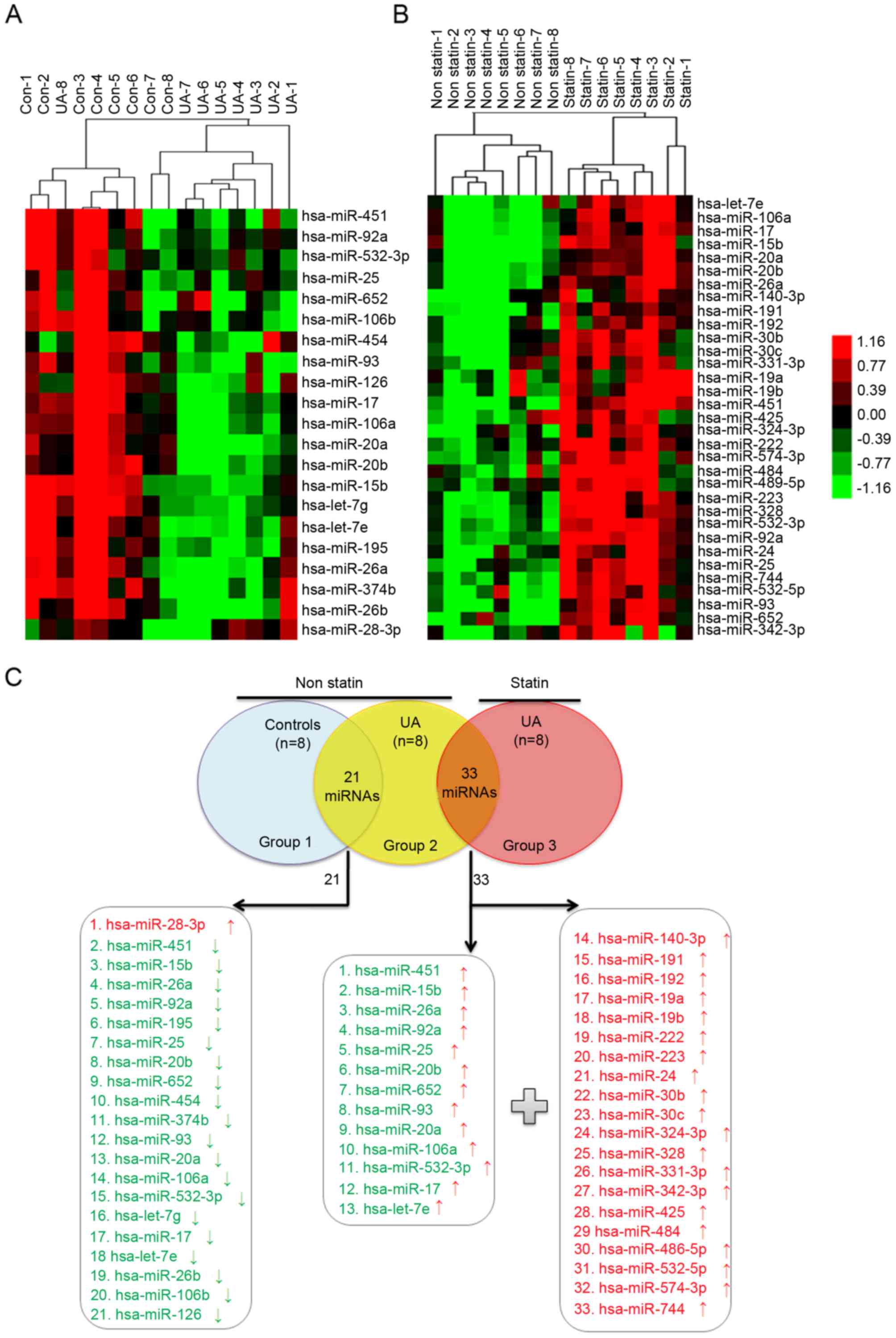
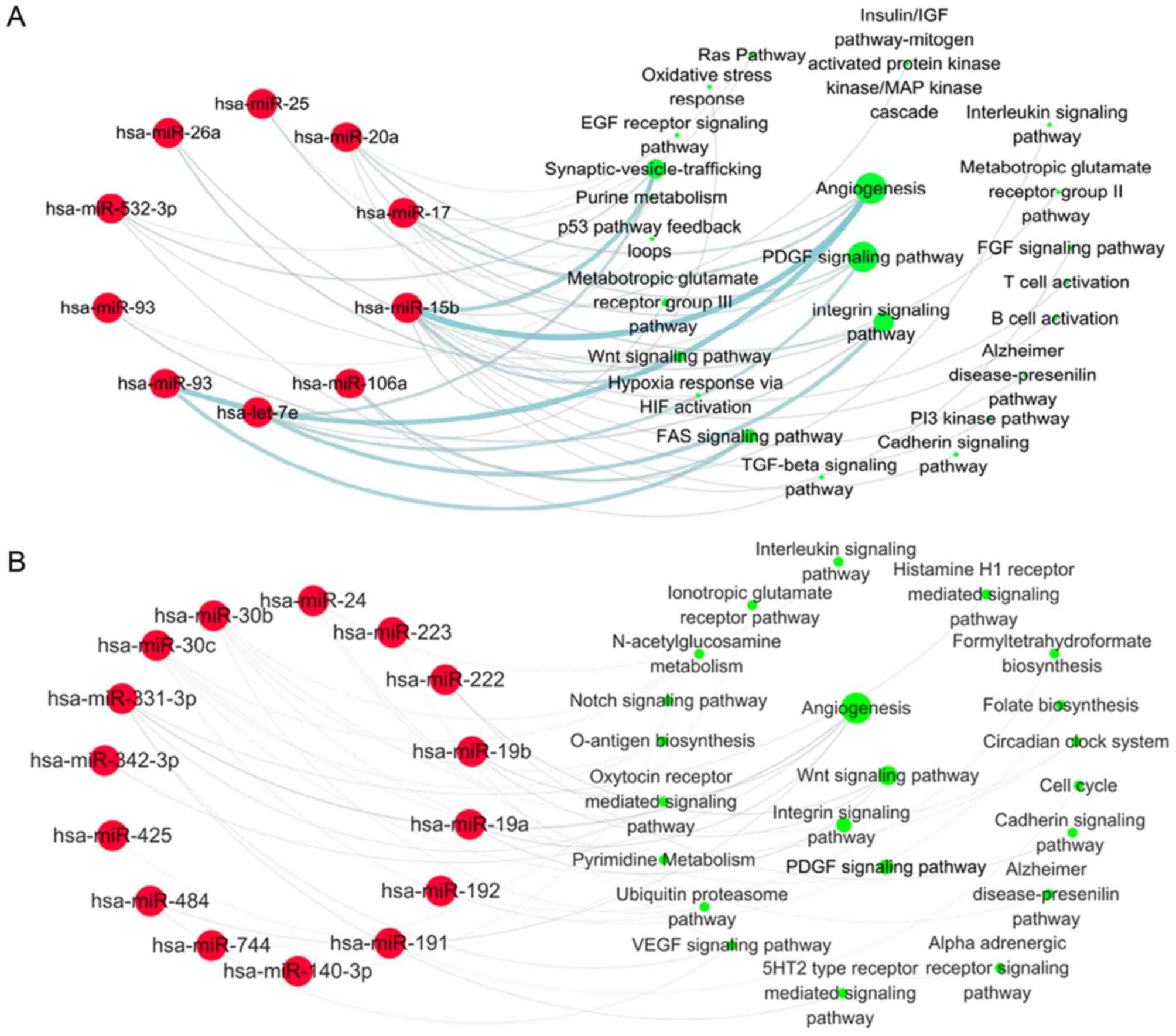
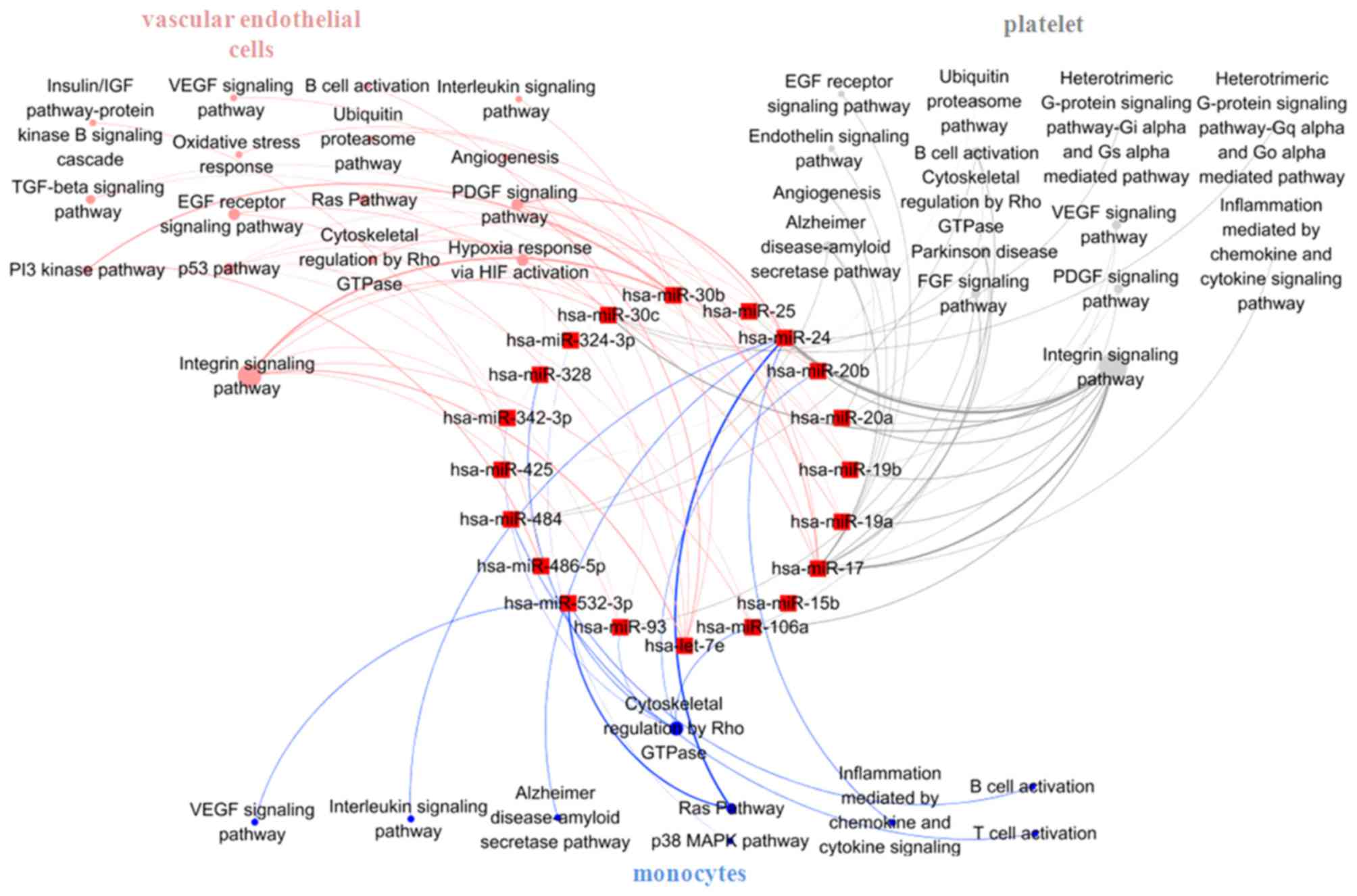
|
1
|
Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA,
Butler J, Dracup K, Ezekowitz MD, Finkelstein EA, Hong Y, Johnston
SC, Khera A, et al: Forecasting the future of cardiovascular
disease in the United States: A policy statement from the American
Heart Association. Circulation. 123:933–944. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
LaRosa JC, Grundy SM, Waters DD, Shear C,
Barter P, Fruchart JC, Gotto AM, Greten H, Kastelein JJ, Shepherd
J, et al: Treating to New Targets (TNT) Investigators: Intensive
lipid lowering with atorvastatin in patients with stable coronary
disease. N Engl J Med. 352:1425–1435. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cannon CP, Braunwald E, McCabe CH, Rader
DJ, Rouleau JL, Belder R, Joyal SV, Hill KA, Pfeffer MA and Skene
AM: Pravastatin or Atorvastatin Evaluation and Infection
Therapy-Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction 22 Investigators:
Intensive versus moderate lipid lowering with statins after acute
coronary syndromes. N Engl J Med. 350:1495–1504. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Schwartz GG, Olsson AG, Ezekowitz MD, Ganz
P, Oliver MF, Waters D, Zeiher A, Chaitman BR, Leslie S and Stern
T: Myocardial Ischemia Reduction with Aggressive Cholesterol
Lowering (MIRACL) Study Investigators: Effects of atorvastatin on
early recurrent ischemic events in acute coronary syndromes: The
MIRACL study: A randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 285:1711–1718.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wright RS, Anderson JL, Adams CD, Bridges
CR, Casey DE Jr, Ettinger SM, Fesmire FM, Ganiats TG, Jneid H,
Lincoff AM, et al: 2011 ACCF/AHA focused update incorporated into
the ACC/AHA 2007 Guidelines for the Management of Patients with
Unstable Angina/Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction: A report of
the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart
Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines developed in
collaboration with the American Academy of Family Physicians,
Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and the
Society of Thoracic Surgeons. J Am Coll Cardiol. 57:e215–e367.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ray KK and Cannon CP: The potential
relevance of the multiple lipid-independent (pleiotropic) effects
of statins in the management of acute coronary syndromes. J Am Coll
Cardiol. 46:1425–1433. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Angeli F, Reboldi G, Mazzotta G, Garofoli
M, Cerasa MF and Verdecchia P: Statins in acute coronary syndrome:
Very early initiation and benefits. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis.
6:163–174. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Chen H, Ren JY, Xing Y, Zhang WL, Liu X,
Wu P, Wang RJ and Luo Y: Short-term withdrawal of simvastatin
induces endothelial dysfunction in patients with coronary artery
disease: A dose-response effect dependent on endothelial nitric
oxide synthase. Int J Cardiol. 131:313–320. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Target recognition
and regulatory functions. Cell. 136:215–233. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu N and Olson EN: MicroRNA regulatory
networks in cardiovascular development. Dev Cell. 18:510–525. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ventura A and Jacks T: MicroRNAs and
cancer: Short RNAs go a long way. Cell. 136:586–591. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Jacobsen A, Silber J, Harinath G, Huse JT,
Schultz N and Sander C: Analysis of microRNA-target interactions
across diverse cancer types. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 20:1325–1332.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rottiers V and Näär AM: MicroRNAs in
metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol.
13:239–250. 2012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Price NL, Ramírez CM and
Fernández-Hernando C: Relevance of microRNA in metabolic diseases.
Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci. 51:305–320. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
De Rosa S, Curcio A and Indolfi C:
Emerging role of microRNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Circ J.
78:567–575. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hagiwara S, Kantharidis P and Cooper ME:
MicroRNA as biomarkers and regulator of cardiovascular development
and disease. Curr Pharm Des. 20:2347–2370. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Creemers EE, Tijsen AJ and Pinto YM:
Circulating microRNAs: Novel biomarkers and extracellular
communicators in cardiovascular disease? Circ Res. 110:483–495.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Loyer X, Vion AC, Tedgui A and Boulanger
CM: Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular
diseases. Circ Res. 114:345–353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Tabuchi T, Satoh M, Itoh T and Nakamura M:
MicroRNA-34a regulates the longevity-associated protein SIRT1 in
coronary artery disease: Effect of statins on SIRT1 and
microRNA-34a expression. Clin Sci (Lond). 123:161–171. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Sun HX, Zeng DY, Li RT, Pang RP, Yang H,
Hu YL, Zhang Q, Jiang Y, Huang LY, Tang YB, et al: Essential role
of microRNA-155 in regulating endothelium-dependent vasorelaxation
by targeting endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Hypertension.
60:1407–1414. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Minami Y, Satoh M, Maesawa C, Takahashi Y,
Tabuchi T, Itoh T and Nakamura M: Effect of atorvastatin on
microRNA 221/222 expression in endothelial progenitor cells
obtained from patients with coronary artery disease. Eur J Clin
Invest. 39:359–367. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang Q, Kandic I and Kutryk MJ:
Dysregulation of angiogenesis-related microRNAs in endothelial
progenitor cells from patients with coronary artery disease.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 405:42–46. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Satoh M, Tabuchi T, Minami Y, Takahashi Y,
Itoh T and Nakamura M: Expression of let-7i is associated with
Toll-like receptor 4 signal in coronary artery disease: Effect of
statins on let-7i and Toll-like receptor 4 signal. Immunobiology.
217:533–539. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Leroyer AS, Isobe H, Lesèche G, Castier Y,
Wassef M, Mallat Z, Binder BR, Tedgui A and Boulanger CM: Cellular
origins and thrombogenic activity of microparticles isolated from
human atherosclerotic plaques. J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:772–777. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Qiao Z, Ren J and Chen H: Simvastatin
reduces expression and activity of lipoprotein-associated
phospholipase A(2) in the aorta of hypercholesterolaemic
atherosclerotic rabbits. J Int Med Res. 37:1029–1037. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Chen H, Ikeda U, Shimpo M, Ikeda M, Minota
S and Shimada K: Fluvastatin upregulates inducible nitric oxide
synthase expression in cytokine-stimulated rat vascular smooth
muscle cells. Hypertension. 36:923–928. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Yahagi K, Kolodgie FD, Otsuka F, Finn AV,
Davis HR, Joner M and Virmani R: Pathophysiology of native
coronary, vein graft, and in-stent atherosclerosis. Nat Rev
Cardiol. 13:79–98. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wu G, Cai J, Han Y, Chen J, Huang ZP, Chen
C, Cai Y, Huang H, Yang Y, Liu Y, et al: LincRNA-p21 regulates
neointima formation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation,
apoptosis, and atherosclerosis by enhancing p53 activity.
Circulation. 130:1452–1465. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Sayin VI, Khan OM, Pehlivanoglu LE,
Staffas A, Ibrahim MX, Asplund A, Agren P, Nilton A, Bergström G,
Bergo MO, et al: Loss of one copy of Zfp148 reduces lesional
macrophage proliferation and atherosclerosis in mice by activating
p53. Circ Res. 115:781–789. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Huang CK, Pang H, Wang L, Niu Y, Luo J,
Chang E, Sparks JD, Lee SO and Chang C: New therapy via targeting
androgen receptor in monocytes/macrophages to
battleatherosclerosis. Hypertension. 63:1345–1353. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Karshovska E, Zhao Z, Blanchet X, Schmitt
MM, Bidzhekov K, Soehnlein O, von Hundelshausen P, Mattheij NJ,
Cosemans JM, Megens RT, et al: Hyperreactivity of junctional
adhesion molecule A-deficient platelets acceleratesatherosclerosis
in hyperlipidemic mice. Circ Res. 116:587–599. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ricci C and Ferri N: Naturally occurring
PDGF receptor inhibitors with potential anti-atherosclerotic
properties. Vascul Pharmacol. 70:1–7. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Heldin CH: Targeting the PDGF signaling
pathway in the treatment of non-malignant diseases. J Neuroimmune
Pharmacol. 9:69–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li X, Liu X, Xu Y, He Y, Liu J and Xie M:
Expression profile of apoptotic and proliferative proteins in
hypoxic HUVEC treated with statins. Int J Oncol. 46:677–684.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Araújo FA, Rocha MA, Mendes JB and Andrade
SP: Atorvastatin inhibits inflammatory angiogenesis in mice through
down regulation of VEGF, TNF-alpha and TGF-beta1. Biomed
Pharmacother. 64:29–34. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Massaro M, Zampolli A, Scoditti E,
Carluccio MA, Storelli C, Distante A and De Caterina R: Statins
inhibit cyclooxygenase-2 and matrix metalloproteinase-9 in human
endothelial cells: Anti-angiogenic actions possibly contributing to
plaque stability. Cardiovasc Res. 86:311–320. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Weis M, Heeschen C, Glassford AJ and Cooke
JP: Statins have biphasic effects on angiogenesis. Circulation.
105:739–745. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Weber C, Erl W, Weber KS and Weber PC:
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors decrease CD11b expression and CD11b-
dependent adhesion of monocytes to endothelium and reduce increased
adhesiveness of monocytes isolated from patients with
hypercholesterolemia. J Am Coll Cardiol. 30:1212–1217. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Relja B, Meder F, Wang M, Blaheta R,
Henrich D, Marzi I and Lehnert M: Simvastatin modulates the
adhesion and growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via decrease
of integrin expression and ROCK. Int J Oncol. 38:879–885. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Chen S, Liu B, Kong D, Li S, Li C, Wang H
and Sun Y: Atorvastatin calcium inhibits phenotypic modulation of
PDGF-BB-induced VSMCs via down-regulation the Akt signaling
pathway. PLoS One. 10:e01225772015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Yoshikawa M, Nakamura K, Nagase S,
Sakuragi S, Kusano KF, Matsubara H and Ohe T: Effects of combined
treatment with angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker and statin on
stent restenosis. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 53:179–186. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang D, Yuan J, Liu G, Ling Z, Zeng H,
Chen Y, Zhang Y, She Q and Zhou X: Angiotensin receptor blockers
and statins could alleviate atrial fibrosis via regulating
platelet-derived growth factor/Rac1/nuclear factor-kappa B Axis.
Int J Med Sci. 10:812–824. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Sawada N and Liao JK: Rho/Rho-associated
coiled-coil forming kinase pathway as therapeutic targets for
statins in atherosclerosis. Antioxid Redox Signal. 20:1251–1267.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|