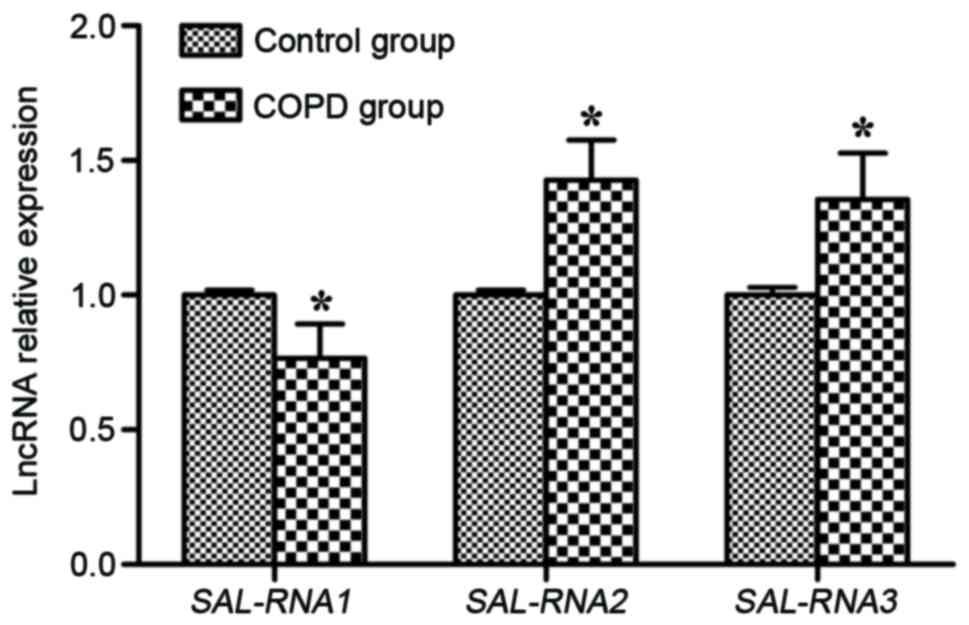
|
1
|
Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive
Lung Disease: Global strategy for the diagnosis, management and
prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Seattle: GOLD;
http://www.goldcopd.com/2015
|
|
2
|
Tsuji T, Aoshiba K and Nagai A: Alveolar
cell senescence exacerbates pulmonary inflammation in patients with
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respiration. 80:59–70. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Siganaki M, Koutsopoulos AV, Neofytou E,
Vlachaki E, Psarrou M, Soulitzis N, Pentilas N, Schiza S, Siafakas
NM and Tzortzaki EG: Deregulation of apoptosis mediators' p53 and
bcl2 in lung tissue of COPD patients. Respir Res. 11:462010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhao CZ, Fang XC, Wang D, Tang FD and Wang
XD: Involvement of type II pneumocytes in the pathogenesis of
chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Respir Med. 104:1391–1395.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Whitsett JA, Wert SE and Weaver TE:
Alveolar surfactant homeostasis and the pathogenesis of pulmonary
disease. Annu Rev Med. 61:105–119. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hoffman AM and Ingenito EP: Alveolar
epithelial stem and progenitor cells: Emerging evidence for their
role in lung regeneration. Curr Med Chem. 19:6003–6008. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Xu W, Yan J, Xia Y, Gu C, Ma Y and
Tao H: Differentiation of human amniotic fluid-derived mesenchymal
stem cells into type II alveolar epithelial cells in vitro. Int J
Mol Med. 33:1507–1513. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Li Y, Gu C, Xu W, Yan J, Xia Y, Ma Y, Chen
C, He X and Tao H: Therapeutic effects of amniotic fluid-derived
mesenchymal stromal cells on lung injury in rats with emphysema.
Respir Res. 15:1202014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Milne JC and Denu JM: The sirtuin family:
Therapeutic targets to treat diseases of aging. Curr Opin Chem
Biol. 12:11–17. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bordo D: Structure and evolution of human
sirtuins. Curr Drug Targets. 14:662–665. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lavu S, Boss O, Elliott PJ and Lambert PD:
Sirtuins--novel therapeutic targets to treat age-associated
diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 7:841–853. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Finkel T, Deng CX and Mostoslavsky R:
Recent progress in the biology and physiology of sirtuins. Nature.
460:587–591. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Satoh A, Stein L and Imai S: The role of
mammalian sirtuins in the regulation of metabolism, aging and
longevity. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 206:125–162. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guterres FA, Martinez GR, Rocha ME and
Winnischofer SM: Simvastatin rises reactive oxygen species levels
and induces senescence in human melanoma cells by activation of
p53/p21 pathway. Exp Cell Res. 319:2977–2988. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kung JT, Colognori D and Lee JT: Long
noncoding RNAs: Past, present and future. Genetics. 193:651–669.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Batista PJ and Chang HY: Long noncoding
RNAs: Cellular address codes in development and disease. Cell.
152:1298–1307. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ohsawa R, Seol JH and Tyler JK: At the
intersection of non-coding transcription, DNA repair, chromatin
structure and cellular senescence. Front Genet. 4:1362013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: Insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Abdelmohsen K, Panda A, Kang MJ, Xu J,
Selimyan R, Yoon JH, Martindale JL, De S, Wood WH III, Becker KG
and Gorospe M: Senescence-associated lncRNAs: Senescence-associated
long noncoding RNAs. Aging Cell. 12:890–900. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Miller MR, Hankinson J, Brusasco V, Burgos
F, Casaburi R, Coates A, Crapo R, Enright P, van der Grinten CP,
Gustafsson P, et al: Standardisation of spirometry. Eur Respir J.
26:319–338. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Caito S, Rajendrasozhan S, Cook S, Chung
S, Yao H, Friedman AE, Brookes PS and Rahman I: SIRT1 is a
redox-sensitive deacetylase that is post-translationally modified
by oxidants and carbonyl stress. FASEB J. 24:3145–3159. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Farkas L, Farkas D, Warburton D, Gauldie
J, Shi W, Stampfli MR, Voelkel NF and Kolb M: Cigarette smoke
exposure aggravates air space enlargement and alveolar cell
apoptosis in Smad3 knockout mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol
Physiol. 301:L391–L401. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Mimae T, Hagiyama M, Inoue T, Yoneshige A,
Kato T, Okada M, Murakami Y and Ito A: Increased ectodomain
shedding of lung epithelial cell adhesion molecule 1 as a cause of
increased alveolar cell apoptosis in emphysema. Thorax. 69:223–231.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gary RK and Kindell SM: Quantitative assay
of senescence-associated beta-galactosidase activity in mammalian
cell extracts. Anal Biochem. 343:329–334. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hara H, Araya J, Takasaka N, Fujii S,
Kojima J, Yumino Y, Shimizu K, Ishikawa T, Numata T, Kawaishi M, et
al: Involvement of creatine kinase B in cigarette smoke-induced
bronchial epithelial cell senescence. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
46:306–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rajendrasozhan S, Yang SR, Kinnula VL and
Rahman I: SIRT1, an antiinflammatory and antiaging protein, is
decreased in lungs of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary
disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 177:861–870. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nakamaru Y, Vuppusetty C, Wada H, Milne
JC, Ito M, Rossios C, Elliot M, Hogg J, Kharitonov S, Goto H, et
al: A protein deacetylase SIRT1 is a negative regulator of
metalloproteinase-9. FASEB J. 23:2810–2819. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gu C, Li Y, Xu WL, Yan JP, Xia YJ, Ma YY,
Chen C, Wang HJ and Tao HQ: Sirtuin 1 activator SRT1720 protects
against lung injury via reduction of type II alveolar epithelial
cells apoptosis in emphysema. COPD. 12:444–452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Yao H, Chung S, Hwang JW, Rajendrasozhan
S, Sundar IK, Dean DA, McBurney MW, Guarente L, Gu W, Rönty M, et
al: SIRT1 protects against emphysema via FOXO3-mediated reduction
of premature senescence in mice. J Clin Invest. 122:2032–2045.
2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Arunachalam G, Samuel SM, Marei I, Ding H
and Triggle CR: Metformin modulates hyperglycaemia-induced
endothelial senescence and apoptosis through SIRT1. Br J Pharmacol.
171:523–535. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ganesan S, Unger BL, Comstock AT, Angel
KA, Mancuso P, Martinez FJ and Sajjan US: Aberrantly activated EGFR
contributes to enhanced IL-8 expression in COPD airways epithelial
cells via regulation of nuclear FoxO3A. Thorax. 68:131–141. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Furukawa A, Tada-Oikawa S, Kawanishi S and
Oikawa S: H2O2 accelerates cellular senescence by accumulation of
acetylated p53 via decrease in the function of SIRT1 by
NAD+ depletion. Cell Physiol Biochem. 20:45–54. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Faghihi MA, Modarresi F, Khalil AM, Wood
DE, Sahagan BG, Morgan TE, Finch CE, St Laurent G III, Kenny PJ and
Wahlestedt C: Expression of a noncoding RNA is elevated in
Alzheimer's disease and drives rapid feed-forward regulation of
beta-secretase. Nat Med. 14:723–730. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Visel A, Zhu Y, May D, Afzal V, Gong E,
Attanasio C, Blow MJ, Cohen JC, Rubin EM and Pennacchio LA:
Targeted deletion of the 9p21 non-coding coronary artery disease
risk interval in mice. Nature. 464:409–412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Chung S, Nakagawa H, Uemura M, Piao L,
Ashikawa K, Hosono N, Takata R, Akamatsu S, Kawaguchi T, Morizono
T, et al: Association of a novel long non-coding RNA in 8q24 with
prostate cancer susceptibility. Cancer Sci. 102:245–252. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Schmidt LH, Spieker T, Koschmieder S,
Schäffers S, Humberg J, Jungen D, Bulk E, Hascher A, Wittmer D,
Marra A, et al: The long noncoding MALAT-1 RNA indicates a poor
prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer and induces migration and
tumor growth. J Thorac Oncol. 6:1984–1992. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|