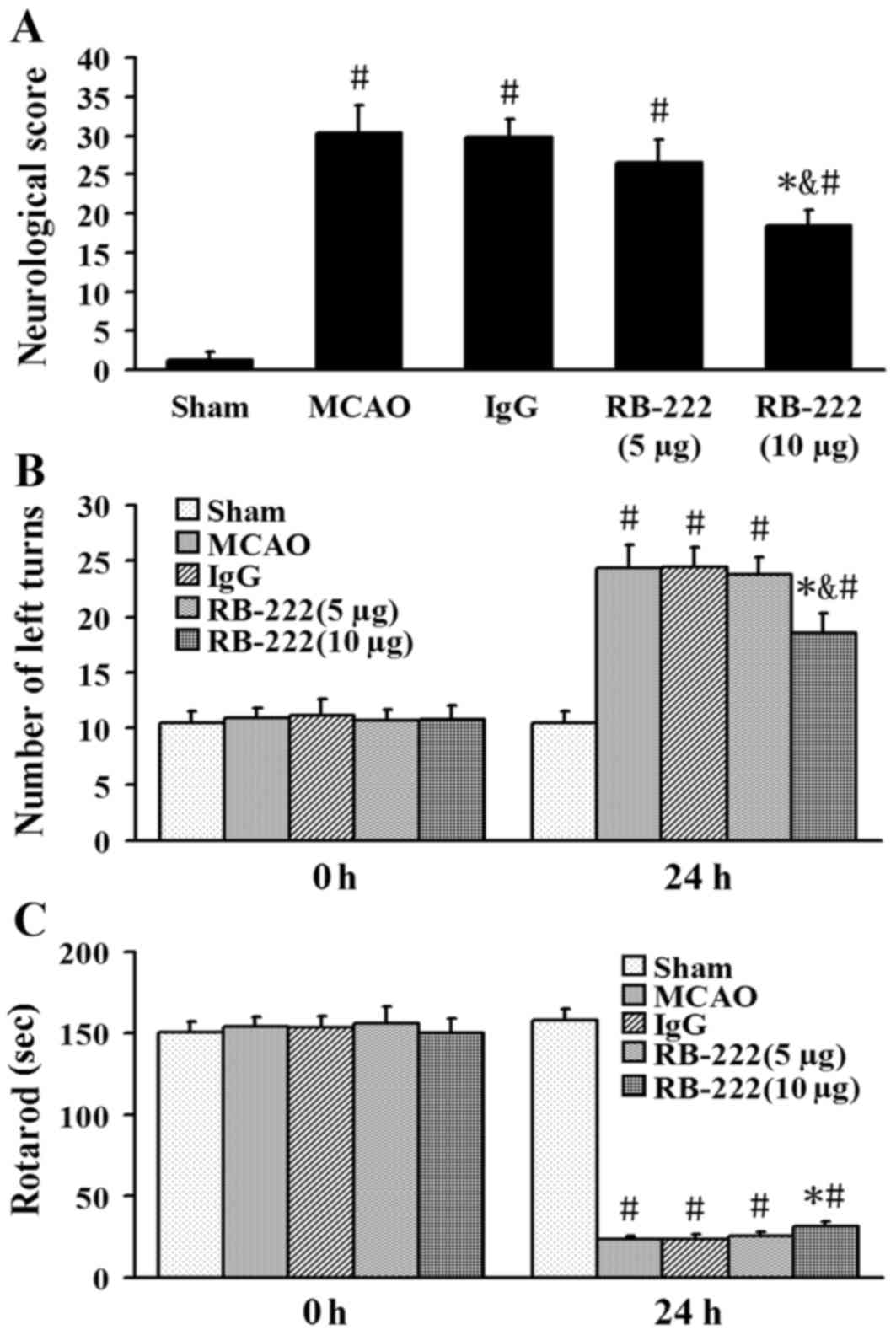
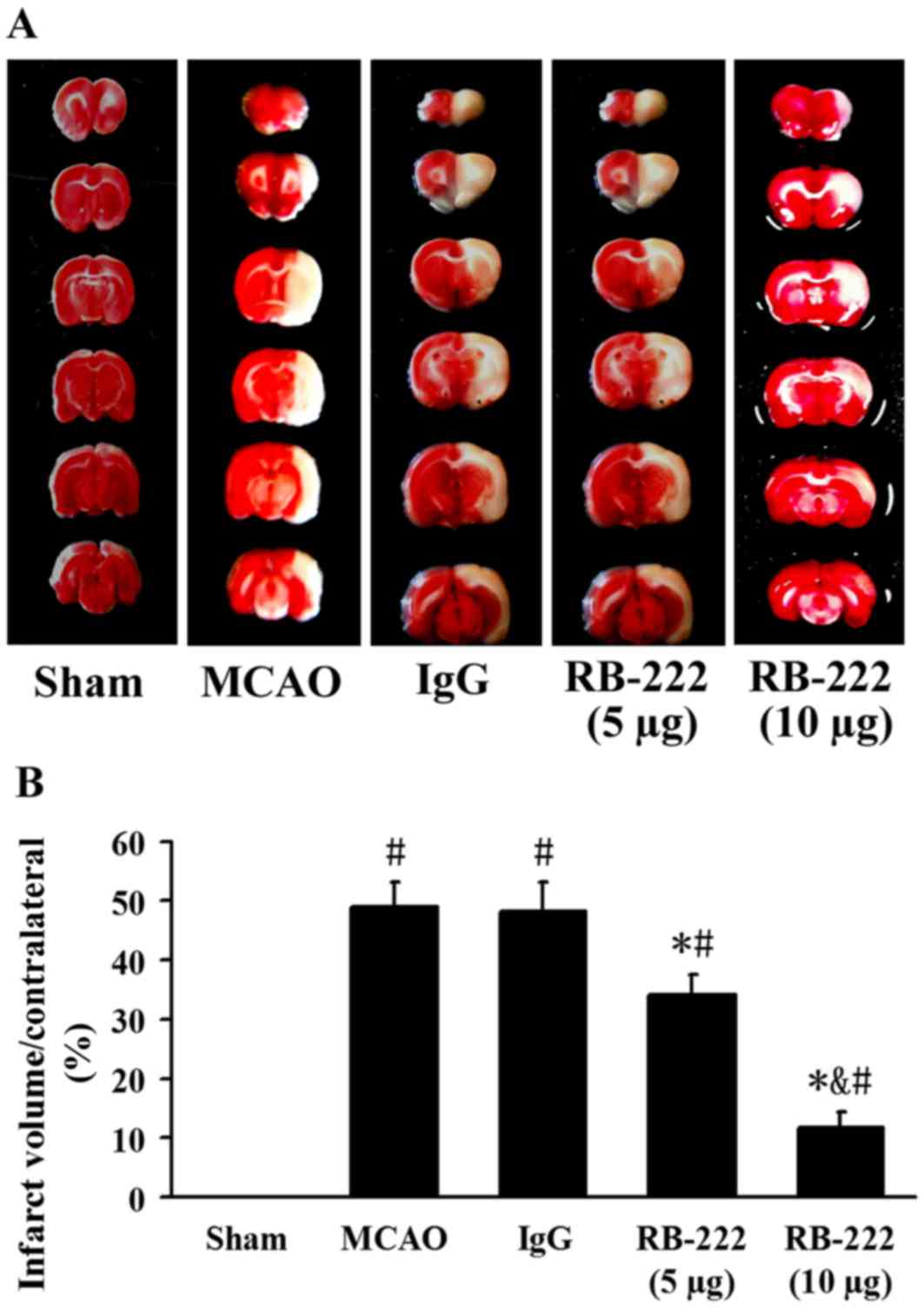
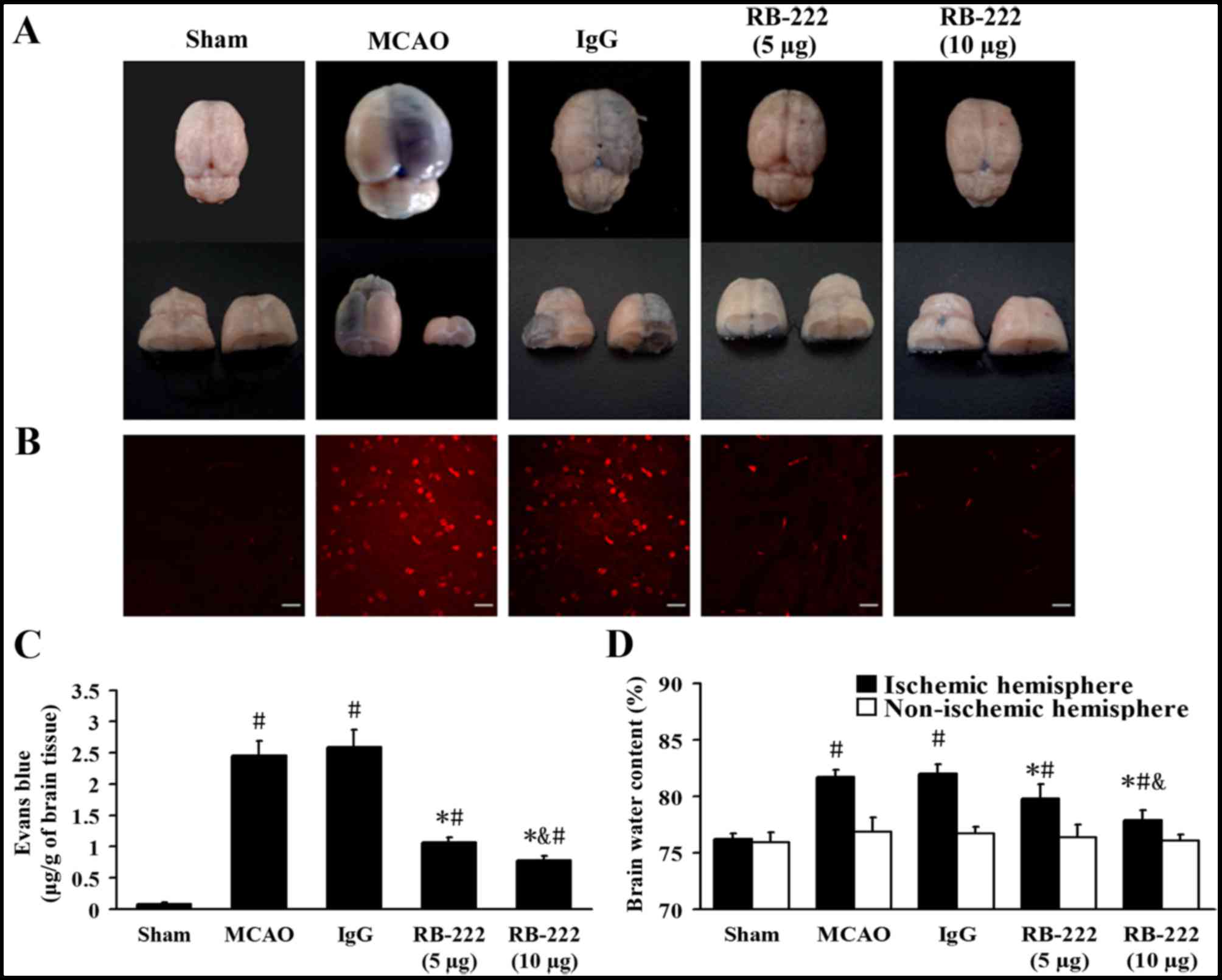
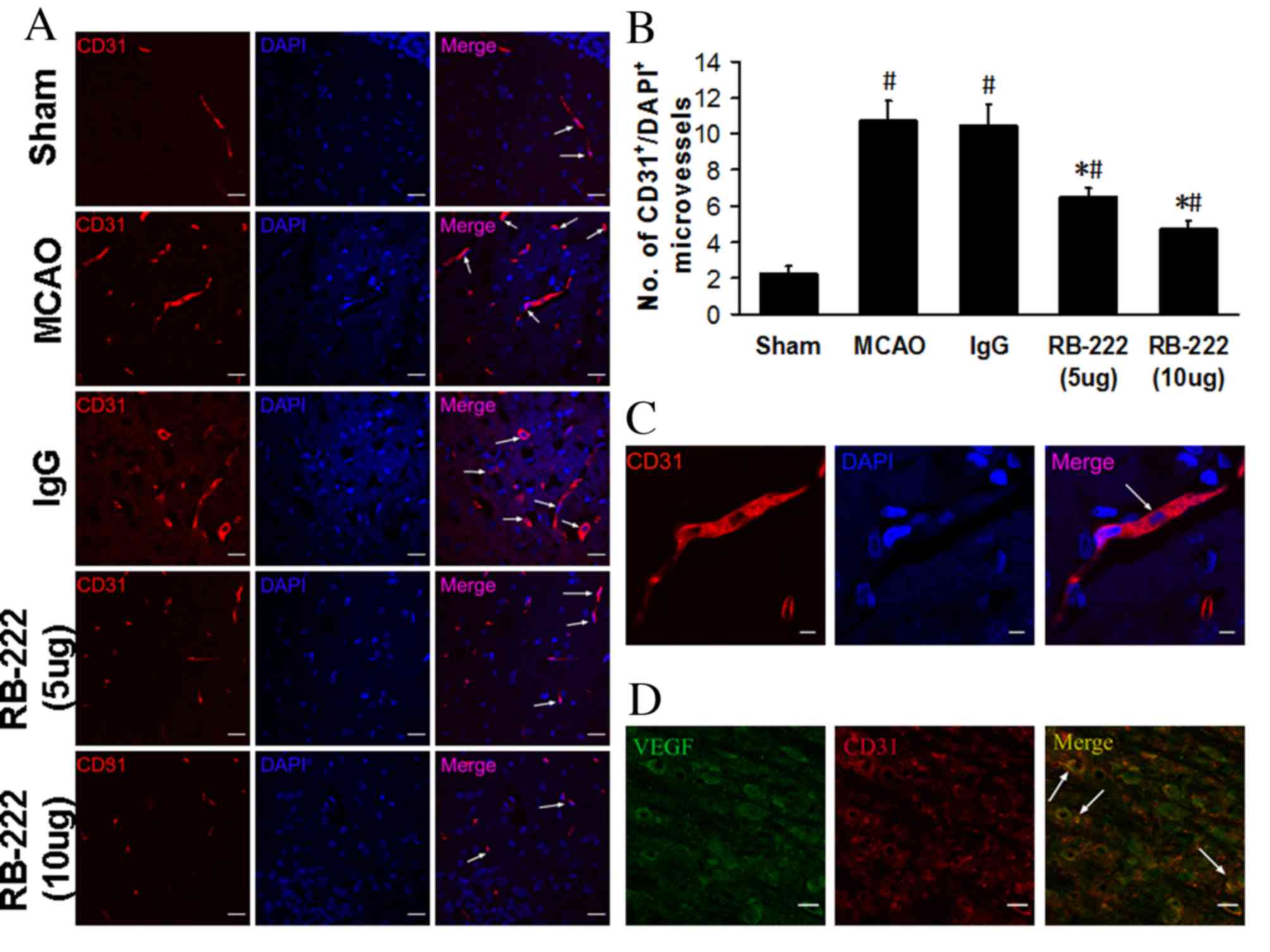
|
1
|
Krueger M, Bechmann I, Immig K,
Reichenbach A, Härtig W and Michalski D: Blood-brain barrier
breakdown involves four distinct stages of vascular damage in
various models of experimental focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb
Blood Flow Metab. 35:292–303. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ayata C and Ropper AH: Ischaemic brain
oedema. J Clin Neurosci. 9:113–124. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Battey TW, Karki M, Singhal AB, Wu O,
Sadaghiani S, Campbell BC, Davis SM, Donnan GA, Sheth KN and
Kimberly WT: Brain edema predicts outcome after nonlacunar ischemic
stroke. Stroke. 45:3643–3648. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Greenberg DA and Jin K: Vascular
endothelial growth factors (VEGFs) and stroke. Cell Mol Life Sci.
70:753–1761. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Hayashi T, Abe K, Suzuki H and Itoyama Y:
Rapid induction of vascular endothelial growth factor gene
expression after transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in
rats. Stroke. 28:2039–2044. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang ZG, Zhang L, Jiang Q, Zhang R,
Davies K, Powers C, Bruggen Nv and Chopp M: VEGF enhances
angiogenesis and promotes blood-brain barrier leakage in the
ischemic brain. J Clin Invest. 106:829–838. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yang Y, Estrada EY, Thompson JF, Liu W and
Rosenberg GA: Matrix metalloproteinase-mediated disruption of tight
junction proteins in cerebral vessels is reversed by synthetic
matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor in focal ischemia in rat. J
Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:697–709. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kurzepa J, Kurzepa J, Golab P, Czerska S
and Bielewicz J: The significance of matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in the ischemic stroke. Int J Neurosci.
124:707–716. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yang Y, Thompson JF, Taheri S, Salayandia
VM, McAvoy TA, Hill JW, Yang Y, Estrada EY and Rosenberg GA: Early
inhibition of MMP activity in ischemic rat brain promotes
expression of tight junction proteins and angiogenesis during
recovery. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 33:1104–1114. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rosenberg GA, Estrada EY and Dencoff JE:
Matrix metalloproteinases and TIMPs are associated with blood-brain
barrier opening after reperfusion in rat brain. Stroke.
29:2189–2195. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Seo JH, Guo S, Lok J, Navaratna D, Whalen
MJ, Kim KW and Lo EH: Neurovascular matrix metalloproteinases and
the blood-brain barrier. Curr Pharm Des. 18:3645–3648. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lenglet S, Montecucco F and Mach F: Role
of matrix metalloproteinases in animal models of ischemic stroke.
Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 13:161–166. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
van Bruggen N, Thibodeaux H, Palmer JT,
Lee WP, Fu L, Cairns B, Tumas D, Gerlai R, Williams SP, van
Lookeren Campagne M and Ferrara N: VEGF antagonism reduces edema
formation and tissue damage after ischemia/reperfusion injury in
the mouse brain. J Clin Invest. 104:1613–1620. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kimura R, Nakase H, Tamaki R and Sakaki T:
Vascular endothelial growth factor antagonist reduces brain edema
formation and venous infarction. Stroke. 36:1259–1263. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Chi OZ, Hunter C, Liu X and Weiss HR:
Effects of anti-VEGF antibody on blood-brain barrier disruption in
focal cerebral ischemia. Exp Neurol. 204:283–287. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kanazawa M, Igarashi H, Kawamura K,
Takahashi T, Kakita A, Takahashi H, Nakada T, Nishizawa M and
Shimohata T: Inhibition of VEGF signaling pathway attenuates
hemorrhage after tPA treatment. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
31:1461–1474. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Reglodi D, Tamás A and Lengvári I:
Examination of sensorimotor performance following middle cerebral
artery occlusion in rats. Brain Res Bull. 59:459–466. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wijdicks EF, Sheth KN, Carter BS, Greer
DM, Kasner SE, Kimberly WT, Schwab S, Smith EE, Tamargo RJ and
Wintermark M: American Heart Association Stroke Council:
Recommendations for the management of cerebral and cerebellar
infarction with swelling: A statement for healthcare professionals
from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association.
Stroke. 45:1222–1238. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Bae ON, Serfozo K, Baek SH, Lee KY,
Dorrance A, Rumbeiha W, Fitzgerald SD, Farooq MU, Naravelta B,
Bhatt A and Majid A: Safety and efficacy evaluation of carnosine,
an endogenous neuroprotective agent for ischemic stroke. Stroke.
44:205–212. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Schaar KL, Brenneman MM and Savitz SI:
Functional assessments in the rodent stroke model. Exp Transl
Stroke Med. 2:132010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Beck H and Plate KH: Angiogenesis after
cerebral ischemia. Acta Neuropathol. 117:481–496. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Krupinski J, Kaluza J, Kumar P, Kumar S
and Wang JM: Role of angiogenesis in patients with cerebral
ischemic stroke. Stroke. 25:1794–1798. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang Y, Wang J, Lin X, Wang L, Shao B, Jin
K, Wang Y and Yang GY: Neural stem cell protects aged rat brain
from ischemia-reperfusion injury through neurogenesis and
angiogenesis. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 34:1138–1147. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao XO,
Logvinova A and Greenberg DA: VEGF-induced neuroprotection,
neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J
Clin Invest. 111:1843–1851. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Liu J, Jin X, Liu KJ and Liu W: Matrix
metalloproteinase-2-mediated occludin degradation and
caveolin-1-mediated claudin-5 redistribution contribute to
blood-brain barrier damage in early ischemic stroke stage. J
Neurosci. 32:3044–3057. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Tsukita S and Furuse M: Pores in the wall:
Claudins constitute tight junction strands containing aqueous
pores. J Cell Biol. 149:13–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hirase T, Kawashima S, Wong EY, Ueyama T,
Rikitake Y, Tsukita S, Yokoyama M and Staddon JM: Regulation of
tight junction permeability and occludin phosphorylation by
Rhoa-p160ROCK-dependent and -independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem.
276:10423–10431. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hawkins BT and Davis TP: The blood-brain
barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol Rev.
57:173–185. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sellner J and Leib SL: In bacterial
meningitis cortical brain damage is associated with changes in
parenchymal MMP-9/TIMP-1 ratio and increased collagen type IV
degradation. Neurobiol Dis. 21:647–656. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wiggins-Dohlvik K, Merriman M, Shaji CA,
Alluri H, Grimsley M, Davis ML, Smith RW and Tharakan B: Tumor
necrosis factor-α disruption of brain endothelial cell barrier is
mediated through matrix metalloproteinase-9. Am J Surg.
208:954–960. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim JY, Kawabori M and Yenari MA: Innate
inflammatory responses in stroke: Mechanisms and potential
therapeutic targets. Curr Med Chem. 21:2076–2097. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Crafts TD, Jensen AR, Blocher-Smith EC and
Markel TA: Vascular endothelial growth factor: Therapeutic
possibilities and challenges for the treatment of ischemia.
Cytokine. 71:385–393. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|