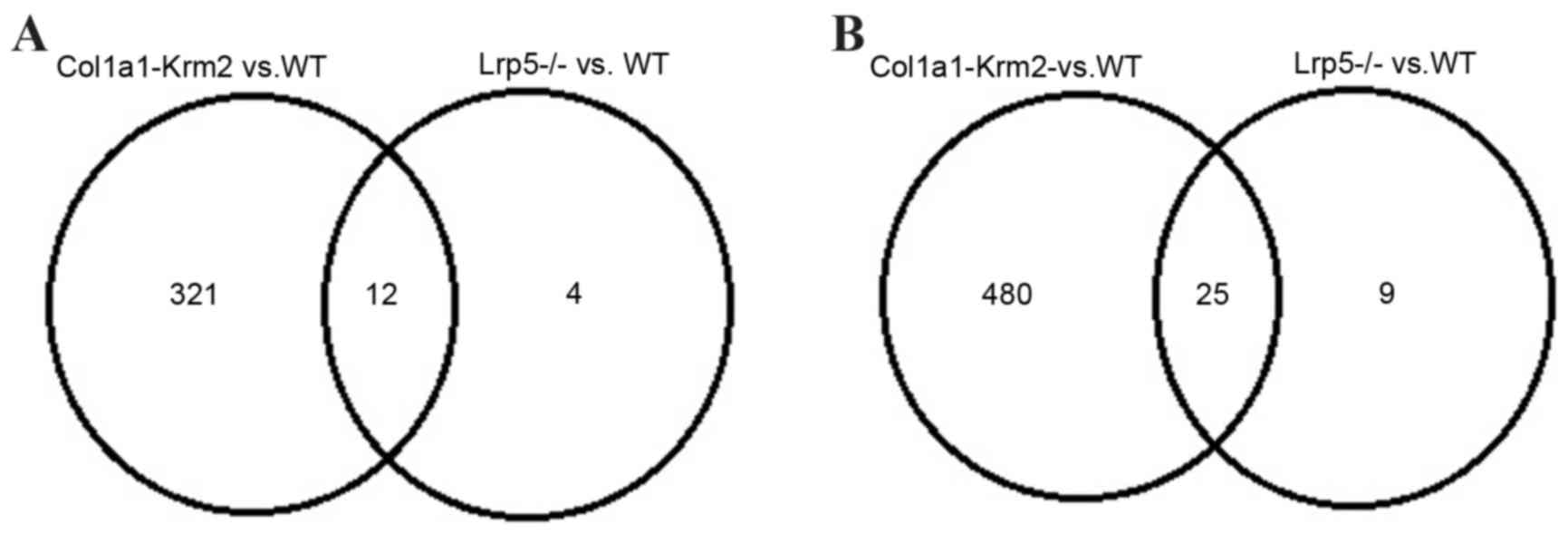
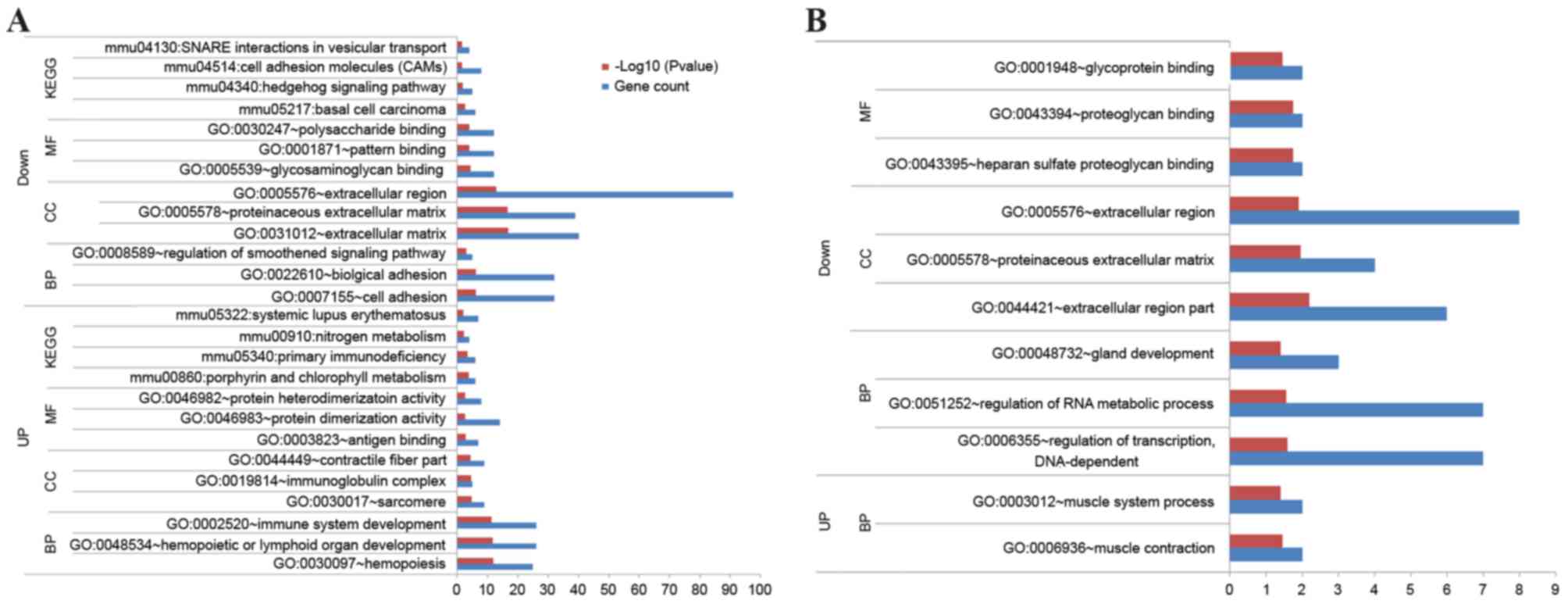
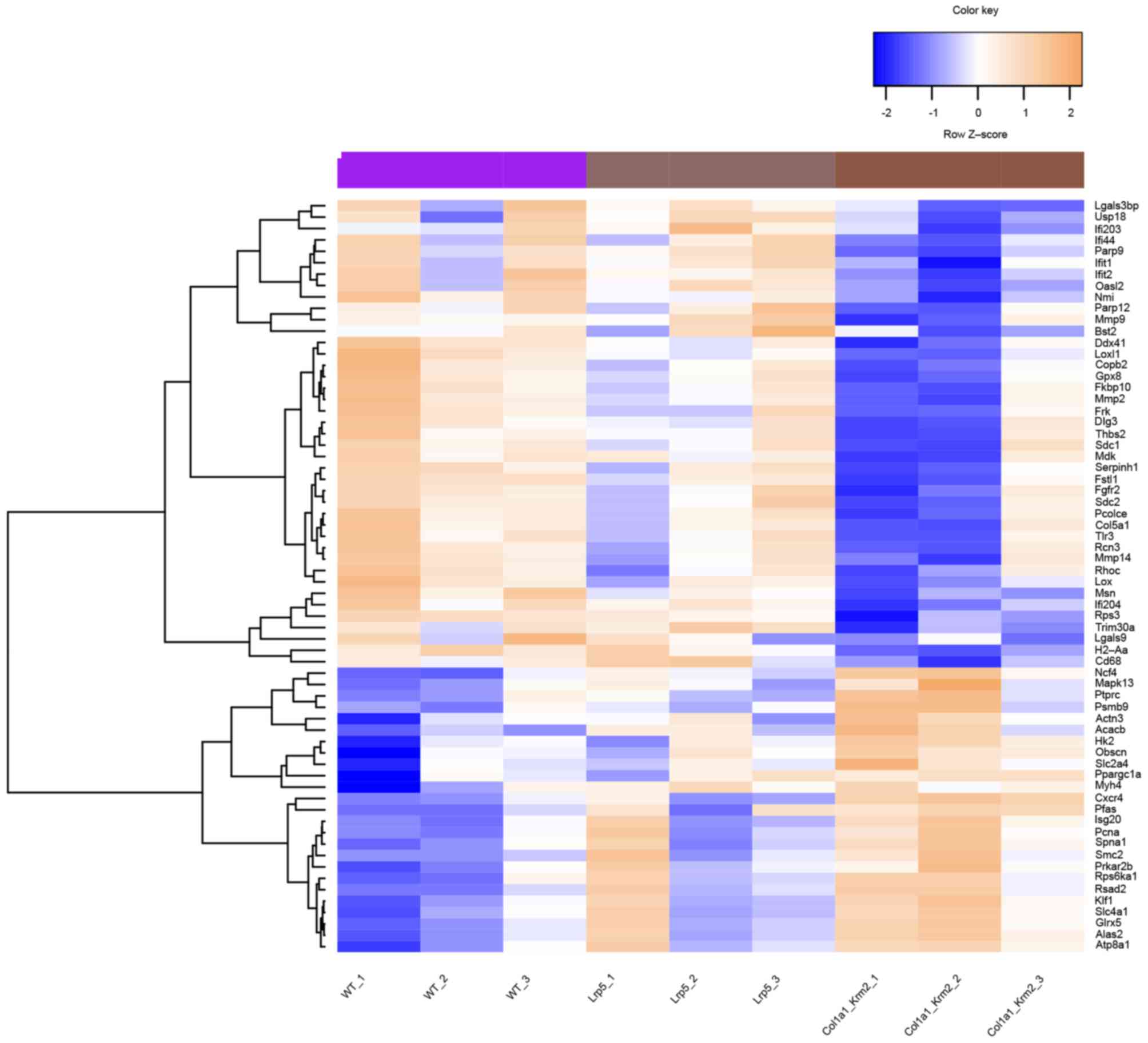
|
1
|
Namkung-Matthai H, Appleyard R, Jansen J,
Hao Lin J, Maastricht S, Swain M, Mason RS, Murrell GA, Diwan AD
and Diamond T: Osteoporosis influences the early period of fracture
healing in a rat osteoporotic model. Bone. 28:80–86. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Johnell O and Kanis JA: An estimate of the
worldwide prevalence and disability associated with osteoporotic
fractures. Osteoporos Int. 17:1726–1733. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Egermann M, Baltzer AW, Adamaszek S, Evans
C, Robbins P, Schneider E and Lill CA: Direct adenoviral transfer
of bone morphogenetic protein-2 cDNA enhances fracture healing in
osteoporotic sheep. Hum Gene Ther. 17:507–517. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Noordin S and Glowacki J: Parathyroid
hormone and its receptor gene polymorphisms: Implications in
osteoporosis and in fracture healing. Rheumatol Int. 36:1–6. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Mizuguchi T, Furuta I, Watanabe Y,
Tsukamoto K, Tomita H, Tsujihata M, Ohta T, Kishino T, Matsumoto N,
Minakami H, et al: LRP5, low-density-lipoprotein-receptor-related
protein 5, is a determinant for bone mineral density. J Hum Genet.
49:80–86. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Kato M, Patel MS, Levasseur R, Lobov I,
Chang BH, Glass DA II, Hartmann C, Li L, Hwang TH, Brayton CF, et
al: Cbfa1-independent decrease in osteoblast proliferation,
osteopenia, and persistent embryonic eye vascularization in mice
deficient in Lrp5, a Wnt coreceptor. J Cell Biol. 157:303–314.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Mao B, Wu W, Davidson G, Marhold J, Li M,
Mechler BM, Delius H, Hoppe D, Stannek P, Walter C, et al: Kremen
proteins are Dickkopf receptors that regulate Wnt/beta-catenin
signalling. Nature. 417:664–667. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Schulze J, Seitz S, Saito H, Schneebauer
M, Marshall RP, Baranowsky A, Busse B, Schilling AF, Friedrich FW,
Albers J, et al: Negative regulation of bone formation by the
transmembrane Wnt antagonist Kremen-2. PLoS One. 5:e103092010.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
9
|
Liedert A, Röntgen V, Schinke T, Benisch
P, Ebert R, Jakob F, Klein-Hitpass L, Lennerz JK, Amling M and
Ignatius A: Osteoblast-specific Krm2 overexpression and Lrp5
deficiency have different effects on fracture healing in mice. PLoS
One. 9:e1032502014. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Gautier L, Cope L, Bolstad BM and Irizarry
RA: affy-analysis of Affymetrix GeneChip data at the probe level.
Bioinformatics. 20:307–315. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Carlson M: org.Hs.eg.db: Genome wide
annotation for Human. R package version 3.4.0. 2015.
|
|
12
|
Dunning M, Lynch A and Eldridge M:
illuminaHumanv3.db: Illumina HumanHT12v3 annotation data (chip
illuminaHumanv3). R package version 1.26.0. 2015.
|
|
13
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43:e472015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
14
|
Glueck DH, Mandel J, Karimpour-Fard A,
Hunter L and Muller KE: Exact calculations of average power for the
Benjamini-Hochberg procedure. Int J Biostat. 4:Article 112008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Oliveros JC: VENNY. An interactive tool
for comparing lists with Venn Diagrams. 2007, http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.htmlNovember
20–2013
|
|
16
|
Huang DW, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR,
Alvord WG, Roayaei J, Stephens R, Baseler MW, Lane HC and Lempicki
RA: The DAVID gene functional classification tool: A novel
biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large
gene lists. Genome Biol. 8:R1832007. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S,
Forslund K, Heller D, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Roth A, Santos
A, Tsafou KP, et al: STRING v10: Protein-protein interaction
networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(Database issue): D447–D452. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Kohl M, Wiese S and Warscheid B:
Cytoscape: Software for visualization and analysis of biological
networks. Methods Mol Biol. 696:291–303. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Jeong H, Mason SP, Barabási AL and Oltvai
ZN: Lethality and centrality in protein networks. Nature.
411:41–42. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Goh KI, Oh E, Kahng B and Kim D:
Betweenness centrality correlation in social networks. Phys Rev E
Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 67:0171012003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Estrada E and Rodriguez-Velázquez JA:
Subgraph centrality in complex networks. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin
Soft Matter Phys. 71:0561032005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Tang Y, Li M, Wang J, Pan Y and Wu FX:
CytoNCA: A cytoscape plugin for centrality analysis and evaluation
of protein interaction networks. Biosystems. 127:67–72. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Suzuki R and Shimodaira H: Pvclust: An R
package for assessing the uncertainty in hierarchical clustering.
Bioinformatics. 22:1540–1542. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Adler J and Parmryd I: Quantifying
colocalization by correlation: The Pearson correlation coefficient
is superior to the Mander's overlap coefficient. Cytometry A.
77:733–742. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
LaBell TL, Milewicz DJ, Disteche CM and
Byers PH: Thrombospondin II: Partial cDNA sequence, chromosome
location, and expression of a second member of the thrombospondin
gene family in humans. Genomics. 12:421–429. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Alford AI and Hankenson KD: Matricellular
proteins: Extracellular modulators of bone development, remodeling,
and regeneration. Bone. 38:749–757. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Hankenson KD, Bain SD, Kyriakides TR,
Smith EA, Goldstein SA and Bornstein P: Increased marrow-derived
osteoprogenitor cells and endosteal bone formation in mice lacking
thrombospondin 2. J Bone Miner Res. 15:851–862. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Delany AM and Hankenson KD:
Thrombospondin-2 and SPARC/osteonectin are critical regulators of
bone remodeling. J Cell Commun Signal. 3:227–238. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
29
|
Ishikawa-Brush Y, Powell JF, Bolton P,
Miller AP, Francis F, Willard HF, Lehrach H and Monaco AP: Autism
and multiple exostoses associated with an X;8 translocation
occurring within the GRPR gene and 3′ to the SDC2 gene. Hum Mol
Genet. 6:1241–1250. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Modrowski D, Baslé M, Lomri A and Marie
PJ: Syndecan-2 is involved in the mitogenic activity and signaling
of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor in osteoblasts.
J Biol Chem. 275:9178–9185. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ishikawa Y, Vranka J, Wirz J, Nagata K and
Bächinger HP: The rough endoplasmic reticulum-resident
FK506-binding protein FKBP65 is a molecular chaperone that
interacts with collagens. J Biol Chem. 283:31584–31590. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Venturi G, Monti E, Carbonare L Dalle,
Corradi M, Gandini A, Valenti MT, Boner A and Antoniazzi F: A novel
splicing mutation in FKBP10 causing osteogenesis imperfecta with a
possible mineralization defect. Bone. 50:343–349. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Schwarze U, Cundy T, Pyott SM,
Christiansen HE, Hegde MR, Bank RA, Pals G, Ankala A, Conneely K,
Seaver L, et al: Mutations in FKBP10, which result in Bruck
syndrome and recessive forms of osteogenesis imperfecta, inhibit
the hydroxylation of telopeptide lysines in bone collagen. Hum Mol
Genet. 22:1–17. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wathelet MG, Clauss IM, Content J and Huez
GA: The IFI-56K and IFI-54K interferon-inducible human genes belong
to the same gene family. FEBS Lett. 231:164–171. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
McDermott JE, Vartanian KB, Mitchell H,
Stevens SL, Sanfilippo A and Stenzel-Poore MP: Identification and
validation of Ifit1 as an important innate immune bottleneck. PLoS
One. 7:e364652012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
36
|
Woeckel VJ, Eijken M, van de Peppel J,
Chiba H, van der Eerden BC and van Leeuwen JP: IFNβ impairs
extracellular matrix formation leading to inhibition of
mineralization by effects in the early stage of human osteoblast
differentiation. J Cell Physiol. 227:2668–2676. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Perwitasari O, Cho H, Diamond MS and Gale
M Jr: Inhibitor of κB kinase epsilon (IKK(epsilon)), STAT1, and
IFIT2 proteins define novel innate immune effector pathway against
West Nile virus infection. J Biol Chem. 286:44412–44423. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
38
|
Zhu J, Ghosh A and Sarkar SN: OASL-a new
player in controlling antiviral innate immunity. Curr Opin Virol.
12:15–19. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|