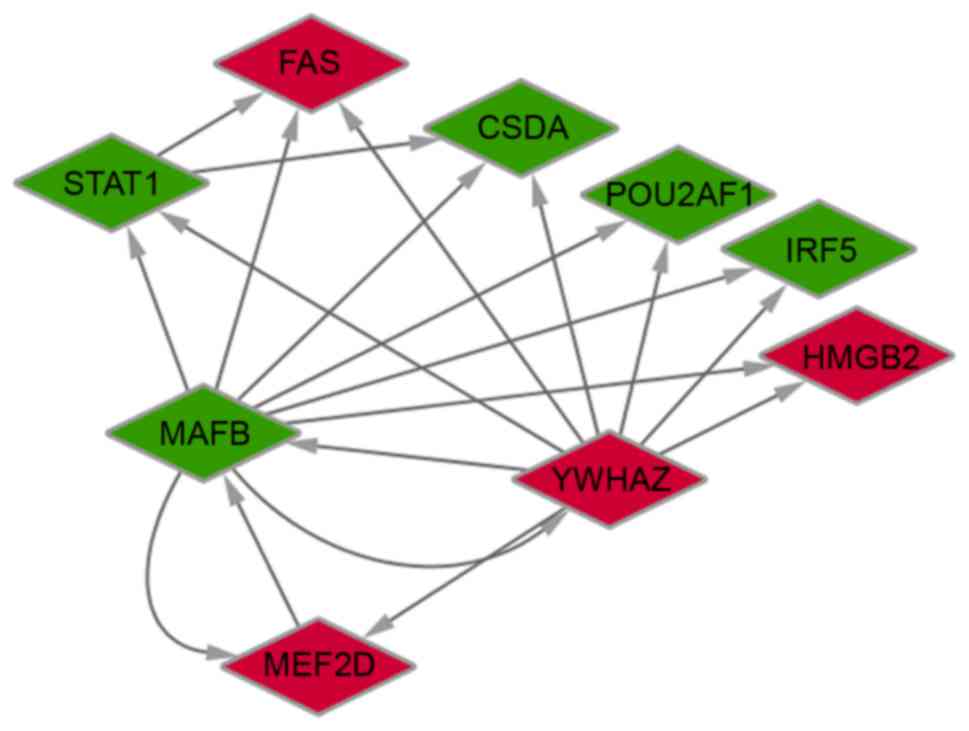
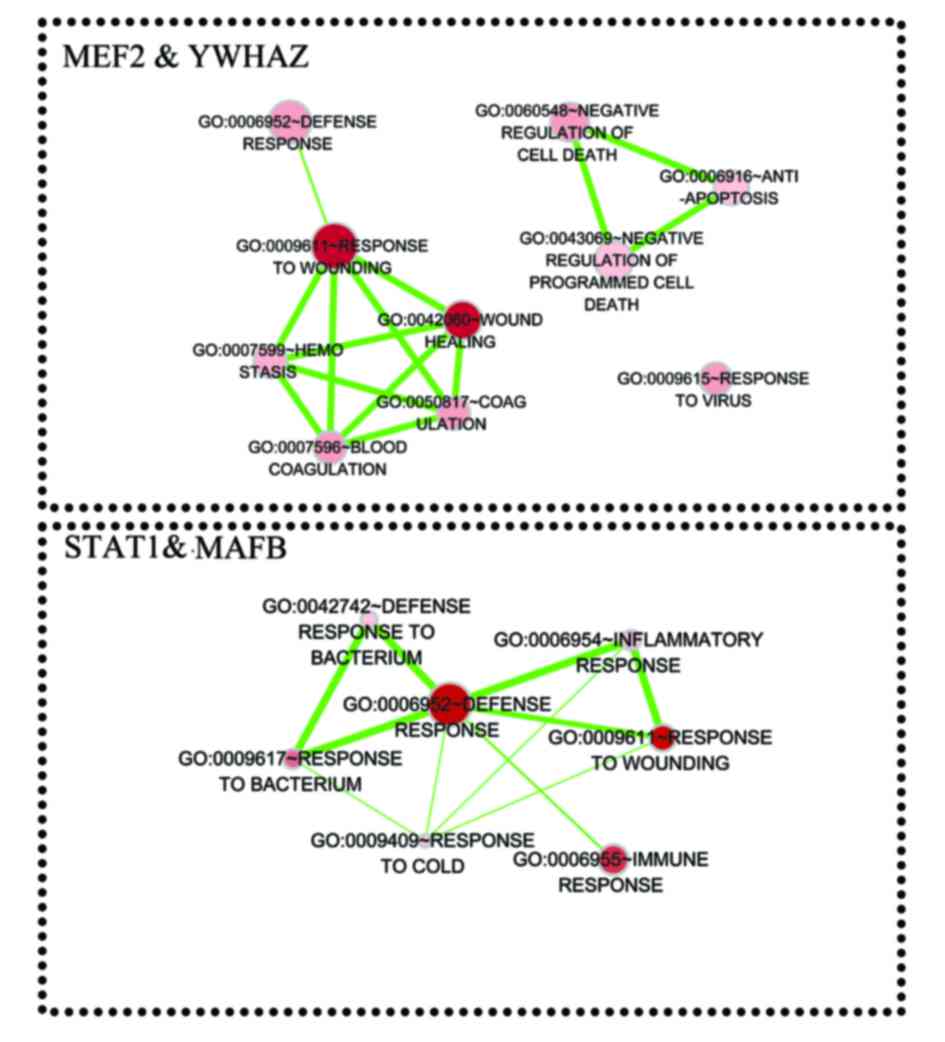
|
1
|
de Souza AWS: Autoantibodies in systemic
vasculitis. Front Immunol. 6:1842015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Stagnaro C, Cioffi E, Talarico R and Rossa
A Della: Systemic vasculitides: A critical digest of the most
recent literature. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 33(2 Suppl 89): S145–S154.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, Basu N,
Cid MC, Ferrario F, Flores-Suarez LF, Gross WL, Guillevin L, Hagen
EC, et al: 2012 revised international chapel hill consensus
conference nomenclature of vasculitides. Arthritis Rheumatism.
65:1–11. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Yang JJ, Preston GA, Alcorta DA, Waga I,
Munger WE, Hogan SL, Sekura SB, Phillips BD, Thomas RP, Jennette JC
and Falk RJ: Expression profile of leukocyte genes activated by
anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies (ANCA). Kidney Int.
62:1638–1649. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wagner EF: Bone development and
inflammatory disease is regulated by AP-1 (Fos/Jun). Annals Rheum
Dis. 69:i86–i88. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Ordonez L, Bernard I, L'Faqihi-Olive FE,
Tervaert JW, Damoiseaux J and Saoudi A: CD45RC isoform expression
identifies functionally distinct T cell subsets differentially
distributed between healthy individuals and AAV patients. PLoS One.
4:e52872009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kobayashi S, Ito A, Okuzaki D, Onda H,
Yabuta N, Nagamori I, Suzuki K, Hashimoto H and Nojima H:
Expression profiling of PBMC-based diagnostic gene markers isolated
from vasculitis patients. DNA Res. 15:253–265. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Okuzaki D, Fukushima T, Tougan T, Ishii T,
Kobayashi S, Yoshizaki K, Akita T and Nojima H: Genopal™: A novel
hollow fibre array for focused microarray analysis. DNA Res.
17:369–379. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Simon R, Lam A, Li MC, Ngan M, Menenzes S
and Zhao Y: Analysis of gene expression data using BRB-array tools.
Cancer Inform. 3:11–17. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhao Y and Simon R: BRB-ArrayTools Data
Archive for human cancer gene expression: A unique and efficient
data sharing resource. Cancer Inform. 6:9–15. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ihaka R and Gentleman R: R: A language for
data analysis and graphics. J Computational and graphical
statistics. 5:299–314. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Yu G, Wang LG, Han Y and He QY:
ClusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among
gene clusters. Omics. 16:284–287. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Reiner-Benaim A: FDR control by the BH
procedure for Two-Sided Correlated Tests with implications to gene
expression Data Analysis. Biom J. 49:107–126. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Benjamini Y and Hochberg Y: Controlling
the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to
multiple testing. J Royal Statistical Soc. 57:289–300. 1995.
|
|
15
|
Franceschini A, Szklarczyk D, Frankild S,
Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Roth A, Lin J, Minguez P, Bork P, von Mering C
and Jensen LJ: STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks,
with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res.
41:D808–D815. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu J and Finley RL: Combining multiple
positive training sets to generate confidence scores for
protein-protein interactions. Bioinformatics. 25:105–111. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS,
Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B and Ideker T: Cytoscape: A
software environment for integrated models of biomolecular
interaction networks. Genome Res. 13:2498–2504. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Csardi G and Nepusz T: The igraph software
package for complex network research. Inter Journal Complex
Systems. 1695:1–9. 2006.
|
|
19
|
Wu G, Dawson E, Duong A, Haw R and Stein
L: ReactomeFIViz: A Cytoscape app for pathway and network-based
data analysis. F1000Res. 3:1462014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tan PK, Downey TJ, Spitznagel EL Jr, Xu P,
Fu D, Dimitrov DS, Lempicki RA, Raaka BM and Cam MC: Evaluation of
gene expression measurements from commercial microarray platforms.
Nucleic Acids Res. 31:5676–5684. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Van Dongen SM: Graph clustering by flow
simulation. 2001.
|
|
22
|
Huang ZX, Tian HY, Hu ZF, Zhou YB, Zhao J
and Yao KT: GenCLiP: A software program for clustering gene lists
by literature profiling and constructing gene co-occurrence
networks related to custom keywords. BMC bioinformatics. 9:3082008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Matys V, Fricke E, Geffers R, Gössling E,
Haubrock M, Hehl R, Hornischer K, Karas D, Kel AE, Kel-Margoulis
OV, et al: TRANSFAC: Transcriptional regulation, from patterns to
profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:374–378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Song KH, Kim YH and Kim BY: Sho-saiko-to,
a traditional herbal medicine, regulates gene expression and
biological function by way of microRNAs in primary mouse
hepatocytes. BMC Complement Altern Med. 14:142014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Nicolle R, Radvanyi F and Elati M:
CoRegNet: Reconstruction and integrated analysis of co-regulatory
networks. Bioinformatics. 31:3066–3068. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kawai T, Sato S, Ishii KJ, Coban C, Hemmi
H, Yamamoto M, Terai K, Matsuda M, Inoue J, Uematsu S, et al:
Interferon-alpha induction through Toll-like receptors involves a
direct interaction of IRF7 with MyD88 and TRAF6. Nat Immunol.
5:1061–1068. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Dillon S, Agrawal A, Van Dyke T, Landreth
G, McCauley L, Koh A, Maliszewski C, Akira S and Pulendran B: A
Toll-like receptor 2 ligand stimulates Th2 responses in vivo, via
induction of extracellular signal-regulated kinase
mitogen-activated protein kinase and c-Fos in dendritic cells. J
Immunol. 172:4733–4743. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wagner EF and Eferl R: Fos/AP-1 proteins
in bone and the immune system. Immunol Rev. 208:126–140. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Tadema H, Abdulahad WH, Stegeman CA,
Kallenberg CG and Heeringa P: Increased expression of Toll-like
receptors by monocytes and natural killer cells in ANCA-associated
vasculitis. PLoS One. 6:e243152011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oh C, Park S, Lee EK and Yoo YJ:
Downregulation of ubiquitin level via knockdown of polyubiquitin
gene Ubb as potential cancer therapeutic intervention. Sci Rep.
3:26232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Le Bras S, Loyer N and Le Borgne R: The
multiple facets of ubiquitination in the regulation of notch
signaling pathway. Traffic. 12:149–161. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Piggott K, Deng J, Warrington K, Younge B,
Kubo JT, Desai M, Goronzy JJ and Weyand CM: Blocking the NOTCH
pathway inhibits vascular inflammation in large-vessel
vasculitisclinical perspective. Circulation. 123:309–318. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Verhelst J, Parthoens E, Schepens B, Fiers
W and Saelens X: Interferon-inducible protein Mx1 inhibits
influenza virus by interfering with functional viral
ribonucleoprotein complex assembly. J Virol. 86:13445–13455. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Vassilopoulos D and Calabrese LH:
Hepatitis C virus infection and vasculitis: Implications of
antiviral and immunosuppressive therapies. Arthritis Rheum.
46:585–597. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ramana CV, Chatterjee-Kishore M, Nguyen H
and Stark GR: Complex roles of Stat1 in regulating gene expression.
Oncogene. 19:2619–2627. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kawazoe Y, Naka T, Fujimoto M, Kohzaki H,
Morita Y, Narazaki M, Okumura K, Saitoh H, Nakagawa R, Uchiyama Y,
et al: Signal transducer and activator of transcription
(STAT)-induced STAT inhibitor 1 (SSI-1)/suppressor of cytokine
signaling 1 (SOCS1) inhibits insulin signal transduction pathway
through modulating insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1)
phosphorylation. J Exp Med. 193:263–270. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Klampfer L: Signal transducers and
activators of transcription (STATs): Novel targets of
chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic drugs. Curr Cancer Drug
Targets. 6:107–121. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Lin W, Choe WH, Hiasa Y, Kamegaya Y,
Blackard JT, Schmidt EV and Chung RT: Hepatitis C virus expression
suppresses interferon signaling by degrading STAT1.
Gastroenterology. 128:1034–1041. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chan AT, Flossmann O, Mukhtyar C, Jayne D
and Luqmani RA: The role of biologic therapies in the management of
systemic vasculitis. Autoimmu Rev. 5:273–278. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Aida Y, Sato-Nishiwaki M, Abe S, Kishi H,
Nunomiya K, Yamauchi K, lnoue S and Shibata Y: MafB suppresses
acute inflammatory responses in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated lung
injury in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 185:A13402012.
|
|
41
|
Nishimura Y, Komatsu S, Ichikawa D, Nagata
H, Hirajima S, Takeshita H, Kawaguchi T, Arita T, Konishi H,
Kashimoto K, et al: Overexpression of YWHAZ relates to tumor cell
proliferation and malignant outcome of gastric carcinoma. Br J
Cancer. 108:1324–1331. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kaganoi J, Watanabe G, Okabe M, Nagatani
S, Kawabe A, Shimada Y, Imamura M and Sakai Y: STAT1
activation-induced apoptosis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
cells in vivo. Ann Surg Oncol. 14:1405–1415. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Jamin C, Duguuguabe G, Okabe M, et al:
STAT1 activation-induced apoptosis of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma cells in vivo. Annals of Surgical Oncology. 14:1405–1415.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|