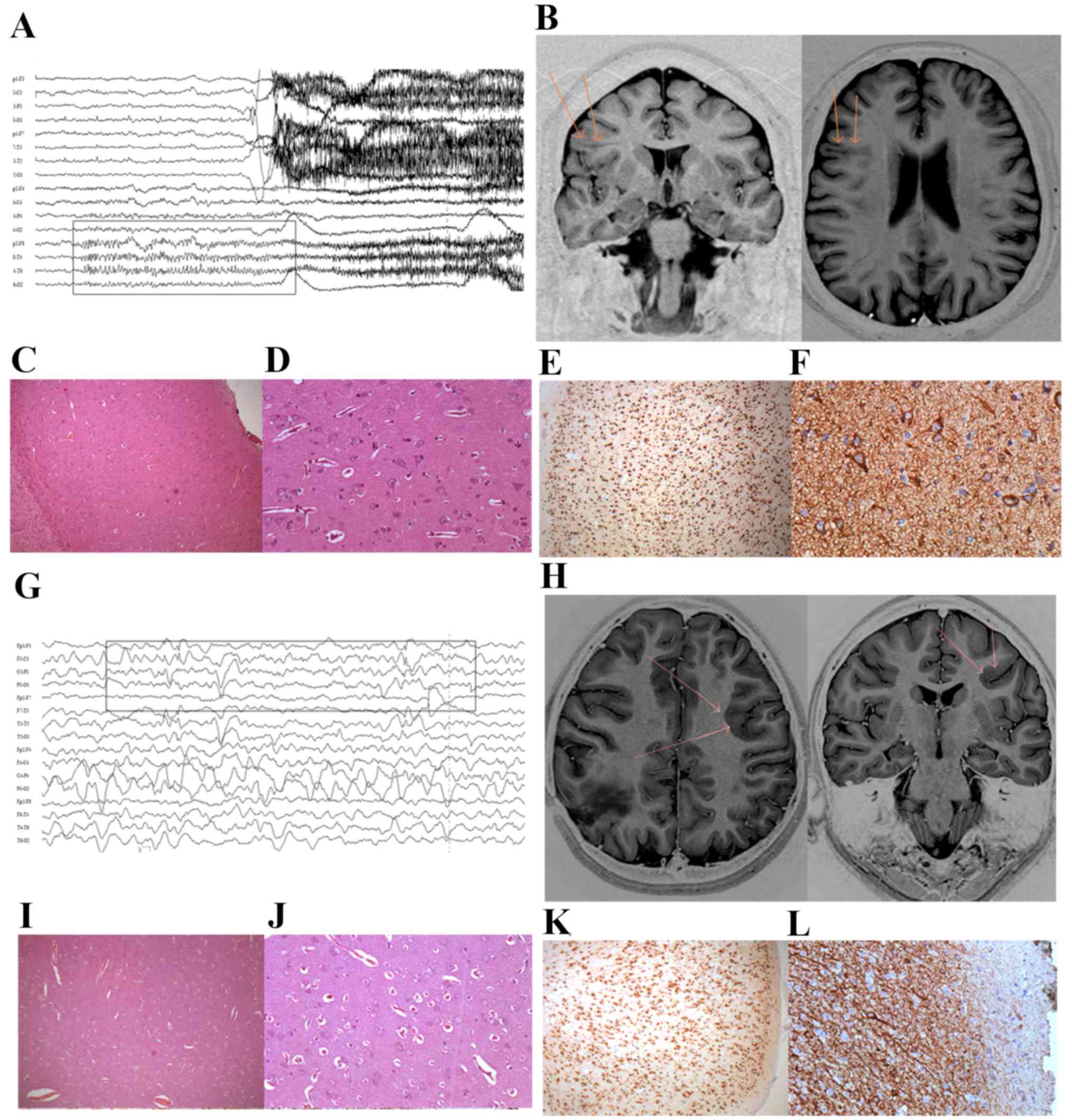
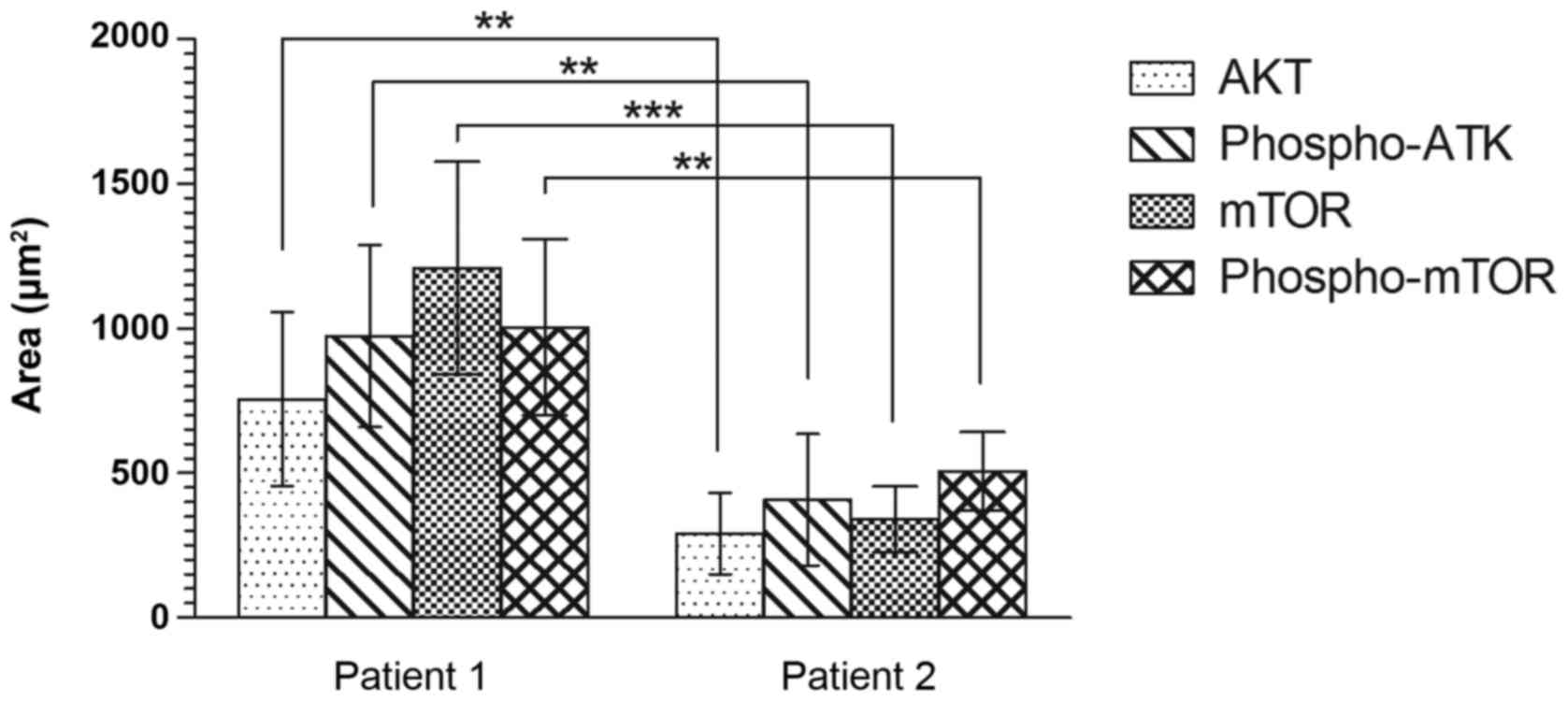
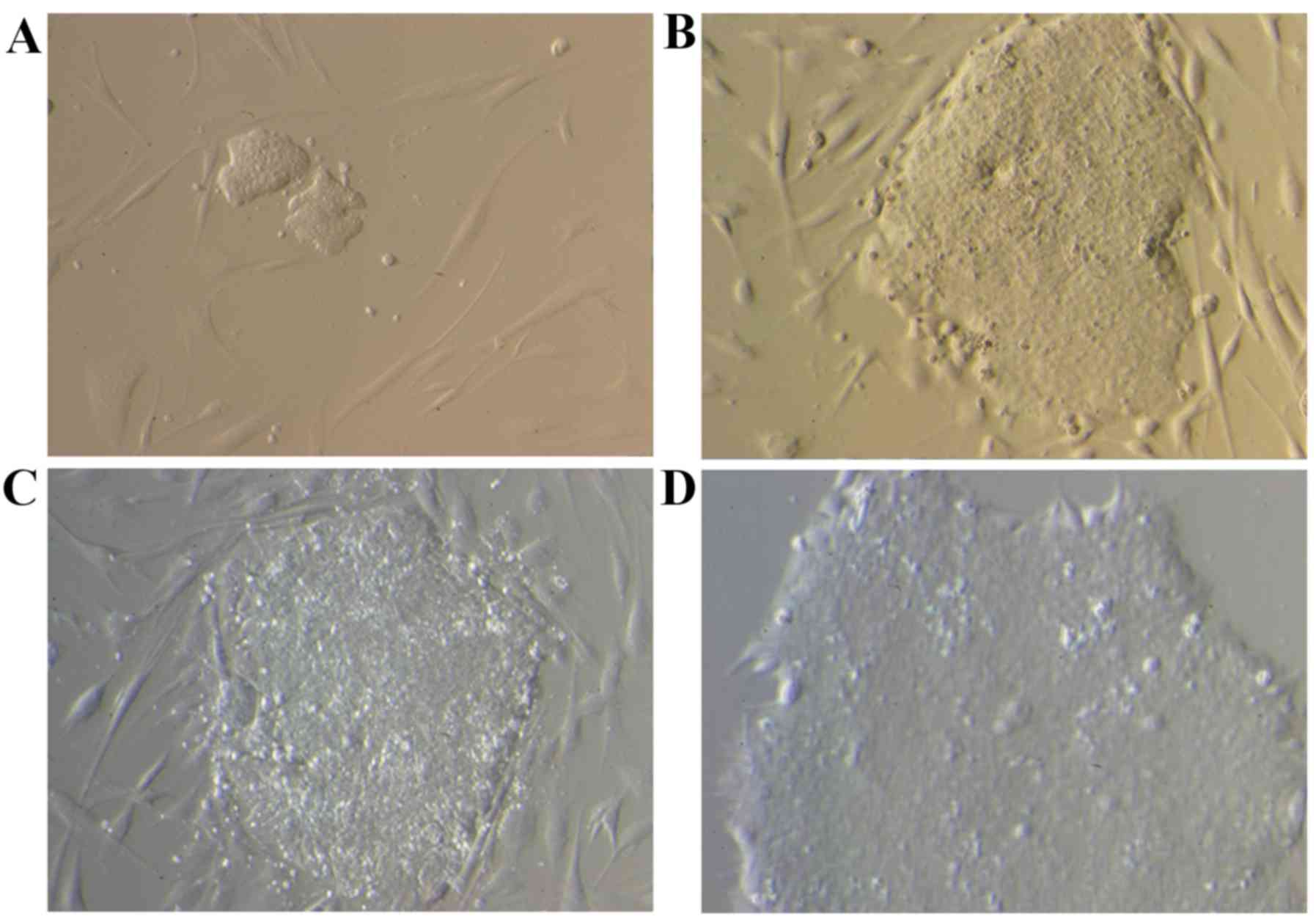
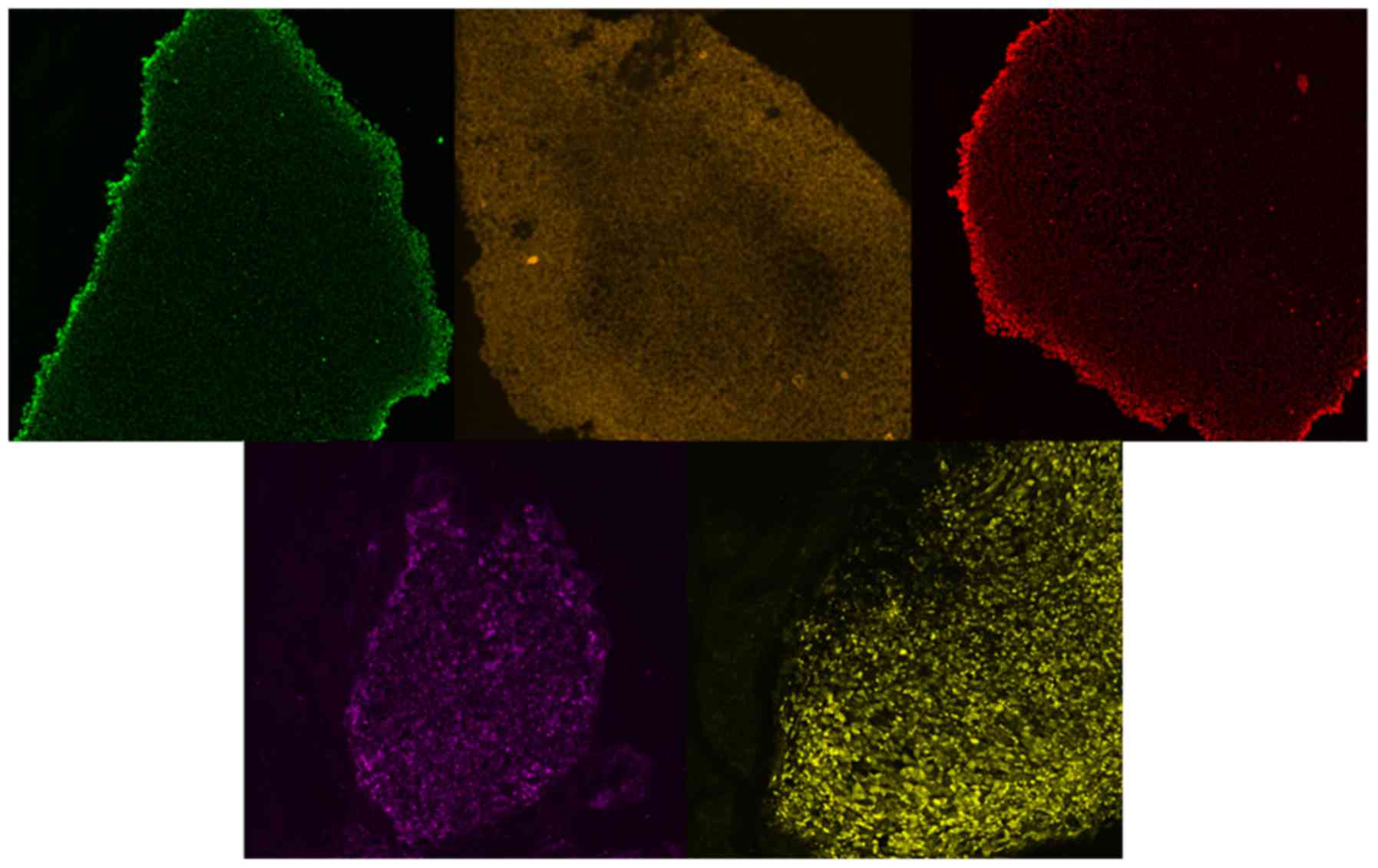
|
1
|
Palmini A, Najm I, Avanzini G, Babb T,
Guerrini R, Foldvary-Schaefer N, Jackson G, Lüders HO, Prayson R,
Spreafico R and Vinters HV: Terminology and classification of the
cortical dysplasias. Neurology. 62:S2–8. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Arai A, Saito T, Hanai S, Sukigara S,
Nabatame S, Otsuki T, Nakagawa E, Takahashi A, Kaneko Y, Kaido T,
et al: Abnormal maturation and differentiation of neocortical
neurons in epileptogenic cortical malformation: Unique distribution
of layer-specific marker cells of focal cortical dysplasia and
hemimegalencephaly. Brain Res. 1470:89–97. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Prayson RA, Spreafico R and Vinters HV:
Pathologic characteristics of the cortical dysplasias. Neurosurg
Clin N Am. 1317–25. (vii)2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Guerrini R, Dobyns WB and Barkovich AJ:
Abnormal development of the human cerebral cortex: Genetics,
functional consequences and treatment options. Trends Neurosci.
31:154–162. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kabat J and Król P: Focal cortical
dysplasia-review. Pol J Radiol. 77:35–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Taylor DC, Falconer MA, Bruton CJ and
Corsellis JA: Focal dysplasia of the cerebral cortex in epilepsy. J
Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 34:369–387. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Blümcke I, Thom M, Aronica E, Armstrong
DD, Vinters HV, Palmini A, Jacques TS, Avanzini G, Barkovich AJ,
Battaglia G, et al: The clinicopathologic spectrum of focal
cortical dysplasias: A consensus classification proposed by an ad
hoc Task Force of the ILAE Diagnostic Methods Commission.
Epilepsia. 52:158–174. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kuzniecky R: Epilepsy and malformations of
cortical development: New developments. Curr Opin Neurol.
28:151–157. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu PP, Kang SA, Rameseder J, Zhang Y,
Ottina KA, Lim D, Peterson TR, Choi Y, Gray NS, Yaffe MB, et al:
The mTOR-regulated phosphoproteome reveals a mechanism of
mTORC1-mediated inhibition of growth factor signaling. Science.
332:1317–1322. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhou J, Blundell J, Ogawa S, Kwon CH,
Zhang W, Sinton C, Powell CM and Parada LF: Pharmacological
inhibition of mTORC1 suppresses anatomical, cellular, and
behavioral abnormalities in neural-specific Pten knock-out mice. J
Neurosci. 29:1773–1783. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cantley LC: The phosphoinositide 3-kinase
pathway. Science. 296:1655–1657. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dolmetsch R and Geschwind DH: The human
brain in a dish: The promise of iPSC-derived neurons. Cell.
145:831–834. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dragunow M: The adult human brain in
preclinical drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:659–666. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ichida JK and Kiskinis E: Probing
disorders of the nervous system using reprogramming approaches.
EMBO J. 34:1456–1477. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Takahashi K, Okita K, Nakagawa M and
Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem cells from fibroblast
cultures. Nat Protoc. 2:3081–3089. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Marinowic DR, Domingues MF, Machado DC and
DaCosta JC: The expression of pluripotency genes and neuronal
markers after neurodifferentiation in fibroblasts co-cultured with
human umbilical cord blood mononuclear cells. In Vitro Cell Dev
Biol Anim. 51:26–35. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Takahashi K and Yamanaka S: Induction of
pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast
cultures by defined factors. Cell. 126:663–676. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Ohnuki M, Narita M,
Ichisaka T, Tomoda K and Yamanaka S: Induction of pluripotent stem
cells from adult human fibroblasts by defined factors. Cell.
131:861–872. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fries KM, Blieden T, Looney RJ, Sempowski
GD, Silvera MR, Willis RA and Phipps RP: Evidence of fibroblast
heterogeneity and the role of fibroblast subpopulations in
fibrosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 72:283–292. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Parent JM and Anderson SA: Reprogramming
patient-derived cells to study the epilepsies. Nat Neurosci.
18:360–366. 2015. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song B, Sun G, Herszfeld D, Sylvain A,
Campanale NV, Hirst CE, Caine S, Parkington HC, Tonta MA, Coleman
HA, et al: Neural differentiation of patient specific iPS cells as
a novel approach to study the pathophysiology of multiple
sclerosis. Stem Cell Res. 8:259–273. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Luo Y, Fan Y, Zhou B, Xu Z, Chen Y and Sun
X: Generation of induced pluripotent stem cells from skin
fibroblasts of a patient with olivopontocerebellar atrophy. Tohoku
J Exp Med. 226:151–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Israel MA, Yuan SH, Bardy C, Reyna SM, Mu
Y, Herrera C, Hefferan MP, Van Gorp S, Nazor KL, Boscolo FS, et al:
Probing sporadic and familial Alzheimer's disease using induced
pluripotent stem cells. Nature. 482:216–220. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yagi T, Ito D, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Nihei
Y, Yoshizaki T, Yamanaka S, Okano H and Suzuki N: Modeling familial
Alzheimer's disease with induced pluripotent stem cells. Hum Mol
Genet. 20:4530–4539. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hossini AM, Megges M, Prigione A, Lichtner
B, Toliat MR, Wruck W, Schröter F, Nuernberg P, Kroll H,
Makrantonaki E, et al: Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived
neuronal cells from a sporadic Alzheimer's disease donor as a model
for investigating AD-associated gene regulatory networks. BMC
Genomics. 16:842015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Duan L, Bhattacharyya BJ, Belmadani A, Pan
L, Miller RJ and Kessler JA: Stem cell derived basal forebrain
cholinergic neurons from Alzheimer's disease patients are more
susceptible to cell death. Mol Neurodegener. 9:32014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Marchetto MC, Carromeu C, Acab A, Yu D,
Yeo GW, Mu Y, Chen G, Gage FH and Muotri AR: A model for neural
development and treatment of Rett syndrome using human induced
pluripotent stem cells. Cell. 143:527–539. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Williams EC, Zhong X, Mohamed A, Li R, Liu
Y, Dong Q, Ananiev GE, Mok JC, Lin BR, Lu J, et al: Mutant
astrocytes differentiated from Rett syndrome patients-specific
iPSCs have adverse effects on wild-type neurons. Hum Mol Genet.
23:2968–2980. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Djuric U, Cheung AY, Zhang W, Mok RS, Lai
W, Piekna A, Hendry JA, Ross PJ, Pasceri P, Kim DS, et al: MECP2e1
isoform mutation affects the form and function of neurons derived
from Rett syndrome patient iPS cells. Neurobiol Dis. 76:37–45.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Livide G, Patriarchi T, Amenduni M,
Amabile S, Yasui D, Calcagno E, Lo Rizzo C, De Falco G, Ulivieri C,
Ariani F, et al: GluD1 is a common altered player in neuronal
differentiation from both MECP2-mutated and CDKL5-mutated iPS
cells. Eur J Hum Genet. 23:195–201. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sareen D, O'Rourke JG, Meera P, Muhammad
AK, Grant S, Simpkinson M, Bell S, Carmona S, Ornelas L, Sahabian
A, et al: Targeting RNA foci in iPSC-derived motor neurons from ALS
patients with a C9ORF72 repeat expansion. Sci Transl Med.
5:208ra1492013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wainger BJ, Kiskinis E, Mellin C, Wiskow
O, Han SS, Sandoe J, Perez NP, Williams LA, Lee S, Boulting G, et
al: Intrinsic membrane hyperexcitability of amyotrophic lateral
sclerosis patient-derived motor neurons. Cell Rep. 7:1–11. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Kiskinis E, Sandoe J, Williams LA,
Boulting GL, Moccia R, Wainger BJ, Han S, Peng T, Thams S,
Mikkilineni S, et al: Pathways disrupted in human ALS motor neurons
identified through genetic correction of mutant SOD1. Cell Stem
Cell. 14:781–795. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Devlin AC, Burr K, Borooah S, Foster D,
Cleary EM, Geti I, Vallier L, Shaw CE, Chandran S and Miles GB:
Human iPSC-derived motoneurons harbouring TARDBP or C9ORF72 ALS
mutations are dysfunctional despite maintaining viability. Nat
Commun. 6:59992015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lee P, Martin NT, Nakamura K, Azghadi S,
Amiri M, Ben-David U, Perlman S, Gatti RA, Hu H and Lowry WE: SMRT
compounds abrogate cellular phenotypes of ataxia telangiectasia in
neural derivatives of patient-specific hiPSCs. Nat Commun.
4:18242013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jiao J, Yang Y, Shi Y, Chen J, Gao R, Fan
Y, Yao H, Liao W, Sun XF and Gao S: Modeling Dravet syndrome using
induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and directly converted
neurons. Hum Mol Genet. 22:4241–4252. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Lee G, Papapetrou EP, Kim H, Chambers SM,
Tomishima MJ, Fasano CA, Ganat YM, Menon J, Shimizu F, Viale A, et
al: Modelling pathogenesis and treatment of familial dysautonomia
using patient-specific iPSCs. Nature. 461:402–406. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Doers ME, Musser MT, Nichol R, Berndt ER,
Baker M, Gomez TM, Zhang SC, Abbeduto L and Bhattacharyya A:
iPSC-derived forebrain neurons from FXS individuals show defects in
initial neurite outgrowth. Stem Cells Dev. 23:1777–1787. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Tiscornia G, Vivas EL, Matalonga L,
Berniakovich I, Barragán Monasterio M, Eguizábal C, Gort L,
González F, Mellet C Ortiz, García F, ernández JM, et al:
Neuronopathic Gaucher's disease: Induced pluripotent stem cells for
disease modelling and testing chaperone activity of small
compounds. Hum Mol Genet. 22:633–645. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Guo X, Disatnik MH, Monbureau M, Shamloo
M, Mochly-Rosen D and Qi X: Inhibition of mitochondrial
fragmentation diminishes Huntington's disease-associated
neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest. 123:5371–5388. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Yao Y, Cui X, Al-Ramahi I, Sun X, Li B,
Hou J, Difiglia M, Palacino J, Wu ZY, Ma L, et al: A
striatal-enriched intronic GPCR modulates huntingtin levels and
toxicity. Elife. 4:2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Mekhoubad S, Bock C, De Boer AS, Kiskinis
E, Meissner A and Eggan K: Erosion of dosage compensation impacts
human iPSC disease modeling. Cell Stem Cell. 10:595–609. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lancaster MA, Renner M, Martin CA, Wenzel
D, Bicknell LS, Hurles ME, Homfray T, Penninger JM, Jackson AP and
Knoblich JA: Cerebral organoids model human brain development and
microcephaly. Nature. 501:373–379. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Reinhardt P, Schmid B, Burbulla LF,
Schöndorf DC, Wagner L, Glatza M, Höing S, Hargus G, Heck SA,
Dhingra A, et al: Genetic correction of a LRRK2 mutation in human
iPSCs links parkinsonian neurodegeneration to ERK-dependent changes
in gene expression. Cell Stem Cell. 12:354–367. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chung CY, Khurana V, Auluck PK, Tardiff
DF, Mazzulli JR, Soldner F, Baru V, Lou Y, Freyzon Y, Cho S, et al:
Identification and rescue of α-synuclein toxicity in Parkinson
patient-derived neurons. Science. 342:983–987. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sanders LH, Laganière J, Cooper O, Mak SK,
Vu BJ, Huang YA, Paschon DE, Vangipuram M, Sundararajan R, Urnov
FD, et al: LRRK2 mutations cause mitochondrial DNA damage in
iPSC-derived neural cells from Parkinson's disease patients:
Reversal by gene correction. Neurobiol Dis. 62:381–386. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Robicsek O, Karry R, Petit I,
Salman-Kesner N, Müller FJ, Klein E, Aberdam D and Ben-Shachar D:
Abnormal neuronal differentiation and mitochondrial dysfunction in
hair follicle-derived induced pluripotent stem cells of
schizophrenia patients. Mol Psychiatry. 18:1067–1076. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Yoon KJ, Nguyen HN, Ursini G, Zhang F, Kim
NS, Wen Z, Makri G, Nauen D, Shin JH, Park Y, et al: Modeling a
genetic risk for schizophrenia in iPSCs and mice reveals neural
stem cell deficits associated with adherens junctions and polarity.
Cell Stem Cell. 15:79–91. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Bda S Paulsen, de Moraes Maciel R, Galina
A, da Silveira M Souza, Souza C dosSantos, Drummond H, Pozzatto E
Nascimento, Silva H Jr, Chicaybam L, Massuda R, et al: Altered
oxygen metabolism associated to neurogenesis of induced pluripotent
stem cells derived from a schizophrenic patient. Cell Transplant.
21:1547–1559. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Guerrini R and Dobyns WB: Malformations of
cortical development: Clinical features and genetic causes. Lancet
Neurol. 13:710–726. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Johnson TE: Caenorhabditis elegans 2007:
The premier model for the study of aging. Exp Gerontol. 43:1–4.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kenyon CJ: The genetics of ageing. Nature.
464:504–512. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
O'Neill C: PI3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling:
Impaired on/off switches in aging, cognitive decline and
Alzheimer's disease. Exp Gerontol. 48:647–653. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Jansen LA, Mirzaa GM, Ishak GE, O'Roak BJ,
Hiatt JB, Roden WH, Gunter SA, Christian SL, Collins S, Adams C, et
al: PI3K/AKT pathway mutations cause a spectrum of brain
malformations from megalencephaly to focal cortical dysplasia.
Brain. 138:1613–1628. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Fusaki N, Ban H, Nishiyama A, Saeki K and
Hasegawa M: Efficient induction of transgene-free human pluripotent
stem cells using a vector based on Sendai virus, an RNA virus that
does not integrate into the host genome. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys
Biol Sci. 85:348–362. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Li HO, Zhu YF, Asakawa M, Kuma H, Hirata
T, Ueda Y, Lee YS, Fukumura M, Iida A, Kato A, et al: A cytoplasmic
RNA vector derived from nontransmissible Sendai virus with
efficient gene transfer and expression. J Virol. 74:6564–6569.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
International Stem Cell Banking
Initiative, ; Andrews PW, Arias-Diaz J, Auerbach J, Alvarez M,
Ahrlund-Richter L, Baker D, Benvenisty N, Ben-Josef D, Blin G, et
al: Consensus guidance for banking and supply of human embryonic
stem cell lines for research purposes. Stem Cell Rev. 5:301–314.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Asprer JS and Lakshmipathy U: Current
methods and challenges in the comprehensive characterization of
human pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Rev. 11:357–372. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|