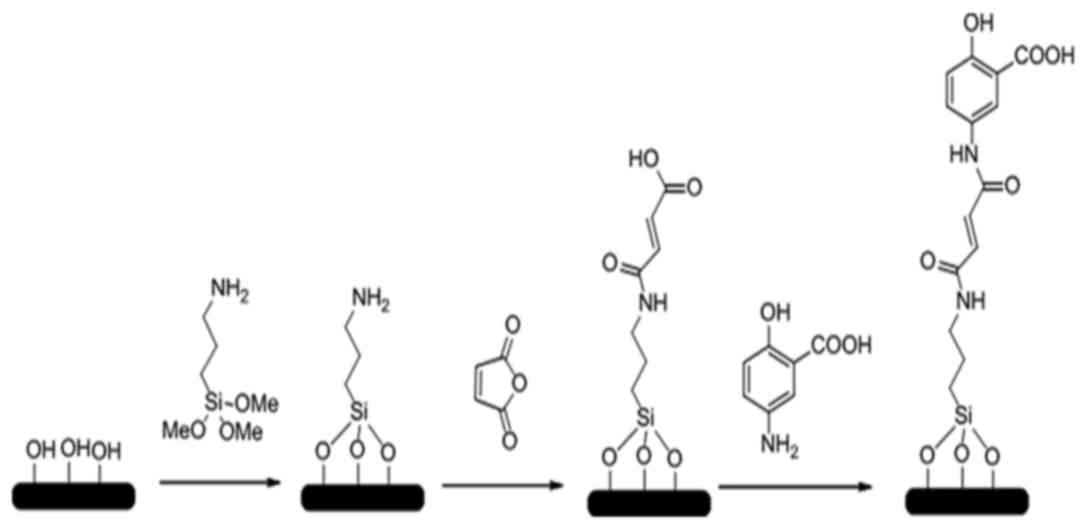
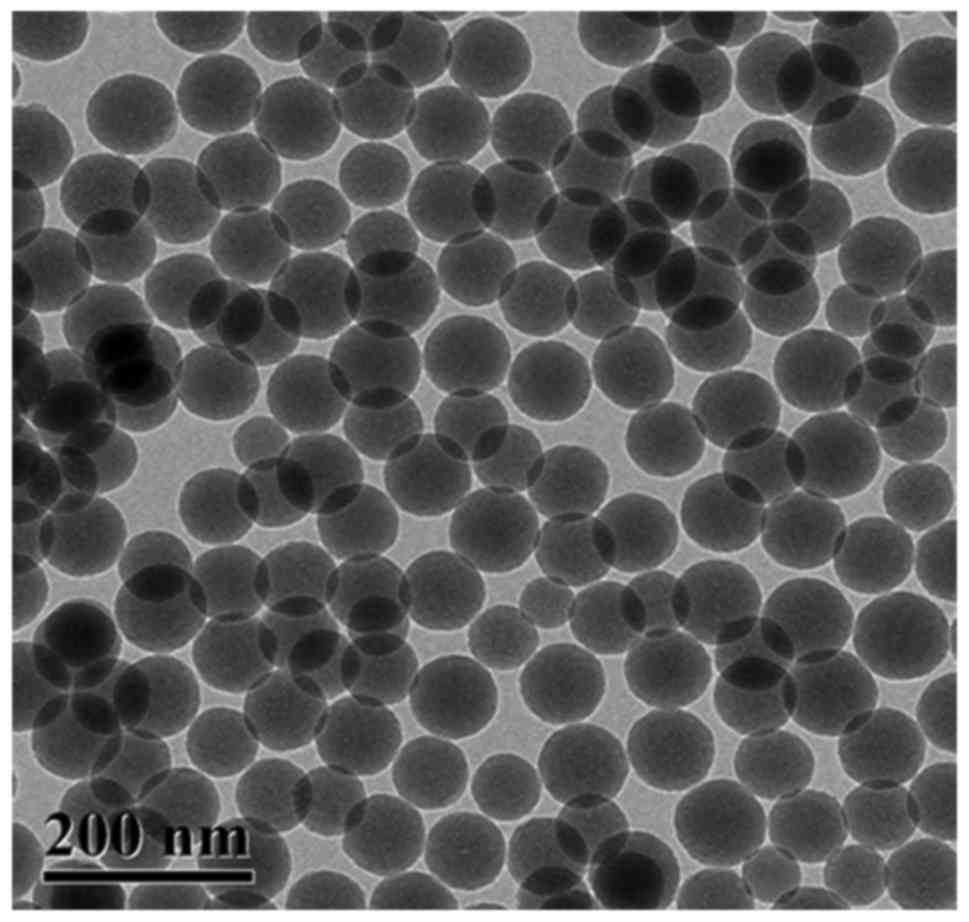
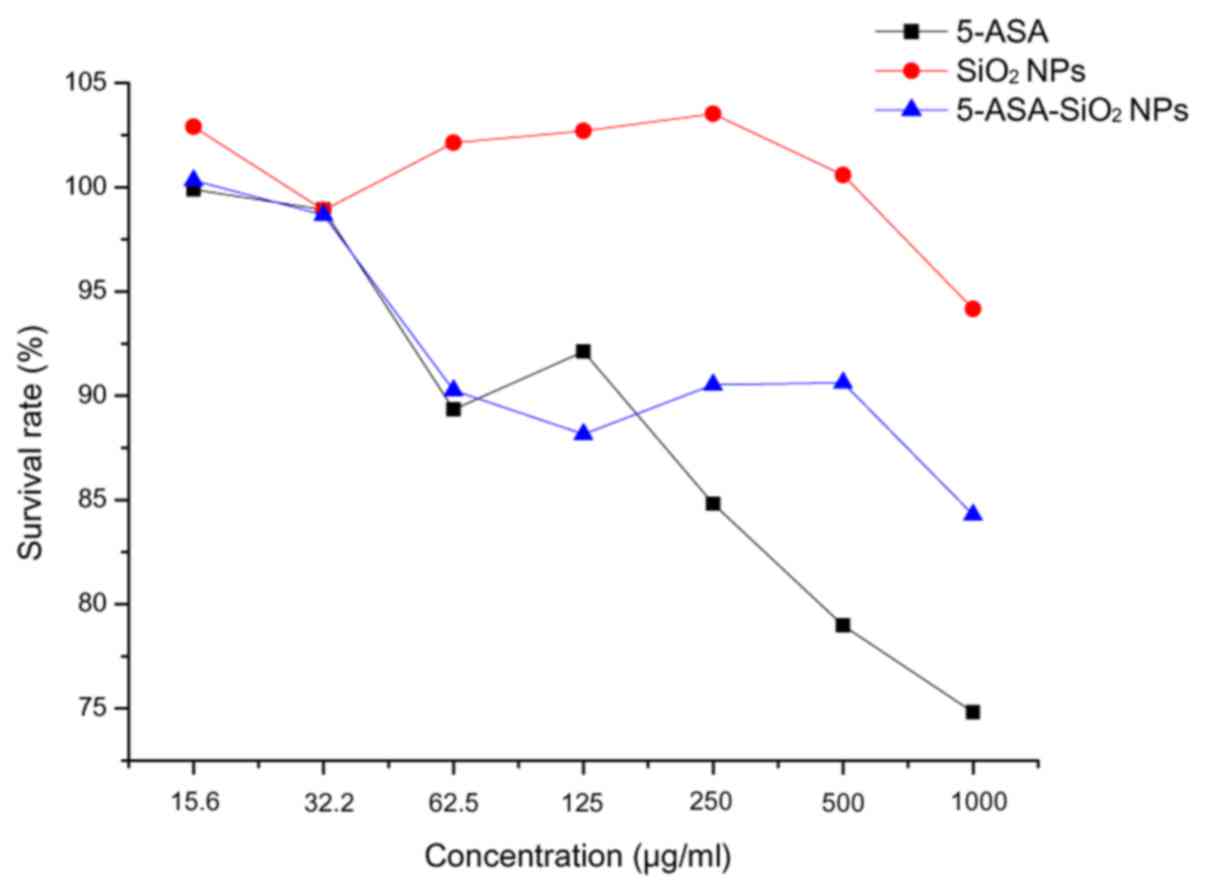
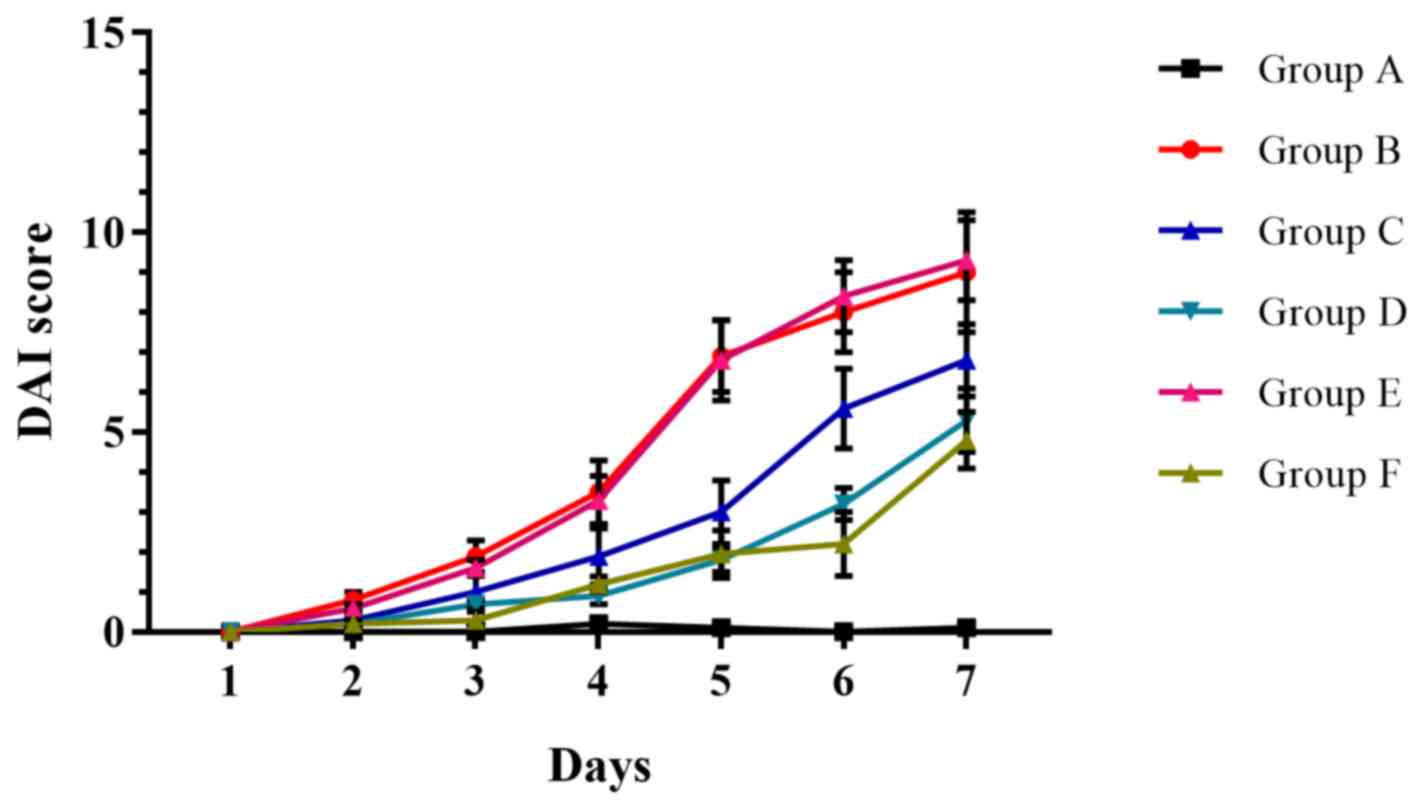
|
1
|
Molodecky NA, Soon IS, Rabi DM, Ghali WA,
Ferris M, Chernoff G, Benchimiol EI, Panaccione R, Ghosh S, Barkema
HW and Kaplan GG: Increasing incidence and prevalence of the
inflammatory bowel diseases with time, based on systematice review.
Gastroenterology. 142:46–54, e42; quiz e30. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lakatos L and Lakatos LP: Is the incidence
and prevalence of inflammatory bowel diseases increasing in Eastern
Europe? Postgrad Med J. 82:332–337. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
de Pineton Chambrun G, Peyrin-Biroulet L,
Lémann M and Colombel JF: Clinical implications of mucosal healing
for the mangement of IBD. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:15–29.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Podolsky DK: Inflammatory bowel disease. N
Engl J Med. 347:417–429. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Min Wang, Chen Chen, Jiping Ma and Jie Xu:
Preparation of superhydrophobic cauliflower-like silica nanosheres
with tunable water adhesion. J Mater Chem. 21:6962–6967. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Hoffmann JC, Pawlowski NN, Kühl AA, Höhne
W and Zeitz M: Animal models of inflammatory bowel disease: An
overview. Pathobiology. 70:121–130. 2002.-2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hartmann G, Bidlingmaier C, Siegmund B,
Albrich S, Schulze J, Tschoep K, Eigler A, Lehr HA and Endres S:
Specific type IV phosphodiesterase inhibitor rolipram mitigates
experimental colitis in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 292:22–30.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cooper HS, Murthy SN, Shah RS and
Sedergran DJ: Clinicopathologic study of dextran sulfate sodium
experimental murine colitis. Lab Invest. 69:238–249.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Murano M, Maemura K, Hirata I, Toshina K,
Nishikawa T, Hamamoto N, Sasaki S, Saitoh O and Katsu K:
Therapeutic effect of intracolonically administered nuclear factor
kappa B (p65) antisense oligonucleotide on mouse dextran sulphate
sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 120:51–58. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lamprecht A: IBD: Selective nanoparticle
adhesion can enhance colitis therapy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol and
Hepatolo. 7:311–312. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Hock SC, Ying YM and Wah CL: A review of
the current scientific and regulatory status of nanomedicines and
the challenges ahead. PDA J Pharm Sci Technol. 65:177–195.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Borbat PP, Costa-Filho AJ, Earle KA,
Moscicki JK and Freed JH: Electron spin resonance in studies of
membranes and proteins. Science. 291:266–269. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pertuit D, Moulari B, Betz T, Nadaradjane
A, Neumann D, Ismaïli L, Refouvelet B, Pellequer Y and Lamprecht A:
5-amio salicylic acid bound nanoparticles for the therapy of
inflammatory bowel disease. J Control Release. 123:211–218. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Lamprecht A, Yamamoto H, Takeuchi H and
Kawashima Y: Nanoparticles enhance therapeutic efficiency by
selectively increased local drug dose in experimental colitis in
rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 315:196–202. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moulari B, Pertuit D, Pellequer Y and
Lamprecht A: The targeting of surface modified silica nanoparticles
to inflamed tissue in experimental colitis. Biomaterials.
29:4554–4560. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kshirsagar SJ, Bhalekar MR, Patel JN,
Mohapatra SK and Shewale NS: Preparation and characterization of
nanocapsules for colon-targeted drug delivery system. Pharm Dev
Technol. 17:607–613. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lamprecht A, Schäfer U and Lehr CM:
Size-dependent bioadhesion of micro-and nanoparticulate carriers to
the inflamed colonic mucosa. Pharm Res. 18:788–793. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schmidt C, Lautenschlaeger C, Collnot EM,
Schumann M, Bojarski C, Schulzke JD, Lehr CM and Stallmach A: Nano-
and microscaled particles for drug targeting to inflamed intestinal
mucosa: A first in vivo study in human patients. J Control Release.
165:139–145. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Walsh AJ, Bryant RV and Travis SP: Current
best practice for disease activity assessment in IBD. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 13:567–579. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou YH, Yu JP, Liu YF, Teng XJ, Ming M,
Lv P, An P, Liu SQ and Yu HG: Effects of Ginkgo biloba extract on
inflammatory mediators (SOD, MDA, TNF-alpha, NF-kappaBp65, IL-6) in
TNBS-induced colitis in rats. Mediators Inflamm. 2006:926422006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Izzo RS, Witkon K, Chen AI, Hadjiyane C,
Weinstein MI and Pellecchia C: Interleukin-8 and neutrophil markers
in colonic mucosa from patients with ulcerative colitis. Am J
Gastroenterol. 87:1447–1452. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lamprecht A, Ubrich N, Yamamoto H, Schäfer
U, Takeuchi H, Maincent P, Kawashima Y and Lehr CM: Biodegradable
nanoparticles for the targeted drug delivery in treatment of
inflammatory bowel disease. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 299:775–781.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niebel W, Walkenbach K, Béduneau A,
Pellequer Y and Lamprecht A: Nanoparticle-based clodronate delivery
mitigates murine experimental colitis. J Control Release.
160:659–665. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Meissner Y, Pellequer Y and Lamprecht A:
Nanoparticles in inflammatory bowel disease: Particle targeting
versus pH-sensitive delivery. Int J Pharm. 316:138–143. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ng SC: Epidemiology of inflammatory bowel
disease: Focus on Asia. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol.
28:363–372. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|