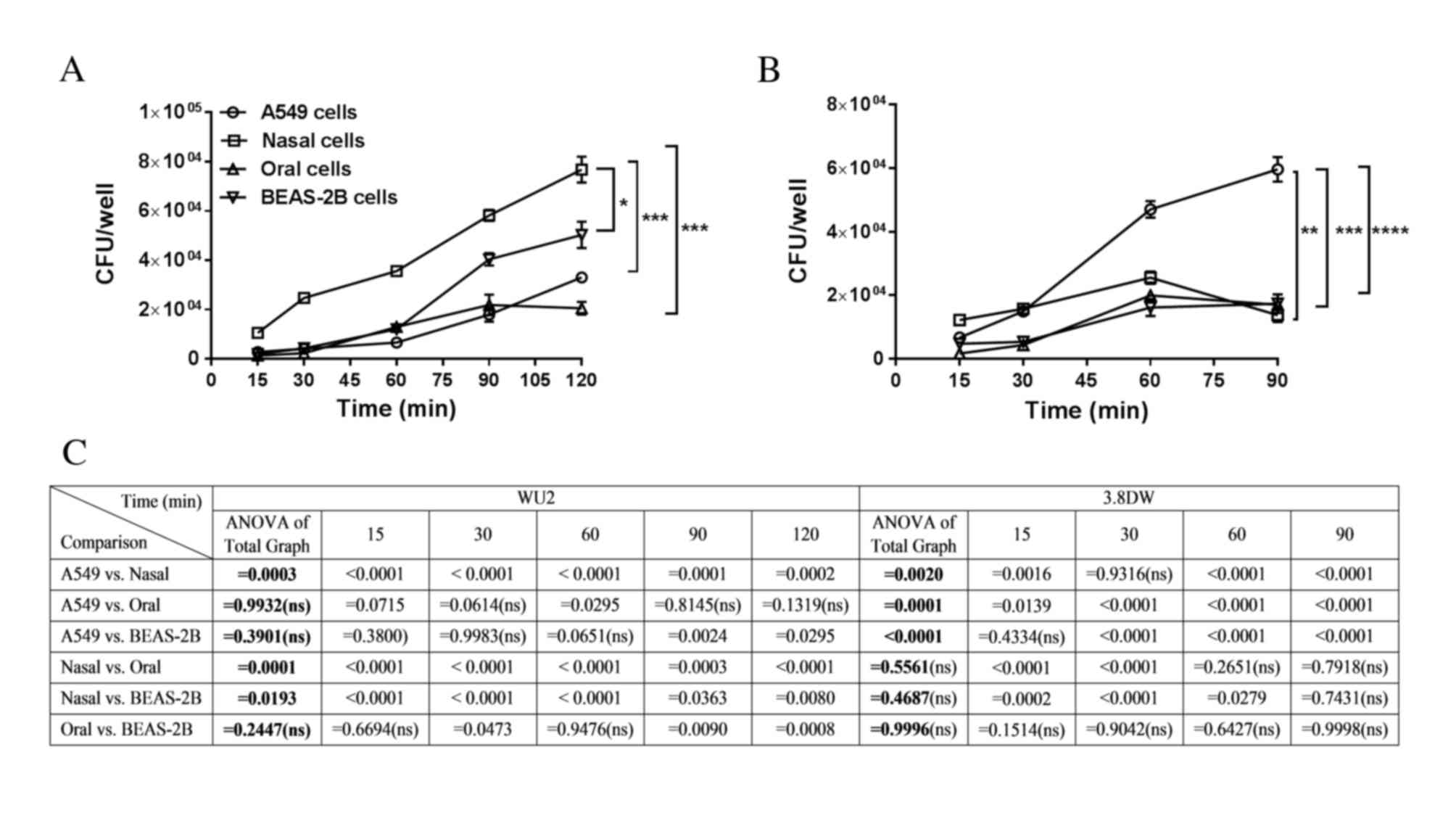
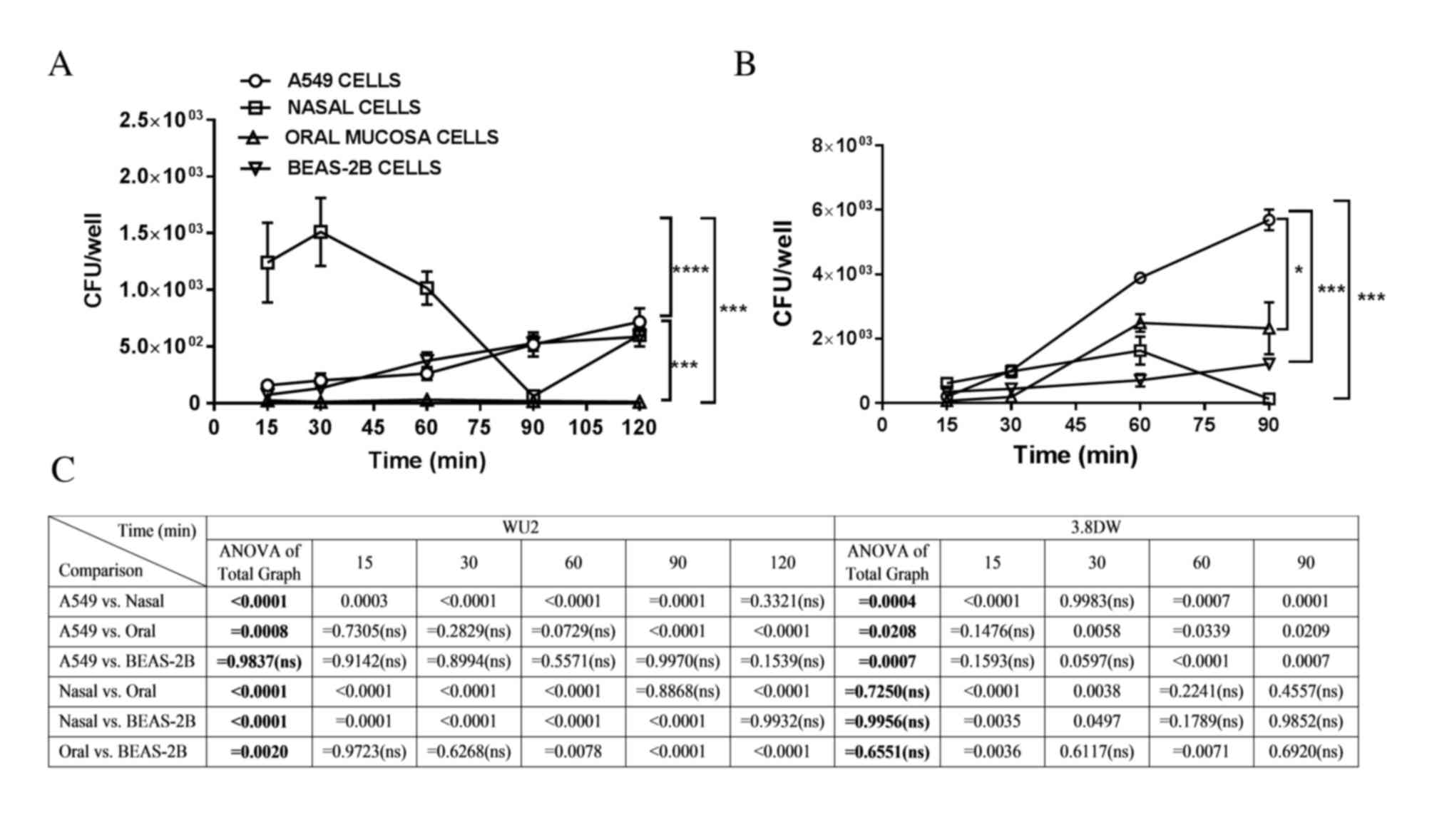
|
1
|
Weinberger DM, Harboe ZB, Sanders EA,
Ndiritu M, Klugman KP, Rückinger S, Dagan R, Adegbola R, Cutts F,
Johnson HL, et al: Association of serotype with risk of death due
to pneumococcal pneumonia: A meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis.
51:692–699. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Harvey RM, Trappetti C, Mahdi LK, Wang H,
McAllister LJ, Scalvini A, Paton AW and Paton JC: The variable
region of pneumococcal pathogenicity island 1 is responsible for
unusually high virulence of a serotype 1 isolate. Infect Immun.
84:822–832. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vernatter J and Pirofski LA: Current
concepts in host-microbe interaction leading to pneumococcal
pneumonia. Curr Opin Infect Dis. 26:277–283. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Simell B, Auranen K, Kayhty H, Goldblatt
D, Dagan R and O'Brien KL: Pneumococcal Carriage Group: The
fundamental link between pneumococcal carriage and disease. Expert
Rev Vaccines. 11:841–855. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van der Poll T and Opal SM: Pathogenesis,
treatment, and prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia. Lancet.
374:1543–1556. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim L, McGee L, Tomczyk S and Beall B:
Biological and epidemiological features of antibiotic-resistant
Streptococcus pneumoniae in pre- and post-conjugate vaccine eras: A
United States perspective. Clin Microbiol Rev. 29:525–552. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brauner A, Fridman O, Gefen O and Balaban
NQ: Distinguishing between resistance, tolerance and persistence to
antibiotic treatment. Nat Rev Microbiol. 14:320–330. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hammitt LL, Bulkow LR, Singleton RJ,
Nuorti JP, Hummel KB, Miernyk KM, Miernyk KM, Zanis C, Whaley M and
Romero-Steiner S: Repeat revaccination with 23-valent pneumococcal
polysaccharide vaccine among adults aged 55–74 years living in
Alaska: No evidence of hyporesponsiveness. Vaccine. 29:2287–2295.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Käyhty H and Eskola J: New vaccines for
the prevention of pneumococcal infections. Emerg Infect Dis.
2:289–298. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Golden AR, Adam HJ and Zhanel GG: Canadian
Antimicrobial Resistance A: Invasive Streptococcus pneumoniae in
Canada, 2011–2014: Characterization of new candidate 15-valent
pneumococcal conjugate vaccine serotypes 22F and 33F. Vaccine.
34:2527–2530. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jauneikaite E, Tocheva AS, Jefferies JM,
Gladstone RA, Faust SN, Christodoulides M, Hibberd ML and Clarke
SC: Current methods for capsular typing of Streptococcus
pneumoniae. J Microbiol Methods. 113:41–49. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Geno KA, Gilbert GL, Song JY, Skovsted IC,
Klugman KP, Jones C, Konradsen HB and Nahm MH: Pneumococcal
capsules and their types: Past, present, and future. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 28:871–899. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hicks LA, Harrison LH, Flannery B, Hadler
JL, Schaffner W, Craig AS, Jackson D, Thomas A, Beall B, Lynfield
R, et al: Incidence of pneumococcal disease due to non-pneumococcal
conjugate vaccine (PCV7) serotypes in the United States during the
era of widespread PCV7 vaccination, 1998–2004. J Infect Dis.
196:1346–1354. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dagan R: Serotype replacement in
perspective. Vaccine. 27:(Suppl 3). C22–C24. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shak JR, Vidal JE and Klugman KP:
Influence of bacterial interactions on pneumococcal colonization of
the nasopharynx. Trends in Microbiol. 21:129–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Hammerschmidt S: Adherence molecules of
pathogenic pneumococci. Curr Opin Microbiol. 9:12–20. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Paterson GK and Orihuela CJ: Pneumococcal
microbial surface components recognizing adhesive matrix molecules
targeting of the extracellular matrix. Mol Microbiol. 77:1–5. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Harfouche C, Filippini S, Gianfaldoni C,
Ruggiero P, Moschioni M, Maccari S, Pancotto L, Arcidiacono L,
Galletti B, Censini S, et al: RrgB321, a fusion protein of the
three variants of the pneumococcal pilus backbone rrgb, is
protective in vivo and elicits opsonic antibodies. Infect Immun.
80:451–460. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Moschioni M, Donati C, Muzzi A, Masignani
V, Censini S, Hanage WP, Bishop CJ, Reis JN, Normark S,
Henriques-Normark B, et al: Streptococcus pneumoniae contains 3
rlrA pilus variants that are clonally related. J Infect Dis.
197:888–896. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Basset A, Zhang F, Benes C, Sayeed S, Herd
M, Thompson C, Golenbock DT, Camilli A and Malley R: Toll-like
receptor (TLR) 2 mediates inflammatory responses to oligomerized
RrgA pneumococcal pilus type 1 protein. J Biol Chem. 288:2665–2675.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bagnoli F, Moschioni M, Donati C,
Dimitrovska V, Ferlenghi I, Facciotti C, Muzzi A, Giusti F, Emolo
C, Sinisi A, et al: A second pilus type in Streptococcus pneumoniae
is prevalent in emerging serotypes and mediates adhesion to host
cells. J Bacteriol. 190:5480–5492. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hammerschmidt S, Wolff S, Hocke A, Rosseau
S, Muller E and Rohde M: Illustration of pneumococcal
polysaccharide capsule during adherence and invasion of epithelial
cells. Infect Immun. 73:4653–4667. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Berry AM and Paton JC: Sequence
heterogeneity of PsaA, a 37-kilodalton putative adhesin essential
for virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun.
64:5255–5262. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Anderton JM, Rajam G, Romero-Steiner S,
Summer S, Kowalczyk AP, Carlone GM, Sampson JS and Ades EW:
E-cadherin is a receptor for the common protein pneumococcal
surface adhesin A (PsaA) of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Microb
Pathog. 42:225–236. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Pracht D, Elm C, Gerber J, Bergmann S,
Rohde M, Seiler M, Kim KS, Jenkinson HF, Nau R and Hammerschmidt S:
PavA of Streptococcus pneumoniae modulates adherence, invasion, and
meningeal inflammation. Infect Immun. 73:2680–2699. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Blau K, Portnoi M, Shagan M, Kaganovich A,
Rom S, Kafka D, Caspi V Chalifa, Porgador A, Givon-Lavi N, Gershoni
JM, et al: Flamingo cadherin: A putative host receptor for
Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Infect Dis. 195:1828–1837. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Muchnik L, Adawi A, Ohayon A, Dotan S,
Malka I, Azriel S, Shagan M, Portnoi M, Kafka D, Nahmani H, et al:
NADH oxidase functions as an adhesin in Streptococcus pneumoniae
and elicits a protective immune response in mice. PloS One.
8:e611282013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nebenzahl Y Mizrachi, Blau K, Kushnir T,
Shagan M, Portnoi M, Cohen A, Azriel S, Malka I, Adawi A, Kafka D,
et al: Streptococcus pneumoniae cell-wall-localized
phosphoenolpyruvate protein phosphotransferase can function as an
adhesin: Identification of its host target molecules and evaluation
of its potential as a vaccine. PloS One. 11:e01503202016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Cundell DR, Gerard NP, Gerard C,
Idanpaan-Heikkila I and Tuomanen EI: Streptococcus pneumoniae
anchor to activated human cells by the receptor for
platelet-activating factor. Nature. 377:435–438. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shivshankar P, Boyd AR, Le Saux CJ, Yeh IT
and Orihuela CJ: Cellular senescence increases expression of
bacterial ligands in the lungs and is positively correlated with
increased susceptibility to pneumococcal pneumonia. Aging Cell.
10:798–806. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nagaoka K, Yanagihara K, Morinaga Y,
Nakamura S, Harada T, Hasegawa H, Izumikawa K, Ishimatsu Y, Kakeya
H, Nishimura M and Kohno S: Prevotella intermedia induces severe
bacteremic pneumococcal pneumonia in mice with upregulated
platelet-activating factor receptor expression. Infect Immun.
82:587–593. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Suri R, Periselneris J, Lanone S,
Zeidler-Erdely PC, Melton G, Palmer KT, Andujar P, Antonini JM,
Cohignac V, Erdely A, et al: Exposure to welding fumes and lower
airway infection with Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Allergy Clin
Immunol. 137:527–534.e7. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Rosenow C, Ryan P, Weiser JN, Johnson S,
Fontan P, Ortqvist A and Masure HR: Contribution of novel
choline-binding proteins to adherence, colonization and
immunogenicity of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Mol Microbiol.
25:819–829. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hammerschmidt S, Talay SR, Brandtzaeg P
and Chhatwal GS: SpsA, a novel pneumococcal surface protein with
specific binding to secretory immunoglobulin A and secretory
component. Mol Microbiol. 25:1113–1124. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Brooks-Walter A, Briles DE and
Hollingshead SK: The pspC gene of Streptococcus pneumoniae encodes
a polymorphic protein, PspC, which elicits cross-reactive
antibodies to PspA and provides immunity to pneumococcal
bacteremia. Infect Immun. 67:6533–6542. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gamez G and Hammerschmidt S: Combat
pneumococcal infections: Adhesins as candidates for protein-based
vaccine development. Curr Drug Targets. 13:323–337. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Plumptre CD, Ogunniyi AD and Paton JC:
Polyhistidine triad proteins of pathogenic streptococci. Trends
Microbiol. 20:485–493. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Khan MN and Pichichero ME: Vaccine
candidates PhtD and PhtE of Streptococcus pneumoniae are adhesins
that elicit functional antibodies in humans. Vaccine. 30:2900–2907.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Kallio A, Sepponen K, Hermand P, Denoël P,
Godfroid F and Melin M: Role of Pht proteins in attachment of
Streptococcus pneumoniae to respiratory epithelial cells. Infect
Immun. 82:1683–1691. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Keller LE, Robinson DA and McDaniel LS:
Nonencapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae: Emergence and
pathogenesis. MBio. 7:e017922016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Alloing G, de Philip P and Claverys JP:
Three highly homologous membrane-bound lipoproteins participate in
oligopeptide transport by the Ami system of the gram-positive
Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Mol Biol. 241:44–58. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Claverys JP, Grossiord B and Alloing G: Is
the Ami-AliA/B oligopeptide permease of Streptococcus pneumoniae
involved in sensing environmental conditions? Res Microbiol.
151:457–463. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Park IH, Kim KH, Andrade AL, Briles DE,
McDaniel LS and Nahm MH: Nontypeable pneumococci can be divided
into multiple cps types, including one type expressing the novel
gene pspK. mBio. 3:e00035–e00112. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Watson DA and Musher DM: Interruption of
capsule production in Streptococcus pneumonia serotype 3 by
insertion of transposon Tn916. Infect Immun. 58:3135–3138.
1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Carvalho SM, Kuipers OP and Neves AR:
Environmental and nutritional factors that affect growth and
metabolism of the pneumococcal serotype 2 strain D39 and its
nonencapsulated derivative strain R6. PloS One. 8:e584922013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Ueda M, Hata K, Horie K and Torii S: The
potential of oral mucosal cells for cultured epithelium: A
preliminary report. Ann Plast Surg. 35:498–504. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Rheinwald JG and Green H: Serial
cultivation of strains of human epidermal keratinocytes: The
formation of keratinizing colonies from single cells. Cell.
6:331–343. 1975. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Rheinwald J: Methods for clonal growth and
serial cultivation of normal human epidermal keratinocytes and
mesothelial cellsCell Growth and Division: A Practical Approach.
Baserga R: IRL Press; Oxford: pp. 81–94. 1989
|
|
49
|
Lieber M, Smith B, Szakal A, Nelson-Rees W
and Todaro G: A continuous tumor-cell line from a human lung
carcinoma with properties of type II alveolar epithelial cells. Int
J Cancer. 17:62–70. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Balis JU, Bumgarner SD, Paciga JE,
Paterson JF and Shelley SA: Synthesis of lung surfactant-associated
glycoproteins by A549 cells: Description of an in vitro model for
human type II cell dysfunction. Exp Lung Res. 6:197–213. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Asano K, Chee CB, Gaston B, Lilly CM,
Gerard C, Drazen JM and Stamler JS: Constitutive and inducible
nitric oxide synthase gene expression, regulation, and activity in
human lung epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
91:10089–10093. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Bergmann S, Schoenen H and Hammerschmidt
S: The interaction between bacterial enolase and plasminogen
promotes adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to epithelial and
endothelial cells. Int J Med Microbiol. 303:452–462. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Briles DE, Nahm M, Schroer K, Davie J,
Baker P, Kearney J and Barletta R: Antiphosphocholine antibodies
found in normal mouse serum are protective against intravenous
infection with type 3 Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Exp Med.
153:694–705. 1981. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Nebenzahl Y Mizrachi, Porat N, Lifshitz S,
Novick S, Levi A, Ling E, Liron O, Mordechai S, Sahu RK and Dagan
R: Virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae may be determined
independently of capsular polysaccharide. FEMS Microbiol Lett.
233:147–152. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Sahu RK, Mordechai S, Pesakhov S, Dagan R
and Porat N: Use of FTIR spectroscopy to distinguish between
capsular types and capsular quantities in Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Biopolymers. 83:434–442. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Mizrachi-Nebenzahl Y, Lifshitz S,
Teitelbaum R, Novick S, Levi A, Benharroch D, Ling E and Dagan R:
Differential activation of the immune system by virulent
Streptococcus pneumoniae strains determines recovery or death of
the host. Clin Exp Immunol. 134:23–31. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Ling E, Feldman G, Dagan R and
Mizrachi-Nebenzahl Y: Cytokine mRNA expression in pneumococcal
carriage, pneumonia, and sepsis in young mice. J Infect Dis.
188:1752–1766. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Whitney CG, Farley MM, Hadler J, Harrison
LH, Bennett NM, Lynfield R, Reingold A, Cieslak PR, Pilishvili T,
Jackson D, et al: Decline in invasive pneumococcal disease after
the introduction of protein-polysaccharide conjugate vaccine. N
Engl J Med. 348:1737–1746. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Daniely D, Portnoi M, Shagan M, Porgador
A, Givon-Lavi N, Ling E, Dagan R and Nebenzahl Y Mizrachi:
Pneumococcal 6-phosphogluconate-dehydrogenase, a putative adhesin,
induces protective immune response in mice. Clin Exp Immunol.
144:254–163. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Nebenzahl Y Mizrachi, Bernstein A, Portnoi
M, Shagan M, Rom S, Porgador A and Dagan R: Streptococcus
pneumoniae surface-exposed glutamyl tRNA synthetase, a putative
adhesin, is able to induce a partially protective immune response
in mice. J Infect Dis. 196:945–953. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zahlten J, Kim YJ, Doehn JM, Pribyl T,
Hocke AC, Garcia P, Hammerschmidt S, Suttorp N, Hippenstiel S and
Hübner RH: Streptococcus pneumoniae-induced oxidative stress in
lung epithelial cells depends on pneumococcal autolysis and is
reversible by resveratrol. J Infect Dis. 211:1822–1830. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Adamou JE, Wizemann TM, Barren P and
Langermann S: Adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to human
bronchial epithelial cells (BEAS-2B). Infect Immun. 66:820–822.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Robson RL, Reed NA and Horvat RT:
Differential activation of inflammatory pathways in A549 type II
pneumocytes by Streptococcus pneumoniae strains with different
adherence properties. BMC Infect Dis. 6:712006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Mushtaq N, Ezzati M, Hall L, Dickson I,
Kirwan M, Png KM, Mudway IS and Grigg J: Adhesion of Streptococcus
pneumoniae to human airway epithelial cells exposed to urban
particulate matter. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 127:1236–1242. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Li-Korotky HS, Lo CY, Zeng FR, Lo D and
Banks JM: Interaction of phase variation, host and pressure/gas
composition: Pneumococcal gene expression of PsaA, SpxB, Ply and
LytA in simulated middle ear environments. Int J Pediatr
Otorhinolaryngol. 73:1417–1422. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Statt S, Ruan JW, Huang CT, Wu R and Kao
CY: Lipidome and transcriptome profiling of pneumolysin
intoxication identifies networks involved in statin-conferred
protection of airway epithelial cells. Sci Rep. 5:106242015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Li P, Shi J, He Q, Hu Q, Wang YY, Zhang
LJ, Chan WT and Chen WX: Streptococcus pneumoniae induces autophagy
through the inhibition of the PI3K-I/Akt/mTOR pathway and ROS
hypergeneration in A549 cells. PloS One. 10:e01227532015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zahlten J, Herta T, Kabus C, Steinfeldt M,
Kershaw O, García P, Hocke AC, Gruber AD, Hübner RH, Steinicke R,
et al: Role of pneumococcal autolysin for KLF4 expression and
chemokine secretion in lung epithelium. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
53:544–554. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Leiberman A, Dagan R, Leibovitz E,
Yagupsky P and Fliss DM: The bacteriology of the nasopharynx in
childhood. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 49:(Suppl). S151–S153.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Siegel SJ and Weiser JN: Mechanisms of
bacterial colonization of the respiratory tract. Annu Rev
Microbiol. 69:425–444. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Schmeck B, Zahlten J, Moog K, van Laak V,
Huber S, Hocke AC, Opitz B, Hoffmann E, Kracht M, Zerrahn J, et al:
Streptococcus pneumoniae-induced p38 MAPK-dependent phosphorylation
of RelA at the interleukin-8 promotor. J Biol Chem.
279:53241–53247. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Ratner AJ, Lysenko ES, Paul MN and Weiser
JN: Synergistic proinflammatory responses induced by polymicrobial
colonization of epithelial surfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
102:3429–3434. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Opitz B, Püschel A, Schmeck B, Hocke AC,
Rosseau S, Hammerschmidt S, Schumann RR, Suttorp N and Hippenstiel
S: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain proteins are innate
immune receptors for internalized Streptococcus pneumoniae. J Biol
Chem. 279:36426–36432. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Iovino F, Brouwer MC, van de Beek D,
Molema G and Bijlsma JJ: Signalling or binding: The role of the
platelet-activating factor receptor in invasive pneumococcal
disease. Cell Microbiol. 15:870–881. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Zhang JR, Mostov KE, Lamm ME, Nanno M,
Shimida S, Ohwaki M and Tuomanen E: The polymeric immunoglobulin
receptor translocates pneumococci across human nasopharyngeal
epithelial cells. Cell. 102:827–837. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Elm C, Rohde M, Vaerman JP, Chhatwal GS
and Hammerschmidt S: Characterization of the interaction of the
pneumococcal surface protein SpsA with the human polymeric
immunoglobulin receptor (hpIgR). Indian J Med Res. 119:(Suppl).
61–65. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Stenfors LE and Räisänen S: Bacterial
adhesion to epithelial cells of the nasopharynx essential in the
development of otitis media. Nord Med. 107:278–279. 1992.(In
Swedish). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Stenfors LE and Räisänen S: In vivo
attachment of Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae
to nasopharyngeal epithelium in children. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol
Relat Spec. 54:25–28. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Nelson AL, Roche AM, Gould JM, Chim K,
Ratner AJ and Weiser JN: Capsule enhances pneumococcal colonization
by limiting mucus-mediated clearance. Infect Immun. 75:83–90. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Mbaki N, Rikitomi N, Akiyama M and
Matsumoto K: In vitro adherence of Streptococcus pneumoniae to
oropharyngeal cells: Enhanced activity and colonization of the
upper respiratory tract in patients with recurrent respiratory
infections. Tohoku J Exp Med. 157:345–354. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
McCullers JA and Tuomanen EI: Molecular
pathogenesis of pneumococcal pneumonia. Front Biosci. 6:D877–D889.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Schembri MA, Dalsgaard D and Klemm P:
Capsule shields the function of short bacterial adhesins. J
Bacteriol. 186:1249–1257. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ring A, Weiser JN and Tuomanen EI:
Pneumococcal trafficking across the blood-brain barrier. Molecular
analysis of a novel bidirectional pathway. J Clin Invest.
102:347–360. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Talbot UM, Paton AW and Paton JC: Uptake
of Streptococcus pneumoniae by respiratory epithelial cells. Infect
Immun. 64:3772–3773. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Cundell DR, Weiser JN, Shen J, Young A and
Tuomanen EI: Relationship between colonial morphology and adherence
of Streptococcus pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 63:757–761.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Weiser JN, Austrian R, Sreenivasan PK and
Masure HR: Phase variation in pneumococcal opacity: Relationship
between colonial morphology and nasopharyngeal colonization. Infect
Immun. 62:2582–2592. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kim JO and Weiser JN: Association of
intrastrain phase variation in quantity of capsular polysaccharide
and teichoic acid with the virulence of Streptococcus pneumoniae. J
Infect Dis. 177:368–377. 1998. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Schaffner TO, Hinds J, Gould KA, Wüthrich
D, Bruggmann R, Küffer M, Mühlemann K, Hilty M and Hathaway LJ: A
point mutation in cpsE renders Streptococcus pneumoniae
nonencapsulated and enhances its growth, adherence and competence.
BMC Microbiol. 14:2102014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Okumura CY and Nizet V: Subterfuge and
sabotage: Evasion of host innate defenses by invasive gram-positive
bacterial pathogens. Annu Rev Microbiol. 68:439–458. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Reed JM, O'Callaghan RJ, Girgis DO,
McCormick CC, Caballero AR and Marquart ME: Ocular virulence of
capsule-deficient Streptococcus pneumoniae in a rabbit keratitis
model. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 46:604–608. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Crum NF, Barrozo CP, Chapman FA, Ryan MA
and Russell KL: An outbreak of conjunctivitis due to a novel
unencapsulated Streptococcus pneumoniae among military trainees.
Clin Infect Dis. 39:1148–1154. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Dixit C, Keller LE, Bradshaw JL, Robinson
DA, Swiatlo E and McDaniel LS: Nonencapsulated Streptococcus
pneumoniae as a cause of chronic adenoiditis. IDCases. 4:56–58.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|