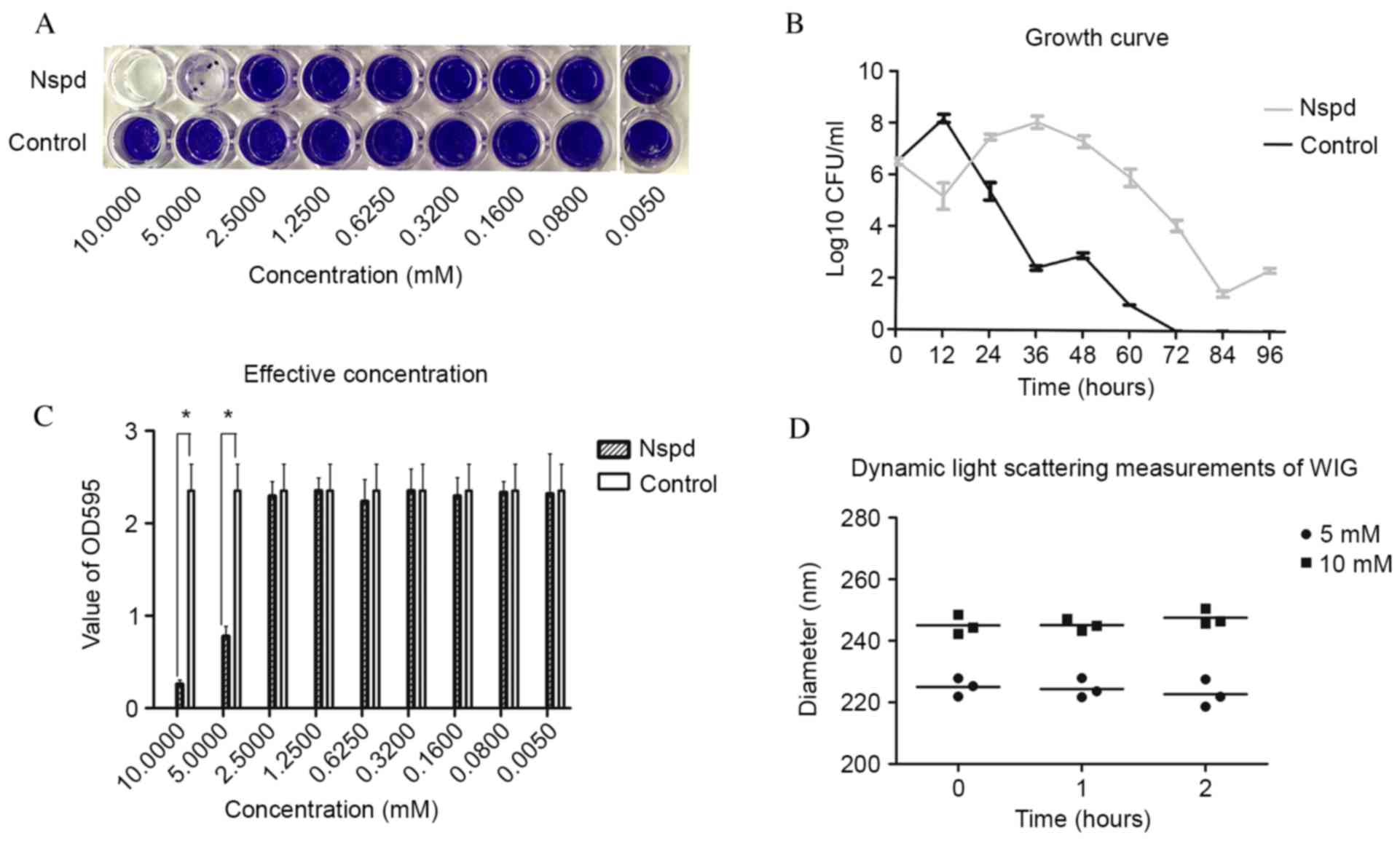
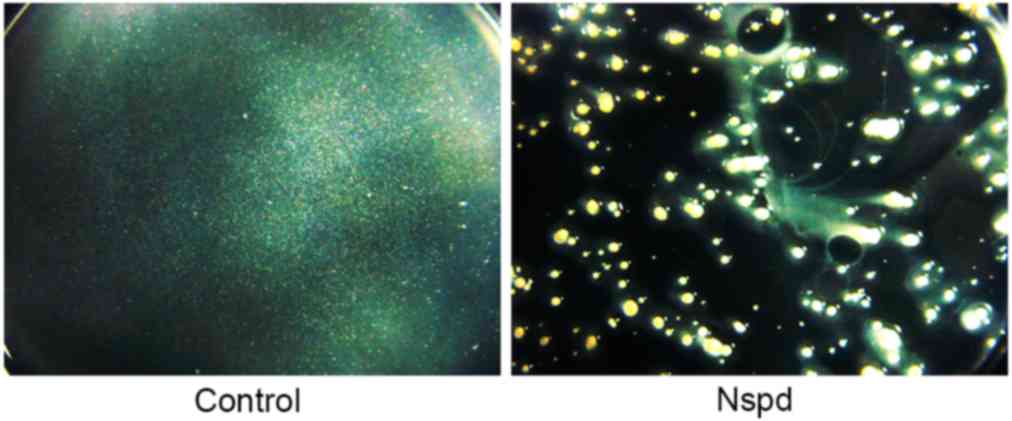
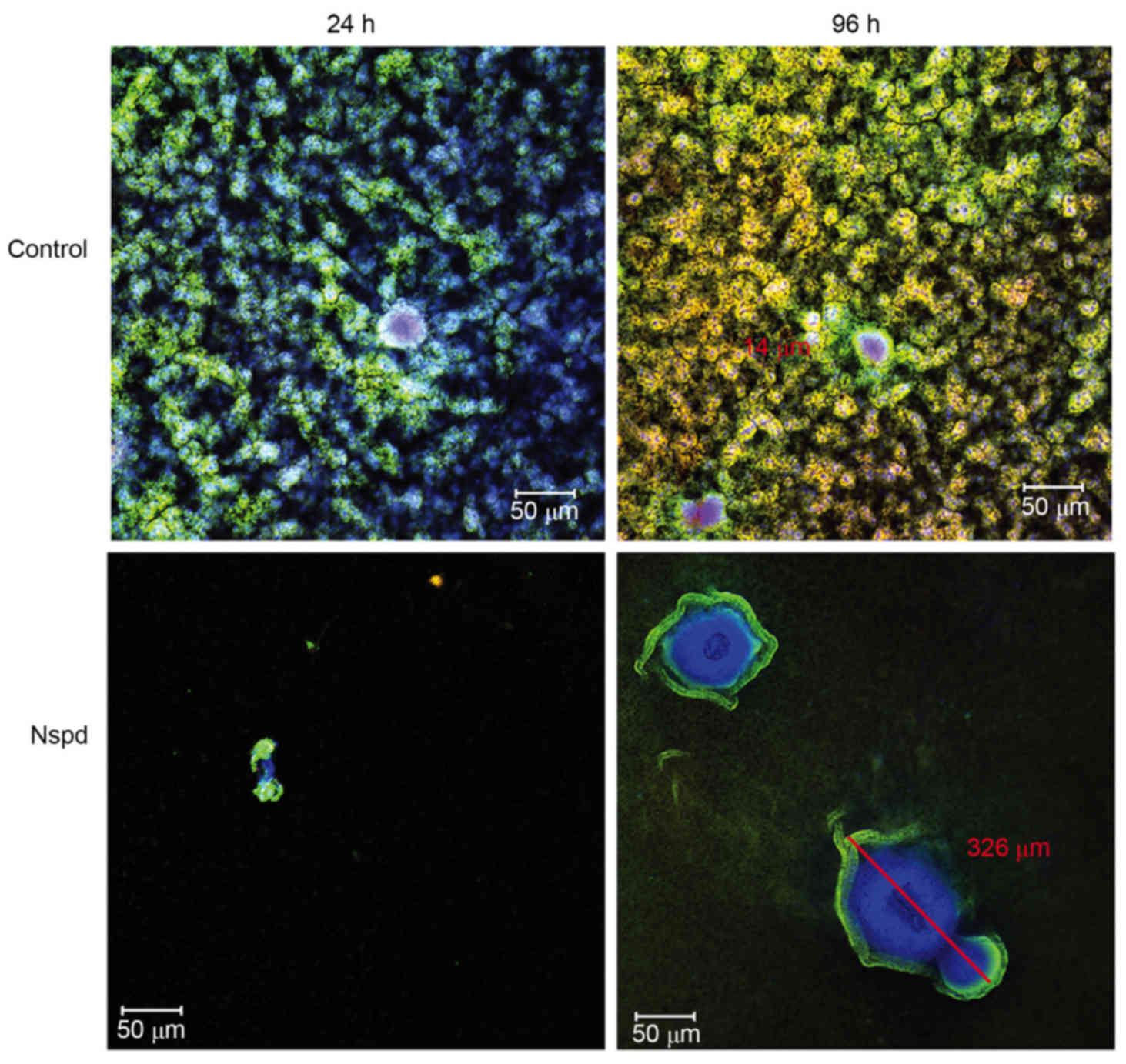
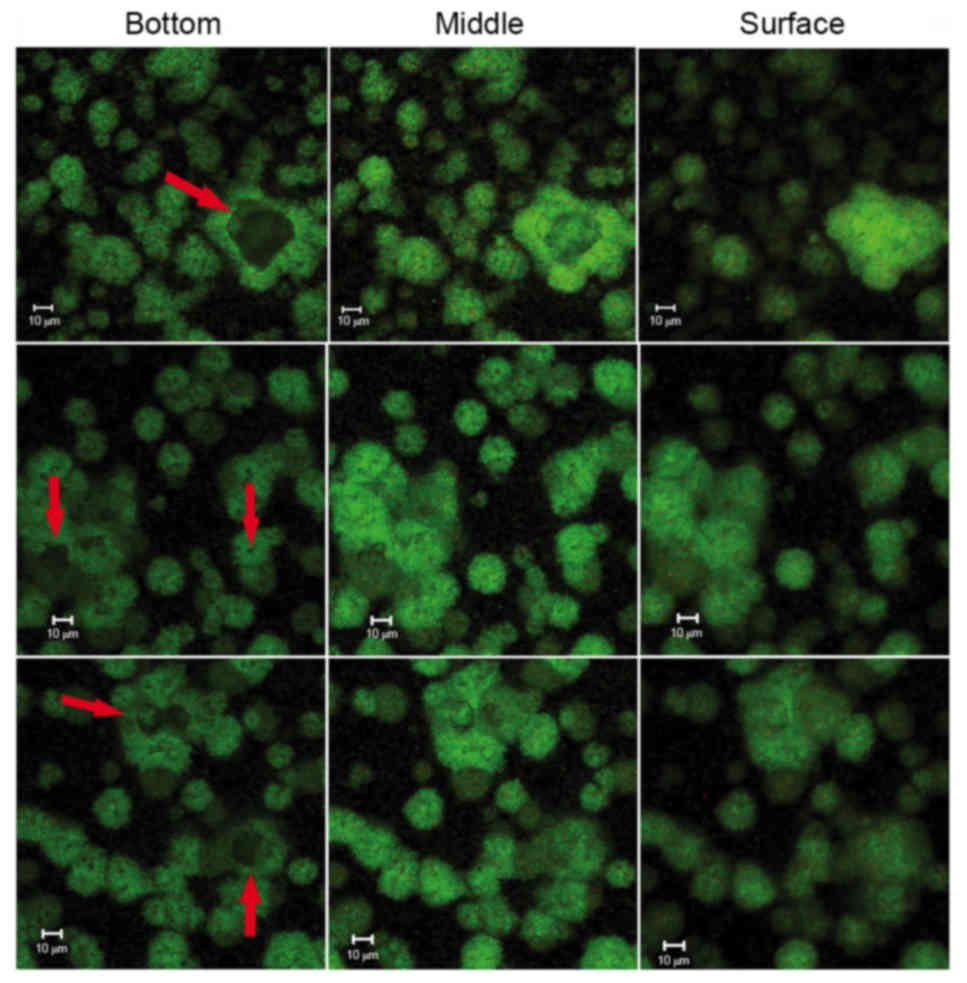
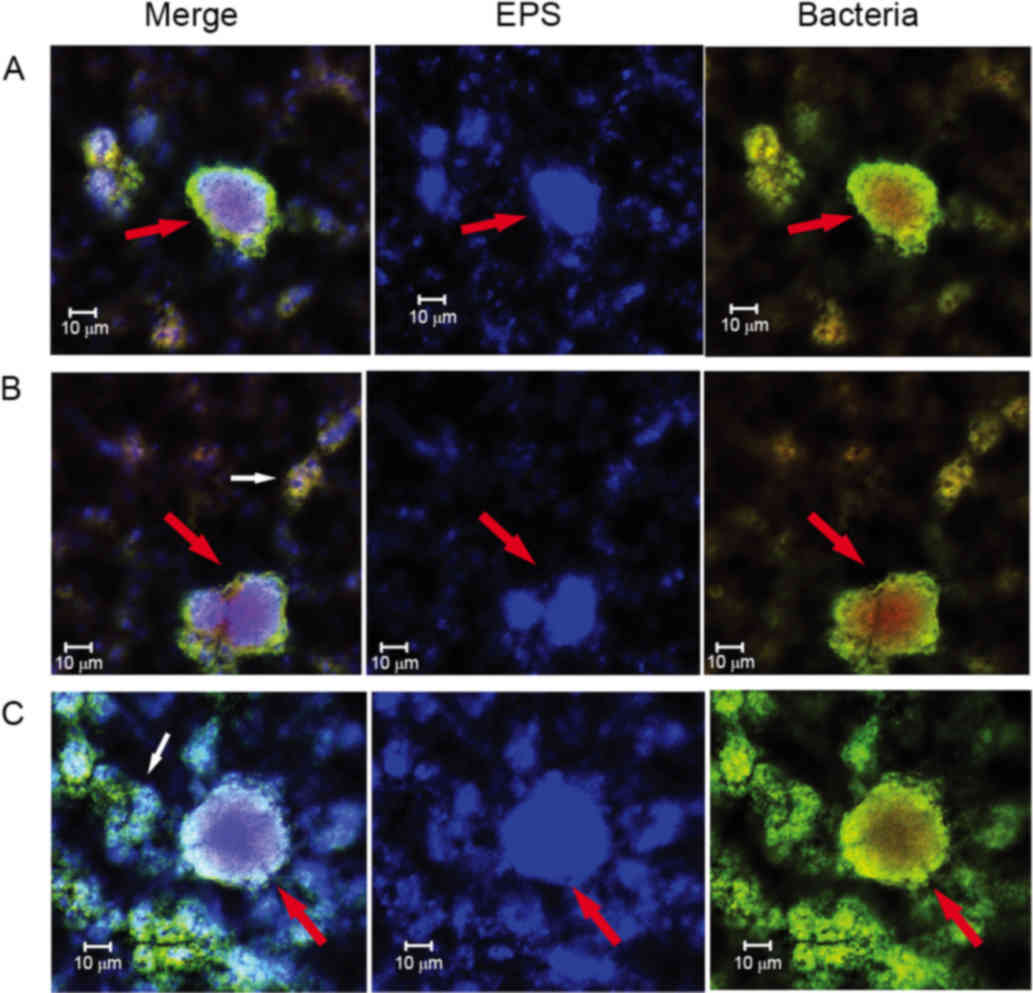
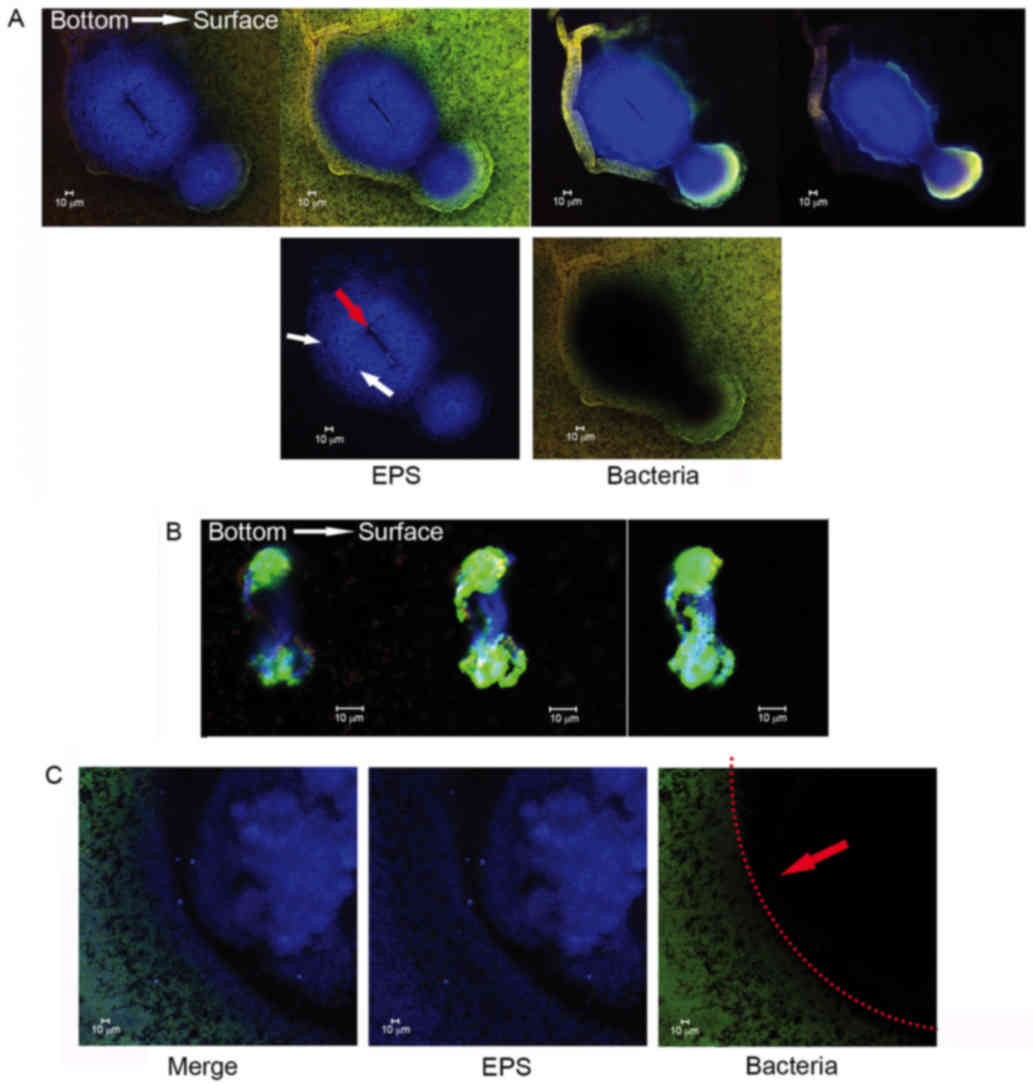
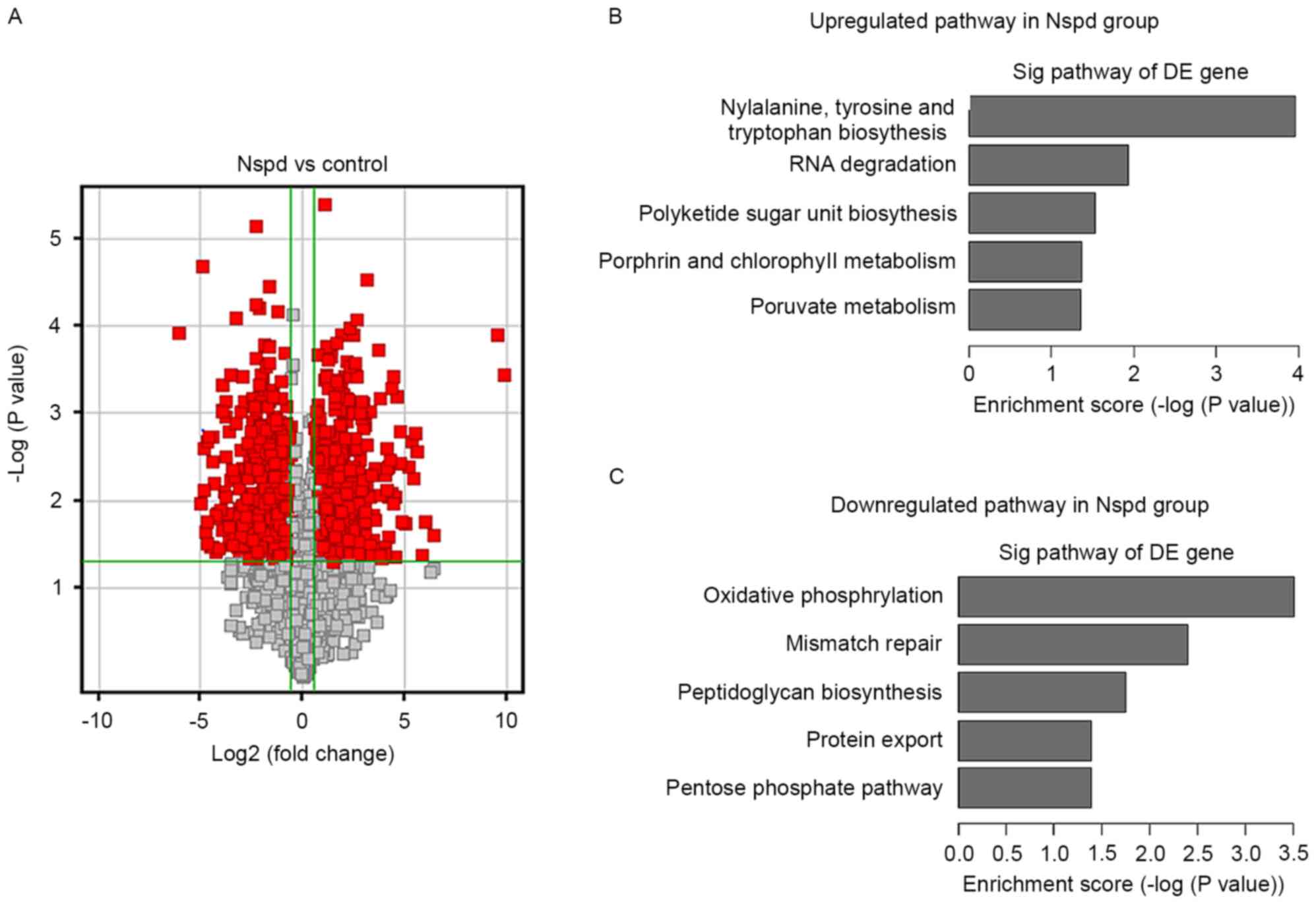
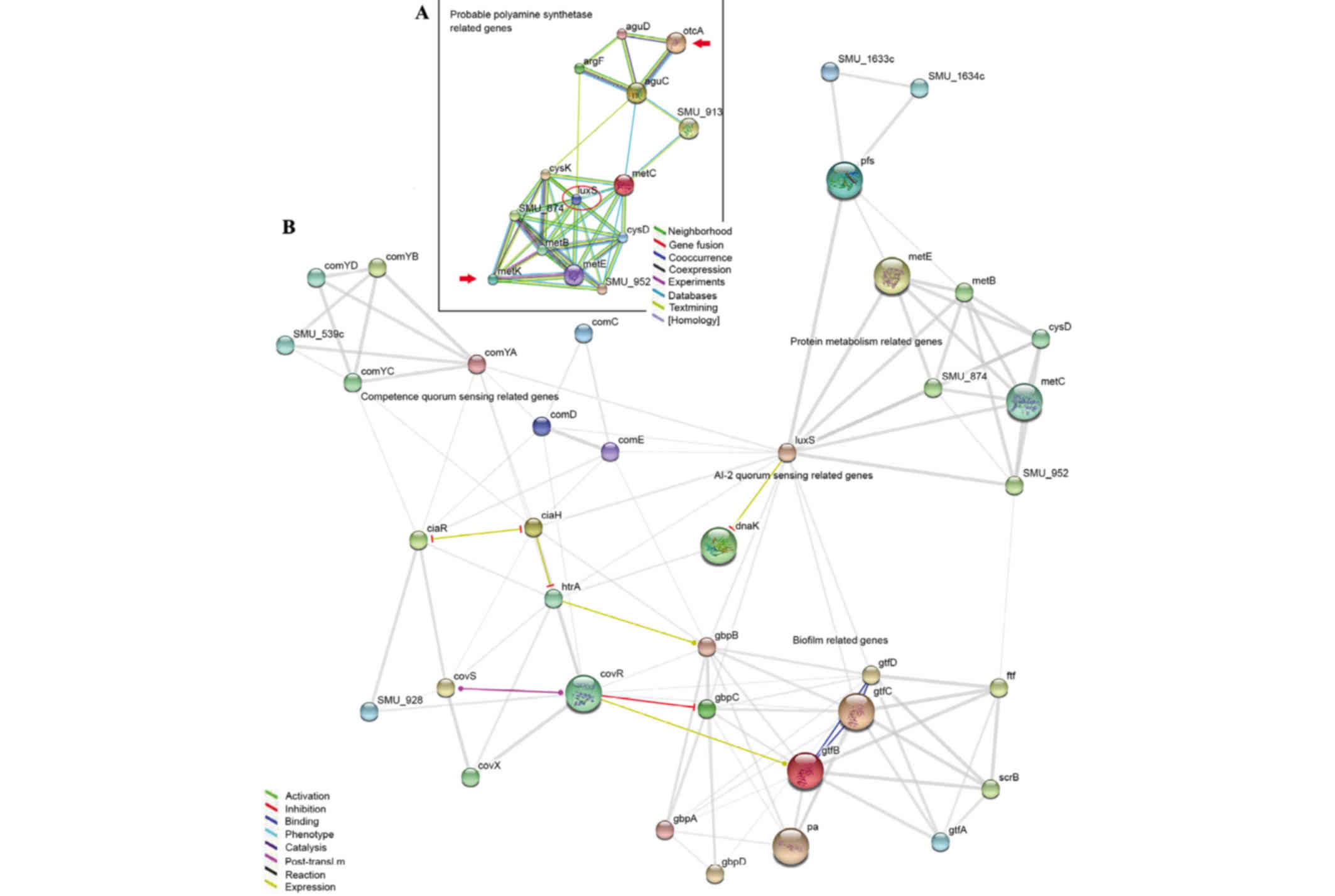
|
1
|
Wallace HM, Fraser AV and Hughes A: A
perspective of polyamine metabolism. Biochem J. 376:1–14. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Romero D and Kolter R: Will biofilm
disassembly agents make it to market? Trends Microbiol. 19:304–306.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Flemming HC, Neu TR and Wozniak DJ: The
EPS matrix: The ‘house of biofilm cells’. J Bacteriol.
189:7945–7947. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Flemming HC and Wingender J: The biofilm
matrix. Nat Rev Microbiol. 8:623–633. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Branda SS, Vik S, Friedman L and Kolter R:
Biofilms: The matrix revisited. Trends Microbiol. 13:20–26. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bowen WH and Koo H: Biology of
Streptococcus mutans-derived glucosyltransferases: Role in
extracellular matrix formation of cariogenic biofilms. Caries Res.
45:69–86. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Xiao J, Klein MI, Falsetta ML, Lu B,
Delahunty CM, Yates JR III, Heydorn A and Koo H: The
exopolysaccharide matrix modulates the interaction between 3D
architecture and virulence of a mixed-species oral biofilm. PLoS
Pathog. 8:e10026232012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hamada S, Tai S and Slade HD: Binding of
glucosyltransferase and glucan synthesis by Streptococcus mutans
and other bacteria. Infect Immun. 21:213–220. 1978.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Koo H, Xiao J, Klein MI and Jeon JG:
Exopolysaccharides produced by Streptococcus mutans
glucosyltransferases modulate the establishment of microcolonies
within multispecies biofilms. J Bacteriol. 192:3024–3032. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Loesche WJ: Role of Streptococcus mutans
in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 50:353–380. 1986.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fuqua C, Parsek MR and Greenberg EP:
Regulation of gene expression by cell-to-cell communication:
Acyl-homoserine lactone quorum sensing. Annu Rev Genet. 35:439–468.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kleerebezem M and Quadri LE: Peptide
pheromone-dependent regulation of antimicrobial peptide production
in Gram-positive bacteria: A case of multicellular behavior.
Peptides. 22:1579–1596. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miller MB and Bassler BL: Quorum sensing
in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 55:165–199. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Miller MB, Skorupski K, Lenz DH, Taylor RK
and Bassler BL: Parallel quorum sensing systems converge to
regulate virulence in Vibrio cholerae. Cell. 110:303–314. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shapiro JA: Thinking about bacterial
populations as multicellular organisms. Annu Rev Microbiol.
52:81–104. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Karatan E and Watnick P: Signals,
regulatory networks, and materials that build and break bacterial
biofilms. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 73:310–347. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wortham BW, Oliveira MA, Fetherston JD and
Perry RD: Polyamines are required for the expression of key Hms
proteins important for Yersinia pestis biofilm formation. Environ
Microbiol. 12:2034–2047. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Sakamoto A, Terui Y, Yamamoto T, Kasahara
T, Nakamura M, Tomitori H, Yamamoto K, Ishihama A, Michael AJ,
Igarashi K and Kashiwagi K: Enhanced biofilm formation and/or cell
viability by polyamines through stimulation of response regulators
UvrY and CpxR in the two-component signal transducing systems and
ribosome recycling factor. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:1877–1886.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sturgill G and Rather PN: Evidence that
putrescine acts as an extracellular signal required for swarming in
Proteus mirabilis. Mol Microbiol. 51:437–446. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kolodkin-Gal I, Cao S, Chai L, Böttcher T,
Kolter R, Clardy J and Losick R: A self-produced trigger for
biofilm disassembly that targets exopolysaccharide. Cell.
149:684–692. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:(Database Issue). D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nishikawa S: Correlation of the
arrangement pattern of enamel rods and secretory ameloblasts in pig
and monkey teeth: A possible role of the terminal webs in
ameloblast movement during secretion. Anat Rec. 232:466–478. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Harmsen M, Yang L, Pamp SJ and
Tolker-Nielsen T: An update on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm
formation, tolerance and dispersal. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol.
59:253–268. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Stoodley P, Dodds I, Boyle JD and
Lappin-Scott HM: Influence of hydrodynamics and nutrients on
biofilm structure. J Appl Microbiol. 85:(Suppl 1). 19S–28S. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Parsek MR and Tolker-Nielsen T: Pattern
formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Curr Opin Microbiol.
11:560–566. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lynch DJ, Fountain TL, Mazurkiewicz JE and
Banas JA: Glucan-binding proteins are essential for shaping
Streptococcus mutans biofilm architecture. FEMS Microbiol Lett.
268:158–165. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Crowley PJ, Brady LJ, Michalek SM and
Bleiweis AS: Virulence of a spaP mutant of Streptococcus mutans in
a gnotobiotic rat model. Infect Immun. 67:1201–1206.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qu YP, Liu JG, Yang P and Yang DQ:
Construction and expression of spap/A eukaryotic expression plasmid
of Streptococcus mutans in mammalian cells. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi
Xue. 18:61–65. 2009.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Durán-Contreras GL, Torre-Martínez HH, de
la Rosa EI, Hernández RM and de la Garza Ramos M: spaP gene of
Streptococcus mutans in dental plaque and its relationship with
early childhood caries. Eur J Paediatr Dent. 12:220–224.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Davis E, Kennedy D, Halperin SA and Lee
SF: Role of the cell wall microenvironment in expression of a
heterologous SpaP-S1 fusion protein by Streptococcus gordonii. Appl
Environ Microbiol. 77:1660–1666. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sato Y, Okamoto-Shibayama K and Azuma T: A
mechanism for extremely weak SpaP-expression in Streptococcus
mutans strain Z1. J Oral Microbiol. 3:2011.
|
|
32
|
Itoh Y, Wang X, Hinnebusch BJ, Preston JR
and Romeo T: Depolymerization of beta-1,6-N-acetyl-D-glucosamine
disrupts the integrity of diverse bacterial biofilms. J Bacteriol.
187:382–387. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sutherland IW: The biofilm matrix-an
immobilized but dynamic microbial environment. Trends Microbiol.
9:222–227. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Rolla G, Ciardi JE and Schultz SA:
Adsorption of glucosyltransferase to saliva coated hydroxyapatite.
Possible mechanism for sucrose dependent bacterial colonization of
teeth. Scand J Dent Res. 91:112–117. 1983.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Vacca-Smith AM and Bowen WH: Binding
properties of streptococcal glucosyltransferases for
hydroxyapatite, saliva-coated hydroxyapatite, and bacterial
surfaces. Arch Oral Biol. 43:103–110. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Schilling KM and Bowen WH: Glucans
synthesized in situ in experimental salivary pellicle function as
specific binding sites for Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun.
60:284–295. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Venkitaraman AR, Vacca-Smith AM, Kopec LK
and Bowen WH: Characterization of glucosyltransferaseB, GtfC, and
GtfD in solution and on the surface of hydroxyapatite. J Dent Res.
74:1695–1701. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
McCabe RM and Donkersloot JA: Adherence of
Veillonella species mediated by extracellular glucosyltransferase
from Streptococcus salivarius. Infect Immun. 18:726–734.
1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Yamashita Y, Bowen WH and Kuramitsu HK:
Molecular analysis of a Streptococcus mutans strain exhibiting
polymorphism in the tandem gtfB and gtfC genes. Infect Immun.
60:1618–1624. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chia JS, Hsieh CC, Yang CS and Chen JY:
Purification of glucosyltransferases (GtfB/C and GtfD) from mutant
strains of Streptococcus mutans. Zhonghua Min Guo Wei Sheng Wu Ji
Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 28:1–12. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Tsai YW, Chia JS, Shiau YY, Chou HC, Liaw
YC and Lou KL: Three-dimensional modelling of the catalytic domain
of Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase GtfB. FEMS Microbiol
Lett. 188:75–79. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Yoshida A and Kuramitsu HK: Streptococcus
mutans biofilm formation: Utilization of a gtfB promoter-green
fluorescent protein (PgtfB:gfp) construct to monitor development.
Microbiology. 148:3385–3394. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lynch DJ, Michalek SM, Zhu M, Drake D,
Qian F and Banas JA: Cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans
glucan-binding protein deletion mutants. Oral Health Dent Manag.
12:191–199. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Banas JA, Fountain TL, Mazurkiewicz JE,
Sun K and Vickerman MM: Streptococcus mutans glucan-binding
protein-A affects Streptococcus gordonii biofilm architecture. FEMS
Microbiol Lett. 267:80–88. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Banas JA, Hazlett KR and Mazurkiewicz JE:
An in vitro model for studying the contributions of the
Streptococcus mutans glucan-binding protein A to biofilm structure.
Methods Enzymol. 337:425–433. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Li YH, Tang N, Aspiras MB, Lau PC, Lee JH,
Ellen RP and Cvitkovitch DG: A quorum-sensing signaling system
essential for genetic competence in Streptococcus mutans is
involved in biofilm formation. J Bacteriol. 184:2699–2708. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Merritt J, Qi F, Goodman SD, Anderson MH
and Shi W: Mutation of luxS affects biofilm formation in
Streptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 71:1972–1979. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yoshida A, Ansai T, Takehara T and
Kuramitsu HK: LuxS-based signaling affects Streptococcus mutans
biofilm formation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 71:2372–2380. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Huang Z, Meric G, Liu Z, Ma R, Tang Z and
Lejeune P: luxS-based quorum-sensing signaling affects Biofilm
formation in Streptococcus mutans. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol.
17:12–19. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|