|
1
|
Chin-Chan M, Navarro-Yepes J and
Quintanilla-Vega B: Environmental pollutants as risk factors for
neurodegenerative disorders: alzheimer and Parkinson diseases.
Front Cell Neurosci. 9:1242015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Fuqua BK, Vulpe CD and Anderson GJ:
Intestinal iron absorption. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 26:115–119.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Schneider SA, Hardy J and Bhatia KP:
Syndromes of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA):
an update on clinical presentations, histological and genetic
underpinnings, and treatment considerations. Mov Disord. 27:42–53.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Smith MA, Zhu X, Tabaton M, Liu G, McKeel
DW Jr, Cohen ML, Wang X, Siedlak SL, Dwyer BE, Hayashi T, et al:
Increased iron and free radical generation in preclinical alzheimer
disease and mild cognitive impairment. J Alzheimers Dis.
19:363–372. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kasarskis EJ, Tandon L, Lovell MA and
Ehmann WD: Aluminum, calcium, and iron in the spinal cord of
patients with sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis using laser
microprobe mass spectroscopy: a preliminary study. J Neurol Sci.
130:203–208. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Dexter DT, Wells FR, Agid F, Agid Y, Lees
AJ, Jenner P and Marsden CD: Increased nigral iron content in
postmortem Parkinsonian brain. Lancet. 2:1219–1220. 1987.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ward RJ, Zucca FA, Duyn JH, Crichton RR
and Zecca L: The role of iron in brain ageing and neurodegenerative
disorders. Lancet Neurol. 13:1045–1060. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jellinger KA: The relevance of metals in
the pathophysiology of neurodegeneration, pathological
considerations. Int Rev Neurobiol. 110:1–47. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hegde ML, Shanmugavelu P, Vengamma B, Rao
TS, Menon RB, Rao RV and Rao KS: Serum trace element levels and the
complexity of inter-element relations in patients with Parkinsons
disease. J Trace Elem Med Biol. 18:163–171. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Fukushima T, Tan X, Luo Y and Kanda H:
Relationship between blood levels of heavy metals and Parkinsons
disease in China. Neuroepidemiology. 34:18–24. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
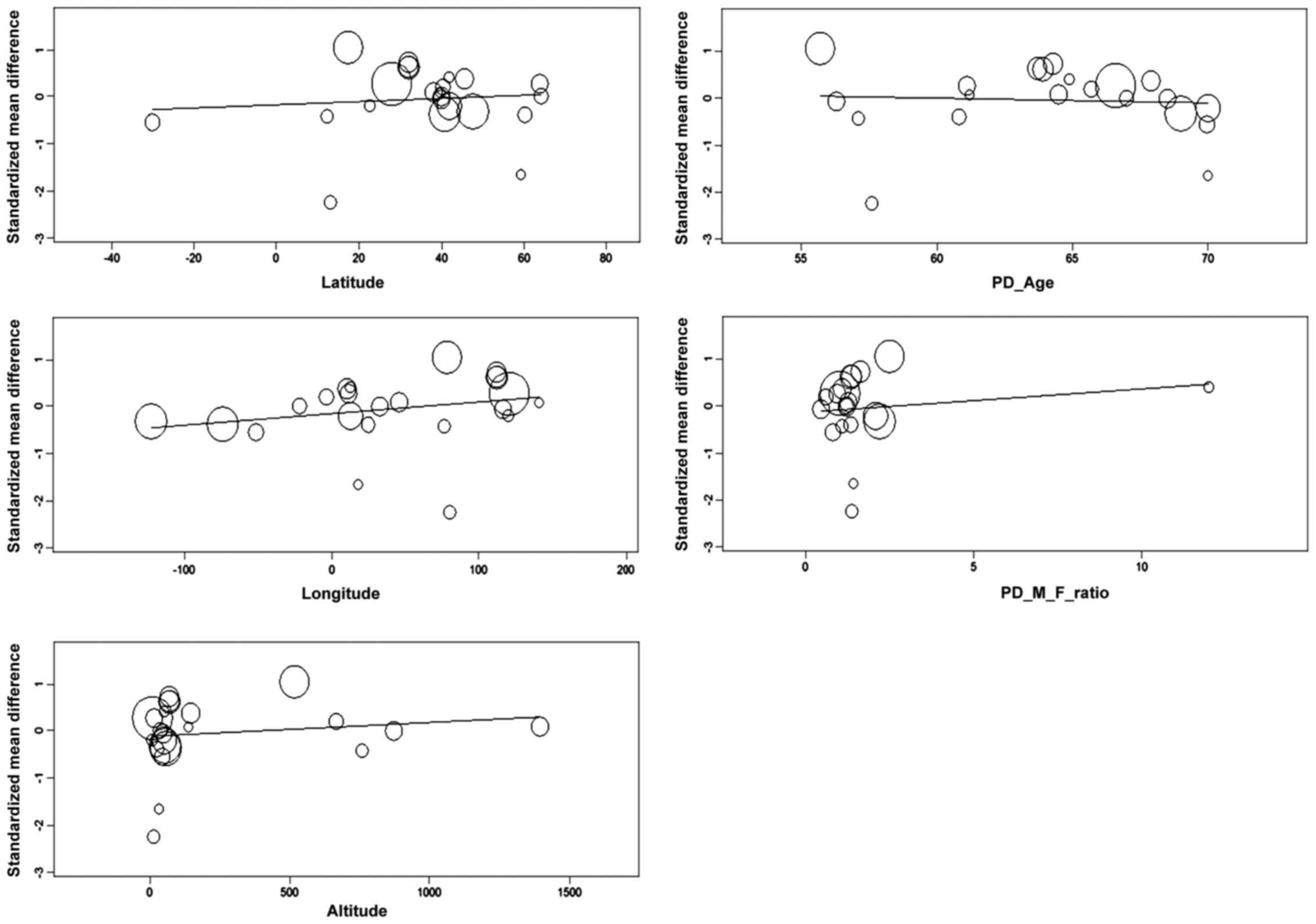
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ and
Altman DG: Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ.
327:557–560. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kirkwood BR and Sterne JAC: Essential
Medical Statistics. 2nd. Blackwell Publishing; Oxford: 2003
|
|
13
|
Rosenthal R: The ‘file drawer problem’ and
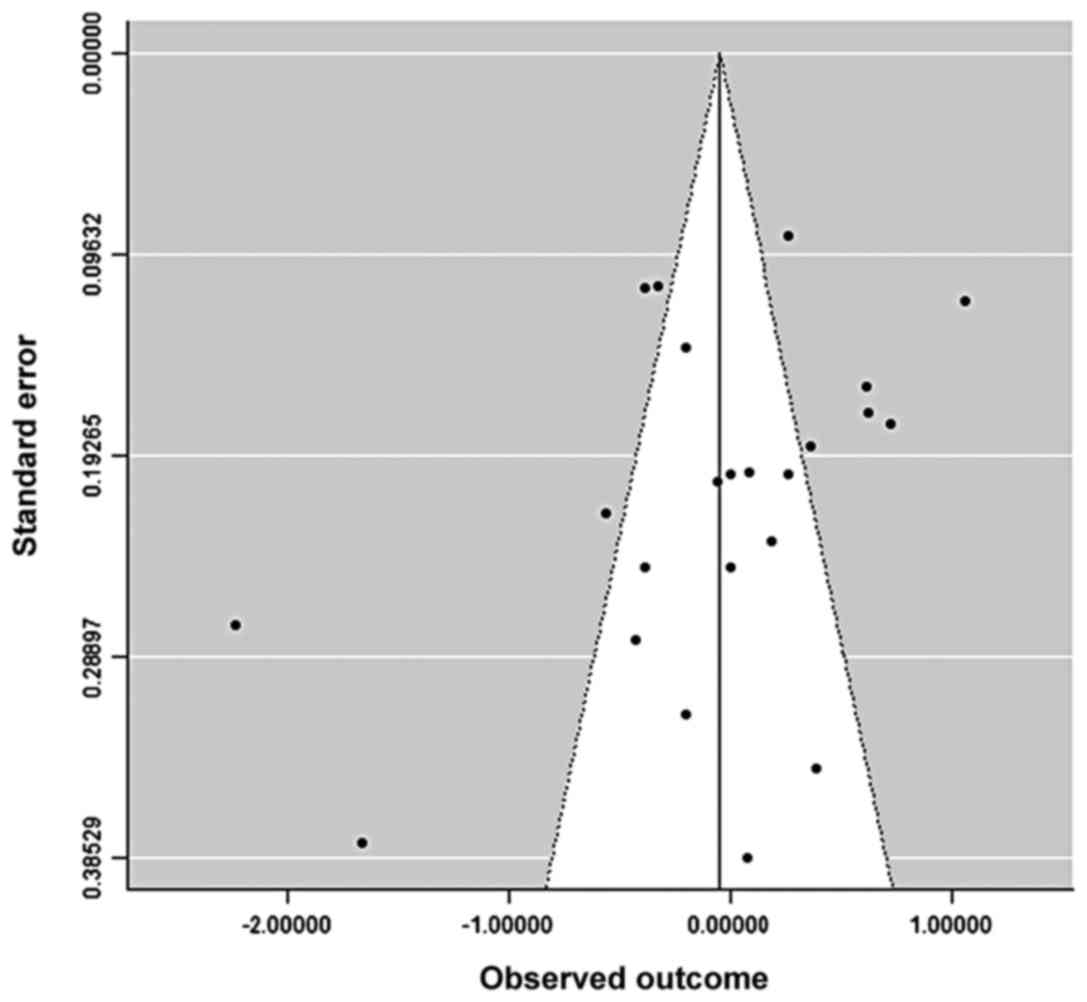
tolerance for null results. Psychol Bull. 86:638–641. 1979.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT and
Rothstein HR: Introduction to Meta-Analysis. Wiley; Chichester, UK:
2009, View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hughes AJ, Daniel SE, Kilford L and Lees
AJ: Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinsons
disease: a clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J Neurol
Neurosurg Psychiatry. 55:181–184. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hoehn MM and Yahr MD: Parkinsonism: onset,
progression and mortality. Neurology. 17:427–442. 1967. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fahn S and Elton RL: Unified Parkinsons
disease rating scaleRecent Developments in Parkinsons Disease. Fahn
S, Marsden CD, Calne DB and Goldstein M: 2. Macmillan; Florham
Park, NJ: pp. 153–163. 1987
|
|
18
|
Mariani S, Ventriglia M, Simonelli I,
Donno S, Bucossi S, Vernieri F, Melgari JM, Pasqualetti P, Rossini
PM and Squitti R: Fe and Cu do not differ in Parkinsons disease: a
replication study plus meta-analysis. Neurobiol Aging. 34:632–633.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiao J, Guo H, He Y, Wang J, Yuan J and Hu
W: Meta-analysis of the association between serum iron levels and
Parkinson's disease: evidence from 11 publications. Brain Res.
1646:490–493. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sahin C, Pala C, Kaynar L, Torun YA, Cetin
A, Kurnaz F, Sivgin S and Sahin FS: Measurement of hair iron
concentration as a marker of body iron content. Biomed Rep.
3:383–387. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
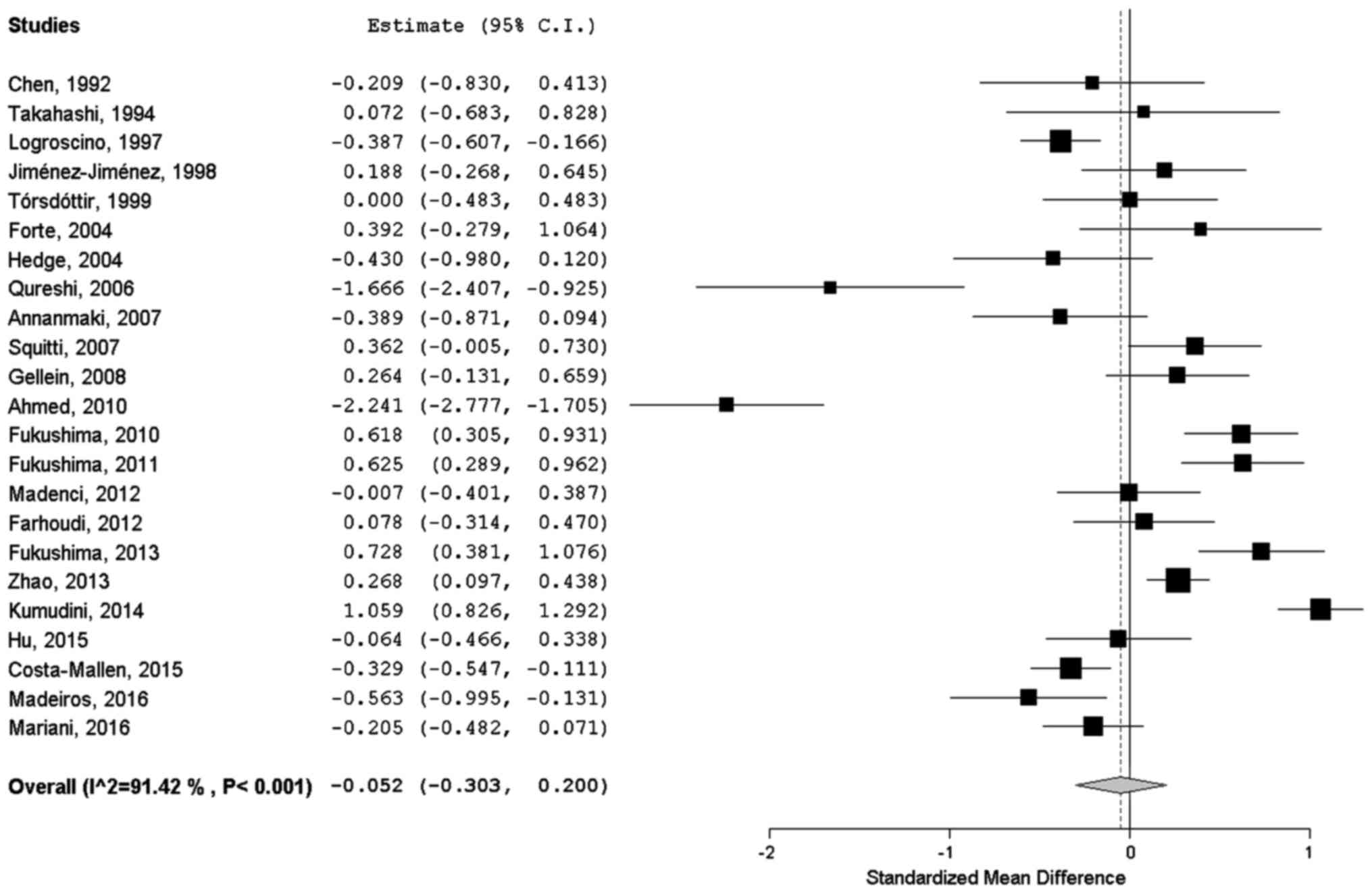
Chen WH and Shih PY: The serum
ferrokinetics in Parkinsons disease. Gaoxiong Yi Xue Ke Xue Za Zhi.
8:581–584. 1992.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Takahashi S, Takahashi J, Osawa N, Abe T,
Yonezawa H, Sera K and Tohgi H: Trace elements analysis of serum
and cerebrospinal fluid with PIXE-effect of age and changes in
Parkinsonian patients. Nippon Ronen Igakkai Zasshi. 31:865–871.
1994.(In Japanese). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Logroscino G, Marder K, Graziano J, Freyer
G, Slavkovich V, LoIacono N, Cote L and Mayeux R: Altered systemic
iron metabolism in Parkinsons disease. Neurology. 49:714–717. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiménez-Jiménez FJ, Molina JA, Aguilar MV,
Meseguer I, Mateos-Vega CJ, González-Muñoz MJ, de Bustos F,
Martínez-Salio A, Ortí-Pareja M, Zurdo M, et al: Cerebrospinal
fluid levels of transition metals in patients with Parkinsons
disease. J Neural Transm Vienna. 105:497–505. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tórsdóttir G, Kristinsson J,
Sveinbjörnsdóttir S, Snaedal J and Jóhannesson T: Copper,
ceruloplasmin, superoxide dismutase and iron parameters in
Parkinsons disease. Pharmacol Toxicol. 85:239–243. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Forte G, Bocca B, Senofonte O, Petrucci F,
Brusa L, Stanzione P, Zannino S, Violante N, Alimonti A and
Sancesario G: Trace and major elements in whole blood, serum,
cerebrospinal fluid and urine of patients with Parkinsons disease.
J Neural Transm Vienna. 111:1031–1040. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qureshi GA, Qureshi AA, Memon SA and
Parvez SH: Impact of selenium, iron, copper and zinc in on/off
Parkinson's patients on L-dopa therapy. J Neural Transm (Suppl).
71:229–236. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Annanmaki T, Muuronen A and Murros K: Low
plasma uric acid level in Parkinsons disease. Mov Disord.
22:1133–1137. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Squitti R, Gorgone G, Binetti G, Ghidoni
R, Pasqualetti P, Draicchio F, Albini E, Benedetti L, Lucchini R
and Rossini PM: Metals and oxidative stress in Parkinsons disease
from industrial areas with exposition to environmental toxins or
metal pollution. G Ital Med Lav Ergon. 29:(Suppl 3). 294–296.
2007.(In Italian). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gellein K, Syversen T, Steinnes E, Nilsen
TI, Dahl OP, Mitrovic S, Duraj D and Flaten TP: Trace elements in
serum from patients with Parkinsons disease: a prospective
case-control study: the Nord-Trøndelag health study (HUNT). Brain
Res. 1219:111–115. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ahmed SS and Santosh W: Metallomic
profiling and linkage map analysis of early Parkinsons disease: a
new insight to aluminum marker for the possible diagnosis. PLoS
One. 5:e112522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fukushima T, Tan X, Luo Y and Kanda H:
Serum vitamins and heavy metals in blood and urine, and the
correlations among them in Parkinsons disease patients in China.
Neuroepidemiology. 36:240–244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Madenci G, Bilen S, Arli B, Saka M and Ak
F: Serum iron, vitamin B12 and folic acid levels in Parkinson's
disease. Neurochem Res. 37:1436–1441. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Farhoudi M, Taheraghdam A, Farid GA,
Talebi M, Pashapou A, Majidi J and Goldust M: Serum iron and
ferritin level in idiopathic Parkinson. Pak J Biol Sci.
15:1094–1097. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Fukushima T, Tan X, Luo Y, Wang P, Song J,
Kanda H, Hayakawa T, Kumagai T, Kakamu T, Tsuji M, et al: Heavy
metals in blood and urine and its relation to depressive symptoms
in Parkinsons disease patients. Fukushima J Med Sci. 59:76–80.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zhao HW, Lin J, Wang XB, Cheng X, Wang JY,
Hu BL, Zhang Y, Zhang X and Zhu JH: Assessing plasma levels of
selenium, copper, iron and zinc in patients of Parkinsons disease.
PLoS One. 8:e830602013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kumudini N, Uma A, Devi YP, Naushad SM,
Mridula R, Borgohain R and Kutala VK: Association of Parkinsons
disease with altered serum levels of lead and transition metals
among south Indian subjects. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 51:121–126.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hu Y, Yu SY, Zuo LJ, Piao YS, Cao CJ, Wang
F, Chen ZJ, Du Y, Lian TH, Liu GF, et al: Investigation on abnormal
iron metabolism and related inflammation in Parkinson disease
patients with probable RBD. PLoS One. 10:e01389972015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Costa-Mallen P, Zabetian CP, Agarwal P, Hu
SC, Yearout D, Samii A, Leverenz JB, Roberts JW and Checkoway H:
Haptoglobin phenotype modifies serum iron levels and the effect of
smoking on Parkinson disease risk. Parkinsonism Relat Disord.
21:1087–1092. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Medeiros MS, Schumacher-Schuh A, Cardoso
AM, Bochi GV, Baldissarelli J, Kegler A, Santana D, Chaves CM,
Schetinger MR, Moresco RN, et al: Iron and oxidative stress in
Parkinsons disease: an observational study of injury biomarkers.
PLoS One. 11:e01461292016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mariani S, Ventriglia M, Simonelli I,
Bucossi S, Siotto M, Donno S, Vernieri F and Squitti R: Association
between sex, systemic iron variation and probability of Parkinsons
disease. Int J Neurosci. 126:354–360. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|