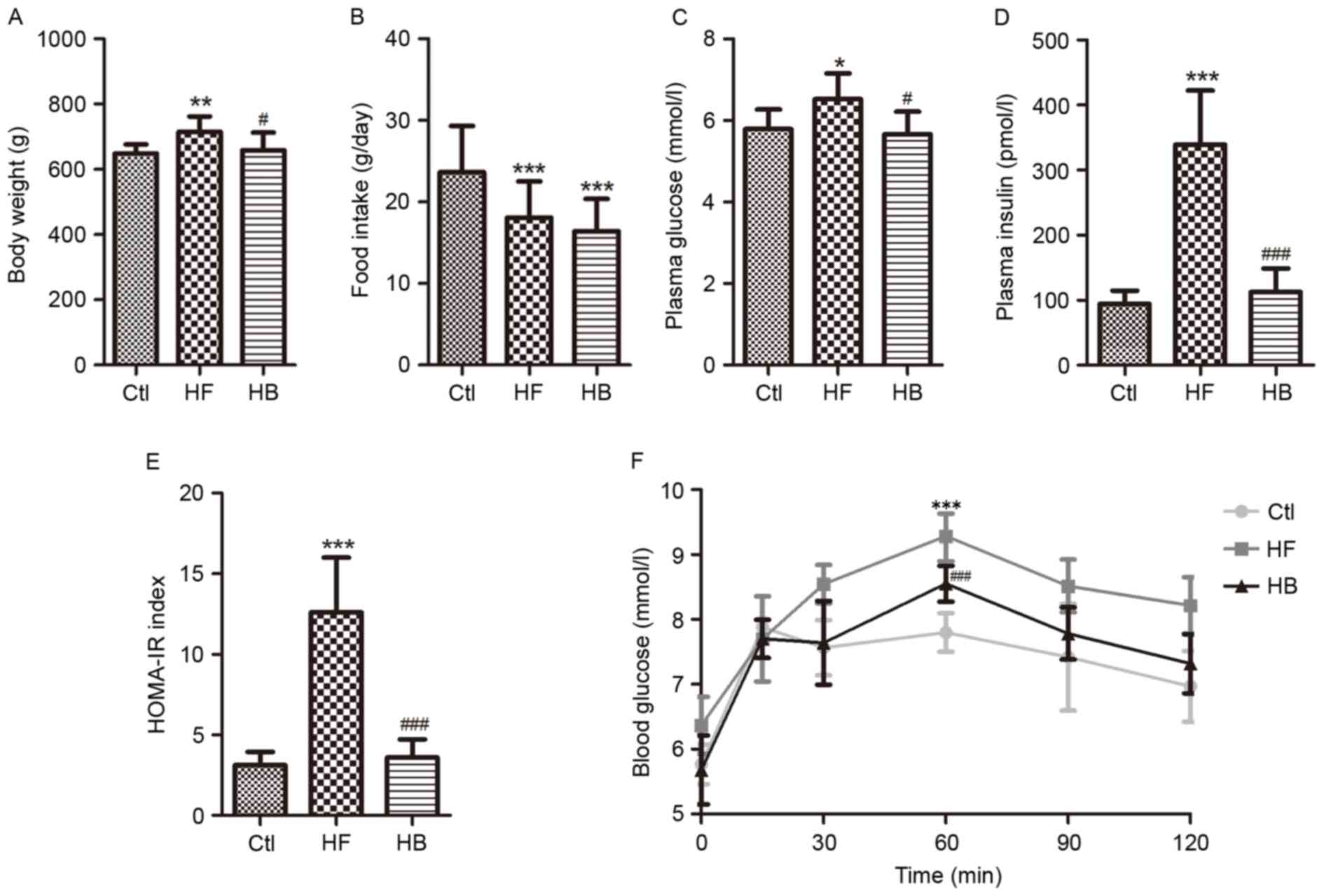
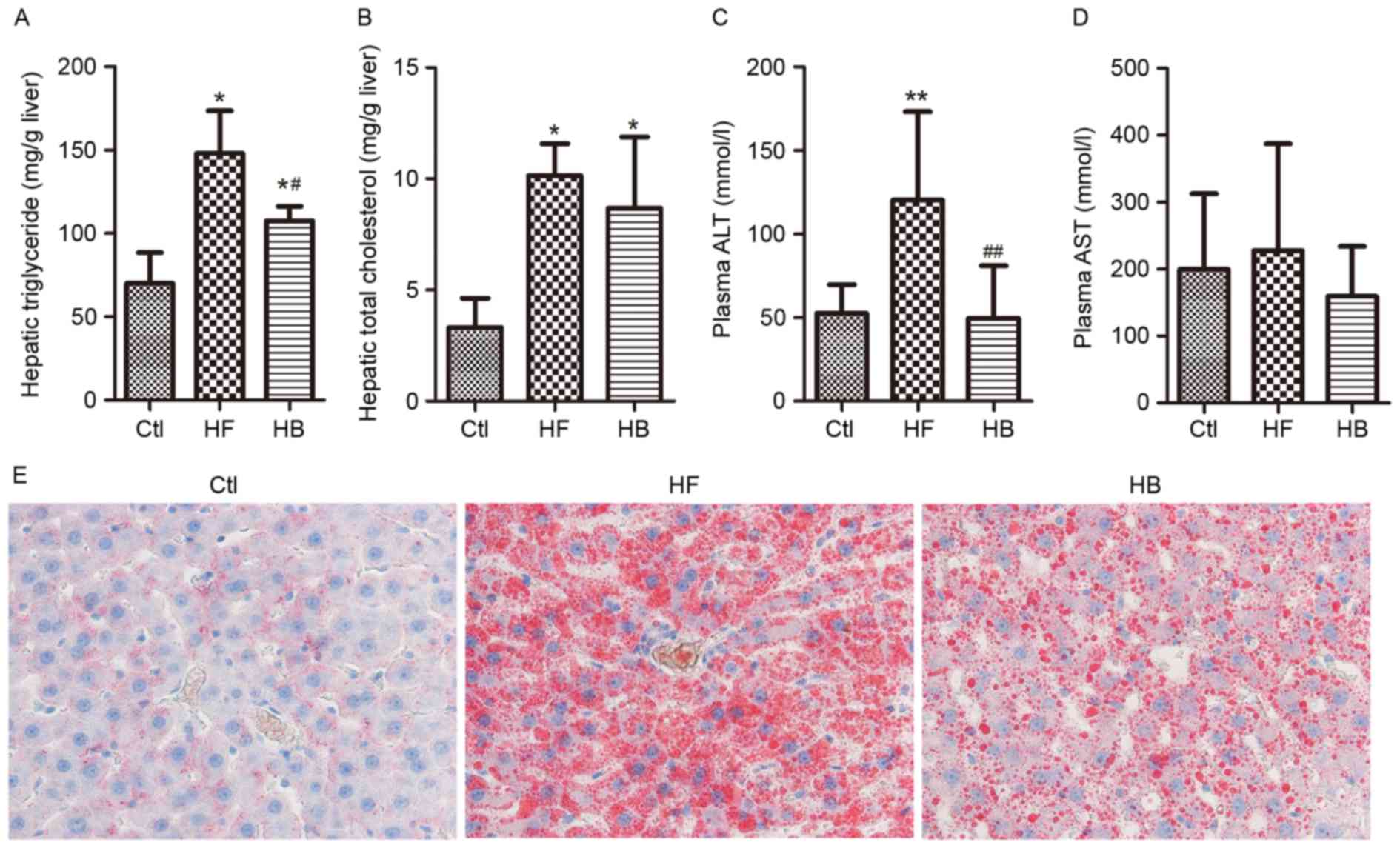
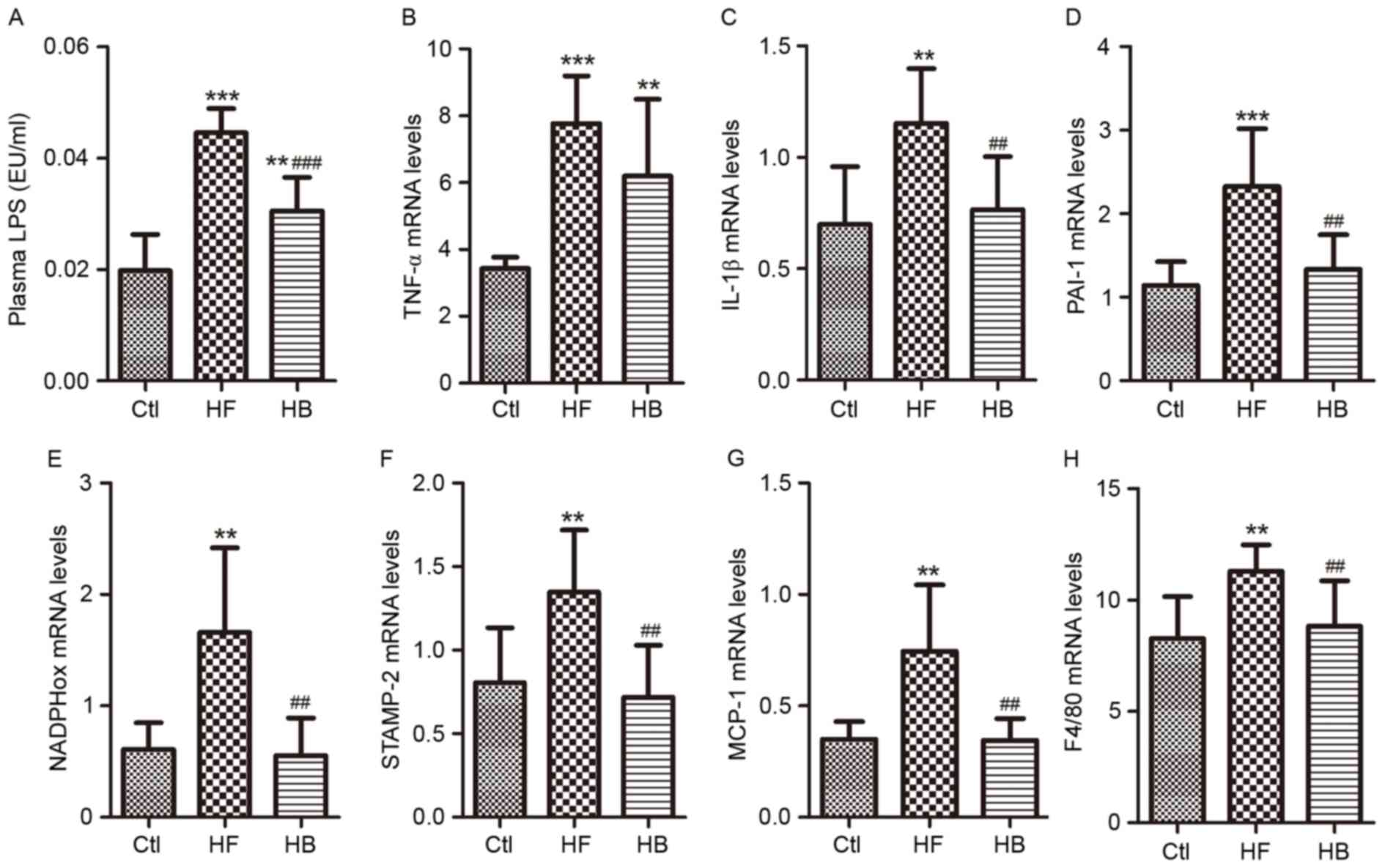
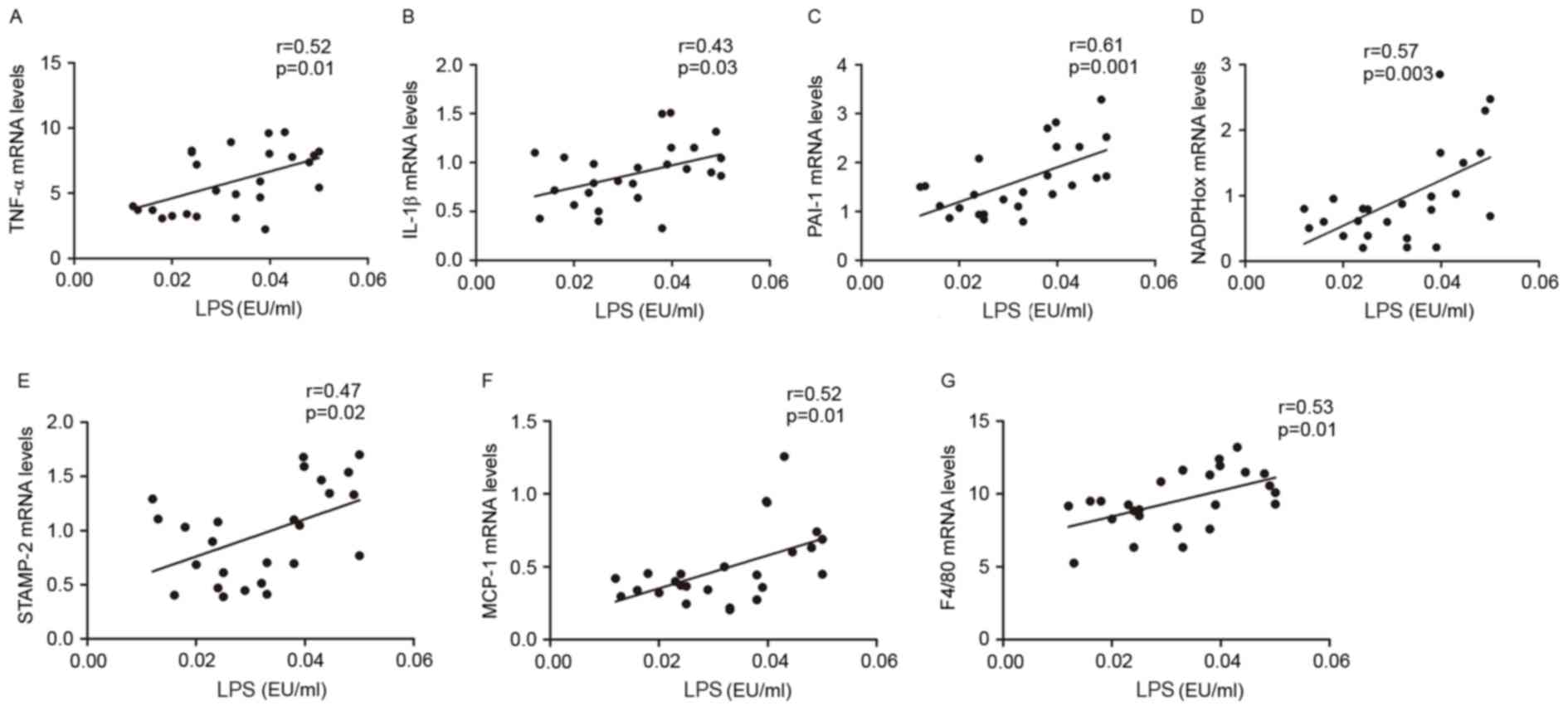
|
1
|
Zhang Y, Li X, Zou D, Liu W, Yang J, Zhu
N, Huo L, Wang M, Hong J, Wu P, et al: Treatment of type 2 diabetes
and dyslipidemia with the natural plant alkaloid berberine. J Clin
Endocrinol Metab. 93:2559–2565. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Xie W, Gu D, Li J, Cui K and Zhang Y:
Effects and action mechanisms of berberine and Rhizoma coptidis on
gut microbes and obesity in high-fat diet-fed C57BL/6J mice. PLoS
One. 6:e245202011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gomes AP, Duarte FV, Nunes P, Hubbard BP,
Teodoro JS, Varela AT, Jones JG, Sinclair DA, Palmeira CM and Rolo
AP: Berberine protects against high fat diet-induced dysfunction in
muscle mitochondria by inducing SIRT1-dependent mitochondrial
biogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1822:185–195. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lee YS, Kim WS, Kim KH, Yoon MJ, Cho HJ,
Shen Y, Ye JM, Lee CH, Oh WK, Kim CT, et al: Berberine, a natural
plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with
beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant
states. Diabetes. 55:2256–2264. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu L, Yu YL, Yang JS, Li Y, Liu YW, Liang
Y, Liu XD, Xie L and Wang GJ: Berberine suppresses intestinal
disaccharidases with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic
states, evidences from in vivo and in vitro study. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 381:371–381. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pan GY, Huang ZJ, Wang GJ, Fawcett JP, Liu
XD, Zhao XC, Sun JG and Xie YY: The antihyperglycaemic activity of
berberine arises from a decrease of glucose absorption. Planta Med.
69:632–636. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kong W, Wei J, Abidi P, Lin M, Inaba S, Li
C, Wang Y, Wang Z, Si S, Pan H, et al: Berberine is a novel
cholesterol-lowering drug working through a unique mechanism
distinct from statins. Nat Med. 10:1344–1351. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wang Y, Yi X, Ghanam K, Zhang S, Zhao T
and Zhu X: Berberine decreases cholesterol levels in rats through
multiple mechanisms, including inhibition of cholesterol
absorption. Metabolism. 63:1167–1177. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Lu SS, Yu YL, Zhu HJ, Liu XD, Liu L, Liu
YW, Wang P, Xie L and Wang GJ: Berberine promotes glucagon-like
peptide-1 (7–36) amide secretion in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats. J Endocrinol. 200:159–165. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yu Y, Liu L, Wang X, Liu X, Liu X, Xie L
and Wang G: Modulation of glucagon-like peptide-1 release by
berberine: In vivo and in vitro studies. Biochem Pharmacol.
79:1000–1006. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu YT, Hao HP, Xie HG, Lai L, Wang Q, Liu
CX and Wang GJ: Extensive intestinal first-pass elimination and
predominant hepatic distribution of berberine explain its low
plasma levels in rats. Drug Metab Dispos. 38:1779–1784. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen W, Miao YQ, Fan DJ, Yang SS, Lin X,
Meng LK and Tang X: Bioavailability study of berberine and the
enhancing effects of TPGS on intestinal absorption in rats. AAPS
PharmSciTech. 12:705–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Aronsson L, Huang Y, Parini P,
Korach-André M, Håkansson J, Gustafsson JÅ, Pettersson S,
Arulampalam V and Rafter J: Decreased fat storage by Lactobacillus
paracasei is associated with increased levels of angiopoietin-like
4 protein (ANGPTL4). PLoS One. 5:e130872010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhang X, Zhao Y, Zhang M, Pang X, Xu J,
Kang C, Li M, Zhang C, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, et al: Structural changes
of gut microbiota during berberine-mediated prevention of obesity
and insulin resistance in high-fat diet-fed rats. PLoS One.
7:e425292012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cani PD, Possemiers S, Van de Wiele T,
Guiot Y, Everard A, Rottier O, Geurts L, Naslain D, Neyrinck A,
Lambert DM, et al: Changes in gut microbiota control inflammation
in obese mice through a mechanism involving GLP-2-driven
improvement of gut permeability. Gut. 58:1091–1103. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Cani PD, Lecourt E, Dewulf EM, Sohet FM,
Pachikian BD, Naslain D, De Backer F, Neyrinck AM and Delzenne NM:
Gut microbiota fermentation of prebiotics increases satietogenic
and incretin gut peptide production with consequences for appetite
sensation and glucose response after a meal. Am J Clin Nutr.
90:1236–1243. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Maton N and Delzenne
NM: Oligofructose promotes satiety in rats fed a high-fat diet:
Involvement of glucagon-like peptide-1. Obes Res. 13:1000–1007.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cani PD, Hoste S, Guiot Y and Delzenne NM:
Dietary non-digestible carbohydrates promote L-cell differentiation
in the proximal colon of rats. Br J Nutr. 98:32–37. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tazoe H, Otomo Y, Karaki S, Kato I, Fukami
Y, Terasaki M and Kuwahara A: Expression of short-chain fatty acid
receptor GPR41 in the human colon. Biomed Res. 30:149–156. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tolhurst G, Heffron H, Lam YS, Parker HE,
Habib AM, Diakogiannaki E, Cameron J, Grosse J, Reimann F and
Gribble FM: Short-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like
peptide-1 secretion via the G-protein-coupled receptor FFAR2.
Diabetes. 61:364–371. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
des Rieux A, Pourcelle V, Cani PD,
Marchand-Brynaert J and Préat V: Targeted nanoparticles with novel
non-peptidic ligands for oral delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
65:833–844. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Psichas A, Sleeth ML, Murphy KG, Brooks L,
Bewick GA, Hanyaloglu AC, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR and Frost G: The
short chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY
secretion via free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int J Obes
(Lond). 39:424–429. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Feng Y, Li Y, Chen C, Lin X, Yang Y, Cai
H, Lv Z, Cao M, Li K, Xu J, et al: Inhibiting roles of berberine in
gut movement of rodents are related to activation of the endogenous
opioid system. Phytother Res. 27:1564–1571. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shan CY, Yang JH, Kong Y, Wang XY, Zheng
MY, Xu YG, Wang Y, Ren HZ, Chang BC and Chen LM: Alteration of the
intestinal barrier and GLP2 secretion in Berberine-treated type 2
diabetic rats. J Endocrinol. 218:255–262. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kim KA, Gu W, Lee IA, Joh EH and Kim DH:
High fat diet-induced gut microbiota exacerbates inflammation and
obesity in mice via the TLR4 signaling pathway. PLoS One.
7:e477132012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Glass CK and Olefsky JM: Inflammation and
lipid signaling in the etiology of insulin resistance. Cell Metab.
15:635–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki
M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M and
Shimomura I: Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact
on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 114:1752–1761. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shoelson SE, Lee J and Goldfine AB:
Inflammation and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 116:1793–1801.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Shoelson SE, Herrero L and Naaz A:
Obesity, inflammation and insulin resistance. Gastroenterology.
132:2169–2180. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jeong HW, Hsu KC, Lee JW, Ham M, Huh JY,
Shin HJ, Kim WS and Kim JB: Berberine suppresses proinflammatory
responses through AMPK activation in macrophages. Am J Physiol
Endocrinol Metab. 296:E955–E964. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Everard A and Cani PD: Diabetes, obesity
and gut microbiota. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 27:73–83.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Amasheh M, Fromm A, Krug SM, Amasheh S,
Andres S, Zeitz M, Fromm M and Schulzke JD: TNFalpha-induced and
berberine-antagonized tight junction barrier impairment via
tyrosine kinase, Akt and NFkappaB signaling. J Cell Sci.
123:4145–4155. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ma JY, Feng R, Tan XS, Ma C, Shou JW, Fu
J, Huang M, He CY, Chen SN, Zhao ZX, et al: Excretion of berberine
and its metabolites in oral administration in rats. J Pharm Sci.
102:4181–4192. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yu LC, Wang JT, Wei SC and Ni YH:
Host-microbial interactions and regulation of intestinal epithelial
barrier function: From physiology to pathology. World J
Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 3:27–43. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Greiner T and Bäckhed F: Effects of the
gut microbiota on obesity and glucose homeostasis. Trends
Endocrinol Metab. 22:117–123. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ichikawa H and Sakata T: Stimulation of
epithelial cell proliferation of isolated distal colon of rats by
continuous colonic infusion of ammonia or short-chain fatty acids
is nonadditive. J Nutr. 128:843–847. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Peng L, Li ZR, Green RS, Holzman IR and
Lin J: Butyrate enhances the intestinal barrier by facilitating
tight junction assembly via activation of AMP-activated protein
kinase in Caco-2 cell monolayers. J Nutr. 139:1619–1625. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lam Y, Ha CW, Campbell CR, Mitchell AJ,
Dinudom A, Oscarsson J, Cook DI, Hunt NH, Caterson ID, Holmes AJ,
et al: Increased gut permeability and microbiota change associate
with mesenteric fat inflammation and metabolic dysfunction in
diet-induced obese mice. PLoS One. 7:e342332012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Everard A, Belzer C, Geurts L, Ouwerkerk
JP, Druart C, Bindels LB, Guiot Y, Derrien M, Muccioli GG, Delzenne
NM, et al: Cross-talk between Akkermansia muciniphila and
intestinal epithelium controls diet-induced obesity. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 110:9066–9071. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Anhê FF, Roy D, Pilon G, Dudonné S,
Matamoros S, Varin TV, Garofalo C, Moine Q, Desjardins Y, Levy E,
et al: A polyphenol-rich cranberry extract protects from
diet-induced obesity, insulin resistance and intestinal
inflammation in association with increased Akkermansia spp.
population in the gut microbiota of mice. Gut. 64:872–883. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Cani PD, Everard A and Duparc T: Gut
microbiota, enteroendocrine functions and metabolism. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 13:935–940. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Everard A, Lazarevic V, Derrien M, Girard
M, Muccioli GG, Neyrinck AM, Possemiers S, Van Holle A, François P,
de Vos WM, et al: Responses of gut microbiota and glucose and lipid
metabolism to prebiotics in genetic obese and diet-induced
leptin-resistant mice. Diabetes. 60:2775–2786. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Hansen KB, Rosenkilde MM, Knop FK, Wellner
N, Diep TA, Rehfeld JF, Andersen UB, Holst JJ and Hansen HS:
2-Oleoyl glycerol is a GPR119 agonist and signals GLP-1 release in
humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 96:E1409–E1417. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|