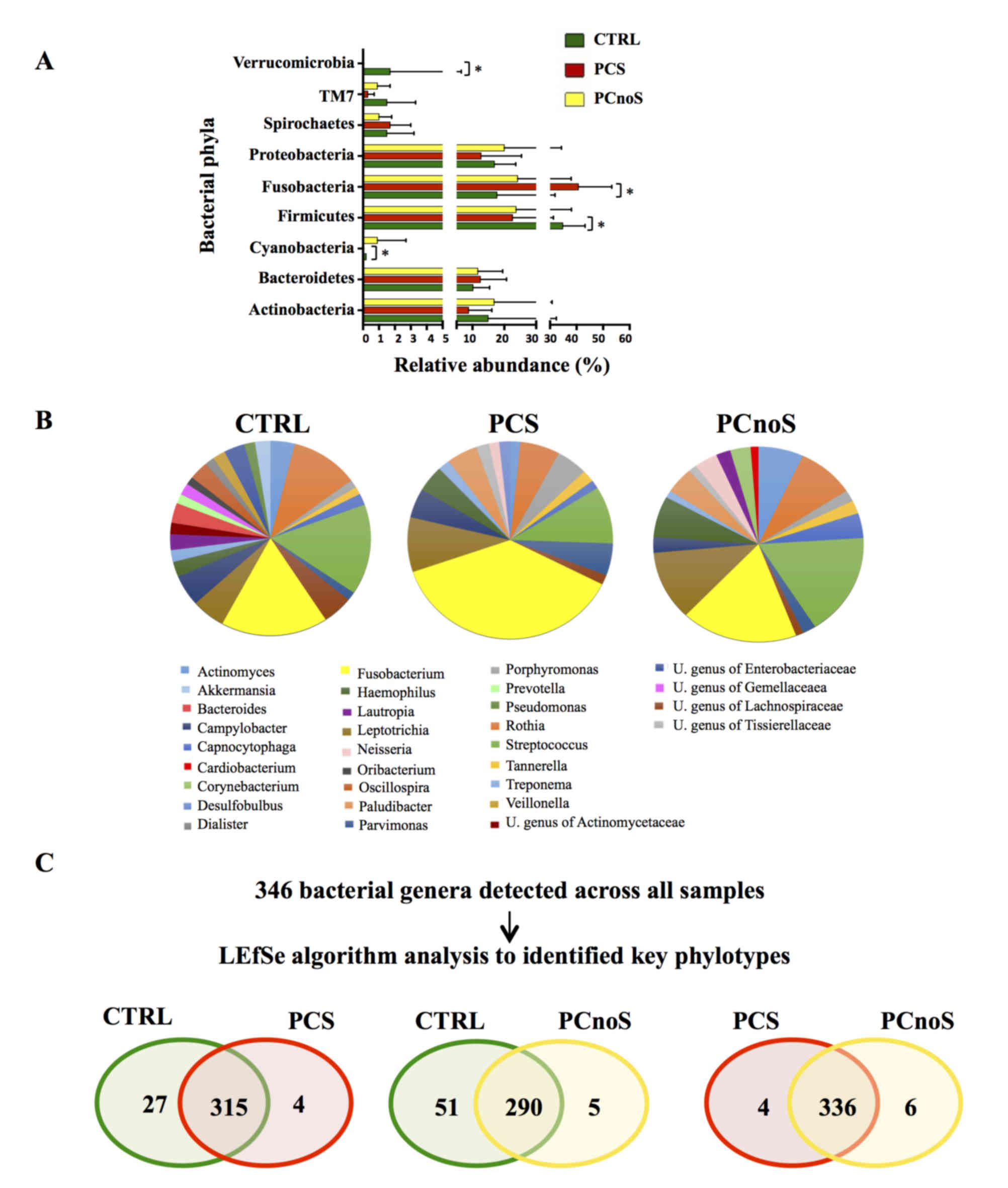
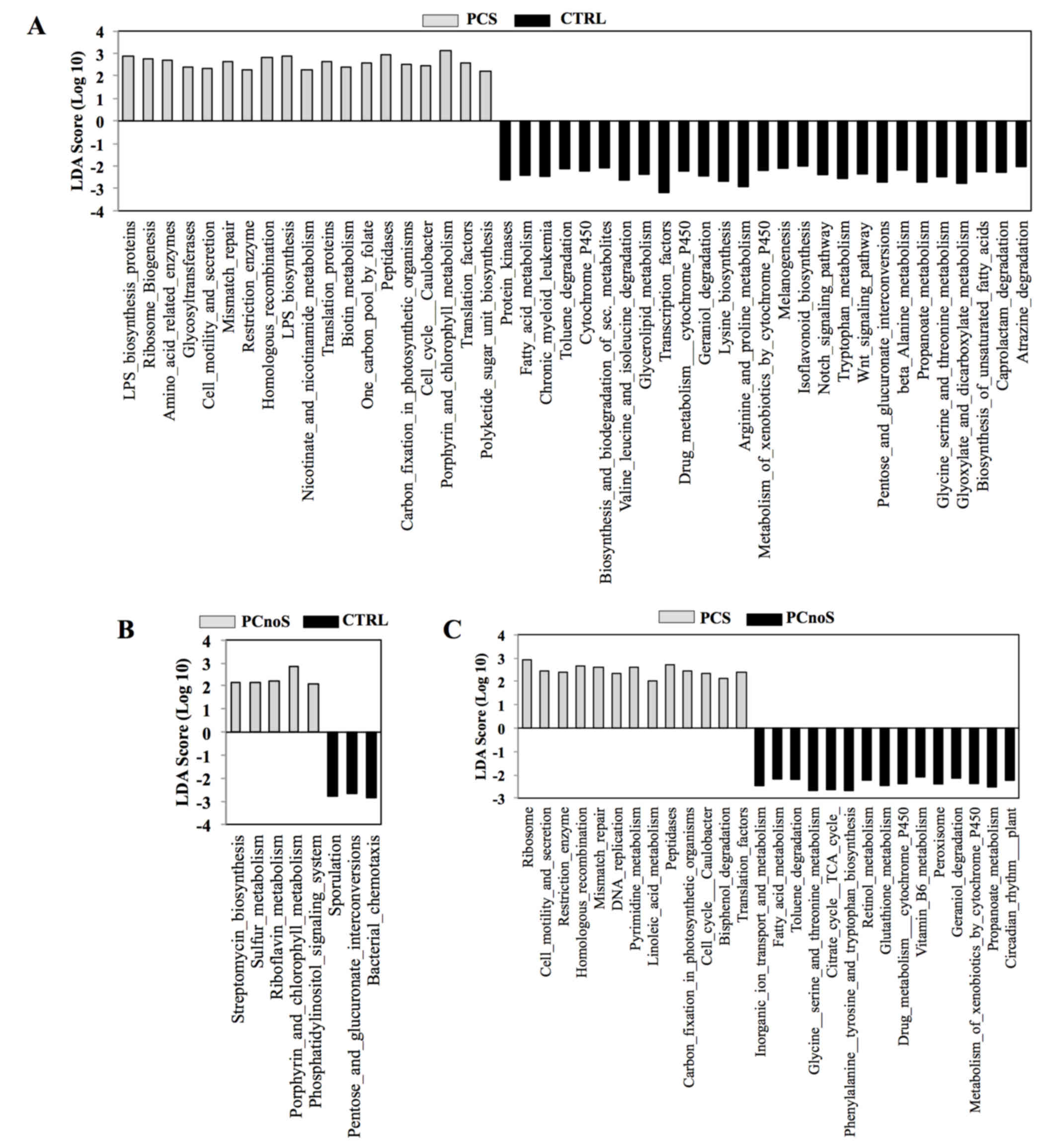
|
1
|
Avila M, Ojcius DM and Yilmaz O: The oral
microbiota: Living with a permanent guest. DNA Cell Biol.
28:405–411. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Cho I and Blaser MJ: The human microbiome:
At the interface of health and disease. Nat Rev Genet. 13:260–270.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Haffajee AD, Teles RP and Socransky SS:
The effect of periodontal therapy on the composition of the
subgingival microbiota. Periodontol 2000. 42:219–258. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dentino A, Lee S, Mailhot J and Hefti AF:
Principles of periodontology. Periodontol 2000. 61:16–53. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Al Harthi LS, Cullinan MP, Leichter JW and
Thomson WM: The impact of periodontitis on oral health-related
quality of life: A review of the evidence from observational
studies. Aust Dent J. 58:274–277; quiz 384. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Seymour GJ, Ford PJ, Cullinan MP, Leishman
S and Yamazaki K: Relationship between periodontal infections and
systemic disease. Clin Microbiol Infect. 13 Suppl 4:S3–S10. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Armitage CG: Comparison of the
microbiological features of chronic and aggressive periodontitis.
Periodontol 2000. 53:70–88. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Socransky SS, Haffajee AD, Cugini MA,
Smith C and Kent RL Jr: Microbial complexes in subgingival plaque.
J Clin Periodontol. 25:134–44. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Page RC and Kornman KS: The pathogenesis
of human periodontitis: An introduction. Periodontol 2000. 14:9–11.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lee J, Taneja V and Vassallo R: Cigarette
smoking and inflammation: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. J Dent
Res. 91:142–149. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Labriola A, Needleman I and Moles DR:
Systematic review of the effect of smoking on nonsurgical
periodontal therapy. Periodontol 2000. 37:124–137. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Haffajee AD and Socransky SS: Relationship
of cigarette smoking to the subgingival microbiota. J Clin
Periodontol. 28:377–88. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Preber H, Bergström J and Linder LE:
Occurrence of periopathogens in smoker and non-smoker patients. J
Clin Periodontol. 19:667–671. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Van der Velden U, Varoufaki A, Hutter JW,
Xu L, Timmerman MF, Van Winkelhoff AJ and Loos BG: Effect of
smoking and periodontal treatment on the subgingival microflora. J
Clin Periodontol. 30:603–610. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dewhirst FE, Chen T, Izard J, Paster BJ,
Tanner AC, Yu WH, Lakshmanan A and Wade WG: The human oral
microbiome. J Bacteriol. 192:5002–5017. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sammartino G, Tia M, Gentile E, Marenzi G
and Claudio PP: Platelet-rich plasma and resorbable membrane for
prevention of periodontal defects after deeply impacted lower third
molar extraction. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 67:2369–2373. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ramfjord SP: Present status of the
modified Widman flap procedure. J Periodontol. 48:558–565. 1977.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Illumina. 16S Metagenomic Sequencing
Library Preparation. 2013.http://support.illumina.com/downloads/16s_metagenomic_sequencing_library_preparation.html
|
|
19
|
Mizrahi-Man O, Davenport ER and Gilad Y:
Taxonomic classification of bacterial 16S rRNA genes using short
sequencing reads: Evaluation of effective study designs. PLoS One.
8:e536082013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Illumina. MiSeq System Denature and Dilute
Libraries Guide. 2016.http://support.illumina.com/downloads/prepare_libraries_for_sequencing_miseq_15039740.html
|
|
21
|
Zhang J, Kobert K, Flouri T and Stamatakis
A: PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR.
Bioinformatics. 30:614–620. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Schmieder R and Edwards R: Quality control
and preprocessing of metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics.
27:863–864. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J,
Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Peña AG, Goodrich
JK, Gordon JI, et al: QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput
community sequencing data. Nat Methods. 7:335–336. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas
M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P and Andersen GL:
Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench
compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol. 72:5069–5072. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Clarke KR: Non-parametric multivariate
analyses of changes in community structure. Aust J Ecol.
18:117–143. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D,
Miropolsky L, Garrett WS and Huttenhower C: Metagenomic biomarker
discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 12:R602011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Langille MG, Zaneveld J, Caporaso JG,
McDonald D, Knights D, Reyes J, Clemente JC, Burkepile DE, Thurber
RL Vega, Knight R, et al: Predictive functional profiling of
microbial communities using 16S rRNA marker gene sequences. Nat
Biotechnol. 31:814–821. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kanehisa M and Goto S: KEGG: kyoto
encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:27–30.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim M, Morrison M and Yu Z: Evaluation of
different partial 16S rRNA gene sequence regions for phylogenetic
analysis of microbiomes. J Microbiol Methods. 84:81–87. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hug LA, Baker BJ, Anantharaman K, Brown
CT, Probst AJ, Castelle CJ, Butterfield CN, Hernsdorf AW, Amano Y,
Ise K, et al: A new view of the tree of life. Nat Microbiol.
1:160482016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang J, Qi J, Zhao H, He S, Zhang Y, Wei S
and Zhao F: Metagenomic sequencing reveals microbiota and its
functional potential associated with periodontal disease. Sci Rep.
3:18432013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kirst ME, Li EC, Alfant B, Chi YY, Walker
C, Magnusson I and Wang GP: Dysbiosis and alterations in predicted
functions of the subgingival microbiome in chronic periodontitis.
Appl Environ Microbiol. 81:783–793. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Arora N, Mishra A and Chugh S: Microbial
role in periodontitis: Have we reached the top? Some unsung
bacteria other than red complex. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 18:9–13.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Bizzarro S, Loos BG, Laine ML, Crielaard W
and Zaura E: Subgingival microbiome in smokers and non-smokers in
periodontitis: An exploratory study using traditional targeted
techniques and a next-generation sequencing. J Clin Periodontol.
40:483–492. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Colombo AP, Boches SK, Cotton SL, Goodson
JM, Kent R, Haffajee AD, Socransky SS, Hasturk H, Van Dyke TE,
Dewhirst F and Paster BJ: Comparisons of subgingival microbial
profiles of refractory periodontitis, severe periodontitis, and
periodontal health using the human oral microbe identification
microarray. J Periodontol. 80:1421–1432. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Gupta RS, Mahmood S and Adeolu M: Erratum:
A phylogenomic and molecular signature based approach for
characterization of the Phylum Spirochaetes and its major clades:
Proposal for a taxonomic revision of the phylum. Front Microbiol.
4:3222013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Bergeron MG, Simard P and Provencher P:
Influence of growth medium and supplement on growth of Haemophilus
influenzae and on antibacterial activity of several antibiotics. J
Clin Microbiol. 25:650–655. 1987.PubMed/NCBI
|