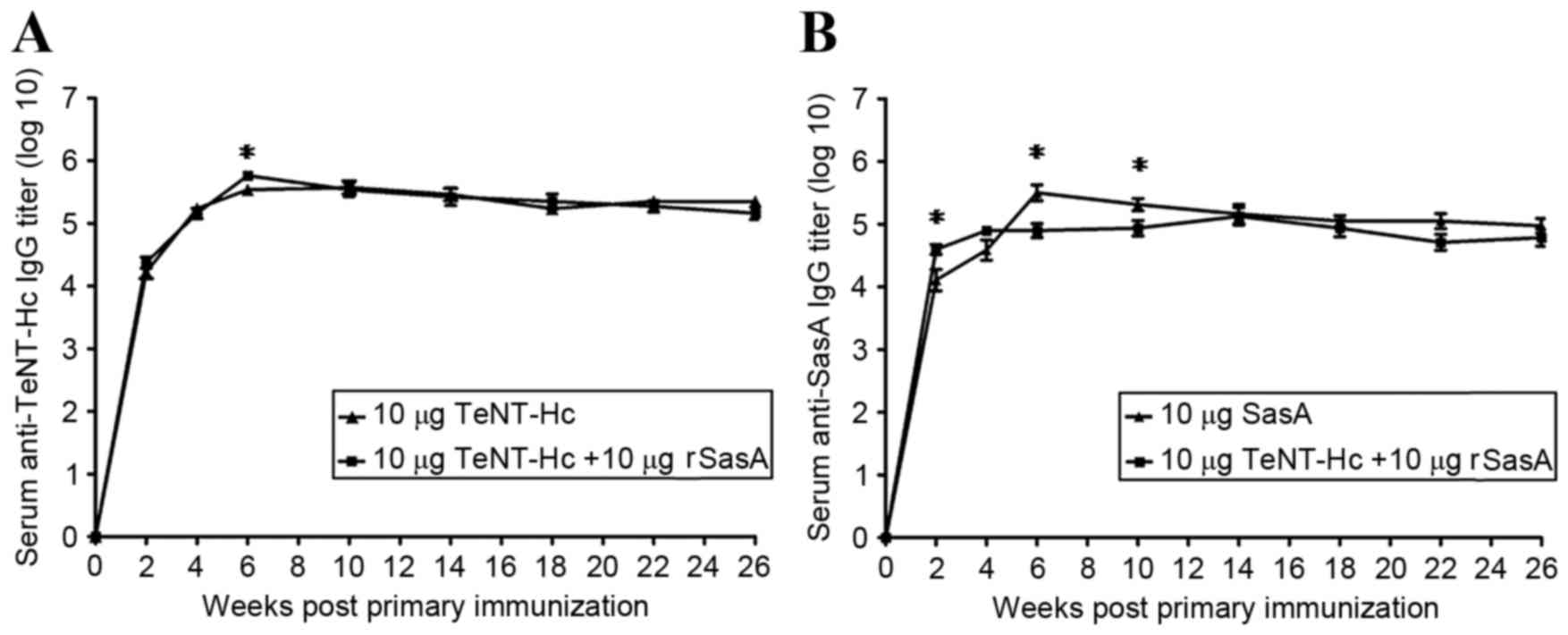
|
1
|
Zhang B, Liu Z, Lin Z, Zhang X and Fu W:
Microbiologic characteristics of pathogenic bacteria from
hospitalized trauma patients who survived Wenchuan earthquake. Eur
J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 31:2529–2535. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Afshar M, Raju M, Ansell D and Bleck TP:
Narrative review: Tetanus-a health threat after natural disasters
in developing countries. Ann Intern Med. 154:329–335. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Udo JJ, Anah MU, Ochigbo SO, Etuk IS and
Ekanem AD: Neonatal morbidity and mortality in Calabar, Nigeria: A
hospital-based study. Niger J Clin Pract. 11:285–289.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Peacock SJ, de Silva I and Lowy FD: What
determines nasal carriage of Staphylococcus aureus? Trends
Microbiol. 9:605–610. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lowy FD: Staphylococcus aureus infections.
N Engl J Med. 339:520–532. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Chalya PL, Mabula JB, Dass RM, Mbelenge N,
Mshana SE and Gilyoma JM: Ten-year experiences with Tetanus at a
Tertiary hospital in Northwestern Tanzania: A retrospective review
of 102 cases. World J Emerg Surg. 6:202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
World Health Organization, . Immunization,
vaccines and biologicals: Tetanus. http://www.who.int/immunization/diseases/teta-nus/enNovember
3–2016.
|
|
8
|
Skibinski DA, Baudner BC, Singh M and
O'Hagan DT: Combination vaccines. J Glob Infect Dis. 3:63–72. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yi SQ, Zhang XY, Yang YL, Yang Y, Liu SL,
Fu L, Yu CM and Chen W: Immunity induced by Staphylococcus aureus
surface protein A was protective against lethal challenge of
Staphylococcus aureus in BALB/c mice. Microbiol Immunol.
56:406–410. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Siboo IR, Chambers HF and Sullam PM: Role
of SraP, a Serine-Rich Surface Protein of Staphylococcus aureus, in
binding to human platelets. Infect Immun. 73:2273–2280. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roche FM, Massey R, Peacock SJ, Day NP,
Visai L, Speziale P, Lam A, Pallen M and Foster TJ:
Characterization of novel LPXTG-containing proteins of
Staphylococcus aureus identified from genome sequences.
Microbiology. 149:643–654. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Montecucco C and Schiavo G: Tetanus and
botulism neurotoxins: A new group of zinc proteases. Trends Biochem
Sci. 18:324–327. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Schiavo G, Benfenati F, Poulain B,
Rossetto O, De Laureto P Polverino, DasGupta BR and Montecucco C:
Tetanus and botulinum-B neurotoxins block neurotransmitter release
by proteolytic cleavage of synaptobrevin. Nature. 359:832–835.
1992. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sinha K, Box M, Lalli G, Schiavo G,
Schneider H, Groves M, Siligardi G and Fairweather N: Analysis of
mutants of tetanus toxin Hc fragment: Ganglioside binding, cell
binding and retrograde axonal transport properties. Mol Microbiol.
37:1041–1051. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu R, Yi S, Yu C, Fang T, Liu S, Yu T,
Song X, Fu L, Hou L and Chen W: A conformational change of C
fragment of tetanus neurotoxin reduces its ganglioside-binding
activity but does not destroy its immunogenicity. Clin Vaccine
Immunol. 18:1668–1672. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu R, Hou L, Yu C, Liu S, Ren J, Fang T,
Zhang X and Chen W: Enhanced expression of soluble recombinant
tetanus neurotoxin Hc in Escherichia coli for use as a tetanus
vaccine candidate. Immunobiology. 216:485–490. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Rauch S, DeDent AC, Kim HK, Wardenburg J
Bubeck, Missiakas DM and Schneewind O: Abscess formation and
alpha-hemolysin induced toxicity in a mouse model of Staphylococcus
aureus peritoneal infection. Infect Immun. 80:3721–3732. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ulrich R and Miller J: Threshold
estimation in two-alternative forced-choice (2AFC) tasks: The
Spearman-Kärber method. Percept Psychophys. 66:517–533. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Booy R, Aitken SJ, Taylor S,
Tudor-Williams G, Macfarlane JA, Moxon ER, Ashworth LA, Mayon-White
RT, Griffiths H and Chapel HM: Immunogenicity of combined
diphtheria, tetanus, and pertussis vaccine given at 2, 3 and 4
months versus 3, 5 and 9 months of age. Lancet. 339:507–510. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
West DJ, Rabalais GP, Watson B, Keyserling
HL, Matthews H and Hesley TM: Antibody responses of healthy infants
to concurrent administration of a bivalent haemophilus influenzae
type b-hepatitis B vaccine with diphtheria-tetanus-pertussis, polio
and measles-mumps-rubella vaccines. BioDrugs. 15:413–418. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Joines RW, Blatter M, Abraham B, Xie F, De
Clercq N, Baine Y, Reisinger KS, Kuhnen A and Parenti DL: A
prospective, randomized, comparative US trial of a combination
hepatitis A and B vaccine (Twinrix) with corresponding monovalent
vaccines (Havrix and Engerix-B) in adults. Vaccine. 19:4710–4719.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ortqvist A, Hedlund J, Burman LA, Elbel E,
Höfer M, Leinonen M, Lindblad I, Sundelöf B and Kalin M: Randomised
trial of 23-valent pneumococcal capsular polysaccharide vaccine in
prevention of pneumonia in middle-aged and elderly people. Swedish
Pneumococcal Vaccination Study Group. Lancet. 351:399–403. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Robbins JB, Schneerson R, Horwith G, Naso
R and Fattom A: Staphylococcus aureus types 5 and 8 capsular
polysaccharide-protein conjugate vaccines. Am Heart J. 147:593–598.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Maira-Litran T, Kropec A, Goldmann D and
Pier GB: Biologic properties and vaccine potential of the
staphylococcal poly-N-acetyl glucosamine surface polysaccharide.
Vaccine. 22:872–879. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Joshi A, Pancari G, Cope L, Bowman EP, Cua
D, Proctor RA and McNeely T: Immunization with Staphylococcus
aureus iron regulated surface determinant B (IsdB) confers
protection via Th17/IL17 pathway in a murine sepsis model. Hum
Vaccin Immunother. 8:336–346. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Josefsson E, Hartford O, O'Brien L, Patti
JM and Foster T: Protection against experimental Staphylococcus
aureus arthritis by vaccination with clumping factor A, a novel
virulence determinant. J Infect Dis. 184:1572–1580. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schaffer AC, Solinga RM, Cocchiaro J,
Portoles M, Kiser KB, Risley A, Randall SM, Valtulina V, Speziale
P, Walsh E, et al: Immunization with Staphylococcus aureus clumping
factor B, a major determinant in nasal carriage, reduces nasal
colonization in a murine model. Infect Immun. 74:2145–2153. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kim HK, Cheng AG, Kim HY, Missiakas DM and
Schneewind O: Nontoxigenic protein A vaccine for
methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in mice. J
Exp Med. 207:1863–1870. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Arrecubieta C, Matsunaga I, Asai T, Naka
Y, Deng MC and Lowy FD: Vaccination with clumping factor A and
fibronectin binding protein A to prevent Staphylococcus aureus
infection of an aortic patch in mice. J Infect Dis. 198:571–575.
2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nilsson IM, Patti JM, Bremell T, Höök M
and Tarkowski A: Vaccination with a recombinant fragment of
collagen adhesin provides protection against Staphylococcus
aureus-mediated septic death. J Clin Invest. 101:2640–2649. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cheng AG, McAdow M, Kim HK, Bae T,
Missiakas DM and Schneewind O: Contribution of coagulases towards
Staphylococcus aureus disease and protective immunity. PLoS Pathog.
6:e10010362010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wardenburg J Bubeck and Schneewind O:
Vaccine protection against Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia. J Exp
Med. 205:287–294. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brown EL, Dumitrescu O, Thomas D, Badiou
C, Koers EM, Choudhury P, Vazquez V, Etienne J, Lina G, Vandenesch
F and Bowden MG: The Panton-Valentine leukocidin vaccine protects
mice against lung and skin infections caused by Staphylococcus
aureus USA300. Clin Microbiol Infect. 15:156–164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
34
|
Hu DL, Omoe K, Narita K, Cui JC, Shinagawa
K and Nakane A: Intranasal vaccination with a double mutant of
staphylococcal enterotoxin C provides protection against
Staphylococcus aureus infection. Microbes Infect. 8:2841–2848.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Hu DL, Omoe K, Sasaki S, Sashinami H,
Sakuraba H, Yokomizo Y, Shinagawa K and Nakane A: Vaccination with
nontoxic mutant toxic shock syndrome toxin 1 protects against
Staphylococcus aureus infection. J Infect Dis. 188:743–752. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Bagnoli F, Bertholet S and Grandi G:
Inferring reasons for the failure of Staphylococcus aureus vaccines
in clinical trials. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2:162012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Diep BA, Gill SR, Chang RF, Phan TH, Chen
JH, Davidson MG, Lin F, Lin J, Carleton HA, Mongodin EF, et al:
Complete genome sequence of USA300, an epidemic clone of
community-acquired meticillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.
Lancet. 367:731–739. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Tacket CO, Galen J, Sztein MB, Losonsky G,
Wyant TL, Nataro J, Wasserman SS, Edelman R, Chatfield S, Dougan G
and Levine MM: Safety and immune responses to attenuated Salmonella
enterica serovar typhi oral live vector vaccines expressing tetanus
toxin fragment C. Clin Immunol. 97:146–153. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lee S, Belitsky BR, Brown DW, Brinker JP,
Kerstein KO, Herrmann JE, Keusch GT, Sonenshein AL and Tzipori S:
Efficacy, heat stability and safety of intranasally administered
Bacillus subtilis spore or vegetative cell vaccines expressing
tetanus toxin fragment C. Vaccine. 28:6658–6665. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Bongat AF, Saksena R, Adamo R, Fujimoto Y,
Shiokawa Z, Peterson DC, Fukase K, Vann WF and Kovác P: Multimeric
bivalent immunogens from recombinant tetanus toxin HC fragment,
synthetic hexasaccharides, and a glycopeptide adjuvant. Glycoconj
J. 27:69–77. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Salgado-Pabón W and Schlievert PM: Models
matter: The search for an effective Staphylococcus aureus vaccine.
Nat Rev Microbiol. 12:585–591. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Stranger-Jones YK, Bae T and Schneewind O:
Vaccine assembly from surface proteins of Staphylococcus aureus.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:16942–16947. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|