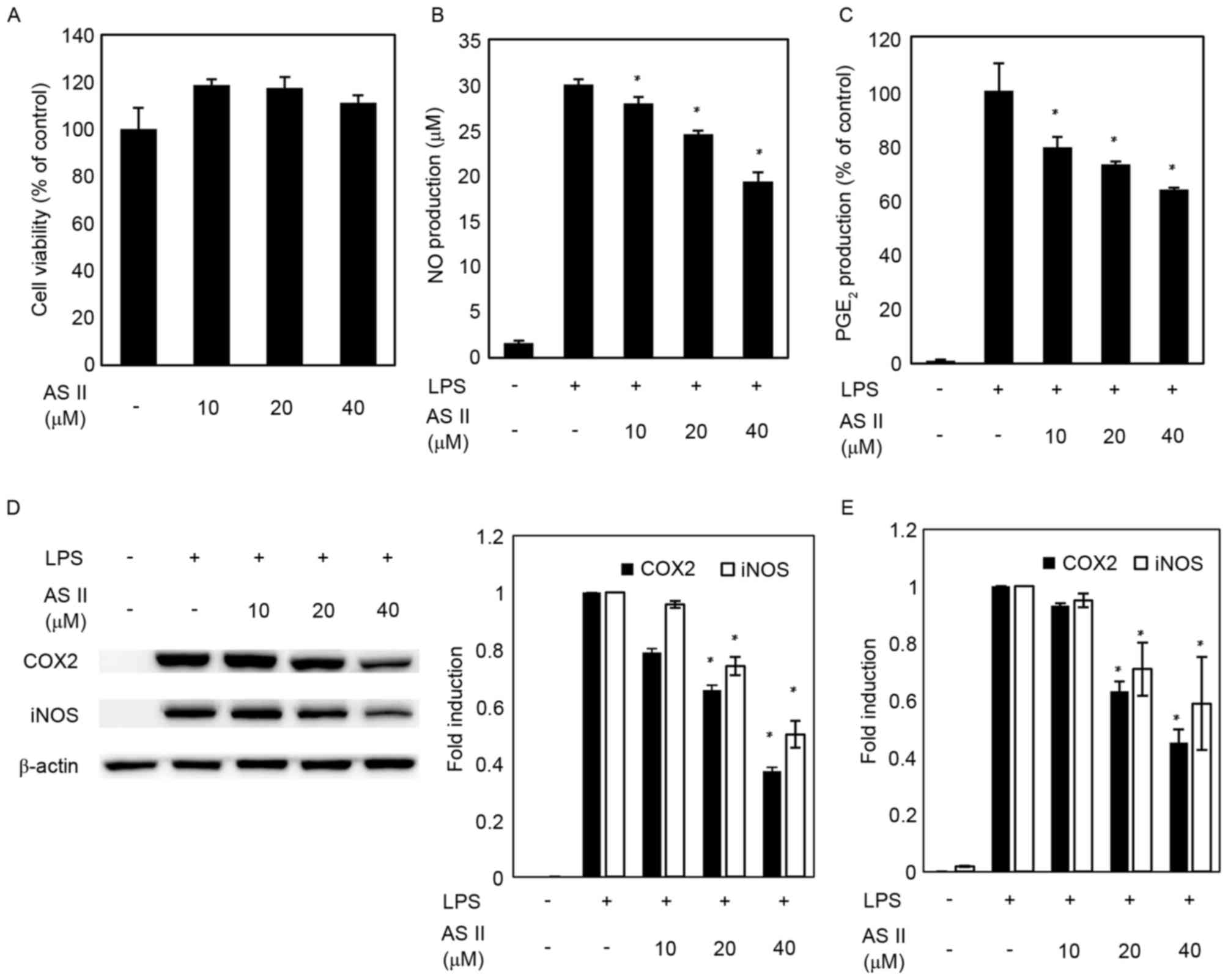
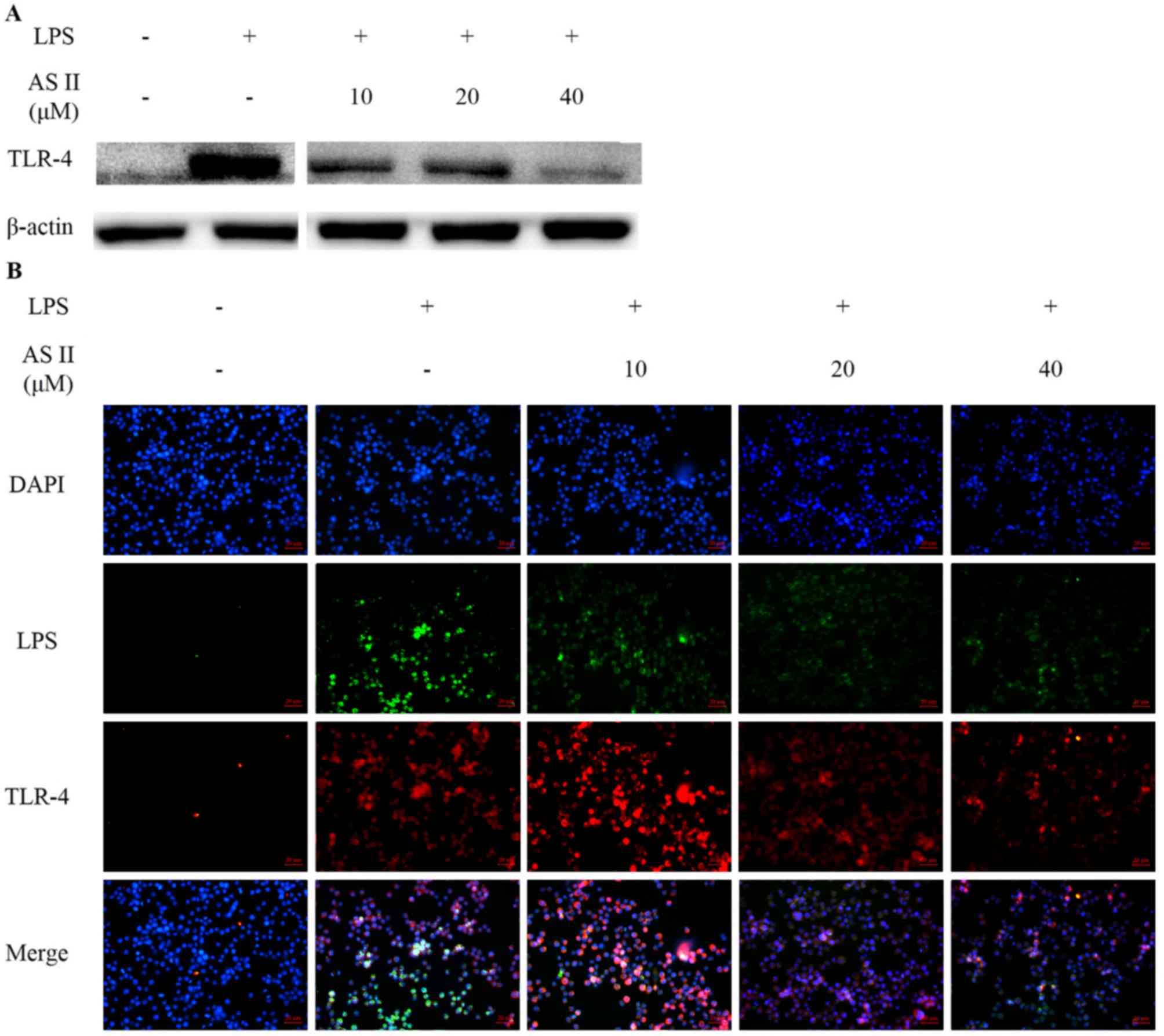
|
1
|
Cho YC, Ju A, Kim BR and Cho S:
Anti-inflammatory effects of Crataeva nurvala Buch. Ham. Are
mediated via inactivation of ERK but not NF-κB. J Ethnopharmacol.
162:140–147. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chawla A, Nguyen KD and Goh YP:
Macrophage-mediated inflammation in metabolic disease. Nat Rev
Immunol. 11:738–749. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jang JC and Nair MG: Alternatively
activated macrophages Revisited: New insights into the regulation
of immunity, inflammation and metabolic function following parasite
infection. Curr Immunol Rev. 9:147–156. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sharma JN, Al-Omran A and Parvathy SS:
Role of nitric oxide in inflammatory diseases.
Inflammopharmacology. 15:252–259. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhou R, Shi X, Gao Y, Cai N, Jiang Z and
Xu X: Anti-inflammatory activity of guluronate oligosaccharides
obtained by oxidative degradation from alginate in
lipopolysaccharide-activated murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. J
Agric Food Chem. 63:160–168. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ci X, Ren R, Xu K, Li H, Yu Q, Song Y,
Wang D, Li R and Deng X: Schisantherin A exhibits anti-inflammatory
properties by down-regulating NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways
in lipopolysaccharide-treated RAW 264.7 cells. Inflammation.
33:126–136. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mi Jeong Sung, Davaatseren M, Kim W, Sung
Kwang Park, Kim SH, Haeng Jeon Hur, Myung Sunny Kim, Kim YS and Dae
Young Kwon: Vitisin A suppresses LPS-induced NO production by
inhibiting ERK, p38, and NF-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells.
Int Immunopharmacol. 9:319–323. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun SC, Chang JH and Jin J: Regulation of
nuclear factor-κB in autoimmunity. Trends Immunol. 34:282–289.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mayne ST: Antioxidant nutrients and
chronic disease: Use of biomarkers of exposure and oxidative stress
status in epidemiologic research. J Nutr. 133:(Suppl 3). 933S–940S.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Gratas-Delamarche A, Derbré F, Vincent S
and Cillard J: Physical inactivity, insulin resistance, and the
oxidative-inflammatory loop. Free Radic Res. 48:93–108. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Golbidi S, Badran M and Laher I:
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of exercise in diabetic
patients. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012:9418682012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kim JH, Liu XQ, Dai L, Yook CS and Lee KT:
Cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory effects of root bark extracts of
Acanthopanax henryi. Chin J Nat Med. 12:121–125. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhang XD, Liu XQ, Kim YH and Whang WK:
Chemical constituents and their acetyl cholinesterase inhibitory
and antioxidant activities from leaves of Acanthopanax
henryi: Potential complementary source against Alzheimer's
disease. Arch Pharm Res. 37:606–616. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim JH, Liu XQ, Dai L, Yook CS and Lee KT:
Cytotoxicity and anti-inflammatory effects of root bark extracts of
Acanthopanax henryi. Chin J Nat Med. 12:121–125. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Miyase T, Shiokawa KI, Zhang DM and Ueno
A: Araliasaponins I–XI, triterpene saponins from the roots of
Aralia descaisneana. Phytochemistry. 41:1411–1418. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shao CJ, Ryoji Kasai, Xu JD and Tanaka O:
Saponins from leaves of Acanthopanax senticosus Harms., Ciwujia:
Structures of Ciwujianosides B, C1, C2, C3, C4, D1, D2 and E. Chem
Pharm Bull. 36:601–608. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang XD, Li Z, Liu GZ, Wang X, Kwon OK,
Lee HK, Whang WK and Liu X: Quantitative determination of 15
bioactive triterpenoid saponins in different parts of
Acanthopanax henryi by HPLC with charged aerosol detection
and confirmation by LC-ESI-TOF-MS. J Sep Sci. 39:2252–2262. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Koike A, Minamiguchi I, Fujimori K and
Amano F: Nitric oxide is an important regulator of heme oxygenase-1
expression in the lipopolysaccharide and interferon-γ-treated
murine macrophage-like cell line J774.1/JA-4. Biol Pharm Bull.
38:7–16. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guzik TJ, Korbut R and Adamek-Guzik T:
Nitric oxide and superoxide in inflammation and immune regulation.
J Physiol Pharmacol. 54:469–487. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Chan AT, Ogino S and Fuchs CS: Aspirin and
the risk of colorectal cancer in relation to the expression of
COX-2. N Engl J Med. 356:2131–2142. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Boscá L, Zeini M, Través PG and Hortelano
S: Nitric oxide and cell viability in inflammatory cells: A role
for NO in macrophage function and fate. Toxicology. 208:249–258.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Guo AK, Hou YY, Hirata H, Yamauchi S, Yip
AK, Chiam KH, Tanaka N, Sawada Y and Kawauchi K: Loss of p53
enhances NF-κB-dependent lamellipodia formation. J Cell Physiol.
229:696–704. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Beg AA, Finco TS, Nantermet PV and Baldwin
AS Jr: Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to
phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: A mechanism for
NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 13:3301–3310. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brown KL, Cosseau C, Gardy JL and Hancock
RE: Complexities of targeting innate immunity to treat infection.
Trends Immunol. 28:260–266. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schröder NW, Opitz B, Lamping N, Michelsen
KS, Zähringer U, Göbel UB and Schumann RR: Involvement of
lipopolysaccharide binding protein, CD14, and Toll-like receptors
in the initiation of innate immune responses by Treponema
glycolipids. J Immunol. 165:2683–2693. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Koo JE, Park ZY, Kim ND and Lee JY:
Sulforaphane inhibits the engagement of LPS with TLR4/MD2 complex
by preferential binding to Cys133 in MD2. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 434:600–605. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Miller SI, Ernst RK and Bader MW: LPS,
TLR4 and infectious disease diversity. Nat Rev Microbiol. 3:36–46.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choi YH, Kim GY and Lee HH:
Anti-inflammatory effects of cordycepin in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages through
Toll-like receptor 4-mediated suppression of mitogen-activated
protein kinases and NF-κB signaling pathways. Drug Des Devel Ther.
8:1941–1953. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nijland R, Hofland T and van Strijp JA:
Recognition of LPS by TLR4: Potential for anti-inflammatory
therapies. Mar Drugs. 12:4260–4273. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Suganami T, Tanimoto-Koyama K, Nishida J,
Itoh M, Yuan X, Mizuarai S, Kotani H, Yamaoka S, Miyake K, Aoe S,
et al: Role of the Toll-like receptor 4/NF-kappaB pathway in
saturated fatty acid-induced inflammatory changes in the
interaction between adipocytes and macrophages. Arterioscler Thromb
Vasc Biol. 27:84–91. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Dou W, Zhang J, Sun A, Zhang E, Ding L,
Mukherjee S, Wei X, Chou G, Wang ZT and Mani S: Protective effect
of naringenin against experimental colitis via suppression of
Toll-like receptor 4/NF-κB signalling. Br J Nutr. 110:599–608.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|